Physical and Chemical Oceanography: Salinity, Layers, and Marine Chemistry
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
42 Terms
What is the effect of evaporation on the salinity of water?
Evaporation leads to an increase in salinity since the concentration goes up while the amount of water decreases.
What are two sources of the ions present in sea water?
Ions come from atmospheric dissolution, run-off, and volcanic eruptions. Chloride and sodium are two sources of ions in seawater.
What are two natural processes that remove ions from sea water?
Harvesting and uptake.
What are three factors that affect the chemical composition of sea water?
Run-off, volcanic activity, and erosion.
What is meant by the term salinity?
Salinity is the total amount of salts dissolved in water, measured in parts per thousand.
What is the relationship between salinity and density?
Higher salinity results in higher density of water.
What is the relationship between salinity and rainwater?
More precipitation leads to lower salinity.
How does depth affect salinity?
As depth increases, salinity increases.
What are two factors, other than temperature, that cause salinity of seawater to change?
Run-off and evaporation.
Why is the salinity of sea water often lower near the coast than in the open ocean?
Coastal water is influenced by run-off from land, bringing excess rainwater, which dilutes the salinity.
How does a salinity gradient form in a water column?
Lower salinity and lower density water floats on top of higher salinity and higher density water.
What causes mixing of ocean layers?
Mixing can occur due to wind, storms, currents, and upwelling.
How does volcanic activity affect the chemical composition of sea water?
Volcanic eruptions release carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, chlorine, and fluorine into the atmosphere and seawater.
What happens to salinity in the halocline?
The halocline is a vertical salinity gradient; salinity usually lowers and can increase beyond the halocline.
How do temperature and salinity gradients form in water columns?
Warm water forms a layer on top of colder, denser water, creating temperature and salinity gradients.
What is the thermocline?
The thermocline is the interface where temperature decreases abruptly with depth.
What is the halocline?
The halocline is where there is a significant change in salinity with depth.
How does temperature affect the density of water?
As temperature increases, the density of water decreases.
What is the general trend of temperature as depth increases?
Temperature generally decreases as depth increases.
What is the relationship between salinity and density in ocean water?
As salinity increases, the density of water also increases.
What happens to warm water in relation to colder water?
Warm water tends to float on top of colder, denser water.
What is the significance of the halocline in oceanography?
It indicates a change in salinity as depth increases.
What role does upwelling play in ocean mixing?
Upwelling brings nutrient-rich water from the depths to the surface, promoting mixing.
How does precipitation affect ocean salinity?
Increased precipitation dilutes seawater, lowering its salinity.
How does the temperature profile of the temperate region differ from that of the tropical region?
In the temperate region, surface temperatures are around 15°C, while in the tropical region, surface temperatures are around 26°C, making the thermocline more pronounced in tropical regions.
Why is the thermocline less pronounced in temperate regions?
The ocean is colder, leading to more uniform mixing of water.
Why is there no thermocline in polar regions?
The water is uniformly cold, which does not create a density gradient.
What biological factors affect the concentration of oxygen in seawater?
Respiration by animals uses up oxygen, photosynthesis produces oxygen, and the number of organisms impacts oxygen concentration.
What physical factors affect the concentration of oxygen in seawater?
Oxygen concentration varies due to temperature, salinity, pressure, and depth.
Why might dissolved oxygen be lower in tropical lagoons than in the open ocean?
Warmer water in lagoons causes oxygen to dissipate faster, and higher animal density leads to more oxygen consumption due to respiration.
Why does oxygen concentration vary with ocean depth?
Greater oxygen concentration occurs due to more light and photosynthesis at the surface, while respiration and decay reduce oxygen with depth.
Why is dissolved oxygen high in surface waters of the ocean?
Photosynthesis by producers occurs in the sunlit area, and water turbulence helps mix oxygen into solution.
What is the relationship between temperature and density in ocean water?
As depth increases, temperature decreases and density increases.
How does the density of pure water change as it cools from 4°C to 0°C?
Density increases as water cools to 4°C, but decreases from 4°C to 0°C due to the formation of ice, which is less dense.
How does the density of saltwater change with temperature?
Density increases as temperature decreases due to the mass added by dissolved salts.
What are the importance of ice floating on liquid water to marine life?
Ice provides habitat, acts as a thermal insulator, prevents the entire water column from freezing, supports ice algae, and creates a barrier between the atmosphere and water below.
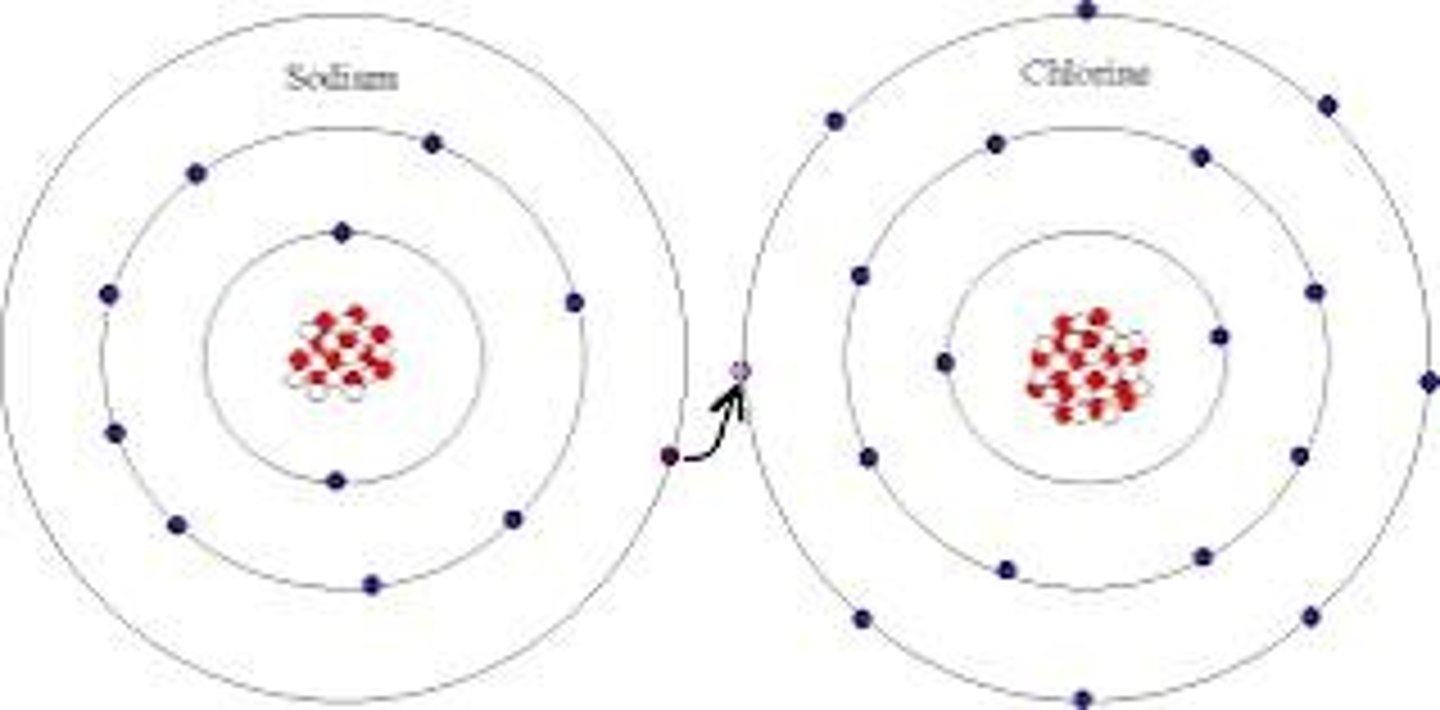
How does ionic structure form from sodium and chlorine atoms?
Chlorine gains one electron and becomes negatively charged, while sodium loses one electron and becomes positively charged.
How does sodium chloride dissolve in water?
Ionic bonds break as water's polar molecules attract sodium and chlorine ions, causing the salt to dissolve.
What does the kinetic particle theory state?
Particles in all matter are always moving, and their energy depends on the amount of movement.
What makes up an atom?
Atoms consist of protons, neutrons, and electrons.
What are ionic, covalent, and hydrogen bonds?
Ionic bonds involve electron transfer, covalent bonds involve electron sharing, and hydrogen bonds are weak attractions between polar molecules.
What are some properties of water?
Adhesion, cohesion, high specific heat, lower density of ice, and being a universal solvent.