Synthesis of Alcohols From Various Things
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Type of reactions alkenes to alcohols
Addition
Type of reaction alkyl halides to alcohols
substitution
Type of reaction ethers to alcohols
substitution
type of reaction ketone/aldehydes to alcohols
reduction
type of reaction carboxylic acids to alcohols
reduction
from alkyl halides reagents (think sn1 and sn2)
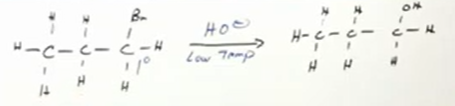
For SN1 reagent is usually neutral like water and sn2 reagent is usually basic like OH-. Both prefer low temperature. SN1 prefers 2nd degree and 3rd degree alkyl halides and SN2 prefers 1st and 2nd degree alkyl halides.
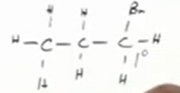
From alkyl halides chains
Remember, synthesis of alcohols from alkyl halides are substitution reactions. Sn2 reaction because 1st degree alkyl halide, so OH- reagent. low temperature and substitute the halide for the alcohol
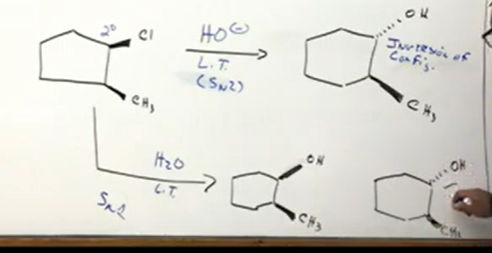
From alkyl halides rings
Secondary alkyl halide meaning it could be sn1 or two. If we choose sn2, remember, inversion of configuration. So when substituting, OH goes into the back in this case.
If we choose sn1, remember the reagent is water not OH like in sn2. sn1 also has inversion of configuration. However, in sn1 there is also retention of configuration, meaning it forms a racemic mixture and there is two products.
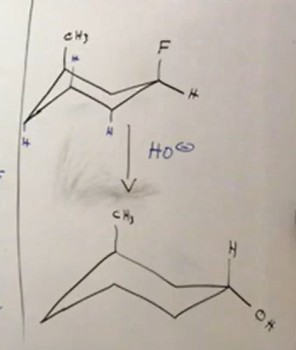
From alkyl halides chair
with sn2 we have inversion of config. because 2nd degree halide, choose sn1 or 2, because we chose oh- it is sn2. We replace F with OH because substitution, and add it to the right in the new chair confirmation. However, oh is now EQUITORIAL.
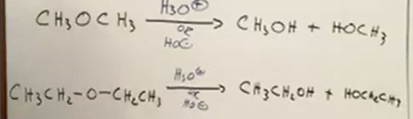
how synthesis from ethers works (remember its substitution)
We take ethers and “cleave” it under acidic or basic conditions to form two alcohols.
Simple ethers to alcohols
Just reagent of H3O+ or OH-
Cyclic from ethers (not symmetrical)
Still reagent of acid or base, OH replaces part on ring and whatever is left on that oh becomes the other product.

Difference between ketone carboxylic acid and aldehyde
For carboxylic acid convert to alcohols (specific) reagents
You can either use LiAlH4 with step 2 H3O+, hydrogenation H2 with a catalyst (Ni Pd Pt) or , or NaH with step 2 H3O+, but not the other reagents.
For ketone or aldehyde convert to alcohols reagents
All reagents used for carboxylic acids: LiAlH4 step 2 H3O+, H2 and a catalyst, or NaH step 2 H3O+
As well as NaBH4 with step 2 H3O+, alkylations with alkyl lithiums RLi or RMgBr with the R usually being methyl CH3.
Hydride nucleophile can be obtained from reagents:
LiAl4, NaH, and NaBH4 all with a H3O+ work up step 2.
R nucleophile obtained from reagents
RLi or RMgBr, however the R group gets added to it as well
from ketones
Ketone bc two R groups on either side of the carbon attatched. That new C-C bond formed is called “couples”
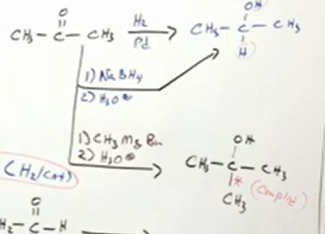
From aldehydes
Notice if creates H nucleophile, H is added to product. If creates R nucleophile, the R group is added to product.
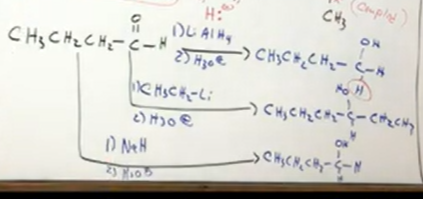
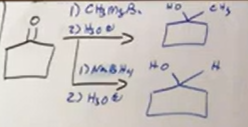
from ketones rings
Again, keep ring the same just replace O with alcohol and R or H. Remember for carbonyls, ketones, and aldehydes, al need the H3O+ make up step as step 2 usually under arrow. Only hydrogenation doesn’t have that.
From carboxylic acids which reagent can you not pick (especially if oxidative level is at 3 or more - count it be how many oxygens and double bonds there are)
You cannot do NaBH4 with H3O+ step 2 or the grinyar R reagants. The R ones dont work well with acids. No reaction would occur.
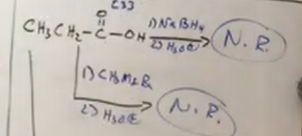
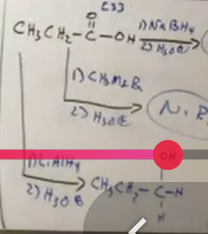
from carboxylic acids you can do
Hydrogenation, or LiAL4 or NaH with work up step. It will form two the alcohol
From alkenes to alcohol basics
Water cannot be added directly, it needs to be under acidic or basic conditions. Remember it is an addition reaction. Reaction favors low temperature. Just change double bond to all single bonds and add an OH above one of the C’s in the double bond.
Alkenes to alcohol reagents
Hg(OAc)/H2O with a step 2 NaBH4 work up step, or BH3 with a step 2 H2O2 work up step.
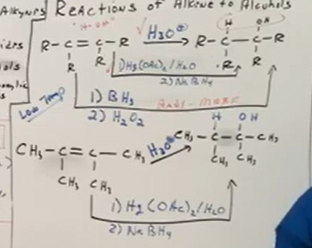
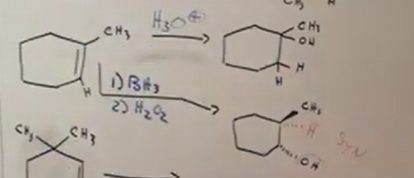
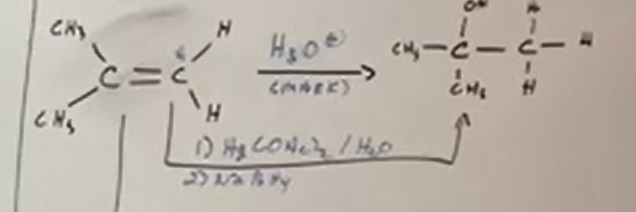
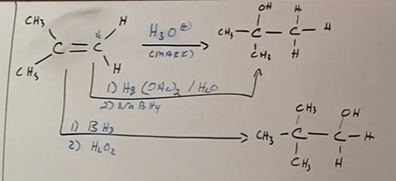
Asymmetrical alkene to alcohol - MAKARVNIKOV
The hydrogen in the OH attatches to the most substituted carbon (which is the carbon attatched to the MOST non-hydrogen groups). Think addition here.
Makarvnikov reactions use the H3O+ or Hg(OAc)2/H2O with NaBH4.
Asymmetrical alkene to alcohol - NON/ANTI MAKARVNIKOV
The markarvnikov raeaction is regioselective, meaning the difference chances structurally with each one. in the anti, the H in OH attatches to the least subsituted carbon (carbon attatched to LEAST non-hydrogen groups).
Anti makarvnikov reactions use BH3 and H2O2 make up step as reagents
(Bottom example in picture with BH3)
Alkene to alcohol in rings (show in mark and anti mark)