AQA A Level Bio Biological Molecules
1/123
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
124 Terms
What is a monomer
A small repeating unit that can be joined together for form a larger one
What is a polymer
A larger unit made up of monomers
Name examples of monomers
Monosaccharide , amino acids , nucleotides
What is a condensation reaction
Two monomers are chemically bonded together , water is formed as a by product
What happens in a hydrolysis reaction
Two monomers are separated by breaking a chemical bond . Water is used up in this reaction .
Name examples of monosaccharides
Glucose , galactose and fructose
What is a disaccharide
A molecule made from 2 monosaccharides
How is a disaccharide formed
A condensation reaction between 2 monosaccharides
What makes up maltose
2 glucose molecules
What makes up sucrose
Glucose and fructose
What makes up lactose
Glucose and galactose
What is an isomer
A variation of a particular molecule . The formula stays the same , but structure is different
What are the isomers of glucose
Alpha and beta glucose
What is the difference between alpha and beta glucose
The hydroxyll group is in different positions
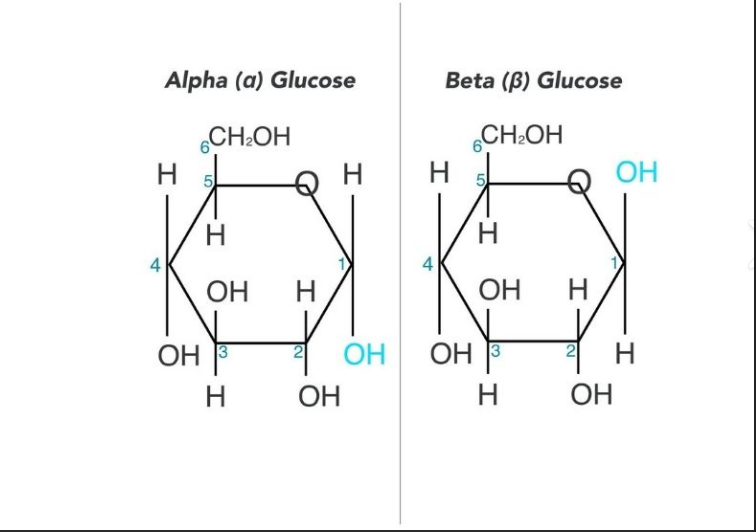
What is a polysaccharide
Multiple monosaccharides formed by condensation reactions
What is glycogen and what is it made out of
A polysaccharide made from multiple a glucose molecules and heavily branched
What is starch made out of
Amylose and amylopectin
What is cellulose
A polysaccharide made from multiple b glucose molecules
What is the purpose of glycogen
It is an energy storage in animals
What is the purpose of starch
It is an energy storage in plants
What is the purpose of cellulose
A structural molecules for plants , espicially for cell wall
What is the structure of glycogen
Heavily branched , 1-4 glycosidic bonds branched with 1-6 glycosidic bonds
How is glycogen’s structure related to its function
Highly branched for rapid glucose release
Compact so can be fit into small spaces
Insoluble so cannot affect water potential of cell
What is the structure of starch
Branched polymer of a glucose molecules , 1-4 glycosidic bonds and branched with 1-6 glycosidic bonds
How is starch structure related to its function
Insoluble so doesn’t affect water potential off cell so cell can’t burst
It is compact so can be stored in small spaces
Amylopectin has branches for rapid hydrolysis
What is the structure of cellulose
Straight lengths of b glucose bonded by 1-4 glycosidic bonds
How are monosaccharides in cellulose arranged
Alternative b glucose molecules are turned upside down
How is cellulose structure related to its function
Made up of b glucose so form long straight unbranched chains that are parallel
Bonded by many hydrogen bonds which provides collective strength .
Molecules are grouped together to form microfibrils which are grouped together to form fibres which provides more strength .
How to test for reducing sugar
1.Add benedicts reagent to sample
2.Heat for 5 minutes
If reducing sugar are present it will go blue to brick red
How to test for non reducing sugars
Use when a reducing sugar test is negative
1.Add hydrochloric acid to sample
2.Add sodium hydrogen carbonate to test
3.Add benedicts reagent
4.Heat for 5 minutes
If sugar is present it will turn blue to brick red
How to test for starch
1.Add iodine solution to sample
If starch present it will turn blue/black
How can we use a colorimeter to do a quantitative Benedict’s test
-Colorimeter measure the absorbance or transmission of light by a coloured solution
-More concentration solutions = more light absorbed/less light transmitted
-Compare to data table or calibration curve
What is the function of lipids
Energy source , Waterproofing , Insulation , Protection
What are the 2 groups of lipids
Triglycerides and phospholipids
What is the structure of a triglyceride
1 glycerol molecules and 3 fatty acids chains bonded by ester bonds
How is the structure of triglycerides related to its properties
-High ratio of energy storing C-H bonds so a good energy store
-Low mass to energy ratio so good storage molecule
-Large and non polar so insoluble in water and does not affect osmosis in cells
-High ratio of H-O atoms so release when water when oxidised to provide a source of water
What reactions occurs to form a triglyceride
A condensation reaction
What bond forms between a fatty acid and glycerol
An ester bond
What can lipids be
Saturated or unsaturated
What is the difference between saturated and unsaturated
Saturated means no double bonds between carbon atoms whilst unsaturated means there are 1 or more double bonds between carbon atoms .
What does having a double bond do to the fatty acid chain
Adds a kink into it , so that it isnt straight
What is the difference in structure between triglyceride and phospholipid
-Phospholipid: 2 fatty acid chains + 1 phosphate group
-Triglyceride: 3 fatty acid chains
Describe the structure of a phospholipid
A hydrophobic tail which orients itself away from water but mixes readily with fat and and a hydrophilic head which interacts with water
What does hydrophobic mean
Water fearing - will not dissolve , repels wate
What does hydrophilic mean
Water loving - will dissolve in water
How do triglyceride reacts to water
They are hydrophobic - repel water
Describe the phospholipid bilayer arrangement
-Hydrophilic head point outwards into water
-Hydrophobic tail points inwards
How to identify lipids
1.Mix sample with ethanol
Mix with water and shake
If lipids are present white emulsion forms
What are the monomers of proteins
Amino acids
What are the elements make up proteins
C,H,O,N,S
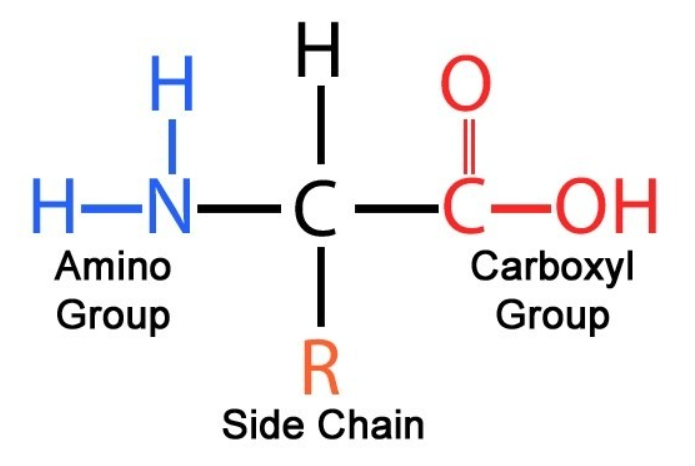
What is the structure of an amino acid
What reaction causes two amino acids to bond together
A condensation reaction
What bonds holds amino acids together
Peptide bond
What is formed when two amino acids bond by condensation reaction
A dipeptide
What is formed when many amino acids bond by condensation reaction
A polypeptide
What is a functional protein
A protein which has a particular role
What is the primary structure of a protein
A sequence of amino acids
What is the secondary structure of a protein
The primary structure folded into either alpha helix or beta pleated sheets which is held together by hydrogen bonds
What is the tertiary structure of a protein
The 3D shape of a protein which determines how the protein interacts. It is held together by hydrogen , ionic and disulfide bonds.
What is the quaternary structure of a protein
Multiple polypeptide chains with the additional prosthetic groups.
How to test for proteins
1.Add biuret solution to sample
2.If proteins are present , sample will turn blue to purple
What are the two main types of proteins
Globular and fibrous
What is the main role of globular proteins
Metabolic reactions
What are metabolic reactions
The sum of all reactions in the organism
What are anabolic reactions
Building up larger molecules
What are catabolic reactions
Breaking down molecules
What are enzymes
Biological catalysts that speed up chemical reactions
Name the energy that is required to start a reaction
Activation energy
How does an enzyme increase rate of reaction
Lowers activation energy
What is the induced fit model
The theory that the active site of an enzyme changes shape as the substrate binds to it . This is so that it can fit exactly to form an enzyme substrate complex .
Name the structure where the enzyme and substrate are bound together
Enzyme - substrate complex
Name the area on the enzyme and binds to and reacts with the substrate
Active site
The active site has a ____ shape to the substrate
Complementary
What determines the active site
The tertiary structure
What factors affect the rate of enzyme
Temperature , pH , enzyme and substrate concentration
How does temperature affect enzyme activity
Increases kinetic energy = more successful collisions = more e-s complexes form
Too high temperature , bonds denature , active site changes shape and e-s complexes can’t form
How does pH affect enzyme activity
Enzymes have an optimum pH
Below and above the optimum pH of an enzyme can cause the ionic bonds to break which alters the active site and e-s complexes can’t form so the enzymes denatured
How does substrate concentration affect enzyme activity
Increases substrate concentration means more e-s complexes can form
This is limited as all active sites eventually become saturated so rate of reaction plateaus
No more e-s complexes can form
How does enzyme concentration affect enzyme activity
Increase in enzyme concentration means more active sites available and more e-s complexes can form
Further increase in enzyme concentration will not increase the reaction rate as all the active sites are full
What is a competitive inhibitor
Similar shape to substrate, bind active site
Effect reduced by increasing substrate concentration
What is Non - competitive inhibitors
Binds allosteric site , change enzyme shape
Effect not reduced by adding more substrates
What are the two types of nucleic acid
RNA and DNA
What is the role of DNA
It carries genetic information
What is the role of RNA
It transfers genetic information from DNA to the ribosomes
Name the monomer of a nucleic acid
Nucleotide
What are the three components of a DNA nucleotide
Deoxyribose sugar , phosphate group , nitrogen - containing base
Name the four DNA bases
Adenine , Thymine , Cytosine , Guanine
What bonds join nucleotides in a single strand
Phosphodiester bond
What reaction joins phosphodiester bonds
Condensation reaction
Describe the structure of DNA
Double helix , Two antiparallel polynucleotide strands held together by hydrogen bonds between complementary base pairs
Which bases pairs together
A-T , C-G
What is the term called when the bases pair together
Complementary base pairing
Which bonds holds complementary base pairing together
Hydrogen bonds
How many hydrogen bonds between A-T and C-G
A-T = 2
C-G = 3
Why is complementary base pairing important
It ensures accurate DNA replication
What does antiparallel mean
One strand runs 5-3 and the other runs 3-5
What is the purpose of DNA replication
To produce identical DNA before cell division
What is semi conservative replication
New DNA molecules contain one original strand and one new strand
Summarise the entire process of DNA replication
DNA replication is semi-conservative. DNA helicase unwinds the double helix by breaking hydrogen bonds between bases, forming two template strands. Free DNA nucleotides are attracted to exposed bases via complementary base pairing (A–T, C–G). DNA polymerase joins adjacent nucleotides with phosphodiester bonds, forming the sugar–phosphate backbone . Each new DNA molecule contains one original strand and one newly synthesised strand.
What did the Meselson -Stahl experiment prove
Semi - conservative replication