W3L2: Peptides, Lipids, Nucleosides, Gases
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
peptides: structure
building blocks of proteins consist of two or more amino acids (either produced naturally in body or consumed through food)
peptides: synthesis
not synthesised from smaller compounds but product of larger compounds (poly-peptides) being broken down into peptides within neuron before release at terminal button
peptides: modulation
serve as modulators but can also act as neurotransmitters and co-release with neurotransmitters (same compound having multiple roles and functions in different contexts)
peptides: opiates
high density of opioid receptors in brain in areas involved in pin
peptides: endogenous opiods
originating internally - opium
peptides: opiates
drugs (morphine, heroin, opium)
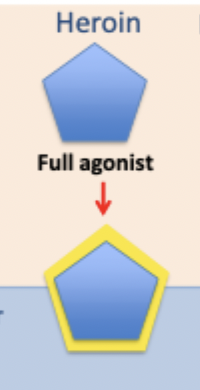
peptides: opiates: heroin
full agonist (not neurotoxic but can cause death/respiratory failure)
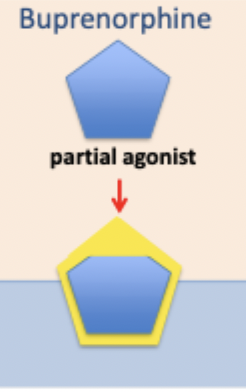
peptides: opiates: buprenorphine
partial agonist at receptors used as treatment for heroin dependence
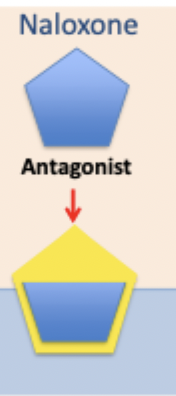
peptides: opiates: naloxone
full antagonist and can be used to rapidly block effect of heroin and prevent overdose (no stimulating effect - blocks receptor so person is brought out of overdose) very painful as it blocks all opioid receptors
peptides: opiates: methadone
agonist and is used in treatment of dependence because it has much slower course than heroin
lipids
naturally occurring molecules that include fats, waxes and others (hydrophobic - water fearing) - main biological function is energy storage, signalling and providing structural components of cell membranes
lipids: synthesis
synthesis pathways remain unclear but many serve as neurotransmitters/modulators
lipids: endocannabinoids
best known lipid neurotransmitters (two receptors CB1 and CB2)
lipids: endocannabinoids: CB1
found in brain - responsible for main psychological effects - receptor activation, shortens duration of action potentials in presynaptic neuron decreasing amount of neurotransmitter released
lipids: endocannabinoids: CB2
found in peripheral tissue
lipids: endocannabinoids: role
shortening duration of action potentials in presynaptic neuron and decreasing amount of release - dampening down and modulating neurons
lipids: CB1: locations
basal ganglia, cerebellum, cerebral cortex, hypothalamus, medulla, hippocampus, spinal cord
lipids: cannabis
THC = active ingredient, acts on CB1 receptors
lipids: cannabis: hippocampus
shortens duration of action potentials, dampening down on hippocampus neuronal qualities (has memory effects)
lipids: CB1 locations: cerebellum
movement
lipids: CB1 locations: basal ganglia
movement
lipids: CB1 locations: cerebral cortex
higher cognitive function
lipids: CB1 locations: hypothalamus
appetite
lipids: CB1 locations: hippocampus
learning, memory, stress
lipids: CB1 locations: medulla
nausea/vomiting, chemoreceptor trigger zone
lipids: CB1 locations: spinal cord
peripheral sensation including pain
nucleosides
subunit of nucleic acids, heredity-controlling components of all living cells (DNA and RNA) - obtained by chemical/enzymatic breakdown of nucleic acids (modulate release of other transmitters)
nucleosides: adenosine
forms breakdown of adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
nucleosides: adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
primary energy source in cells for transport systems and many enzymes
nucleosides: adenosine: levels
when you are awake levels gradually rise and in normal conditions promotes sleep and suppresses arousal
nucleosides: adenosine: at synapse
where adenosine is primary neurotransmitter, high postsynaptic firing rate leads to sleepiness (increased firing = reduced activation/arousal)
nucleosides: caffeine
acts as adenosine-receptor antagonist and blocks bodies natural action of adenosine
nucleosides: caffeine: plants
acts as natural pesticide that paralyses and kills insects that attempt to feed on the plants
nucleosides: caffeine: increase altertness
because adenosine increases firing rate in brain areas that promote sleepiness, caffeine increases alterness by reducing firing/activation of these neurons
gases: gases in neurotransmitters
nitric oxide and carbon monoxide
gases: nitric oxide (NO)
main role in dilating blood vessels - produced from amino acid Arginine in subpopulation of 1-2% of neurons in cortex
gases: nitric oxide: function
involved n learning and memory through effects on synaptic plasticity, dilates blood vessels in regions of brain that become metabolically active (rush of blood in all areas of brain)
gases: nitric oxide: difference from traditional neurotransmitters
not synthesised and stored in vesicles, produced throughout cell including dendrites and defuses out of cell as soon as produced, doesn’t activate receptors but simply enters neighbouring cell, short lived and degraded or acted within few seconds of being produced