Inflation and deflation
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
8 Terms
Inflation
A continuous rise in the price of goods and services.

Consumer Price Index
The key measure of inflation- the change in the cost of buying a fixed basket of goods and services.
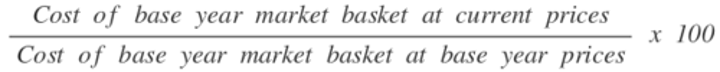
Deflation
A sustained drop in the price level.

Causes of inflation
- Cost-push inflation
- Demand-pull inflation
Cost-push
- Rising raw material costs, as a result of world demand for materials
- Higher wage demands
- Decreased exchange rate, increased prices of imported goods
Advantages of low rates of inflation to businesses
- Costs can be passed more easily to customers if the there is a general price inflation
- Real value of debt decreases, creating a fall in real value if liabilities
- Company's assets and capital can increase in value, making it seem more financially secure
- Inventories are bought in advance, and sold later there can be an increase in profit margin
Disadvantages of high rates of inflation to businesses
- Employees might demand higher wages
- Increased interest rates
- Consumers may become price sensitive and look for bargains
- If inflation is higher in one country than the other, then it can make a business uncompetitive internationally
- Consumers may stockpile items and cut back on non-essential item spending
- Cash flow problems may occur if businesses are unable to finance higher costs of materials and supplies
Disadvantages of deflation to businesses
- Consumers may delay purchases hoping for decrease in prices which causes a reduction in demand, and possible recession
- Businesses with long-terms debts make interest loans with money that has risen in value since the original loan was taken out
- As prices fall, the future profitability of new investment projects appears doubtful
- Inventories of materials and finished goods fall in value