AQA GCSE Physics P6 Molecules and matter SEPARATE
0.0(0)
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/45
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
1
New cards
State the equation that links mass, volume and density
mass = density x volume (my dense vulture)
2
New cards
What are the units of density?
kg/m³
3
New cards
What are the units of volume?
m³
4
New cards
What are the units of mass?
kg
5
New cards
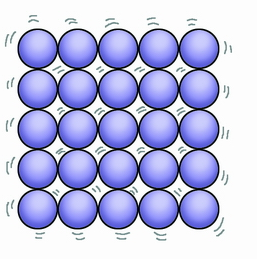
Describe the arrangement and motion of particles in a solid
particles are close together, in a regular pattern, in fixed positions, vibrating
6
New cards
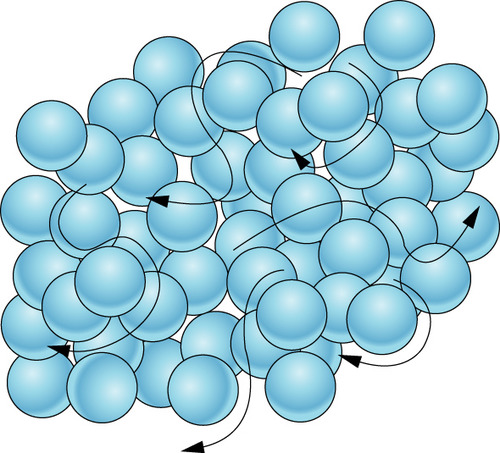
Describe the arrangement and motion of particles in a liquid
particles are close together, in a random arrangement, can move around
7
New cards
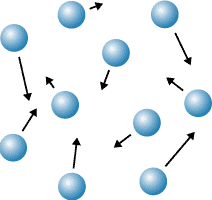
Describe the arrangement and motion of particles in a gas
particles are far apart, moving in all directions, move fast with a range of speeds
8
New cards
Use kinetic theory to explain why solids have a fixed shape
Because particles are in fixed positions and have strong forces of attraction between them (holding them together strongly)
9
New cards
Use kinetic theory to explain why gases will fill the entire container.
Because particles move in all directions at fast speeds with negligible forces of attraction between them.
10
New cards
Use kinetic theory to explain why gases are easy to compress
Because particles are far apart with large spaces between them (so can be pushed much closer together)
11
New cards
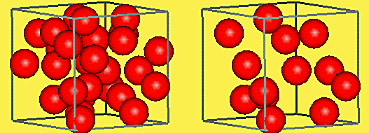
Describe the density of a solid or liquid
High density (large mass per unit volume)
Particles are close together.
Particles are close together.
12
New cards
Describe the density of a gas
Low density (small mass per unit volume).
Particles are far apart.
Particles are far apart.
13
New cards
Density required practical (method, equipment, calculation)
Measure mass in kg using a balance.
Measure volume using a ruler (dimensions of a regular solid V=wxlxh) or a measuring cylinder (liquids) or a displacement (Eureka) can with water level with spout, add irregular solid so V=volume of water displaced into a measuring cylinder.
Use the equation: density=mass/volume
Measure volume using a ruler (dimensions of a regular solid V=wxlxh) or a measuring cylinder (liquids) or a displacement (Eureka) can with water level with spout, add irregular solid so V=volume of water displaced into a measuring cylinder.
Use the equation: density=mass/volume

14
New cards
Mass is conserved when substances change state because...
no particles are gained or lost, they are just arranged differently.
15
New cards
What happens when a solid melts?
Solid changes into liquid.
Internal energy increases.
Potential energy of the particles increase as bonds break.
Temperature remains constant as average kinetic energy of the particles stays constant.
Internal energy increases.
Potential energy of the particles increase as bonds break.
Temperature remains constant as average kinetic energy of the particles stays constant.

16
New cards
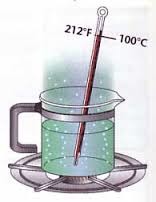
What happens when a liquid boils?
Liquid changes into gas.
Internal energy increases.
Potential energy of the particles increase as bonds break and particles move far apart.
Temperature remains constant as average kinetic energy of the particles stays constant.
Internal energy increases.
Potential energy of the particles increase as bonds break and particles move far apart.
Temperature remains constant as average kinetic energy of the particles stays constant.
17
New cards
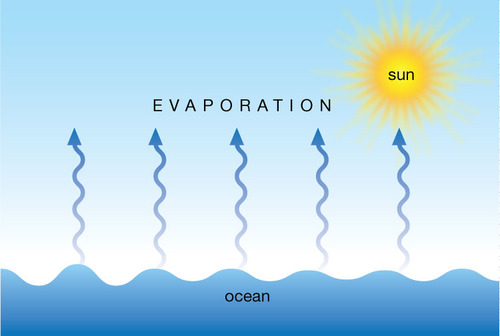
What happens when a liquid evaporates?
liquid changes into gas (can be below boiling point - eg a puddle on a cool day)
18
New cards
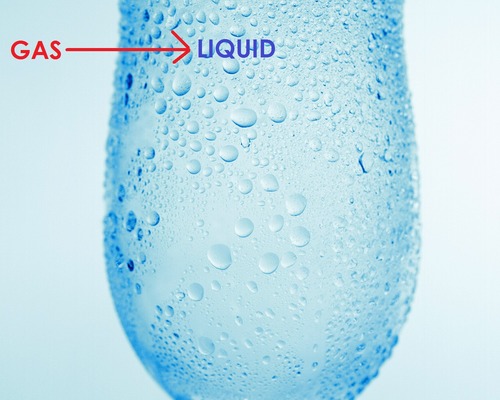
What happens when a gas condenses?
Gas changes to a liquid.
Internal energy decreases.
Potential energy of the particles decreases as stronger bonds are formed and particles get closer together.
Temperature remains constant as average kinetic energy of the particles stays constant.
Internal energy decreases.
Potential energy of the particles decreases as stronger bonds are formed and particles get closer together.
Temperature remains constant as average kinetic energy of the particles stays constant.
19
New cards
Explain what happens when a liquid freezes
Liquid changes into a solid
Internal energy decreases.
Potential energy of the particles decreases as stronger bonds are formed.
Temperature remains constant as average kinetic energy of the particles stays constant.
Internal energy decreases.
Potential energy of the particles decreases as stronger bonds are formed.
Temperature remains constant as average kinetic energy of the particles stays constant.
20
New cards
What is subliming?
Change of state from solid to gas.
(not in the Physics course)
(not in the Physics course)

21
New cards
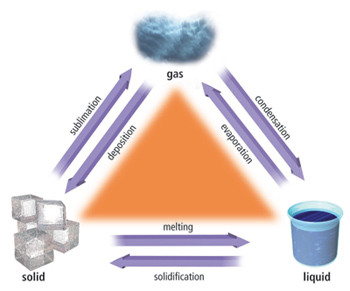
What are physical changes?
Changes of state are physical changes because the material recovers its original properties if the change is reversed.
For example, changes of state.
For example, changes of state.
22
New cards
What is internal energy?
The total energy stored inside a system by its particles.
Internal energy =total k.e. + total p.e.
(of all the particles)
Internal energy =total k.e. + total p.e.
(of all the particles)
23
New cards
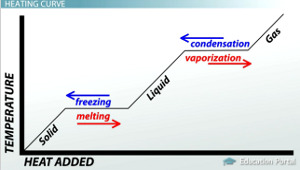
When does internal kinetic energy increase?
When the temperature of a substance increases (sloped part of graph)
24
New cards
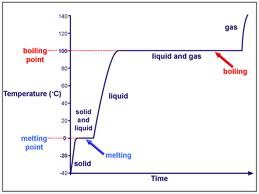
When does internal potential energy increase?
When the particles move apart, mainly during a change of state (horizontal part of graph).
No effect on temperature.
No effect on temperature.
25
New cards
What happens to the temperature and internal energy of a substance as it is changing state?
Temperature stays constant.
Internal energy increases due to increase in potential energy of particles.
(it is still being heated but the heat energy breaks bonds between particles and moves them further apart instead of raising the temperature)
Internal energy increases due to increase in potential energy of particles.
(it is still being heated but the heat energy breaks bonds between particles and moves them further apart instead of raising the temperature)
26
New cards
State 2 things that can happen when a substance is heated.
1. Temperature rise
2. Change of state
(NOT both at the same time)
2. Change of state
(NOT both at the same time)
27
New cards
State the units of temperature
°C

28
New cards
State the units of energy (change)
Joules (J)
29
New cards
Define Specific Heat Capacity
The energy needed to raise the temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1°C
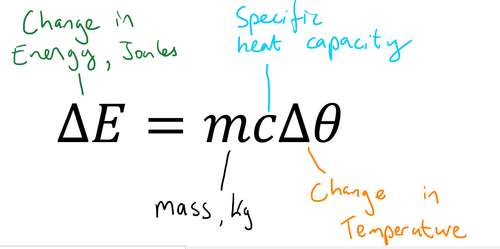
30
New cards
Define Specific Latent Heat
The energy needed to change the state of 1kg of a substance at constant temperature
31
New cards
What is fusion?
It means melting
32
New cards
What is vaporisation?
It means boiling
33
New cards
What are the units of specific latent heat?
J/kg
34
New cards
What is the temperature of a gas directly proportional to?
The average kinetic energy of its particles
(when an object is heated, it's particles gain k.e. and move faster)
(when an object is heated, it's particles gain k.e. and move faster)
35
New cards
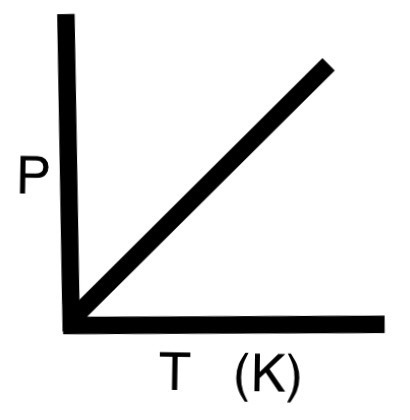
Explain the effect of temperature change on gas pressure
If temperature of a gas is increased, the pressure increases (if the volume remains constant) because the particles have more kinetic energy so move faster and collide with the walls of the container more often and with more force.
36
New cards
What causes gas pressure?
Gas molecules colliding with the walls of the container, exerting a force.

37
New cards
Why does ice melt?
Because the internal energy of the ice increases when energy is transferred from the surroundings to the ice.
(due to the temperature difference)
(due to the temperature difference)
38
New cards
Explain why thermal energy moves from place to place
Because of temperature differences, energy flows from warmer places to cooler places
39
New cards
Why do substances have different melting points?
They have different strength of bonds between particles so different amounts of energy needed to break the bonds
40
New cards
State 2 ways to make a gas condense
1. lower the temperature
2. increase the pressure (particles move closer together)
2. increase the pressure (particles move closer together)
41
New cards
Which direction is the force produced by gas pressure?
At right angles to the walls of the container or surface
42
New cards
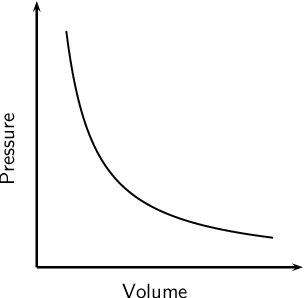
Explain the effect of changing volume on pressure (at constant temperature)
When the volume of the gas decreases, pressure increases.
Pressure is inversely proportional to volume because...
- in a smaller volume, the number of collisions each second between the gas molecules and the walls of the container increases
- so the force on the inside surfaces increases
- so the pressure increases
Pressure is inversely proportional to volume because...
- in a smaller volume, the number of collisions each second between the gas molecules and the walls of the container increases
- so the force on the inside surfaces increases
- so the pressure increases
43
New cards
How is work done on a gas?
A force is exerted on it to reduce its volume
44
New cards
What is the effect of doing work on a gas?
(for example, using a force to compress it)
(for example, using a force to compress it)
The internal energy of the gas increases which can cause the temperature to increase.
45
New cards
Why does the internal energy of air increase as a bicycle tyre is inflated?
Work is done on the air so the average kinetic energy of the particles increases so the temperature of the air increases.
46
New cards
Explain how to prove that the pressure is inversely proportional to the volume of a gas?
Show that p x V equals a constant value.
Take 3 sets of values from a line graph or data table.
Take 3 sets of values from a line graph or data table.