module 5 p1
1/216
Earn XP
Description and Tags
dosage form
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
217 Terms
Drug products/preparations containing: • Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API)/ Drug • Excipients/ Additives/Adjuncts
Dosage Forms
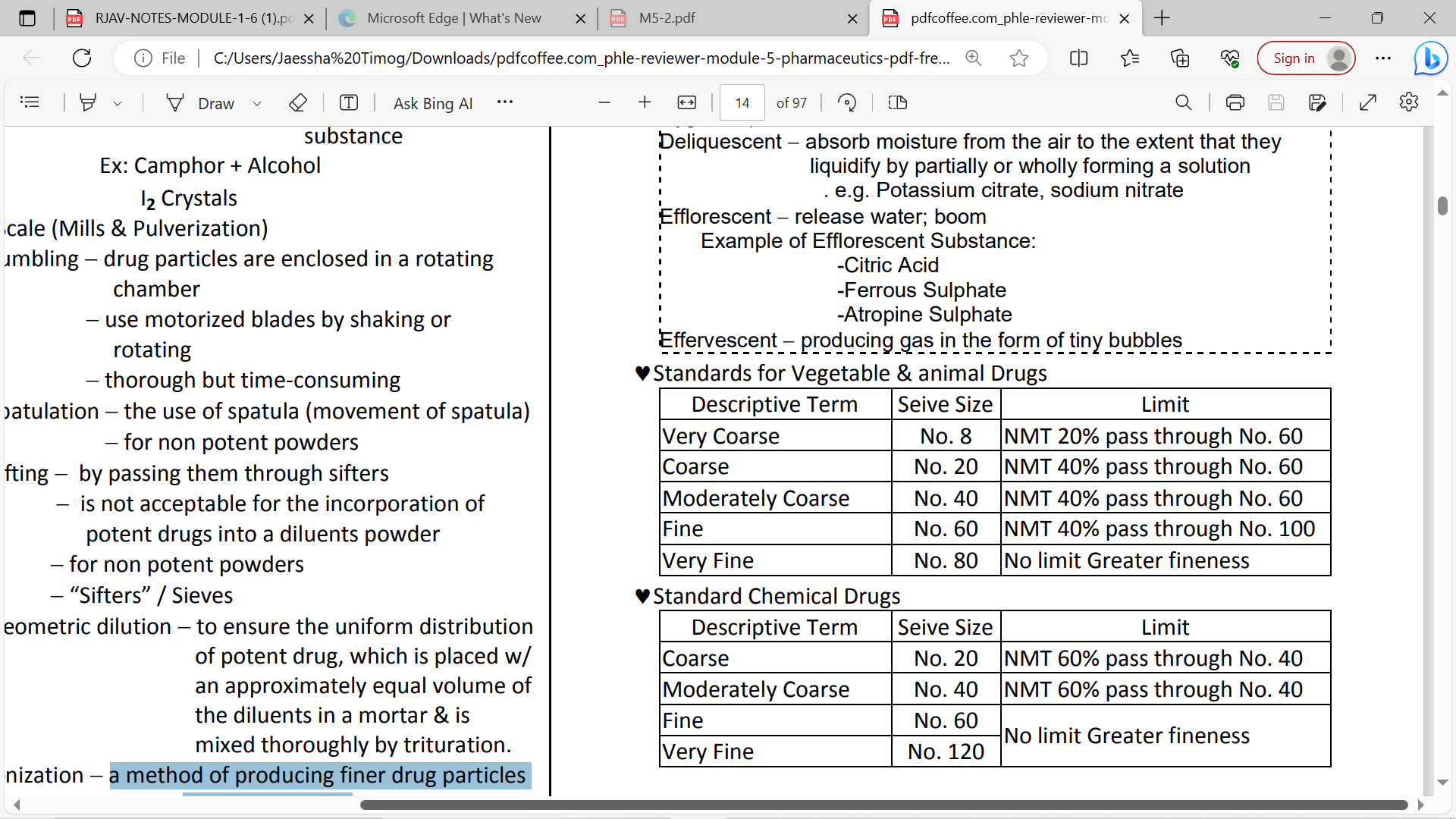
Sieve number
no. of square openings per linear inch
very coarse
sieve no. 8 no. 40 fine no. 60 very fine no. 80
coarse
sieve no. 20
moderately coarse
seive no.40
fine
sieve no.60
very fine
sieve #80
Drug Delivery
process whereby drugs are delivered to their site of action using a minimum amount of drug necessary to provide & maintain therapy. Effect over a certain period of time with minimum toxicity.
Drug Delivery System
means administering drugs as formulated preparations
formulations which provide a therapeutic amount of drug to the proper site in the body promptly & maintain the desired drug concentration
products that allow for the uniform release or targeting of drugs into the body
encompass the drug formulation, interaction among drugs, formulation matrix, the container & the patient
Drug Product
the finished dosage form that contains the active ingredient, generally, but not necessarily, in association with one or more other ingredients
Three Types of Mortar & Pestle:
1)Porcelain
2)Wedgewood
3)Glass
Porcelain
for comminution
soft aggregates/ crystals
Rough inner surface
Wedgewood
FOR CRYSTALS;
rougher surface
Glass
smooth surface/ non porous
solution, suspension, & ointment
used for staining substance
Levigation
forming a paste by the addition of a levigating agent
(ex. mineral oil, glycerin, PEG)
Pulverization by Intervention
addition of volatile substance to a gummy material (ex. camphor + alcohol; I2crystals + ether)
Spatulation
Blending of powders with a spatula on a tile or paper
• Use: small quantities, non-potent drugs, eutectic mixtures
Sifting
• Powders are passed through sifters
• Results in light, fluffy product
• Not for potent substances
Geometric Dilution
addition of an equal volume of diluent to a potent substance placed in a mortar
Tumbling
large containers rotated by a motorized process
thorough but time-consuming
Bulk Powders
-Oral Powders, Dentifrices,Dusting Powders,Douche Powders,Insufflations,. Trituration
Divided Powders/Chartulae
Types of Powders
Micronization
a method of producing finer drug particles under 10m size.
Oral Powders
• dissolved in water prior to use
. Dentifrices
• used to clean and polish teeth
• contain a soap, mild abrasive and
anticariogenic agent(prevents cavity formation)
. Dusting Powders
locally applied non-toxic powders that have no systemic action by sprinkling or by means of sifter-top containers.
Douche Powders
dissolve in warm water prior to introduction into a body cavity
Insufflations
blown into body cavities using an insufflator
Boric Acid or Sodium Borate
Astringents, for example, potassium, alum, ammonium alum, zinc sulfate
Antimicrobials, for example, oxyquinoline sulfae, povidone iodine
Quaternary Ammonium Compounds, for example, Benxethonium Chloride
Detergents, for example, Sodium Lauryl Sulfate
Oxidizing Agents, for example, Sodium Perborate g. Salts, for example, Sodium Citrate, Sodium Chloride
h. Aromatics, for example, Methol, Thymol, Eucalyptol, Methyl Salicylate, Phenol
Components of Douche Powders:
Trituration
dilutions of potent powdered drugs (10% API)
Divided Powders/Chartulae
dispensed in individual doses usually in folded papers;
block-and-divide method
White Bond Paper
OPAQUE paper with NO MOISTURE resistance
Vegetable Parchment
thin, semi-opaque, moisture resistant paper(LIMITED)
Glassine Paper
GLAZED TRANSPARENT moisture-resistant paper(LIMITED)
Waxed Paper
transparent waterproof paper; suitable for deliquescent and hygroscopic drugs
GRANULES
dry aggregates of powder particles
NORMAL SIEVE no. 4 to 12
TABLET FORMULATION: SIEVE no. 12 to 20
• Flow well compared to powders
• Less tendency to cake or harden
• More stable to humidity
• More easily wetted by liquids
Advantages of Granules over Powder
Hygroscopic
absorb moisture from the air
Deliquescent
absorb moisture from the air to the extent that they liquidify by partially or wholly forming a solution .
e.g. Potassium citrate, sodium nitrate( absorb water and dissolves)
Efflorescent
release water; boom
Example of Efflorescent Substance:
-Citric Acid
-Ferrous Sulphate
-Atropine Sulphate
Compounding of Granules
1. Wet Granulation
2. Dry Granulation
Wet Granulation
addition of granulating fluid or liquid binder
• most common;
Advantages: -Increased Compressibility
-Improved Dissolution
Disadvantage: -Its not applicable to water/ moisture & heat sensitive (ex: Aspirin)
moisten the mass screen
granulating fluids H2O
*fluid bed processing alcohol isopropanol
fluid bed granulation (liquid is sprayed on suspended powders)
wet granulation
Dry Granulation
for moisture-sensitive and heat labile materials
• use compaction/ compression forces
Disadvantage: Messy
Roll Compaction
Slugging
Processes: dry granulation
Roll Compaction
uses thin sheets
powders are rolled into dense sheets
sheets are granulated using a mechanical granulator
sieve granules to obtain desired size
Slugging
tablet pressed
slugging of powders (formation of large tablets called a “slugs”)
slugs are granulated using an appropriate equipment
sieve the granules to obtain desired size
poorly formed tablet
Preparation:
• Dry/Fusion Method – binder is 1 mol of H20 in citric acid
• Wet Method – binder is H20 + alcohol
Effervescent Granules
TABLETS
solid dosage forms which are prepared mainly by compression or molding
• uniform content
• less manufacturing cost
• easy to package and ship
• simple to identify
• most stable of all oral dosage form
• tamperproof
Advantages OF TABLETS
• some drugs resist compression
• some drugs that require encapsulation prior to compression
Disadvantages OF TABLETS
Compressed Tablets
• formed by compression
• some are scored
Layered tablets Multiple Compressed Tablets
– formed by compressing 2 or 3 layers of formulation against each other
(ex. Neozep tablet)
Compression coated tablets – Multiple Compressed Tablets
formed by compressing an outer shell around a tablet core
Sugar Coated Tablets – coated with sucrose-based solution
Film Coated Tablets – coated with a thin layer of polymer material
Enteric-Coated Tablets – remain intact in the stomach but disintegrate in the small intestine
Coated Tablets
Chewable Tablets
• chewed first before swallowing
• diluent: mannitol and xylitol
• (ex. Multivitamins, antacids)
Rapidly/ Orally Disintegrating Tablets
• liquefy on the tongue and then the patients swallow the liquid
• (ex. Risperidone, Ondansetron)
. Buccal Tablets
placed in the lining of the cheeks
• disintegrate slowly (4 hours)
• (ex. Progesterone
Sublingual Tablets
placed under the tongue for systemic absorption
• disintegrate rapidly (2-3 minutes)
• (ex. Nitroglycerin, ISDN
Lozenges
solid dosage forms in a hard candy or sugar base that dissolve slowly in mouth for local effect
• (ex. Strepsils® - dicholorobenzyl alcohol + amylmetacresol
Compounding/ Dispensing Tablets
contain a large amount of API used by pharmacists in compounding multiple dosage units
• no longer use
Hypodermic Tablets
• used by physicians to prepare parenteral solutions • no longer use
Types OF LOZENGES
• Troches – compressed lozenges
• Pastilles – molded lozenges
• Lollipops – lozenges on sticks
Molded Tablets/ Tablet Triturate
prepared by moistening powders and then putting on a triturate mold (may be compressed)
• results to cylindrical tablets which are very soluble in water
Gelatin
partial hydrolysis of collagen from the skin/bones of animals
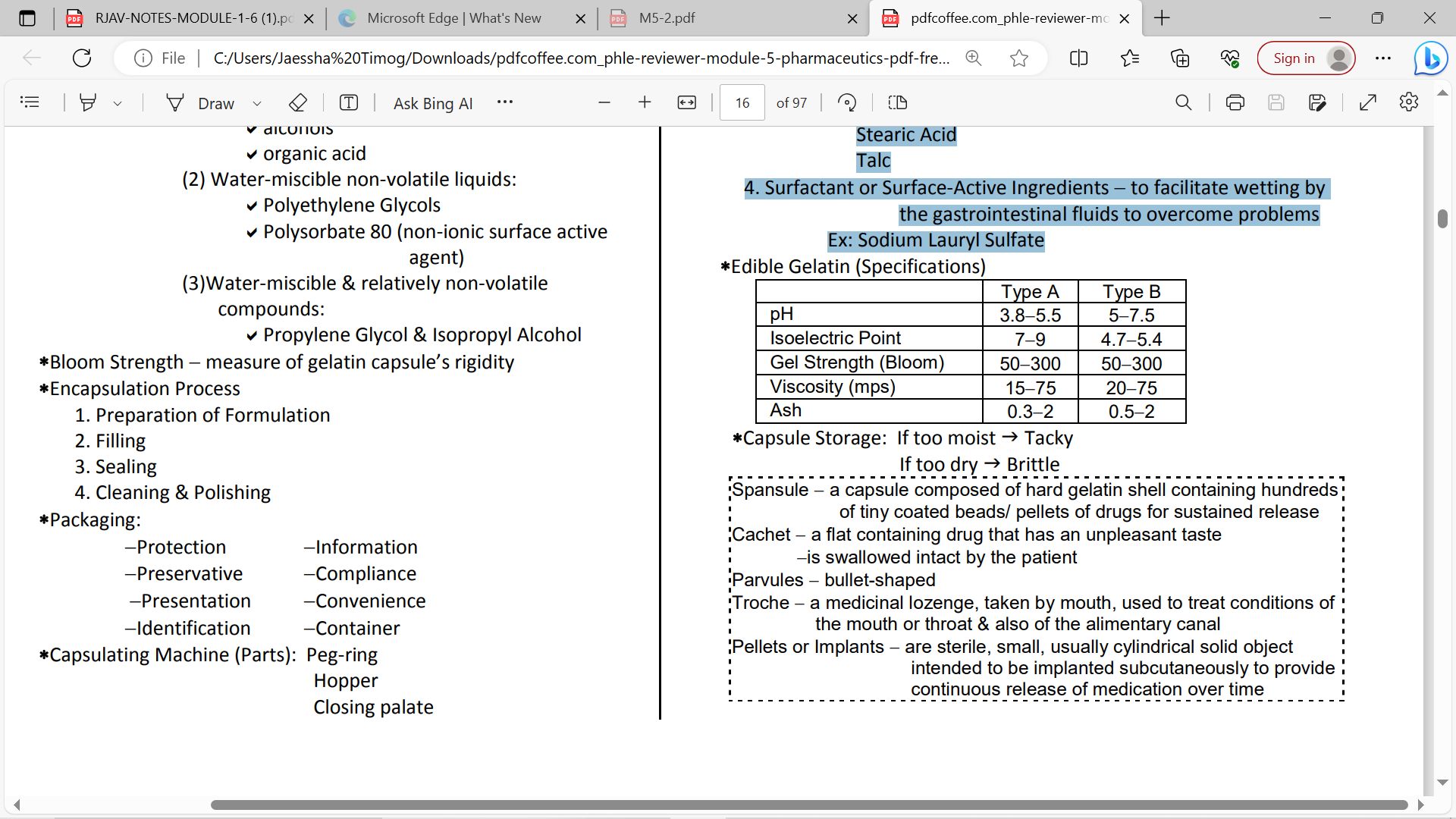
Types OF GELATIN
• Type A – mainly from pork skin; acid processing
• Type B – from bones and animal skins; alkaline processing
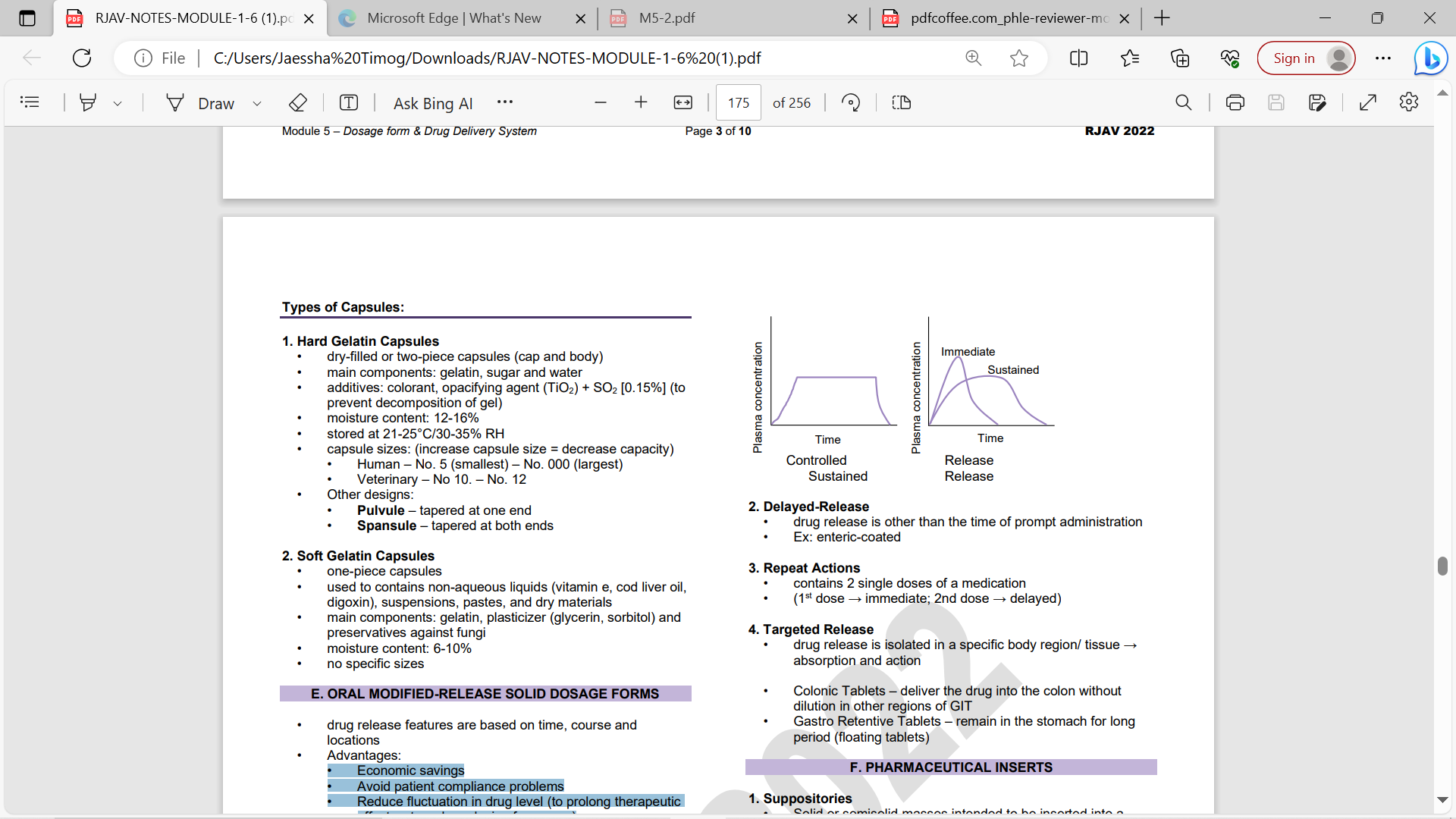
Vegetable Capsules
alternative hydroxypropyl methylcellulose (HPMC) or hard starch
Hard Gelatin Capsules
dry-filled or two-piece capsules (cap and body)
• main components: GELATIN, SUGAR, H20
• additives: colorant, opacifying agent (TiO2) + SO2 [0.15%] (to prevent decomposition of gel)
• moisture content: 12-16% • stored at 21-25°C/30-35% RH
capsule sizes
: (increase capsule size = decrease capacity)
• Human – No. 5 (smallest) – No. 000 (largest)
• Veterinary – No 10. – No. 12
OTHER DESIGN HARD GELATIN CAPSULES
PULVULE- TAPERED AT ONE END
SPANSULE- TAPERED AT BOTH ENDS
Soft Gelatin Capsules
one-piece capsules
• used to contains non-aqueous liquids (vitamin e, cod liver oil, digoxin), suspensions, pastes, and dry materials
• main components: gelatin, plasticizer (glycerin, sorbitol) and preservatives against fungi
• moisture content: 6-10%
• no specific sizes
Order of Capsule Shell Manufacturing
Dipping, Spinning, Drying, Stripping, Trimming, Joining
Encapsulation Procedure of Capsules from start to finish
Rectification —> Separation—→Filling—→ Joining——→ Printing———> Banding ——>Ducting & polishing
1. Diluent or Filler
to produce the proper capsule fill volume
Ex: Lactose, Microcrystalline Cellulose ,Starch
2. Disintegrants
to assist the breakup & distribution of the capsule’s contents in the stomach
Ex: Pregelatinized Starch Eroscarmellose Sodium starch Glycolate
3. Lubricants or Glidants to enhance flow properties
Ex: Fumed Silicon Dioxide Magnesium Stearate Calcium Stearate Stearic Acid Talc
4. Surfactant or Surface-Active Ingredients
to facilitate wetting by the gastrointestinal fluids to overcome problems Ex: Sodium Lauryl Sulfate
Capsule Excipients:
ORAL MODIFIED-RELEASE SOLID DOSAGE FORMS
drug release features are based on time, course and locations
Advantages OF ORAL MODIFIED RELEASE DOSAGE FORMS
• Economic savings
• Avoid patient compliance problems
• Reduce fluctuation in drug level (to prolong therapeutic effect → to reduce dosing frequency)
• Minimize or eliminate side effects
Extended-Release
provides a prompt desired effect followed by a gradual release of remaining amount
• Problem: dose dumping
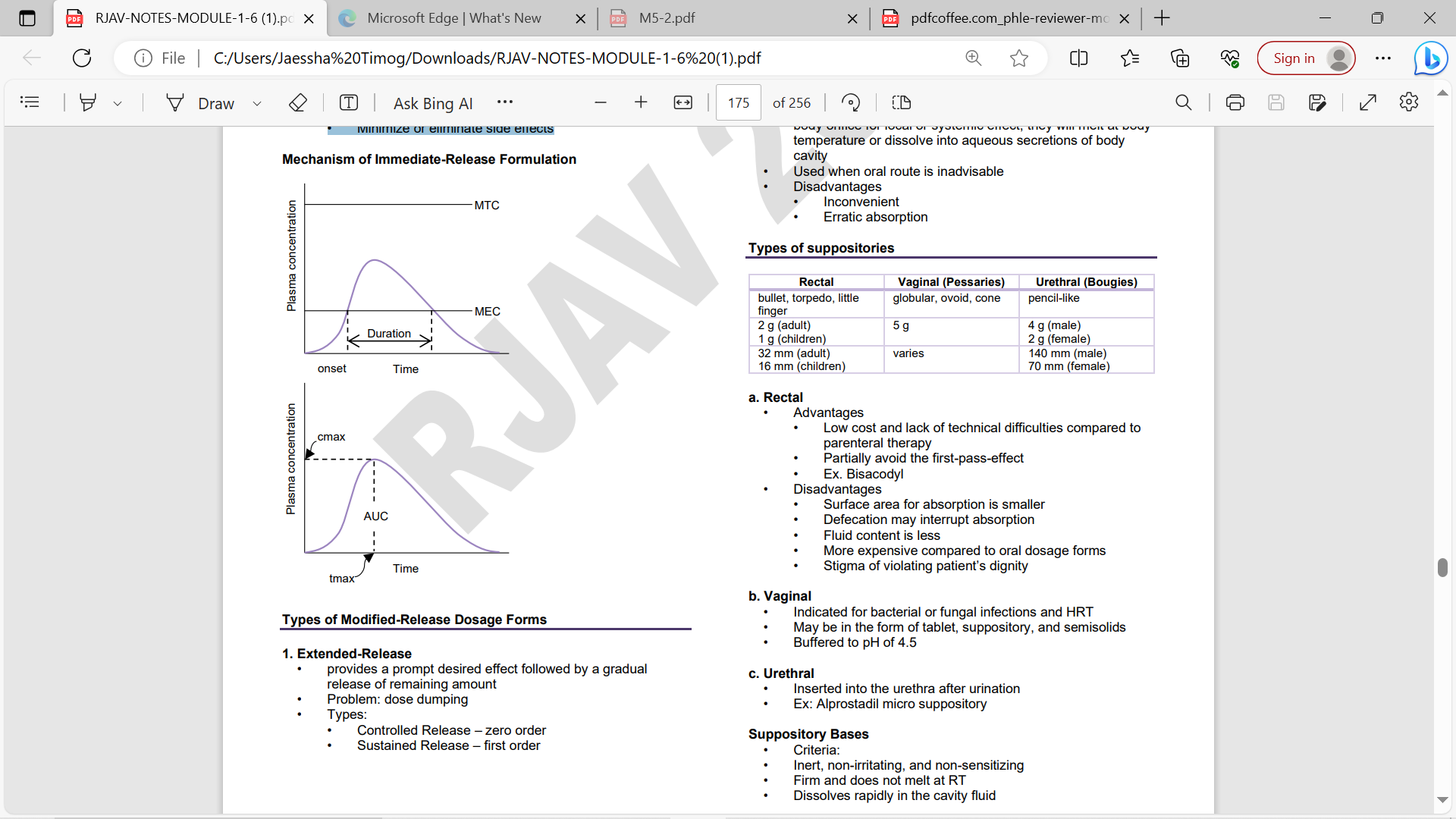
TYPES OF EXTENDED-RELEASE
• Controlled Release – zero order
Sustained Release – first order
drug release is other than the time of prompt administration
• Ex: enteric-coated
Repeat Actions
contains 2 single doses of a medication
(1st dose → immediate; 2nd dose → delayed)
Targeted Release
• drug release is isolated in a specific body region/ tissue → absorption and action
Colonic Tablets
deliver the drug into the colon without dilution in other regions of GIT
Rectal suppositories
bullet, torpedo, little finger
2 g (adult) 1 g (children)
32 mm (adult) 16 mm (children)
Vaginal (Pessaries)
globular, ovoid, cone
5 g
Indicated for bacterial or fungal infections and HRT • May be in the form of tablet, suppository, and semisolids • Buffered to pH of 4.5
Urethral (Bougies)
pencil-like
4 g (male) 2 g (female)
140 mm (male) 70 mm (female)
Inserted into the urethra after urination
• Ex: Alprostadil micro suppository
Suppository Bases • Criteria
• Inert, non-irritating, and non-sensitizing
• Firm and does not melt at RT
• Dissolves rapidly in the cavity fluid
Cocoa Butter – most common and good base for rectal suppository; solid at 32°C, melts at 34-35°C; exhibits polymorphism (ȣ - least stable [18°C]; α; β’; β – most stable [34.5°C]
• Wecobee – from coconut oil
• Witepsol – lauric acid is the major component; saturated fatty acids (C12-C18)
. Oleaginous Base
Water-Soluble/Miscible Base
• Glycerinated Gelatin – most common base for vaginal suppositories
• Polyethylene Glycol (PEG)
Vaginal Tablets/Inserts
• Ovoid or bullet-shaped tablets inserted into the vagina using a plastic inserter for local effects • contains antimicrobial agents
Implants/Pellets
• long-acting dosage forms that provide continuous release of the drug to the body
• administered parenterally or subcutaneously
• Pellet implants – small, sterile, cylindrical masses
• Levonorgestrel (Norplant ®) – 5 years
• Leuprolide acetate (Viadur®) – prostate cancer 1 year
OINTMENTS
semisolid dosage forms intended for external use
• Uses: • emollient • occlusive • vehicle
Oleaginous/ Hydrocarbon Base
have emollient, occlusive
• greasy, anhydrous, non-water washable
Petrolatum, USP (Yellow Petrolatum, Petroleum Jelly or Vaseline®)
– purified mixture of semisolid hydrocarbon from petroleum
White Petrolatum, USP
bleached or decolorized
Yellow Wax (Beeswax)
wax obtained from the honeycomb of Apis mellifera
White Wax
bleached or decolorized yellow wax/beeswax
Yellow Ointment, USP (Simple Ointment)
yellow petrolatum + yellow wax
White Ointment, USP
– white petrolatum + white wax