Brain and Spinal Cord Flashcards
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Meninges
three connective tissue membranes that envelop the brain
Where do the meninges lay?
between nervous tissue and bone
What are the three layers of meninges?
dura mater
arachnoid mater
pia mater
What do the meninges do?
they protect the brain and provide structural framework for its arteries and veins
Cerebrospinal fluid:
a clear, colorless liquid that fills the ventricles and canals of the CNS and bathes the outer surface of the brain and spinal cord.
How does the production of cerebrospinal fluid begin?
with the filtration of blood plasma through the capillaries of the brain. Specifically, ependymal cells modify the filtrate, so CSF has more Na+ and Cl- than plasma, but less K+, Ca+2, and glucose
What are the three functions of the cerebrospinal fluid?
buoyancy
protection
chemical stability
How does the Cerebrospinal fluid allow for buoyancy?
it allows the brain to attain considerable size without being impaired by its own weight
How does the Cerebrospinal fluid protect the brain?
its thicker consistency protects the brain from striking the cranium when the head is jolted
How does the Cerebrospinal fluid allow for chemical stability in the brain?
the flow of CSF rinses away metabolic wastes from nervous tissue and regulates its chemical environment
The brain is only 2% of the adult body weight, and receives ____ percent of the blood.
15%
What happens if blood flow is interrupted for 10 seconds?
loss of consciousness may occur
What happens if blood flow is interrupted for 1-2 minutes?
significant impairment of neural function may occur
What happens if blood flow is interrupted for 4 minutes?
irreversible brain damage may occur
What are the six sections of the brain?
frontal lobe
temporal lobe
brainstem
parietal lobe
occipital lobe
cerebellum
What is the Frontal Lobe responsible for?
motor control
problem solving
speech production
What is the Temporal Lobe responsible for?
auditory processing (hearing)
language comprehension
memory retrieval
What is the Parietal Lobe responsible for?
touch perception
body orientation and sensory discrimination
What is the Occipital Lobe responsible for?
sight
visual reception and interpretation
What is the Cerebellum responsible for?
balance and coordination
What is the brainstem responsible for?
involuntary responses
Cerebral lateralization
the difference in the structure and function of the cerebral hemispheres
What does the left hemisphere of the brain specialize in?
spoken and written language
sequential and analytical reasoning (math and science)
breaks info into fragments and analyzes it in a linear way
What does the right hemisphere of the brain specialize in?
perceives information in a more integrated holistic way
imagination and insight
musical and artistic skill
perception of patterns and spatial relationships
comparison of sights, sounds, smells, and taste
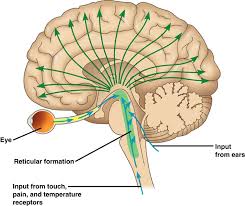
Reticular Formation
loosely organized web of grey matter than runs vertically through all levels of the brainstem