Lecture 1 Water, Acids, Bases and Buffers
1/32
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
33 Terms
What is the property of water? what kind of compounds does it dissolve? How does it interact? pH? Shape of water molecule?
-It is a Polar molecule
-dissolves hydrophilic compounds
-interacts through hydrogen bonds
-pH of 7
-asymmetrical shape
-highest heat capacity
-only substance naturally in all 3 states
What is polarity caused by?
-the difference in electronegativity
what is eletronegativity?
-An atom’s attraction to electrons
Hydrophilic molecules in water are?
-soluble in water
-usually polar molecules
Hydrophobic molecules in water are?
-not soluble in water
-usually non-polar molecules
what is amphipathic/amphiphilic?
-both hydrophilic and hydrophobic regions
what two major forces stabilize hydrophilicity?
-electrostatic attraction (ion-dipole, dipole-dipole)
-hydrogen bonding
What are the 4 different weak noncovalent bonds?
Hydrogen bonds
ionic interactions
hydrophobic interactions
van der waals interaction
What is a Hydrogen bond?
-a weak bond involving a hydrogen donor and an acceptor
Why are hydrogen bonds disrupted by water?
-there is a competition for donor and acceptor
What is a hydrophobic interaction?
-a passive interaction that doesn’t need energy input.
-It minimizes the loss of hydrogen bonds between water molecules
What powers protein folding?
-the hydrophobic effect
-hydrophobic residue hidden inside while hydrophilic residue is exposed
what is the van der waals interaction?
-nonspecific interaction of any 2 atoms within 3-4 A of each other
-via electrostatic interaction by transient asymmetric distribution of electronic charge around an atom
What are the functions of weak bonds?
-a large number of weak bonds may contribute to stability
-allow for transient and specific interactions
What are the 4 hydrogen concentrations of pH?
Hydrogen ion (H+)
Hydride (H-)
Hydrogen (H)
Hydroxide (OH-)
Acid/Base which is the donor and the acceptor?
-Acid is the proton donor
-Base is the proton acceptor
What is the difference between a strong acid and a weak acid and base?
-Strong acids and bases are completely ionized in an aqueous solution
-Weak acids and bases are incompletely ionized in aqueous solutions
Is water ionized?
-to a small extent water is ionized
-the ion product of water is constant at a specific temperature
What is pH and pOH?
-pH = -log10[H+]
-pOH = -log10[OH-]
what is a constant for a water based solution and at what temperature?
-Kw(1014M2) is a constant at 25*C
What is the definition of pKa for weak acids and bases?
-HA is a weak acid with A- as the conjugate base
-A- is a base and HA is the conjugate acid
pH = pKa when?
[A-] = [HA]
what is the equilibrium constant and what defines pKa?
-Ka
-log(1/Ka)
The formula for a base/acid conjugate acid varying on pH
-pH=pKa + log ( [A-]/[HA] )
If pH>pKa & log[A-]/[HA]>0 means?
if pH<pKa & log[A-]/[HA]<0 means?
-base form dominates
-acid form dominates
What is titration?
-an acid neutralized by an increasing amount of base or vice versa
what generates buffering (smaller pH change)?
-the same amount of OH- being added
What is a buffer?
-a solution (weak) whose pH resists change when small amount of acid or base is added
What is used as buffer system? what is not used?
-usually weak acids and bases
-no buffering using water
What is an equivalence point?
-ideal point where all the (titrant) starting acid or base is neutralized
What effects buffer capacity?
-concentrations of the buffer (higher conc.=higher buffer copacity)
what is the best buffering capacity at?
-when pH is close to pKa
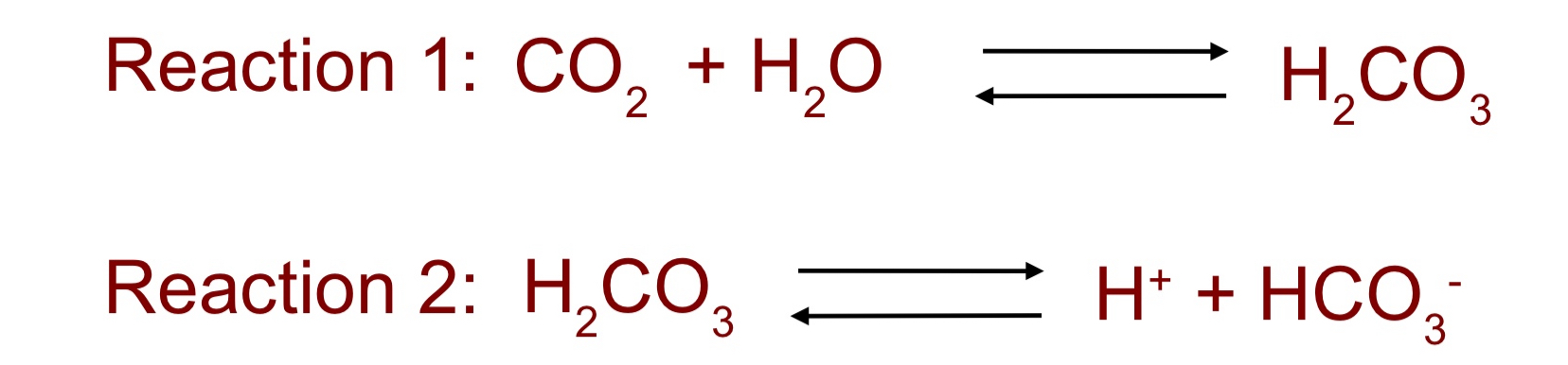
which reaction buffers pH in the blood?
what happens if too much acid is added to the blood?
-reaction 2
-reaction 2 moves left releasing CO2 via reaction 1 using respiration