531 Lec 33
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 2:11 AM on 4/24/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
1
New cards
What nervous system is dopamine found
Peripheral
2
New cards
Can dopamine cross the BBB
No
3
New cards
What affects does dopamine have in the periphery
Inhibits NE release and acts as a vasodilator in the blood vessels
Increases sodium excretion and urine output in the kidneys
Reduces insulin production in the pancreas
Reduces GI motility and protects intestinal mucosa
Reduces activity of lymphocytes in immune system
Increases sodium excretion and urine output in the kidneys
Reduces insulin production in the pancreas
Reduces GI motility and protects intestinal mucosa
Reduces activity of lymphocytes in immune system
4
New cards
Know the enzymes and substrates and transformations of the biosynthetic pathway leading to dopamine production from L-tyrosine.
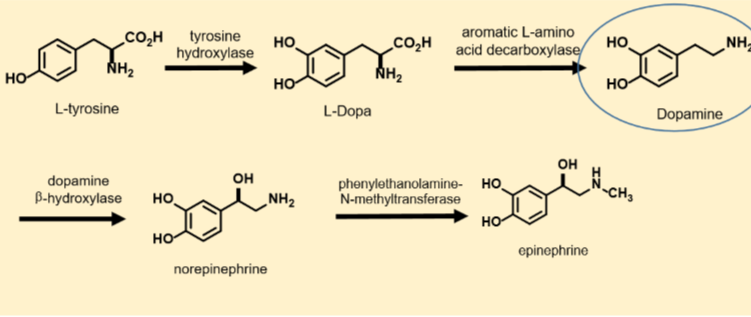
5
New cards
Know the catabolic pathways (enzymes/substrates/transformations) that break down dopamine into homovanillic acid.
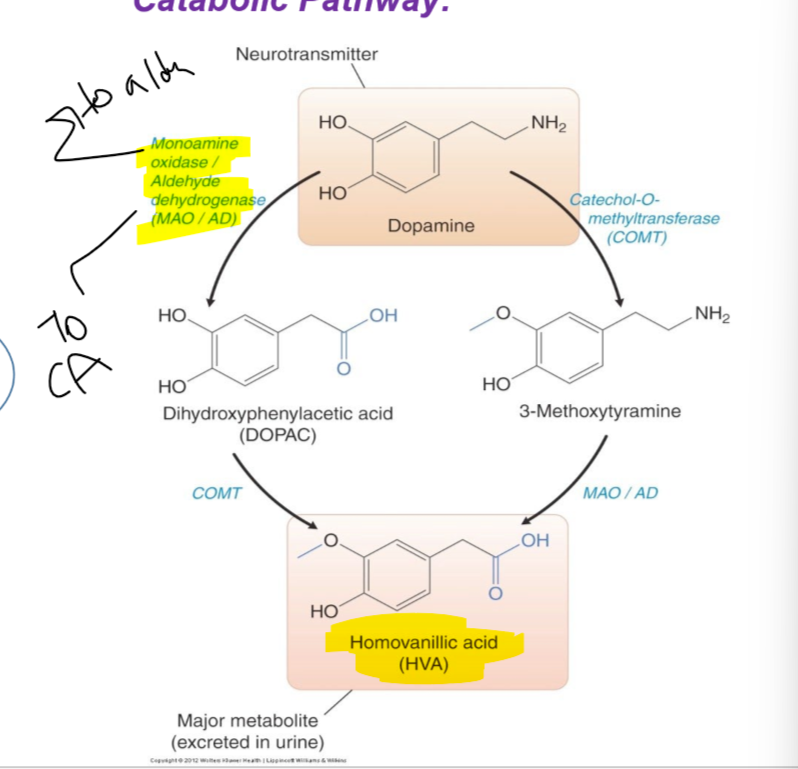
6
New cards
Dopamine receptors are….
G protein coupled receptors
7
New cards
D1 type receptors
D1, D5
8
New cards
D2 type receptors
D2, D3, D4
9
New cards
Understand the dopamine hypothesis and how it relates to Schizophrenia and associated therapeutics
States that overactive dopaminergic transmission in the CNS causes psychosis
\
\*No direct evidence for this
\
\*No direct evidence for this
10
New cards
positive cognitive symptoms.
Change in thoughts / feelings that add in to a person’s experience
\-Hallucinations
\-Delusions
\
(mesolimbic system hyperactivity)
\-Hallucinations
\-Delusions
\
(mesolimbic system hyperactivity)
11
New cards
negative cognitive symptoms.
Reflect a decrease in, or loss of, normal functions
\
\-Little display/range of emotions (affective flattening)
\-Lowered levels of motivation or drive (avolition)
\-Lack of interest in other people
\-Inability to feel pleasure
\-Inability to speak due to mental confusion (alogia)
\
(mesocortical system hyperactivity)
\
\-Little display/range of emotions (affective flattening)
\-Lowered levels of motivation or drive (avolition)
\-Lack of interest in other people
\-Inability to feel pleasure
\-Inability to speak due to mental confusion (alogia)
\
(mesocortical system hyperactivity)
12
New cards
Know the 4 dopamine pathways relevant in Schizophrenia – know how dopamine activity is imbalanced in the mesolimbic and mesocortical areas and what symptoms are associated with each.– you absolutely need to know this and it will appear in some form on a quiz/exam
1)Mesolimbic- increase in DA transmission here causes positive symptoms
2)Mesocortical- decrease in DA transmission here causes negative symptoms
3)Nigrostriatal- Schizophrenia drugs acting here cause EPS
4)Tuberoinfundebulum- Schizophrenia drugs acting here causes hyperprolacteinemia
2)Mesocortical- decrease in DA transmission here causes negative symptoms
3)Nigrostriatal- Schizophrenia drugs acting here cause EPS
4)Tuberoinfundebulum- Schizophrenia drugs acting here causes hyperprolacteinemia
13
New cards
EPS
extrapyramidal symptoms- involuntary movements, jerkiness, tremors, spasms
14
New cards
Hyperprolactinemia
Higher than normal plasma levels of prolactin, produced by pituitary to stimulate breast milk production 2
15
New cards
Understand how D2 type receptor antagonism helps treat Schizophrenia by altering dopamine action in a specific region of the brain and how this same action in other areas of the brain can exacerbate side effects.
An antagonist binding the D2 receptor blocks DA from binding. NO signaling occurs while the antagonist is bound
\
The net effect is less DA transmission in hyperactive and hypoactive areas
\
Suppresses hyperactive DA transmission in the Mesolimbic which helps alleviate positive symptoms
\
Hypoactive transmission in the Mesocortical is not improved which does not help negative symptoms
\
The net effect is less DA transmission in hyperactive and hypoactive areas
\
Suppresses hyperactive DA transmission in the Mesolimbic which helps alleviate positive symptoms
\
Hypoactive transmission in the Mesocortical is not improved which does not help negative symptoms
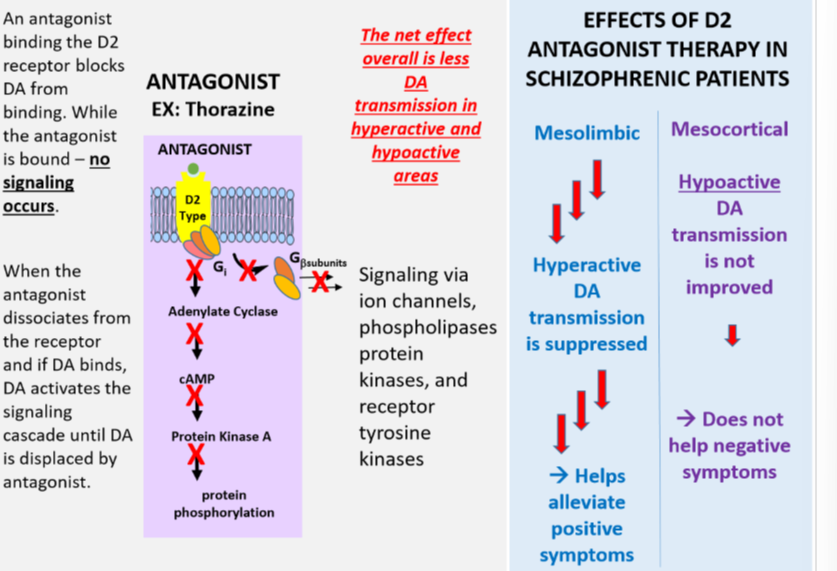
16
New cards
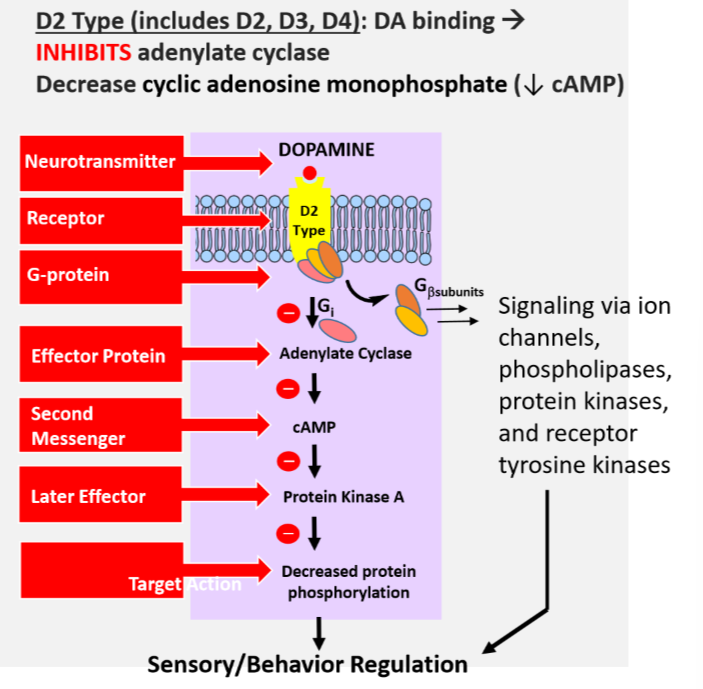
D1 Type receptor type impact on adenylate cyclase and cAMP level
Stimulates adenylate cyclase → increase cAMP
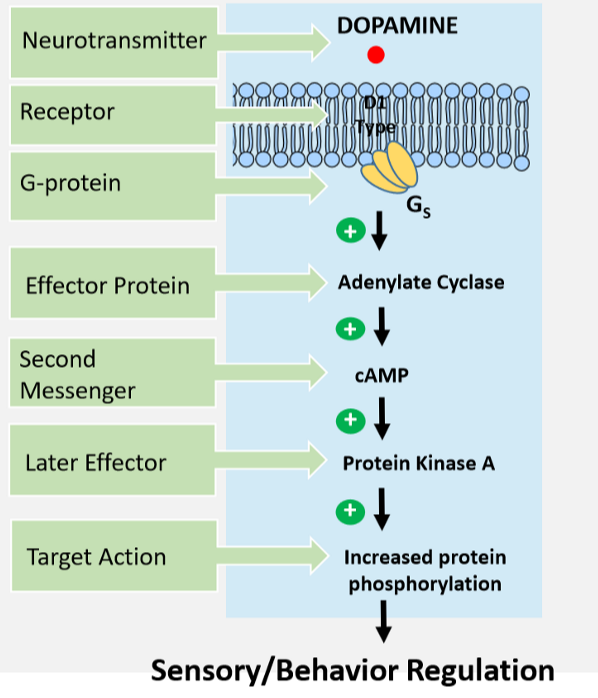
17
New cards
D2 Type receptor type impact on adenylate cyclase and cAMP level
Inhibits adenylate cyclase → decreased cAMP
18
New cards
Typical antipsychotics
•Antagonize mesolimbic and mesocortical D2 receptors
•Adverse effects likely mediated by binding to D2 receptors
•EPS side effects associated with >80% occupancy of D2 receptor by drug though this is not an absolute rule
\
\*Less commonly used due to side effects
•Adverse effects likely mediated by binding to D2 receptors
•EPS side effects associated with >80% occupancy of D2 receptor by drug though this is not an absolute rule
\
\*Less commonly used due to side effects
19
New cards
Atypical Antipsychotics
•Generally, show combined antagonist activities at D2 and 5HT2 receptors
•Avoid EPS side effects but may be due to weaker affinity at dopamine receptors
\
\*First line for schizophrenia, fewer side effects, more expensive
•Avoid EPS side effects but may be due to weaker affinity at dopamine receptors
\
\*First line for schizophrenia, fewer side effects, more expensive
20
New cards
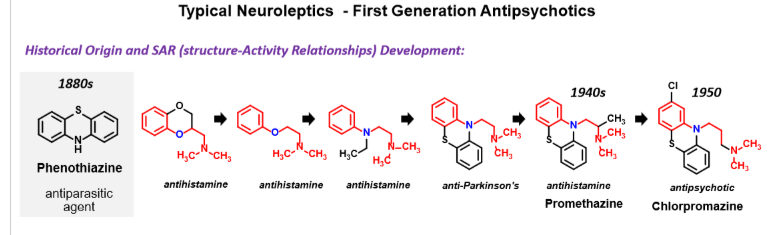
Know the pharmacophoric model for phenothiazine based, typical neuroleptics.
An electron withdrawing substituent is important to activity (Cl)
Side chain amine is protonated at pH7 (important)
Side chain has a 3 carbon linker often separated by 2 amines (need 3 for antipsychotic activity)
Side chain amine is protonated at pH7 (important)
Side chain has a 3 carbon linker often separated by 2 amines (need 3 for antipsychotic activity)
21
New cards
chloropromazine/Thorazine
•First antipsychotic discovered
•Usually administered as an injectable
•Complex metabolism→ 100 metabolites, some active at D2 receptor
•Black box warning for death of elderly with dementia
\
**Side effects: Sedative, EPS**
•Usually administered as an injectable
•Complex metabolism→ 100 metabolites, some active at D2 receptor
•Black box warning for death of elderly with dementia
\
**Side effects: Sedative, EPS**
22
New cards
Why are long acting neuroleptics helpful in treating schizophrenia?
→Adherence is a problem especially in this patient population
23
New cards
incorporating long chain fatty acid esters leads to ______acting neuroleptics because…
Long acting because long chain fatty acid esters are released slowly into bloodstream from lipophilic tissue
24
New cards
What physiochemical characteristic of long chain fatty acid esters imparts longer duration of action – be able to put them in order of shortest acting to longest acting.
Longer chain= longer duration of action
25
New cards
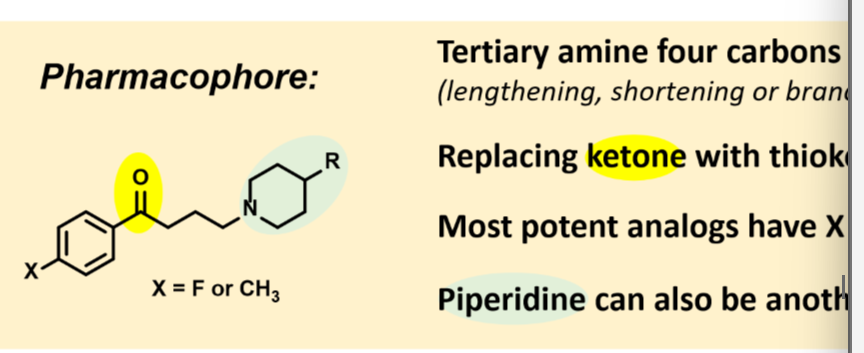
Know the pharmacophore of butyrophenone-based typical neuroleptics.
Tertiary amine four carbons away from phenyl group
Ketone
Most potent analogs have X=F at the 4 position
Piperidine can also be another cyclic amine
Ketone
Most potent analogs have X=F at the 4 position
Piperidine can also be another cyclic amine
26
New cards
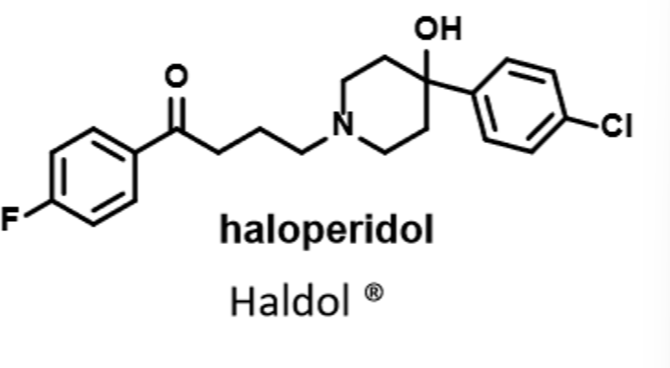
haloperidol
Typical neuroleptic- 1st gen antipsychotics
Butyrophenones
>affinity for DA receptors than chlorpromazine
Less weight gain than chlorpromazine
Used for manic phase of bipolar disorder
Butyrophenones
>affinity for DA receptors than chlorpromazine
Less weight gain than chlorpromazine
Used for manic phase of bipolar disorder
27
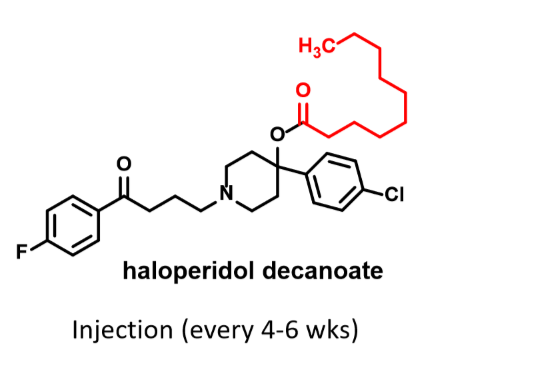
New cards
haloperidol decanoate
Typical neuroleptic- 1st gen antipsychotics
Butyrophenones
Injection (every 4-6 weeks)
Butyrophenones
Injection (every 4-6 weeks)
28
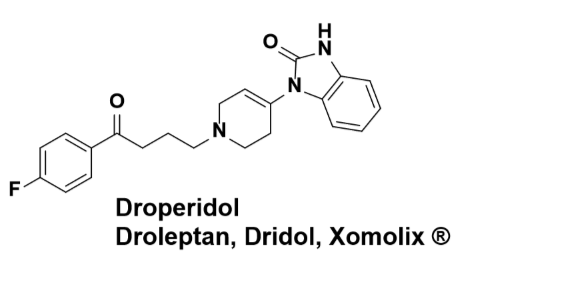
New cards
Droperidol
Typical neuroleptic- 1st gen antipsychotics
Butyrophenones
Short acting
Use: anesthesia for its sedating and antiemetic effects
Use: psychiatric emergency as a sedative neuroleptic
Butyrophenones
Short acting
Use: anesthesia for its sedating and antiemetic effects
Use: psychiatric emergency as a sedative neuroleptic
29
New cards
Know what distinguishes the Atypical/second generation neuroleptics from Typical/first generation neuroleptics
→Additional antipsychotic action at other receptors in addition to or instead of DA D2 receptor antagonism
→ Significant activity at 5HT2 muscarinic, adrenergic alpha1&2 and histamine in addition to DA receptors
→Weaker affinity for D2 receptor compared to first gen
→Difficult to classify agonism/antagonsim
→Fewer extrapyramidal effects compared to first gen neuroleptics
→Better at reating negative and positive symptoms
→Side effect profile and effectiveness against - and + symptoms distinguishes typical vs atypical drugs
→ Significant activity at 5HT2 muscarinic, adrenergic alpha1&2 and histamine in addition to DA receptors
→Weaker affinity for D2 receptor compared to first gen
→Difficult to classify agonism/antagonsim
→Fewer extrapyramidal effects compared to first gen neuroleptics
→Better at reating negative and positive symptoms
→Side effect profile and effectiveness against - and + symptoms distinguishes typical vs atypical drugs
30
New cards
Atypical neuroleptic- Second gen antipsychotics
Lumateperone (Caplyta)
Clozapine
Olanzapine
Quetiapine
Loxapine/Amoxapine
Asenapine
Risperidone
Ziprasidone
Apripiprazole
Brexipiprazole
Cariprazine
\
Clozapine
Olanzapine
Quetiapine
Loxapine/Amoxapine
Asenapine
Risperidone
Ziprasidone
Apripiprazole
Brexipiprazole
Cariprazine
\
31
New cards
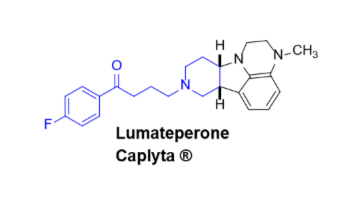
Lumateperone (Caplyta)
Atypical neuroleptic- Second gen antipsychotics
Antagonist at D2 receptors and 5HT receptors
Treats positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia
Oral administration
Antagonist at D2 receptors and 5HT receptors
Treats positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia
Oral administration
32
New cards
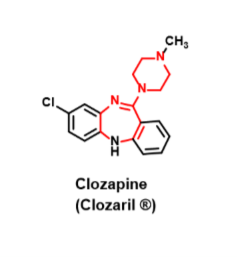
clozapine
Atypical neuroleptic- Second gen antipsychotics
•5HT2A antagonist, moderate D4 and weak D2 receptor antagonism
•Good for patients who dont respond to 1st gen
•Minimal EPS
•Also treats negative symptoms of schizophrenia
•1-2% patients suffer fatal agranulocytosis
•Incidence of weight gain is high with clozapine
•Orally active, metabolized mostly by CYP1A2
\
Drug interaction: Smoking indices CYP1A2 (adjust dose up)
Drug interaction: ciprofloxacin inhibits CYP1A2(adjust dose down)
•5HT2A antagonist, moderate D4 and weak D2 receptor antagonism
•Good for patients who dont respond to 1st gen
•Minimal EPS
•Also treats negative symptoms of schizophrenia
•1-2% patients suffer fatal agranulocytosis
•Incidence of weight gain is high with clozapine
•Orally active, metabolized mostly by CYP1A2
\
Drug interaction: Smoking indices CYP1A2 (adjust dose up)
Drug interaction: ciprofloxacin inhibits CYP1A2(adjust dose down)
33
New cards
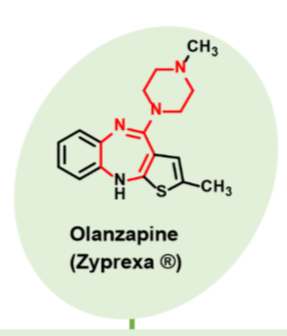
Olanzapine (Zyprexa)
Atypical neuroleptic- Second gen antipsychotics
•Higher affinity at DA D2 and 5HT2A receptors receptors than clozapine
•Antagonist activity at these receptors
•Similar side effect profile to clozapine
•**agranulocytosis not observed**
•Minimal EPS
•Treats negative and positive symptoms of schizophrenia
•Orally active
•Schizophrenia and bipolar
•Higher affinity at DA D2 and 5HT2A receptors receptors than clozapine
•Antagonist activity at these receptors
•Similar side effect profile to clozapine
•**agranulocytosis not observed**
•Minimal EPS
•Treats negative and positive symptoms of schizophrenia
•Orally active
•Schizophrenia and bipolar
34
New cards
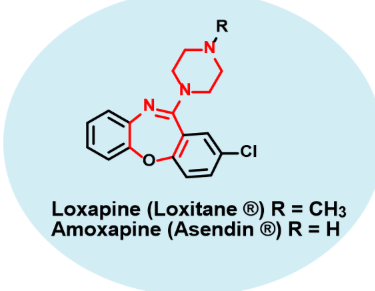
Amoxapine
Atypical neuroleptic- Second gen antipsychotics
metabolite of loxapin via N dealkylation
•High affinity at D2, 5HT2 and H1 receptors
•Amoxapine has moderate SERT and NET blocking activity which gives it some antidepressanr activity too
•Schizophrenia and bipolar
metabolite of loxapin via N dealkylation
•High affinity at D2, 5HT2 and H1 receptors
•Amoxapine has moderate SERT and NET blocking activity which gives it some antidepressanr activity too
•Schizophrenia and bipolar
35
New cards
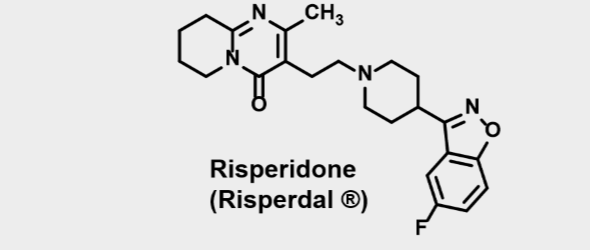
Risperidone
Atypical neuroleptic- Second gen antipsychotics
•Very high affinity for 5HT2A - antagonist
•High affinity for dopamine D2- antagonist
•High affinity for H1 and alpha1 receptors
•No affinity for muscarinic receptors
•Higher incidence of EPS than other 2nd gen neuroleptics
•Weight gain
•Treats both positive and negative symptoms
•Very high affinity for 5HT2A - antagonist
•High affinity for dopamine D2- antagonist
•High affinity for H1 and alpha1 receptors
•No affinity for muscarinic receptors
•Higher incidence of EPS than other 2nd gen neuroleptics
•Weight gain
•Treats both positive and negative symptoms
36
New cards
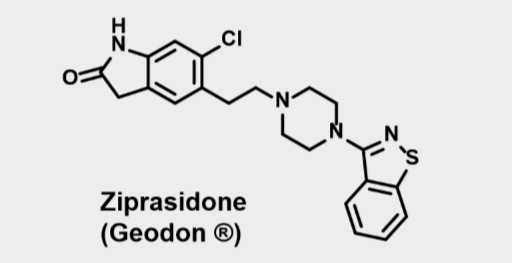
Ziprasidone
Atypical neuroleptic- Second gen antipsychotics
•High affinity for 5HT2A, D2, H1, alph1&2- antagonist
•Partial agonist activity at 5HT1a
•Lower incidence of EPS•Blocks reuptake of SERT and NE
•Treats both positive and negative symptoms
•High affinity for 5HT2A, D2, H1, alph1&2- antagonist
•Partial agonist activity at 5HT1a
•Lower incidence of EPS•Blocks reuptake of SERT and NE
•Treats both positive and negative symptoms
37
New cards
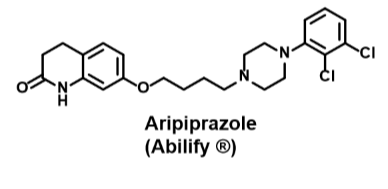
Abilify/aripiprazole
Atypical neuroleptic- Second gen antipsychotics
•Partial agonist at D2
•High affinity for D2/D3
•High affinity for 5HT receptors
•Moderate affinity for H1 and alpha1/2
•Lacks affinity for muscarinic receptors
•Low propensity to cause EPS
•Low incidence of hyperprolactinemia
•Partial agonist at D2
•High affinity for D2/D3
•High affinity for 5HT receptors
•Moderate affinity for H1 and alpha1/2
•Lacks affinity for muscarinic receptors
•Low propensity to cause EPS
•Low incidence of hyperprolactinemia
38
New cards
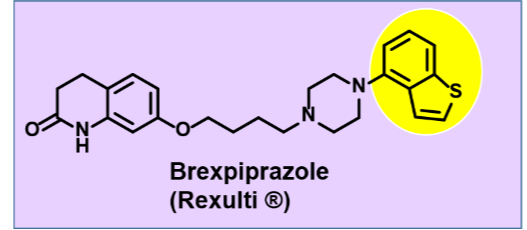
Rexulti/Brexpiprazole
Atypical neuroleptic- Second gen antipsychotics
•Partial agonist at D2
•Used to treat schizophrenia
•Used as adjunct therapy for major depressive disorder
•Less EPS than abilify
•Partial agonist at D2
•Used to treat schizophrenia
•Used as adjunct therapy for major depressive disorder
•Less EPS than abilify
39
New cards
Cariprazine/Vraylar.
Atypical neuroleptic- Second gen antipsychotics
•Partial agonist at D2 and D3
•Selectivity at D3>D2
•Used to treat schizophrenia
•Used ad adjunct therapy for Major Depressive Disorder
•Also used for: bipolar mania, bipolar depression
•Negative and posotive sumptoms
\
•Longer half life than abilify
•Partial agonist at D2 and D3
•Selectivity at D3>D2
•Used to treat schizophrenia
•Used ad adjunct therapy for Major Depressive Disorder
•Also used for: bipolar mania, bipolar depression
•Negative and posotive sumptoms
\
•Longer half life than abilify