APES Unit 9: Global Change
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
Greenhouse Effect
Important planetary function where certain atmospheric gases allow visible light to pass but traps infrared heat heat
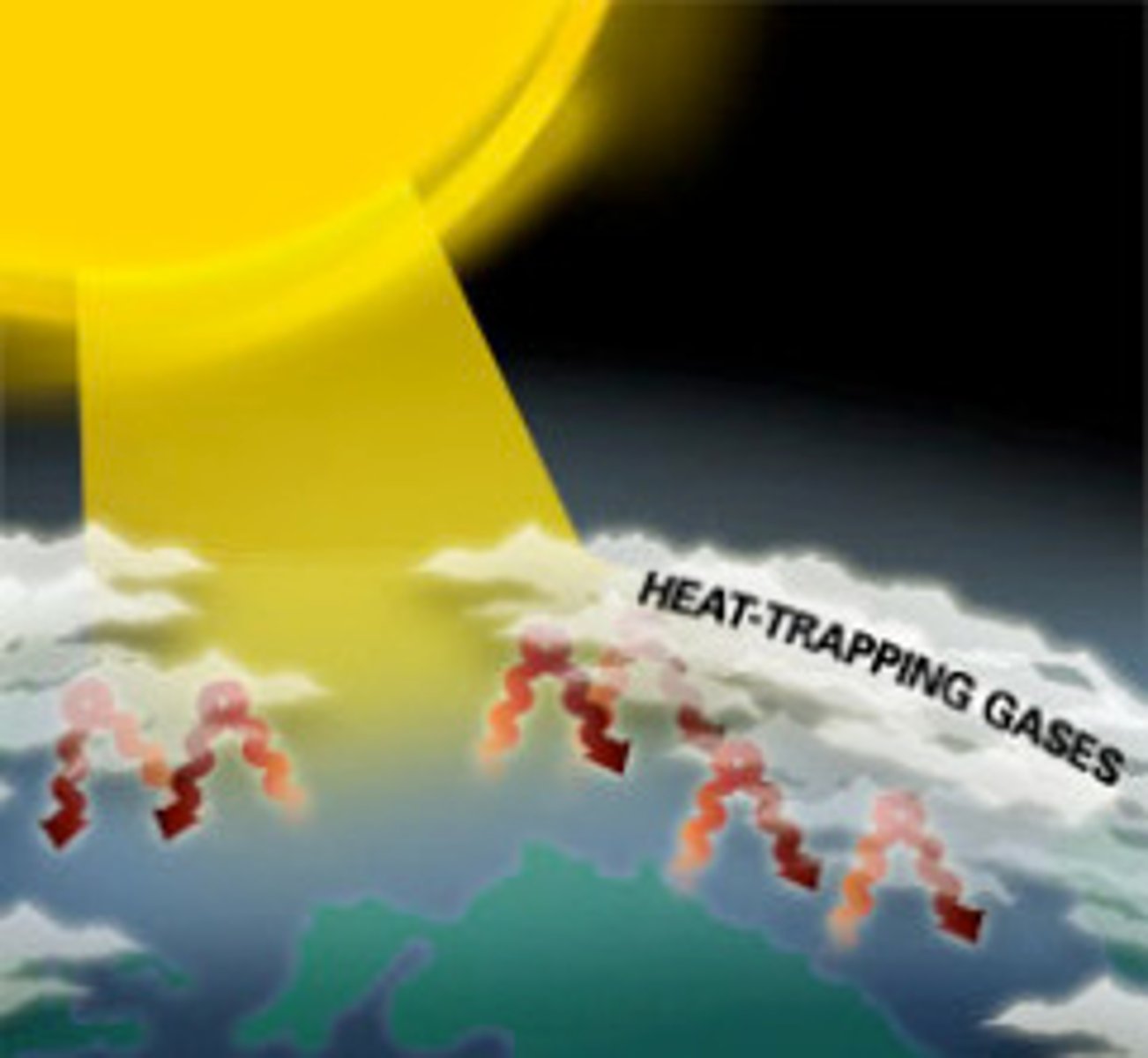
Greenhouse Gases
Gases such as water vapor, carbon dioxide, and methane that absorb heat leaving the Earth's surface.

Climate Change
Change in the statistical properties of the climate system when considered over periods of decades
Sea Level Rise
Increase in average sea level over time. Caused by thermal expansion of seawater and melting of land-based glaciers. Results in coastal flooding and more severe storm surge.
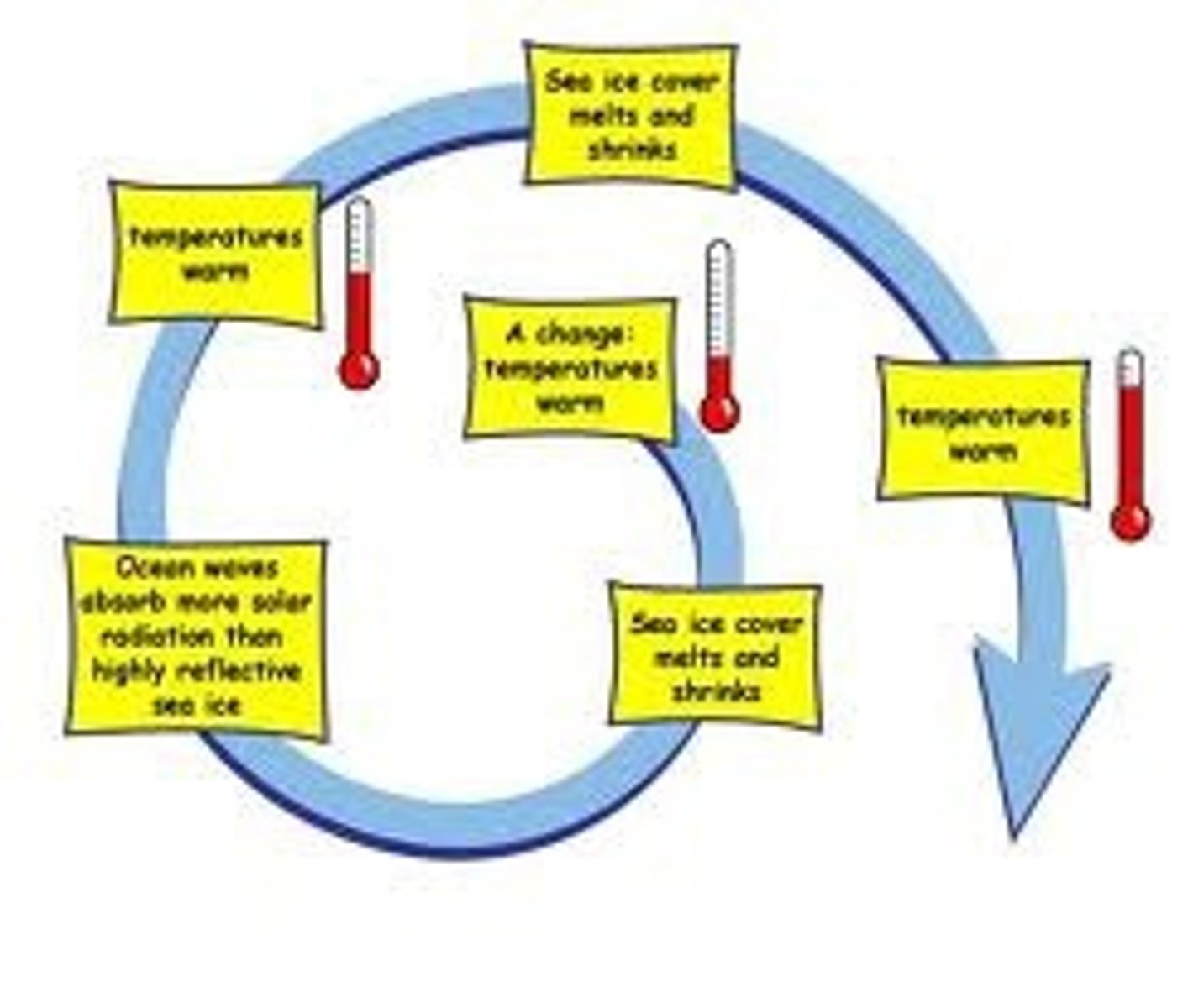
Positive Feedback Loop
Causes a system to change further in the same direction.
Kyoto Protocol
1997 treaty that calls for industrialized countries to reduce greenhouse gas emissions
Biodiversity
The number and variety of organisms in a given area during a specific period of time. Measured at ecosystem, species, and genetic levels.
Ecosystem Diversity
A measure of the diversity of ecosystems or habitats that exist in a particular region
Genetic Diversity
The range of genetic material present in a gene pool or population of a species.
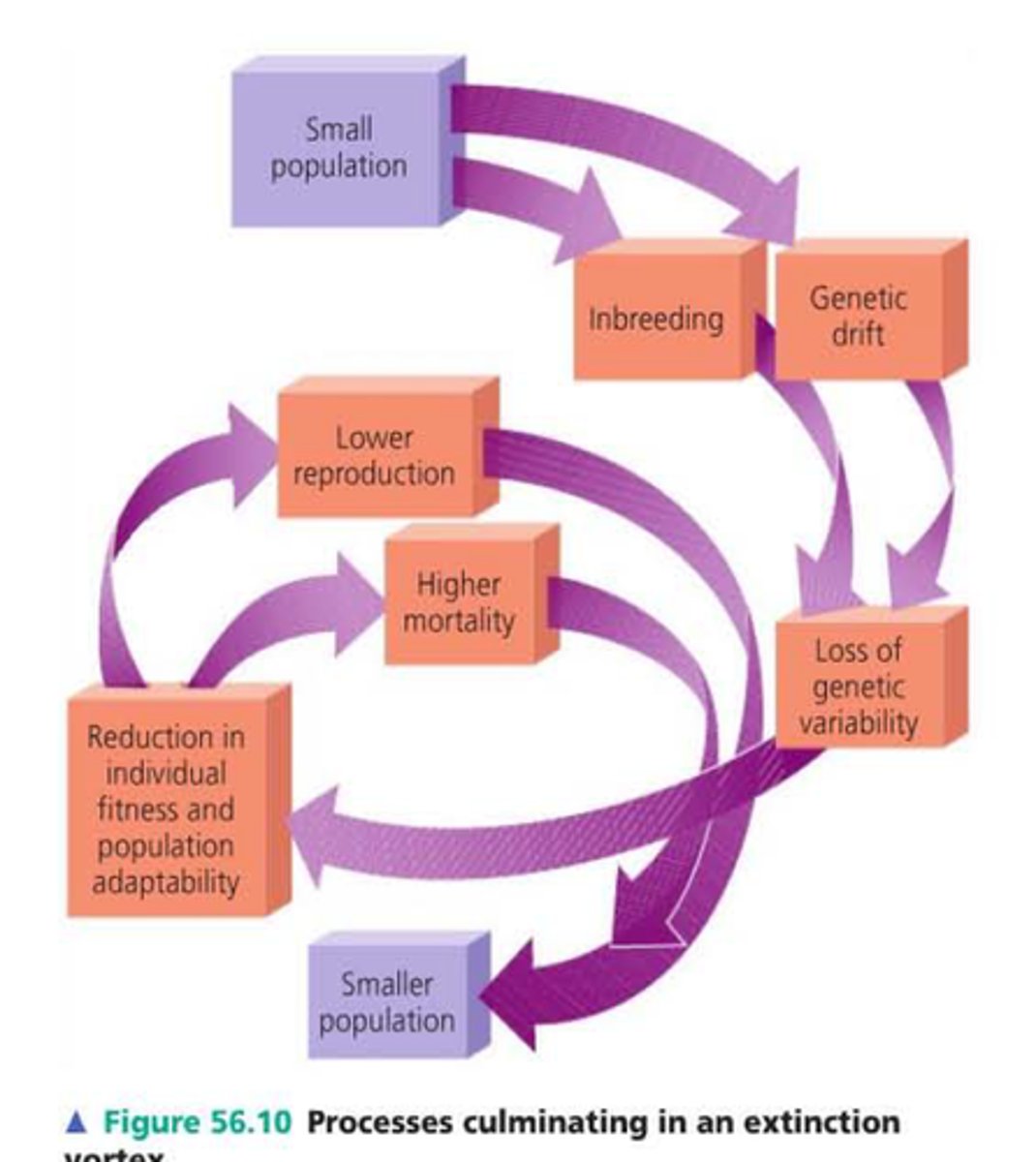
Extinction Vortex
Phenomenon experienced by endangered species. Small populations result in genetic drift and inbreeding, which decreases the fitness of individuals and causes the population to decrease even further.
Species Richness
The number of species in a given area
Species Evenness
The relative proportion of different species in a given area
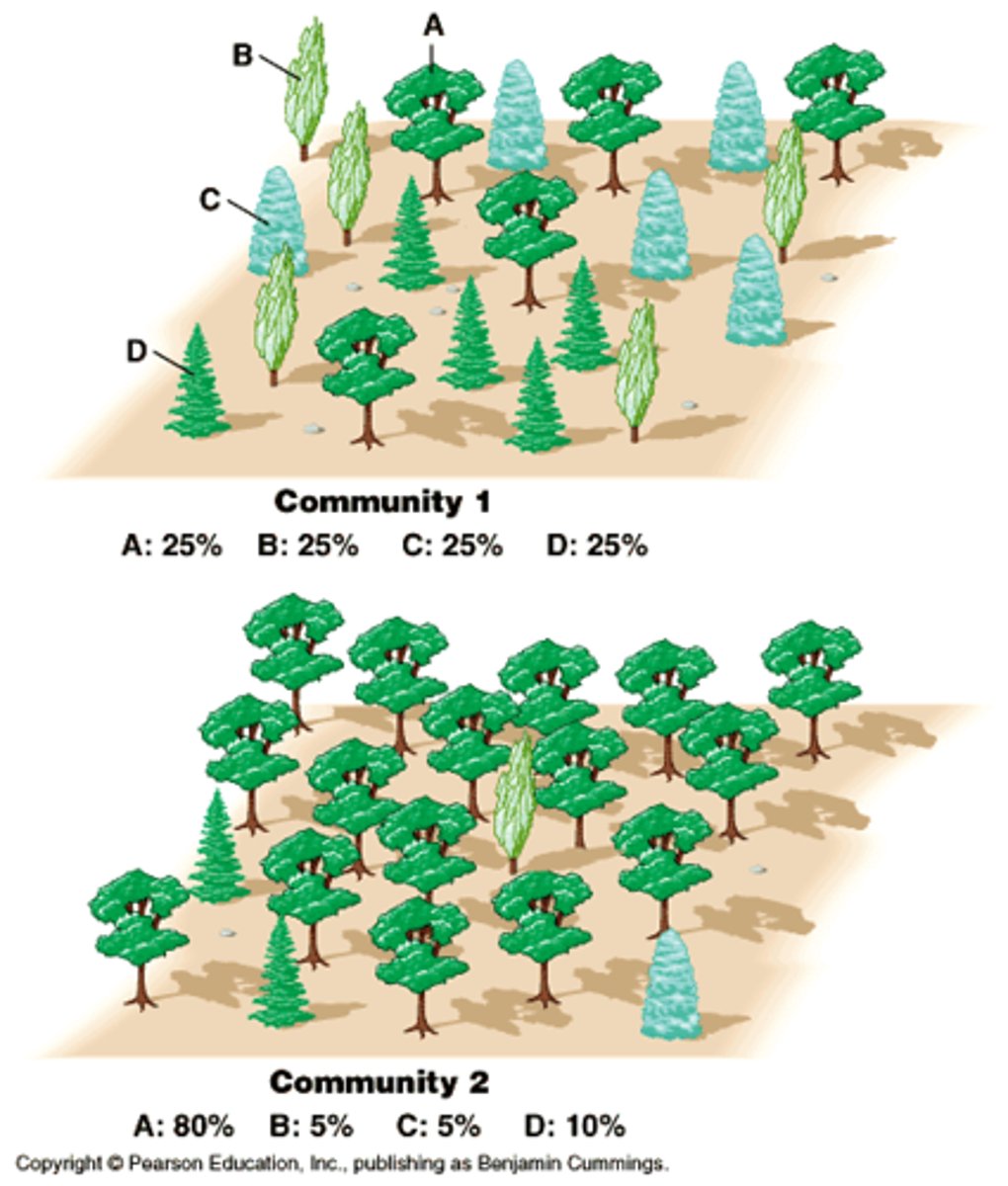
Ecosystem Stability
The ability of an ecosystem to survive and maintain a balance among the organisms; depends on high biodiversity.
Background Extinction
The continuous, low-level extinction of species that has occurred throughout much of history.
Mass Extinction
Event during which many species become extinct during a relatively short period of time
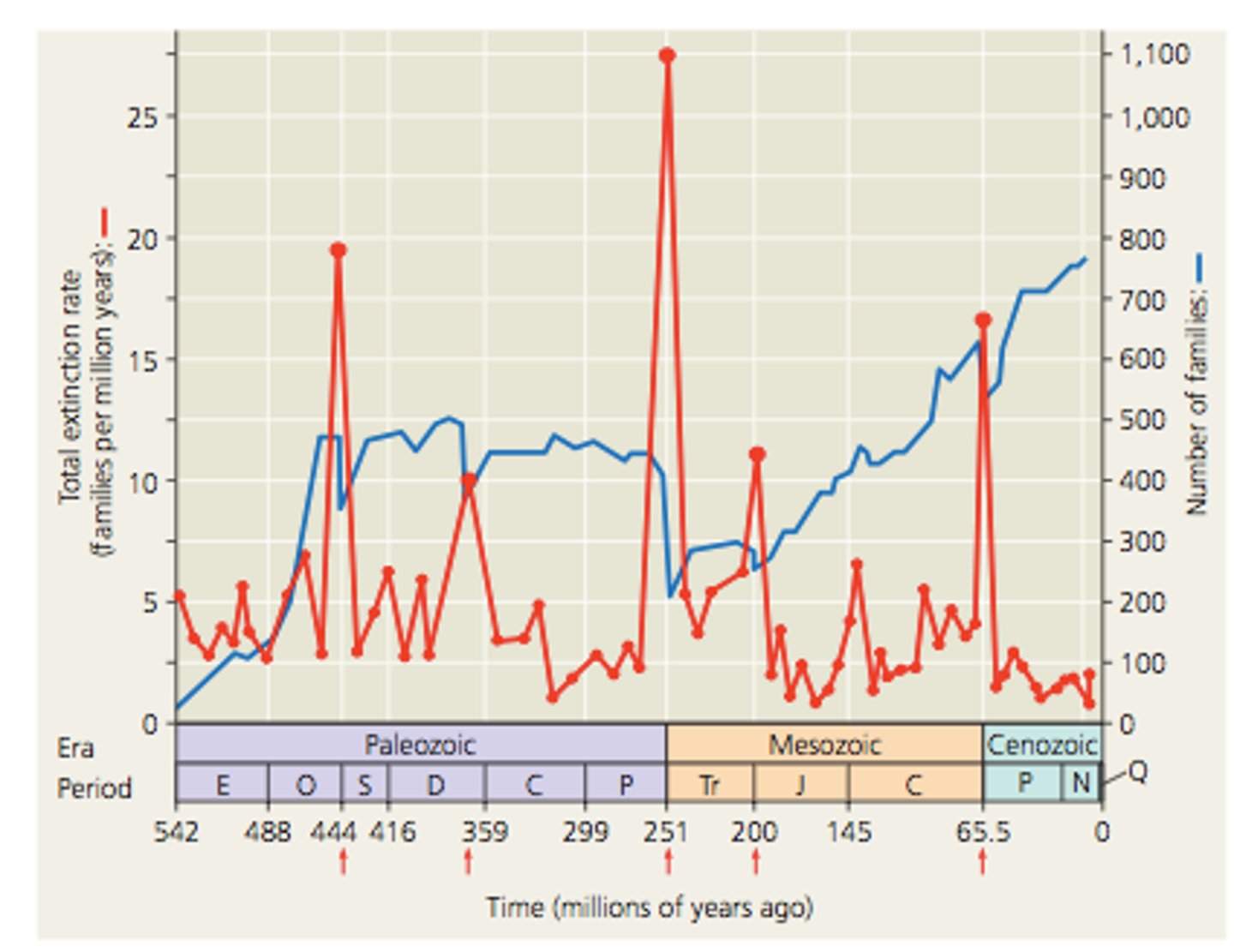
Extinction Rate
A percentage or number of species that go extinct within a certain time period; 100-1,000 times higher due to human impact.
Habitat Loss
The destruction of habitats that usually results from human activities
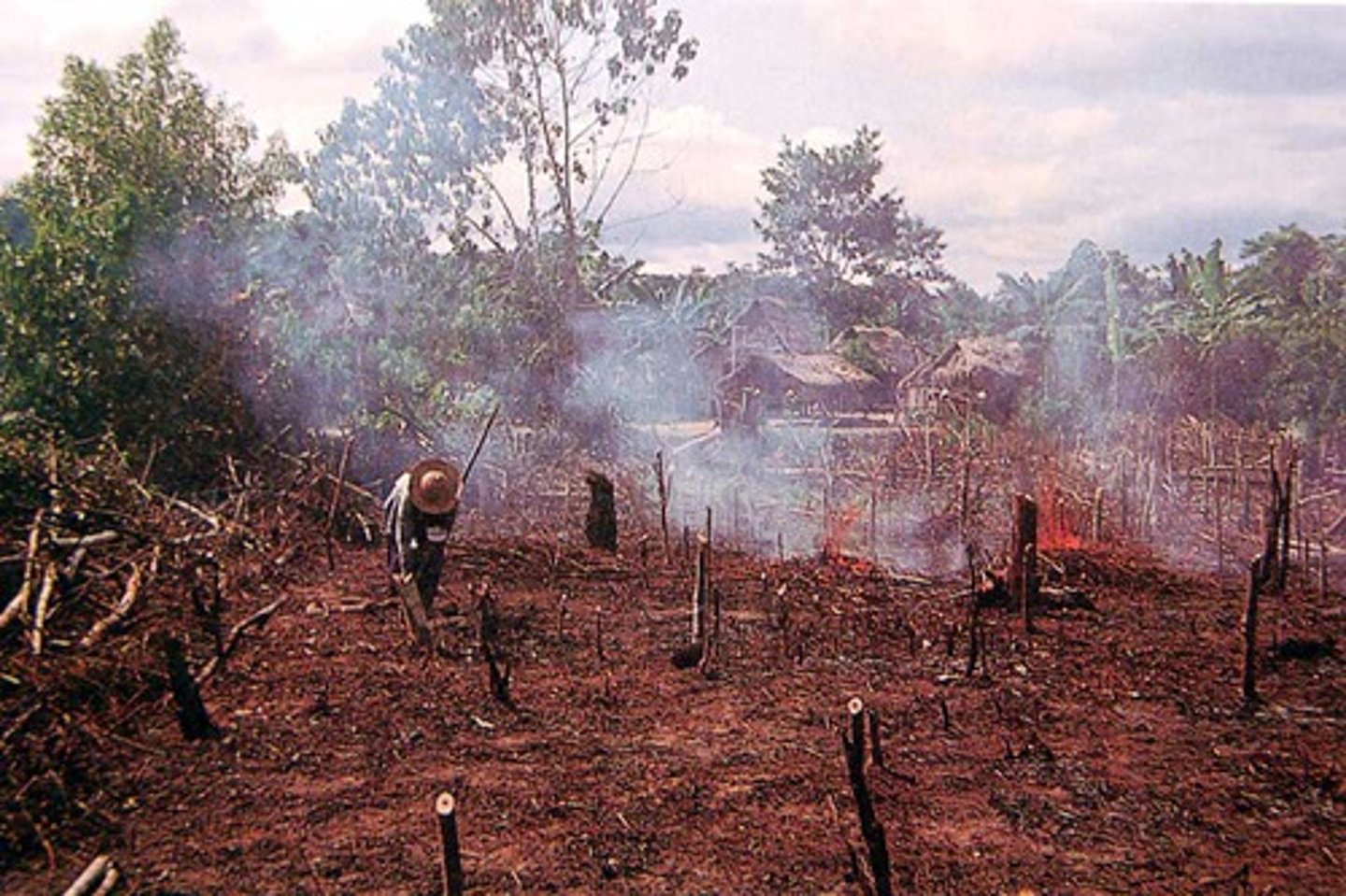

Habitat Fragmentation
Breakup of a habitat into smaller pieces, usually as a result of human activities.

Invasive Species
Species generally introduced by humans, that take hold outside of their native range. Typically decrease the biodiversity of native species.

Overharvesting
Overuse of species with economic value--a factor in species extinction

Ocean Acidification
When CO2 dissolves in seawater, it reacts with water to form carbonic acid, which lowers ocean pH
Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species
(CITES) lists species that cannot be commercially traded as live specimens or wildlife products.
Endangered Species Act
1973 U.S. legislation that implements CITES, designed to protect species from extinction; identifies/protects threatened and endangered species
Endangered Species
A species that is in danger of extinction throughout all or a significant portion of its range.
Threatened Species
A species that has been identified to be likely to become endangered in the foreseeable future.
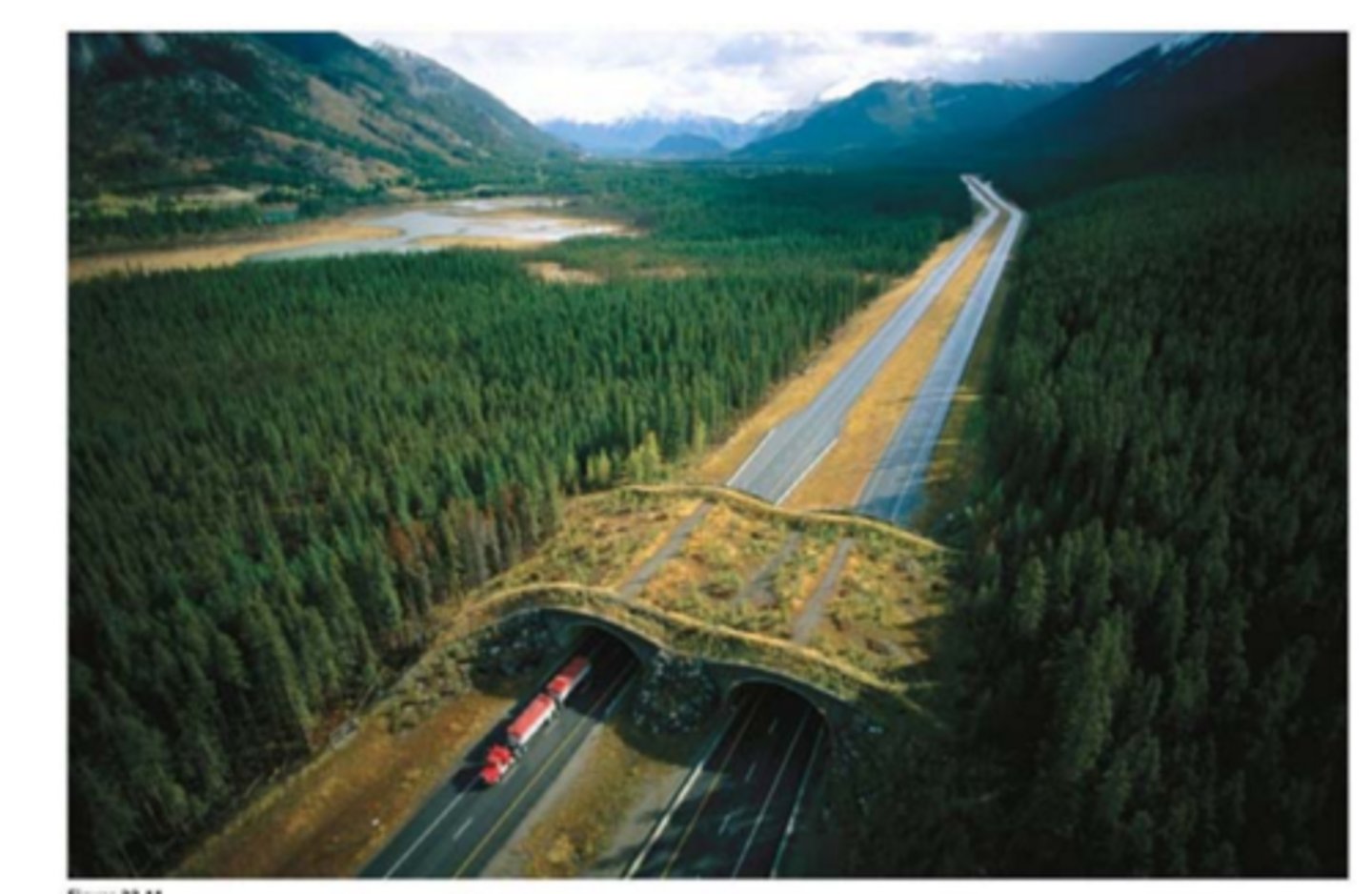
Habitat Corridors
Helps connect fragmented habitats used by different species

Marine Protected Area
A region in or near an ocean where human activity is limited in order to preserve marine life.
edge habitat
A habitat that occurs where two different communities come together, typically forming an abrupt transition. This often has an effect on biodiversity due to overlapping habitats
biosphere reserves
protected areas consisting of zones that vary in the amount of permissible human impact
carbon sequestration
an approach to stabilizing greenhouse gases by removing CO2 from the atmosphere
Externalities
economic side effects or by-products that are usually absorbed by a community or society at-large
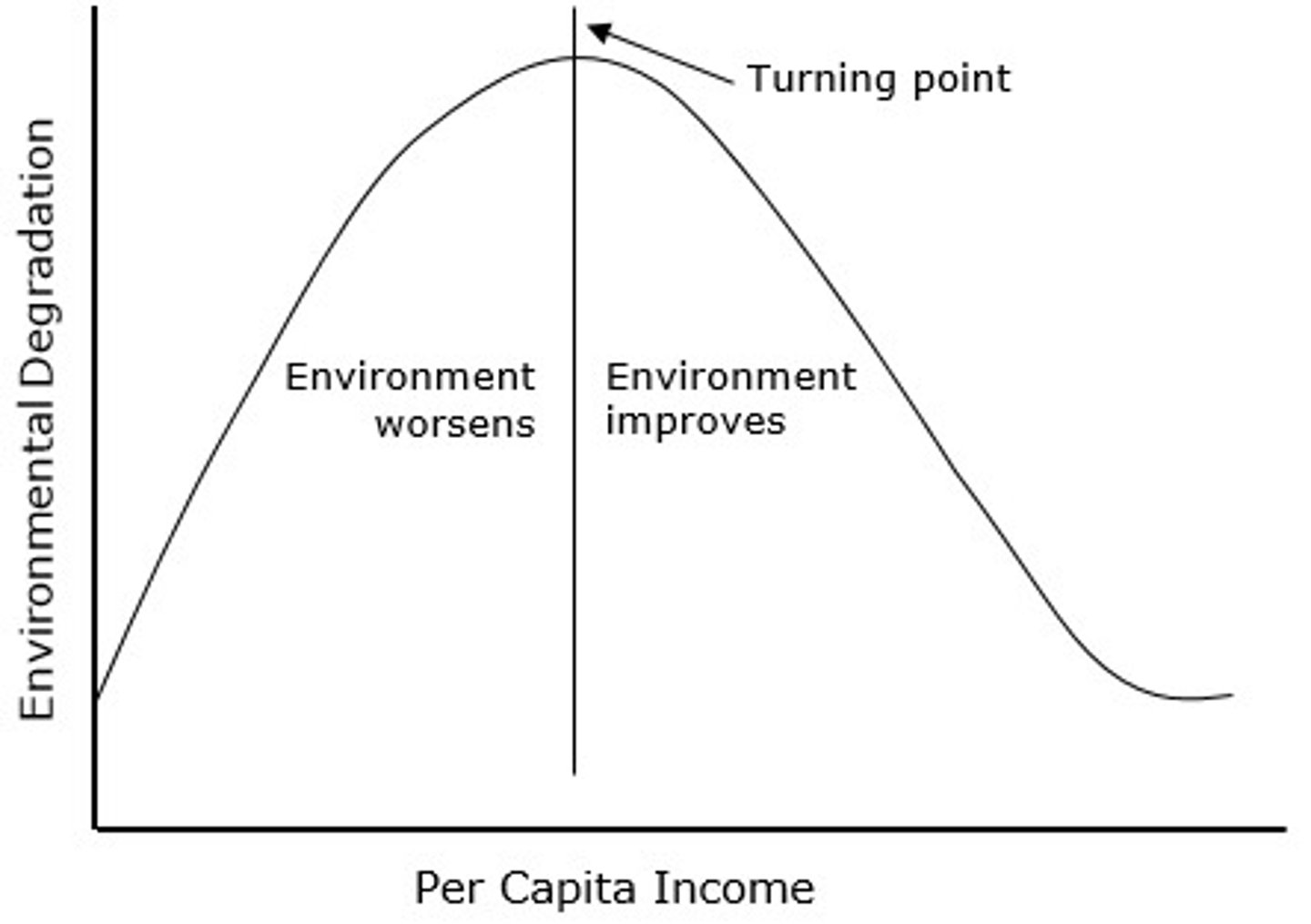
Kuznets Curve
graphs the hypothesis that as an economy develops, market forces first increase and then decrease environmental degradation
Genuine Progress Indicator (GPI)
A measurement of the economy that considers personal consumption, income distribution, levels of higher education, resource depletion, pollution, and the health of the population.
precautionary principle
the idea that one should not undertake a new action until the consequences of that action are well understood. The opposite of 'innocent-until-proven-guilty'
command-and-control approach
a strategy for pollution control that involves regulations and enforcement mechanisms
incentives-based approach
Uses taxation or tax refunds or some other positive enforcement for behavior that benefits the environment