Magnetism and electromagnetism
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
they produce magnetic fields
what do magnets produce?
2 poles- north and south
what do all magnets have?
a magnetic field is a region where magnetic materials (iron) experience a force.
what is a magnetic field?
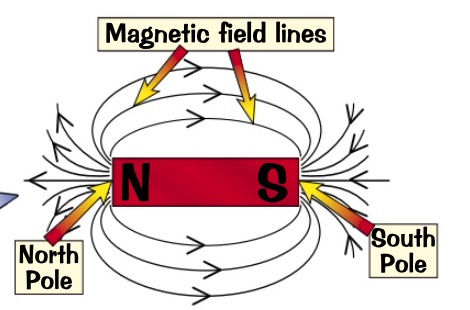
they are used to show the size and direction of magnetic field.
ALWAYS point from NORTH- SOUTH
what are magnetic field lines?

when placing the north and south poles of two permanent bar magnets near each other ;
creates a uniform field between the 2 magnets
what is a uniform field?
seen using compasses
or iron filings
how can you see magnetic field patterns?
practical to see magnetic field patterns

they affect magnetic materials and other magnets
e.g poles repel each other and opposite poles attract
what do magnets affect?
both poles that are not magnets.
what attract magnetic materials?
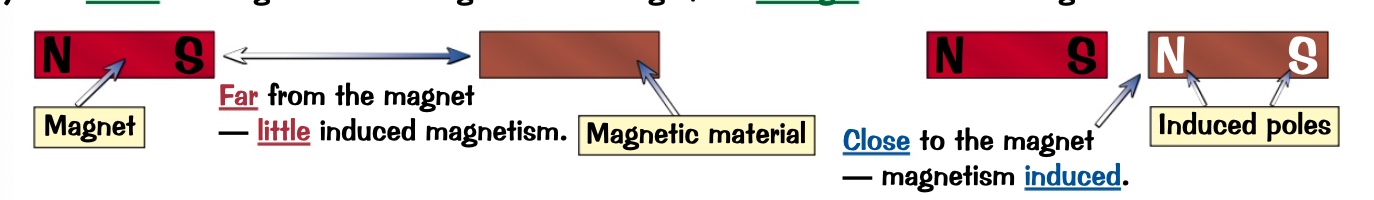
that material acts as a magnet
this magnetism has been induced by the original magnet,
the closer the magnet and the magnetic material get the stronger the induced magnetism will be.
what happens when magnetic materials are brought near to a magnet?
creates a magnetic field
1- an electric current in a conductor produces a magnetic field around it
2- the larger the electric current, the stronger the magnetic field
3- the direction of the magnetic field depends on the direction of the current.
what does a current- carrying wire create?
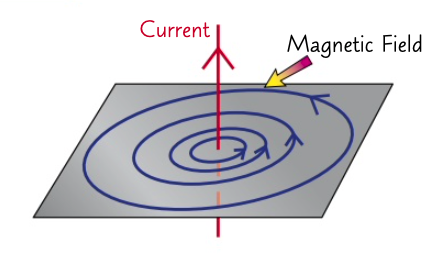
if there is a magnetic field around a straight current carrying wire
then the field is made up of concentric circles with the wire in the centre
what happens to a magnetic field around a straight wire?
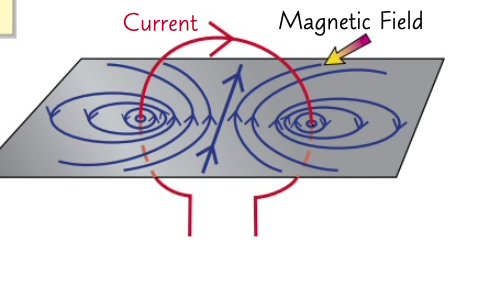
the magnetic field in the centre of a flat circular coil of wire is similar to that of a bar magnet
there are concentric ellipses (stretched circles) of magnetic field lines around the coil
what happens if there is a magnetic field around a flat circular coil?
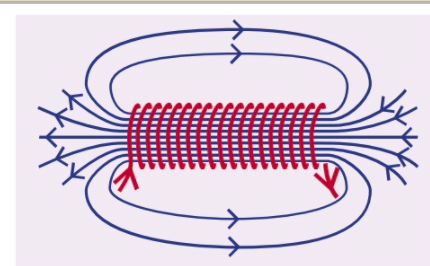
the magnetic field inside a current carrying solenoid (a coil of wire) is strong and uniform.
outside the coil, the field is just like the one around a bar magnet.
this means that the end of a solenoid acts like the North Pole and South Pole of a bar magnet.
This type of magnet is called an electromagnet.
what happens to the magnetic field around a solenoid?
soft or hard
what are the 2 types of properties that magnetic materials can be?
usually considered soft if it loses its induced magnetism quickly
or hard if it keeps it permanently.
what type of property is usually for a magnetic material?
iron is an example of a soft magnetic material
steel is an example of a hard magnetic material
what are examples of soft and hard magnetic materials?
iron is used in transformers because of this property- it needs to be magnetise and demagnetise 50 times a second.
what is an example of when iron is used?
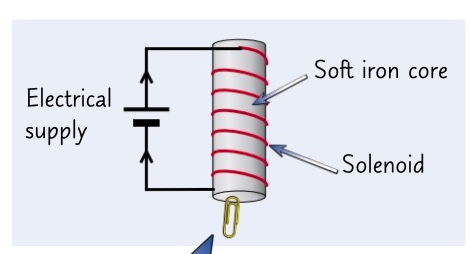
by adding a magnetically soft iron core through the middle of the coil
how can you increase the strength of the magnetic field around a solenoid
the 2 magnetic fields affect one another. the results is a force on the wire. This can cause the wire to move. this is the MOTOR EFFECT.
charged particles moving through a magnetic field will experience a force, as long as they’re not moving parallel to the field lines.
what happens when a current-carrying wire is put between magnetic poles?
the wire has to be at 90 degrees to the magnetic field. If the wire runs along the magnetic field, it will not experience any force at all.
how to experience a full force?
always acts in the same direction relative to the magnetic field of the magnets and the direction of the current in the wire
where does the force always act?
to apply a current to a set of rails inside a horseshoe magnet
a bar is placed on the rails, which completes the circuit. this generates a force that rolls the bar along the rails.
what is a good way of showing the direction of the force?
it increases with the strength of the magnetic field. the force also increases with the amount of current passing through the conductor
what happens to the magnitude (strength) of the force?
it also reverses the direction of the force
what happens if you the reverse the current or the magnetic field?
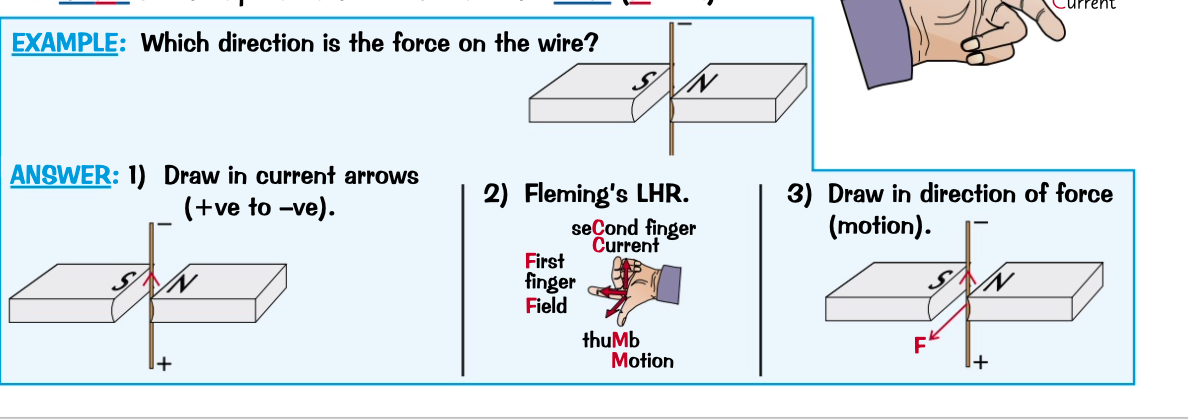
tells you which way the force acts
using your left hand, point your first finger in the direction of the field and second finger in the direction of the current.
your thumb will then point in the direction of the force.
what is Fleming’s left hand rule?
1- more current
2- more turns on the coil
3- stronger magnetic field
4- a soft iron core in the coil
which factors speed up a simple D.C electric motor?
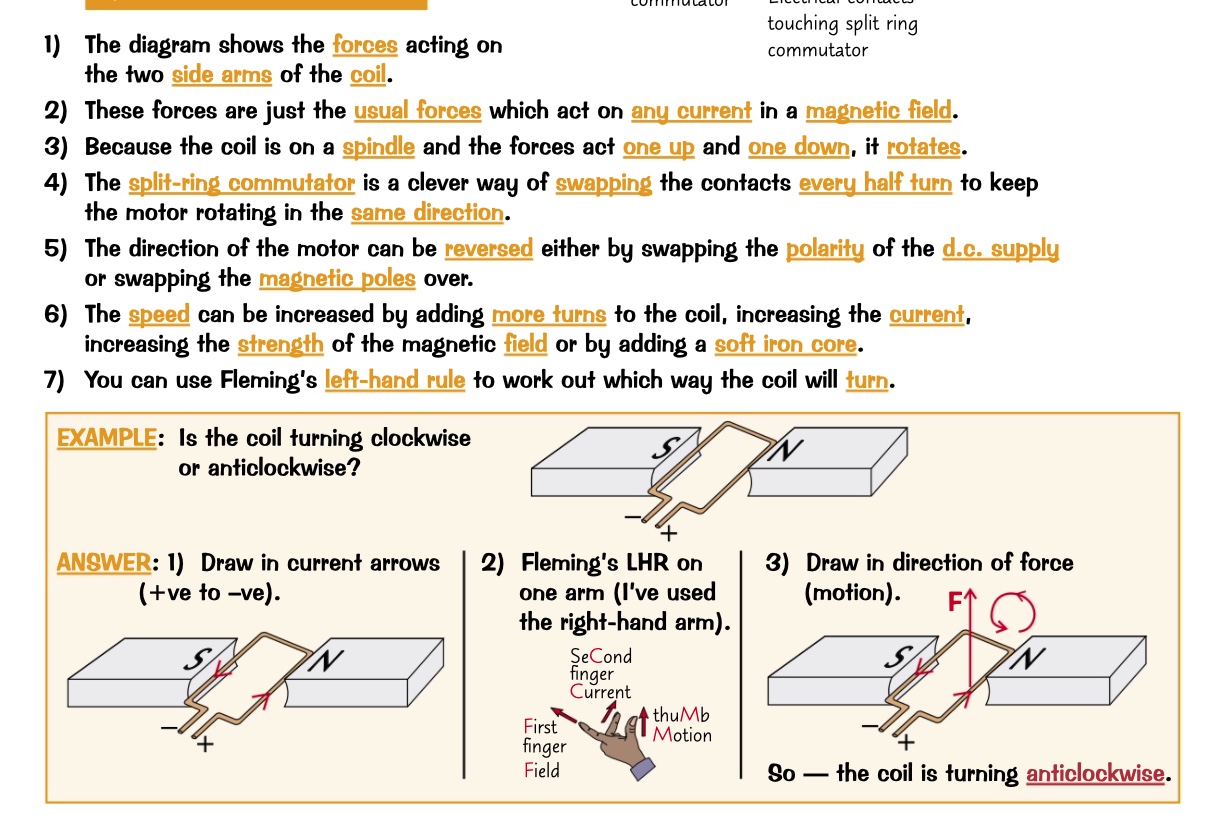
diagram of simple D.C motor
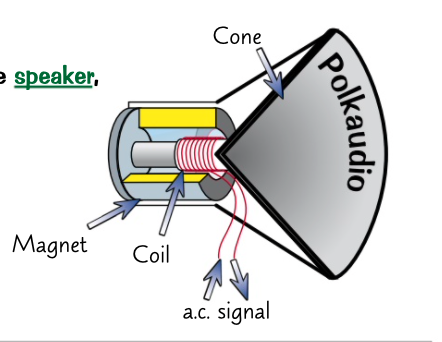
loudspeaker
A.c electrical signals from an amplifier are fed to a coil of wire in the speaker, which is wrapped around the base of a cone.
the coil is surrounded by a permanent magnet, so the a.c signals causes a force on the coil and makes it move back and forth.
these movement make the cone vibrate and creates sound.
what is an example of an equipment that will work because of the motor effect?
the creation of a voltage and maybe current in a wire which is experiencing a change in magnetic field
what is electromagnetic induction?
when using electromagnetic induction to generate electricity using energy from kinetic energy stores.
in a power station this energy is provided by the turbine.
what is the dynamo effect?
1- an electrical conductor ( a coil of wire is often used) moves through a magnetic field
2- the magnetic field through an electrical conductor changes gets bigger or smaller.
what are the 2 different situation to get EM induction?
by connecting an ammeter to a conductor and moving the conductor through a magnetic field
ammeter will show the magnitude and direction of the induced current.
how can you test the dynamo effect?
then the induced voltage/current will be reversed to.
if the direction of the movement is reversed?
1- strength of the magnet
2- number of turns on the coil
3- the speed of movement
how to get a bigger voltage? increase what?
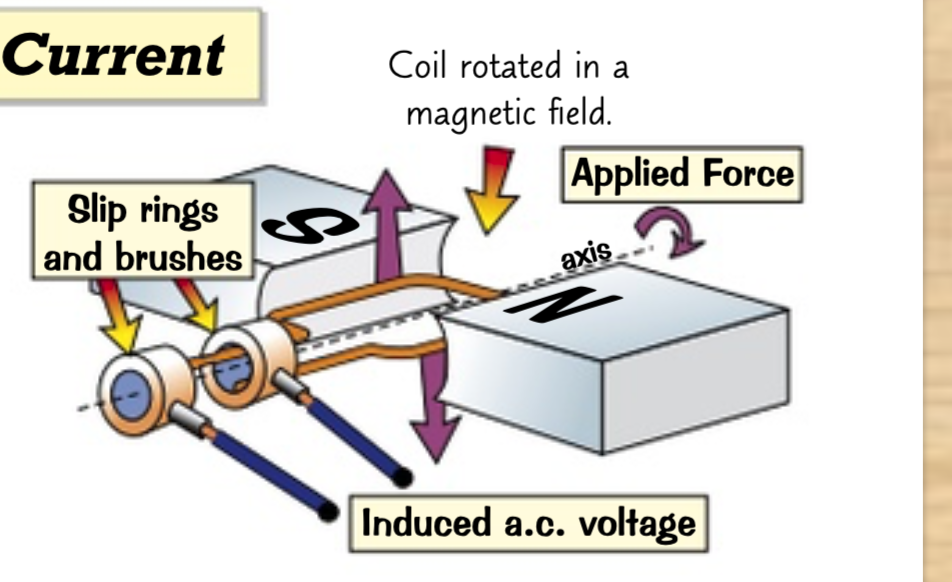
1- generators rotate a coil in a magnetic field
2- their construction is like a motor
3- as the coil spins, a current is induced in the coil. this current changes direction every half turn
4- instead of a split-ring commutator, a.c generators have slip rings and brushes so the contacts dont swap every half turn
5- produce a.c voltage as shown on CRO displays. faster revolutions produced more peaks but higher overall voltage.
6- power station use a.c generator to produce electricity.
how does a simple/a.c generator work?
only work with a.c current
change the size of the voltage of an alternating current
all have 2 coils, primer and secondary joined with an iron core.
what are transformers?
the magnetically soft iron core magnetises and demagnetises quickly. this induces an alternating voltage in the secondary coil.
ratio b/w primary and secondary voltage is the same as the ratio between the number of turns on the primary and secondary coil.
what happens when an alternating voltage is applied across the primary coil?
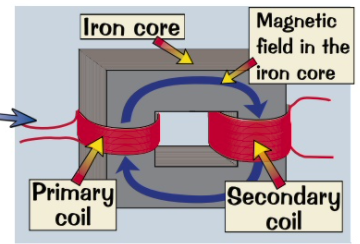
increase the voltage. they have more turns on the secondary coil than the primary coil
what do step up transformers do?
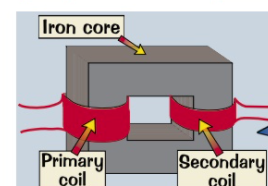
decrease the voltage. they have more turns on the primary coil than the secondary.
what do step down transformers do?

how to calculate the output voltage from a transformer from the input voltage and the number of turns on each coil?
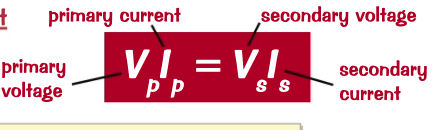
how to find power and voltage for transformers
make transmitting main electricity more efficient
what do transformers make?
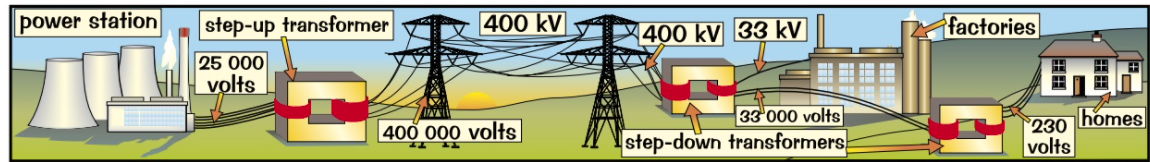
transmitting electricity diagram from power station
used when transmitting electricity across the country.
when are step up and step down transformers do?
too low to be transmitted efficiently. the lower the voltage the higher the current for a given amount of power, current causes wire to heat up.
step up transformers is used to boost voltage before transmitted
step down are used at the end of the journey to reduce the voltage so more useful and safer.
what happens to the voltage produced by power station?