Pericyclic Reactions
1/51
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
52 Terms
Show how ionic reactions are pericyclic reactions
electron pairs move
clear sense of direction of electron pair movement
Show how radical reactions are pericyclic reactions
electron moves one by one
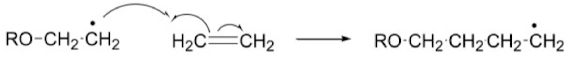
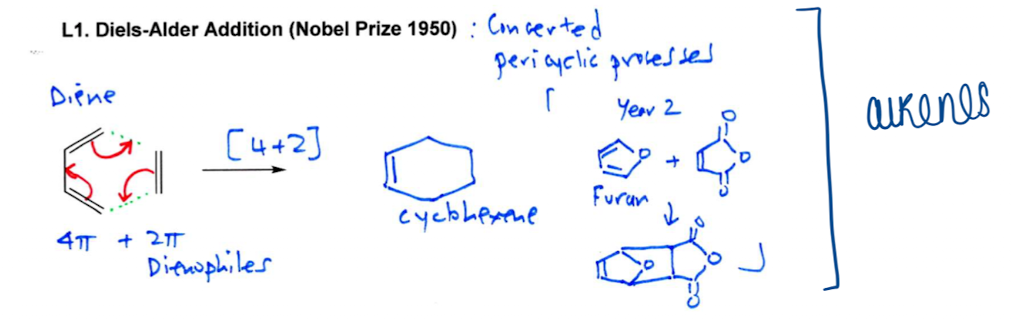
Show how Diels-Alder Addition reactions are pericyclic reactions
Define pericyclic reactions
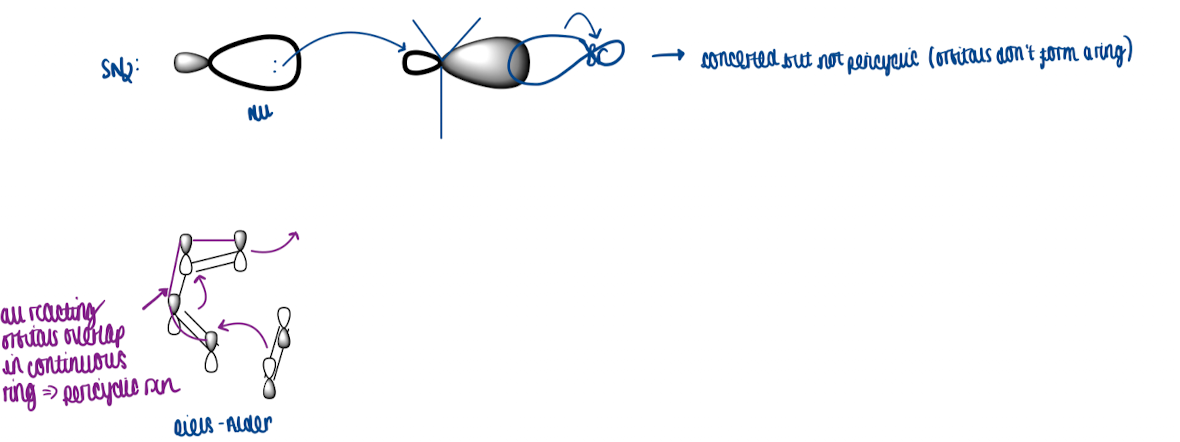
concerted processes in which bond orbitals overlap in a continuous cycle in the transition state
What does concerted mean using a diagram
all bond breaking and making happens simultaneously
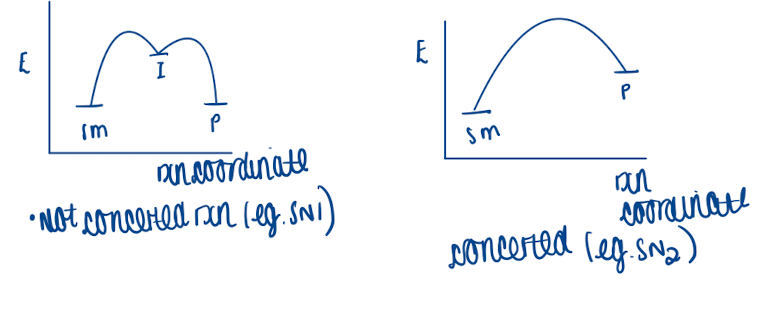
What is a continuous cycle and show a diagram of SN2
critical feature of pericyclic chemistry
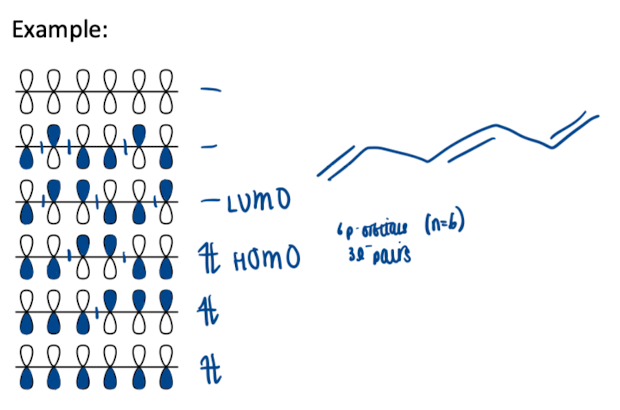
What does Huckel theory do?
simple way to predict MOs for conjugated systems
How would you approach to determine the phases of orbitals only
for an alkene with n p-orbitals, draw n horizontal stacked on top of each other (MOs)
each line, draw n p-orbitals with an increasing no of nodes starting from zero nodes
shade p-orbitals - phase is inverted at each node
fill orbitals with electrons - two per each MO
lower orbital filled with electrons is HOMO, one above is LUMO
What is an approach to determine orbital coefficient
draw a line with n+2 spaced dots for an alkene with p-orbitals eg. for butane draw 6 dots
superimpose sine waves onto line
height of p-orbitals on each dot equals the size of corresponding orbital coefficient
phase inverted at each node
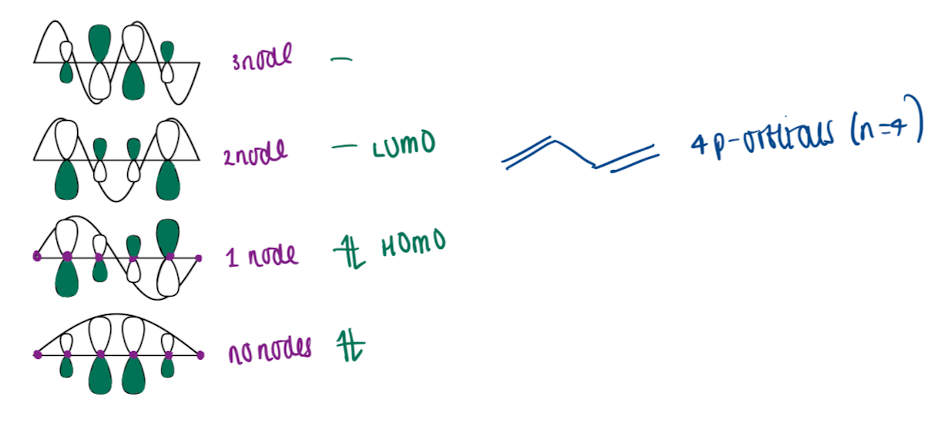
How do you approach the orbital coefficient for substituted polyalkenes
replace an EWG with a CH2+ group and an EDG with a CH2- group
determine the orbital coefficient as normal
HOMO and LUMO coefficient for the substituted alkene are assumed to be average between the unsubstituted compound and the alkene fragment of compound with CH2+/CH2- groups
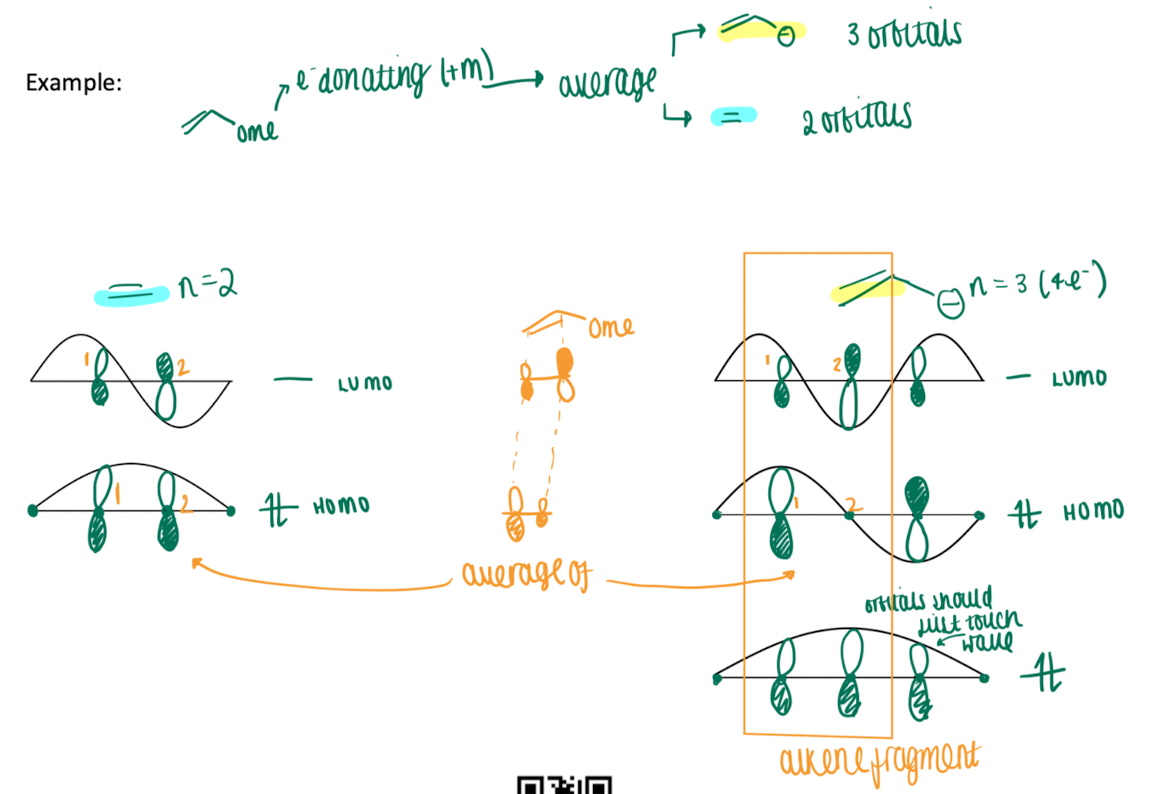
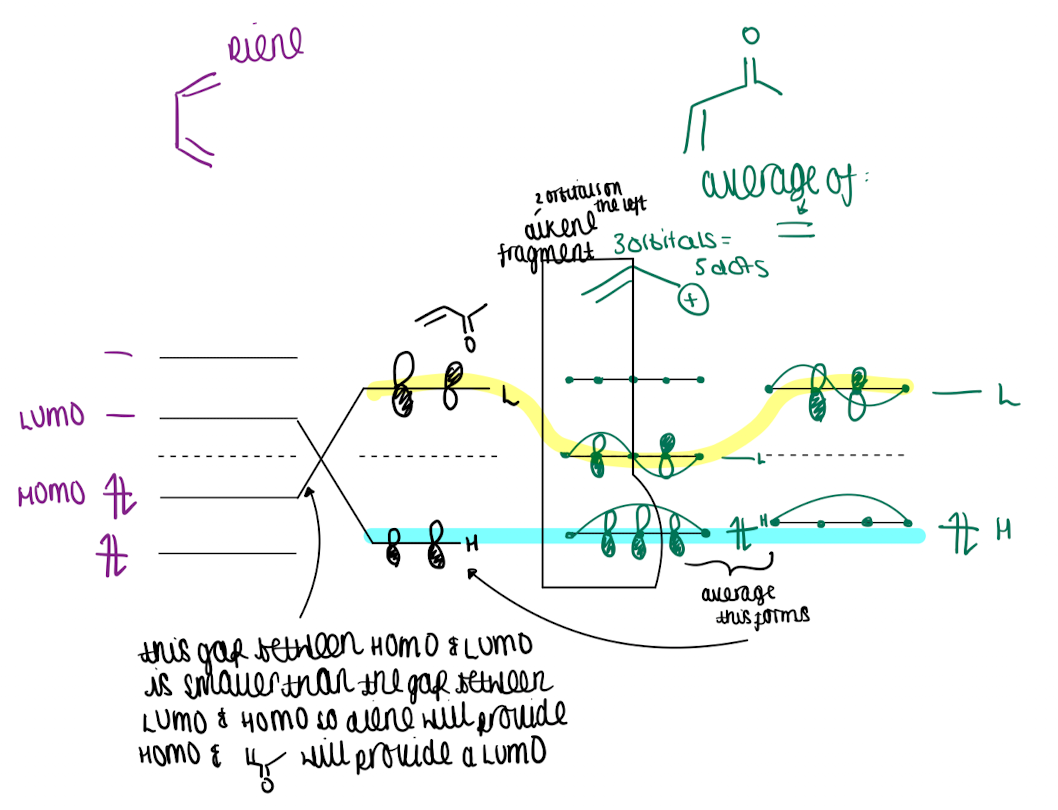
How do you approach the relative energy of MO orbitals
longer conjugation length, smaller the HOMO-LUMO gap
add electron to orbital with EDG makes easier to remove electron
HOMO and other orbitals increase in energy
removing electrons w EDG makes it easier to add new ones hence LUMO decreases in energy
What does the conservation of orbital symmetry mean?
symmetry of the orbitals with respect to any symmetry operation of the molecule must be conserved in moving from the starting material to product
Show a diagram of an orbital correlation diagram
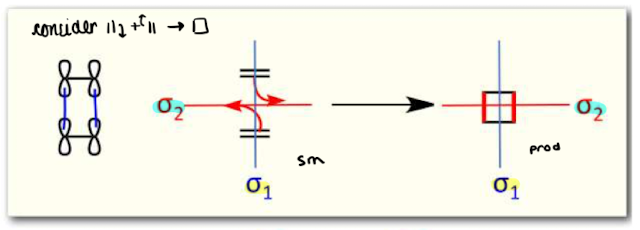
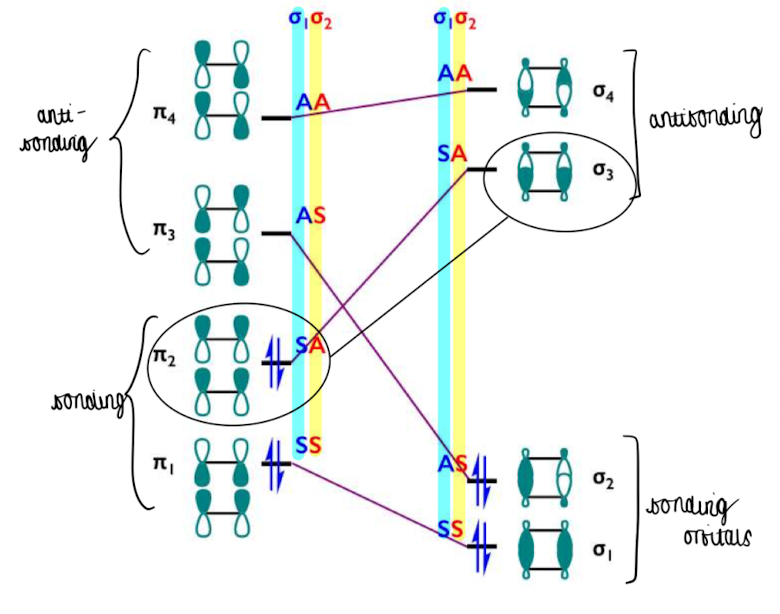
Show an orbital diagram of the orbital correlation diagram
bonding orbital π2 correlates with σ3 which is unfavourable so the reaction is symmetry forbidden
How do we understand pericyclic reaction using the frontier molecular orbital approach - use an example
draw a curly arrow mechanism and a 3D shape
work out component will use HOMO and which use LUMO for overlao
determine the phases of overlapping orbitals
phases of orbitals forming new bonds should match
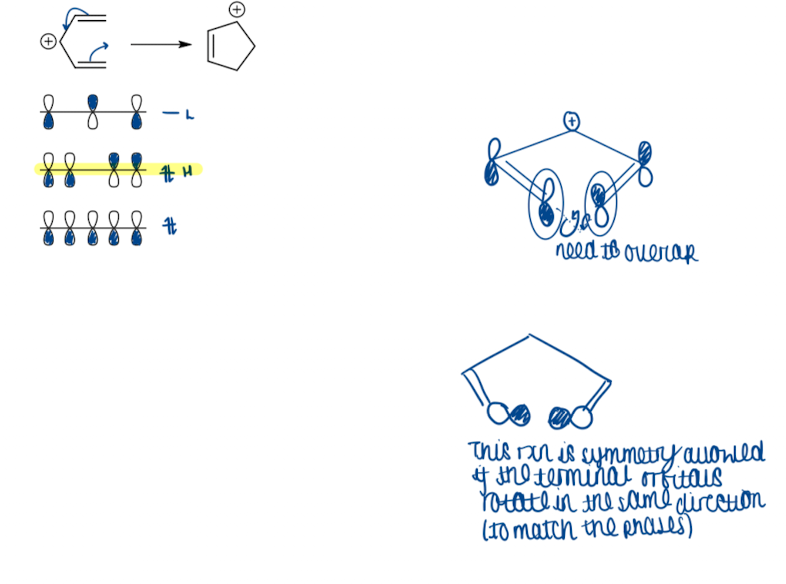
What is the KEY Woodward-Hoffman Rule?
a thermal pericyclic reaction is symmetry allowed if (4q + 2) + (4r)a is an odd number
q is an integer → components with 2,6,10 electrons
4r → components with 4,8,12 electrons
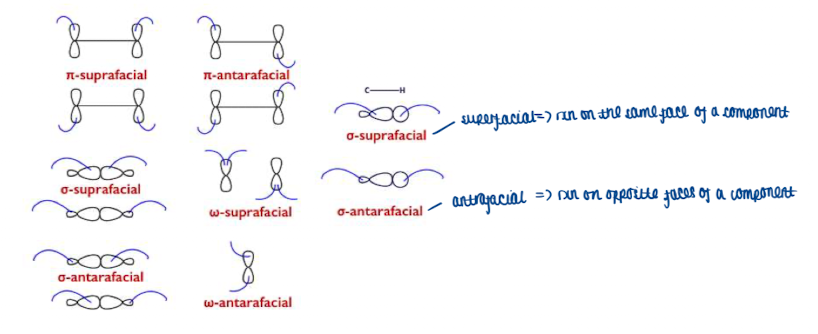
What is ()s and ()a
supra- and antarafacial components
What are all the different types of σ,π,ω for supra facial and antarafacial
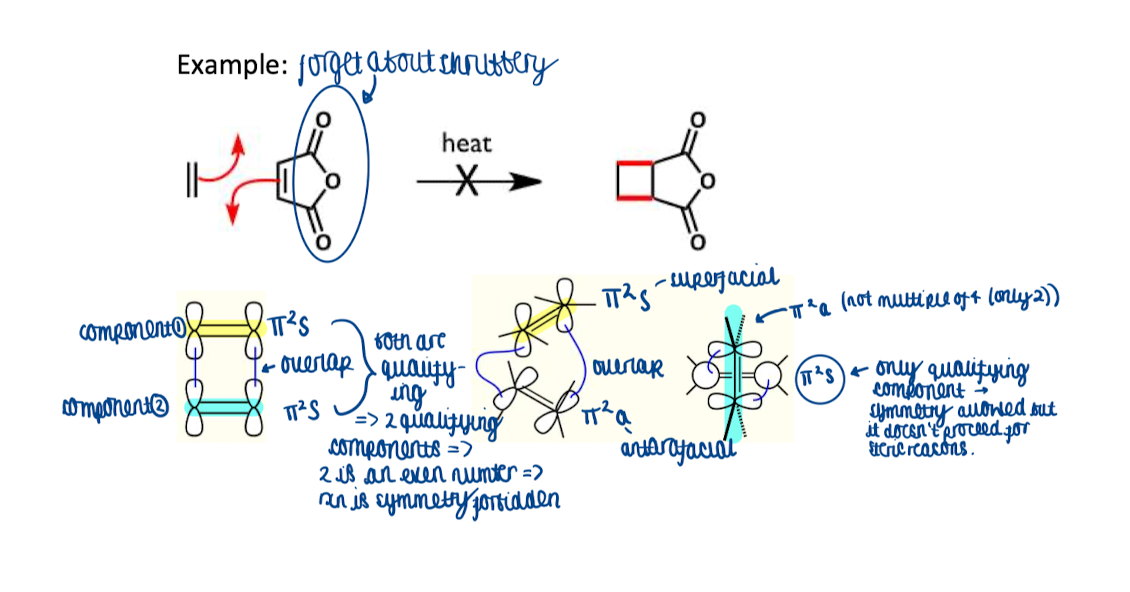
How do you actually use the Woodward-Hoffman rule?
draw curly arrow mechanism
identify components
draw a 3D shape of the reaction to show overlapping components
label components as supra- or antarafacial and use Woodward Hoffman rule
Do an example of how Woodward-Hoffman rule works
When is a photochemical pericyclic reactions symmetry allowed? Is it different for thermal reactions?
if (4q + 2)s + (4r)a is an even number which is opposite to thermal rules
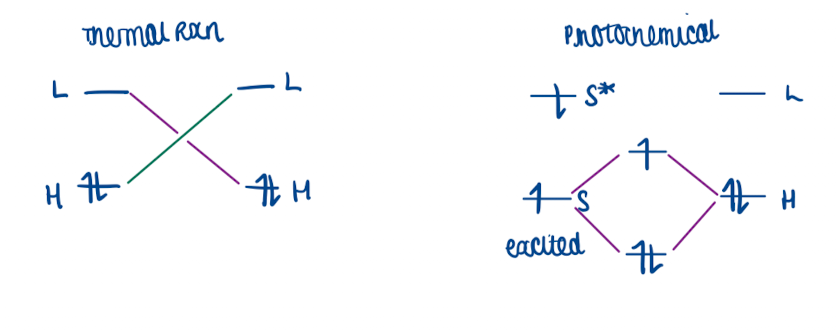
Show how cycloaddition is a pericyclic reactions
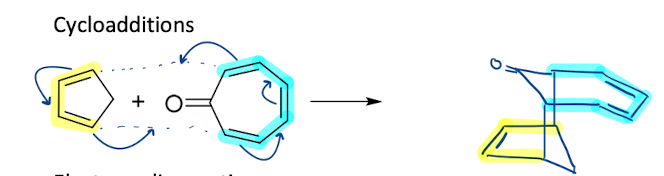
Show how electrocyclic reactions is a pericyclic reactions
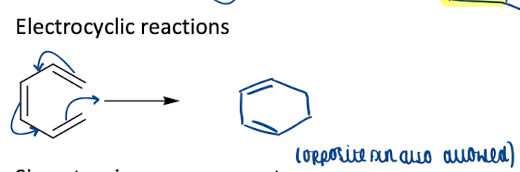
Show how sigmatropic rearrangements is a pericyclic reactions
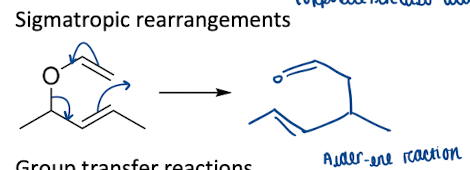
Show how group transfer reactions is a pericyclic reactions
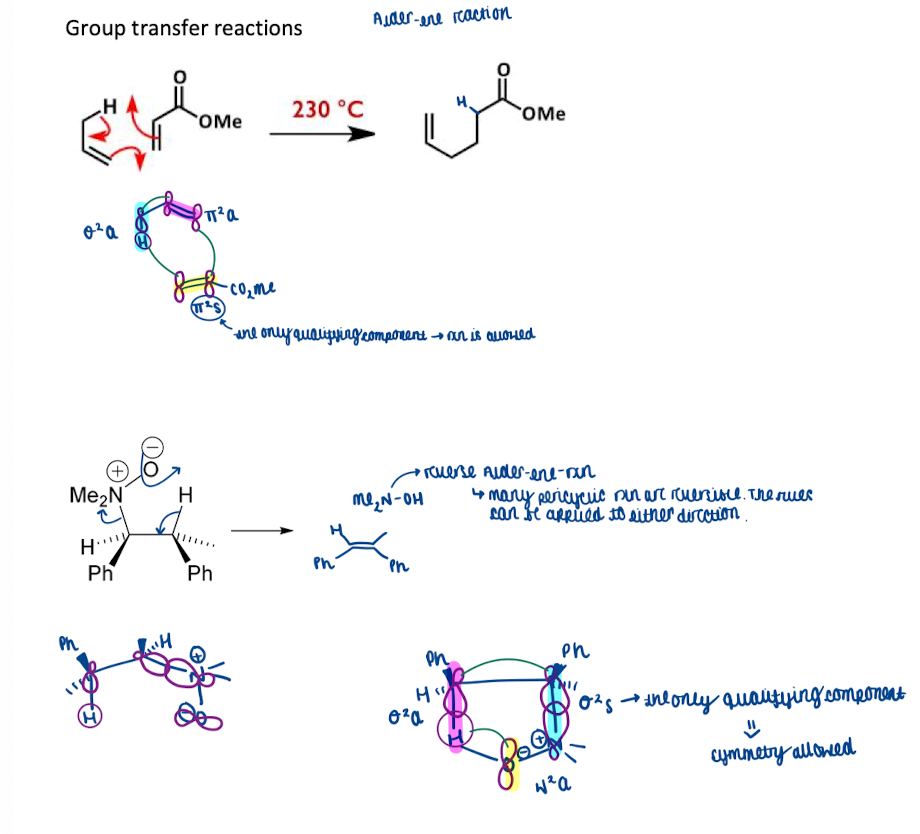
What is the nomenclature of cycloaddition?
[m+n] where m and n are the number of electrons in which component
Diels-Alder reaction is [4+2]-cycloaddition
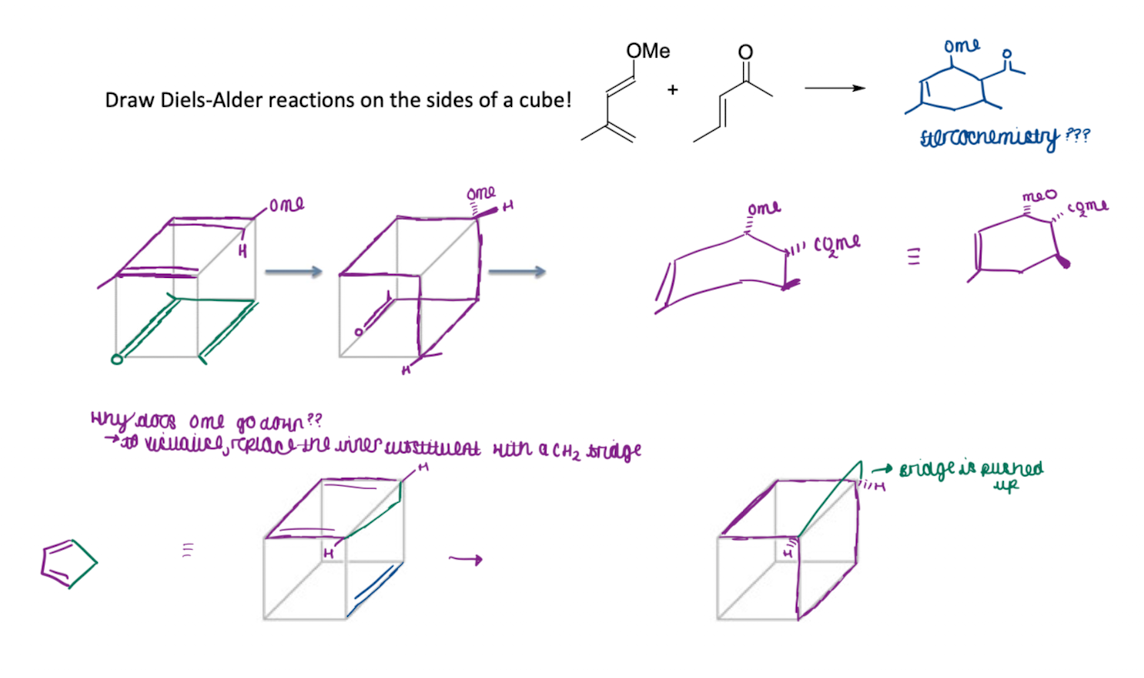
Draw a pericyclic reaction using cubes
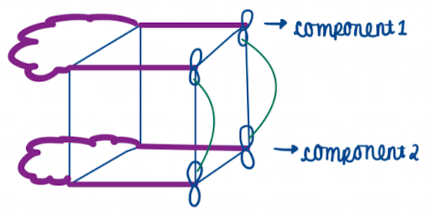
Show how Woodward-Hoffman treatment is in cycloadditions and diels-alder reactions
Show how frontier molecular orbital treatment is in cycloadditions and diels-alder reactions

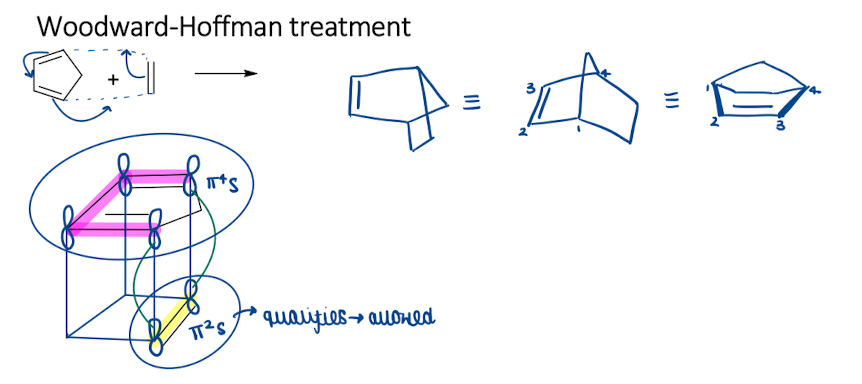
Show an example of how Diels-Alder reactions are more difficult to recognise
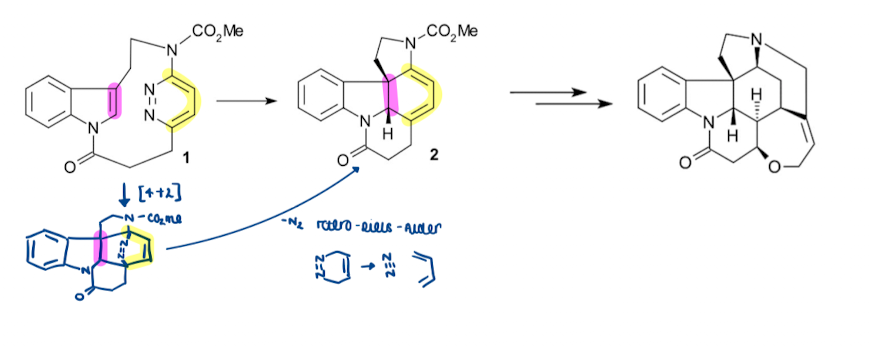
Show the conformations in diels-alder reactions for a s-cis vs s-trans dienes
secondary interactions at the back of molecule favourable
if DA reaction is reversible in eqm the thermodynamic product (exo) will dominate
Show energetics and catalysis of DA reaction of normal and inverse electronic demand
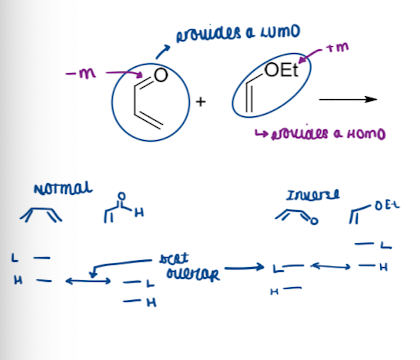
‘normal’ DA reactions accelerated by EWG on dienophile and EDG on diene (provides HOMO)
inverse DA reactions are rare. Require EDG on dienophile and EWG on diene
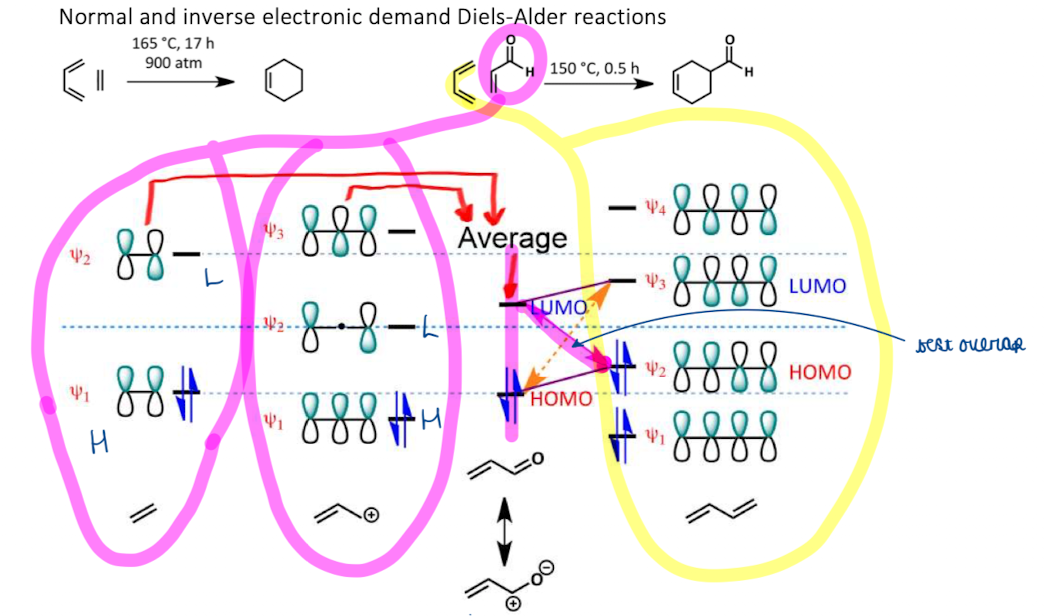
Show diagram of normal and inverse electronic demand DA reaction
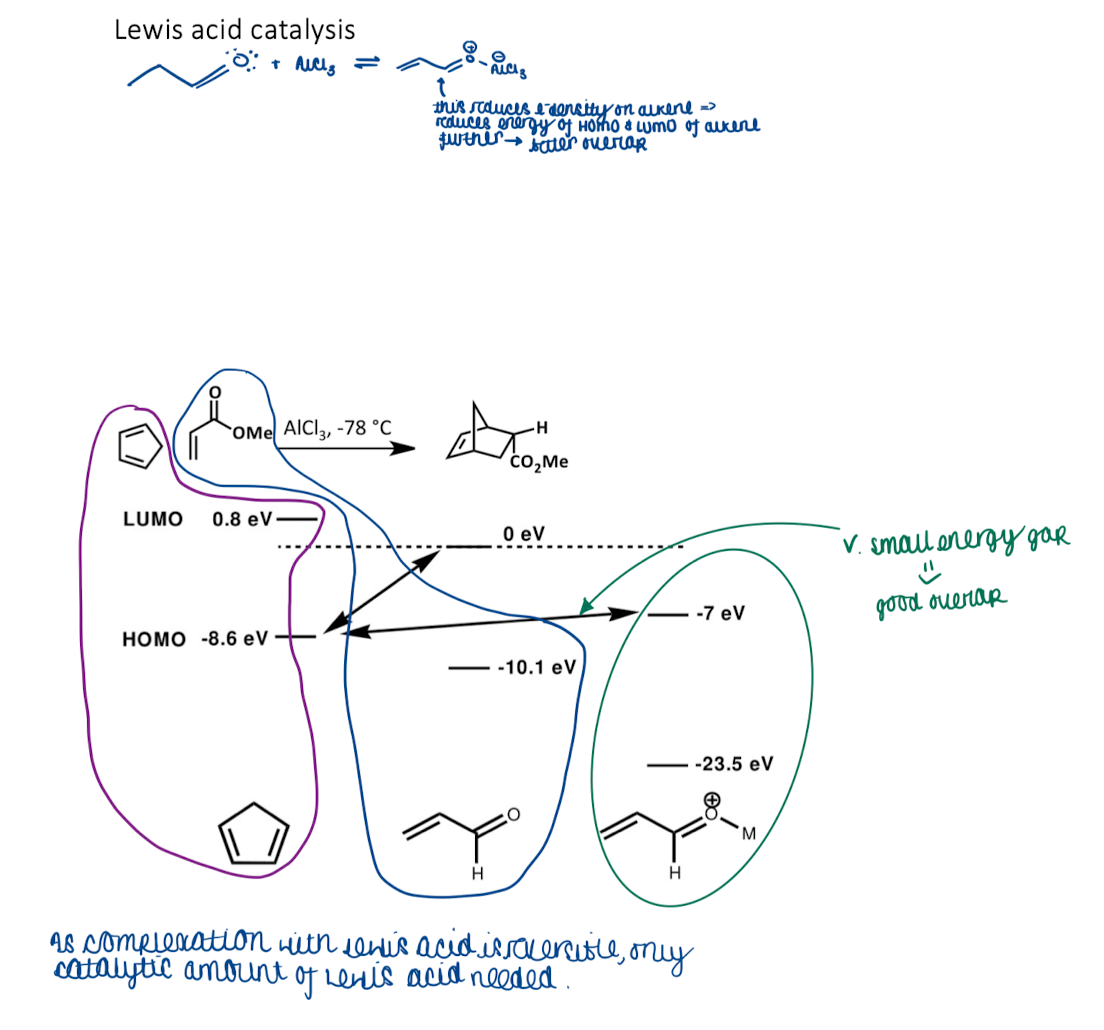
Show a lewis acid catalysis reaction with HOMO and LUMO values
as complexation with LA is reversible only catalytic around of LA needed
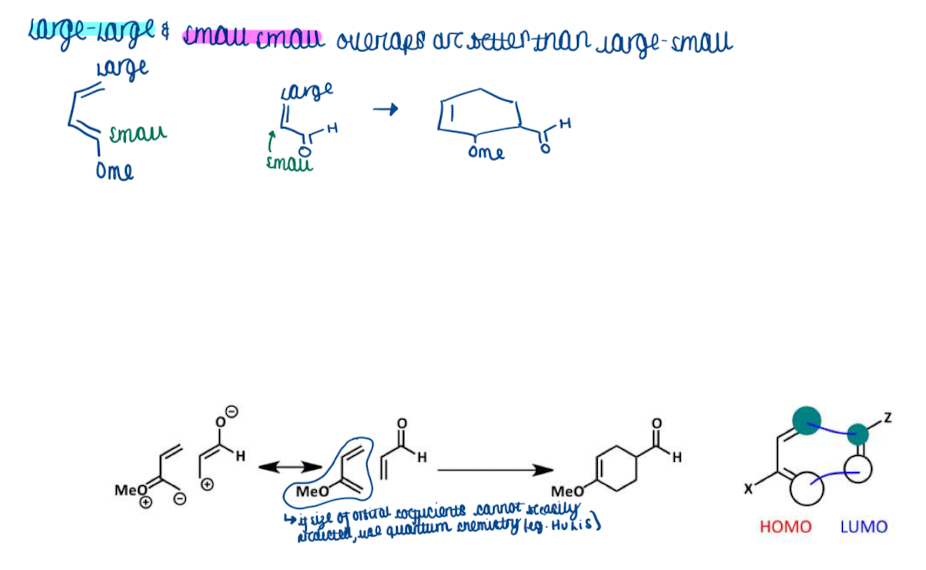
Show an example of substituent effect on DA reaction - regiochemistry
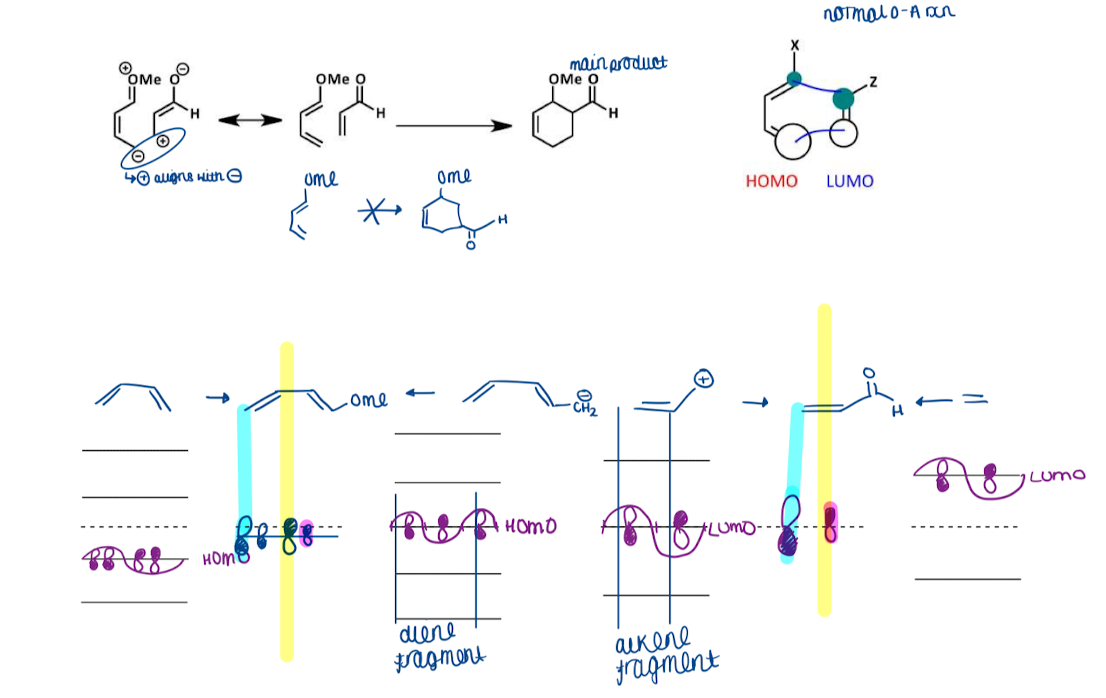
Show the difference between large and small overlaps for substituent effects on DA reactions
Draw a DA reaction on the sides of a cube. Why does OMe go down?
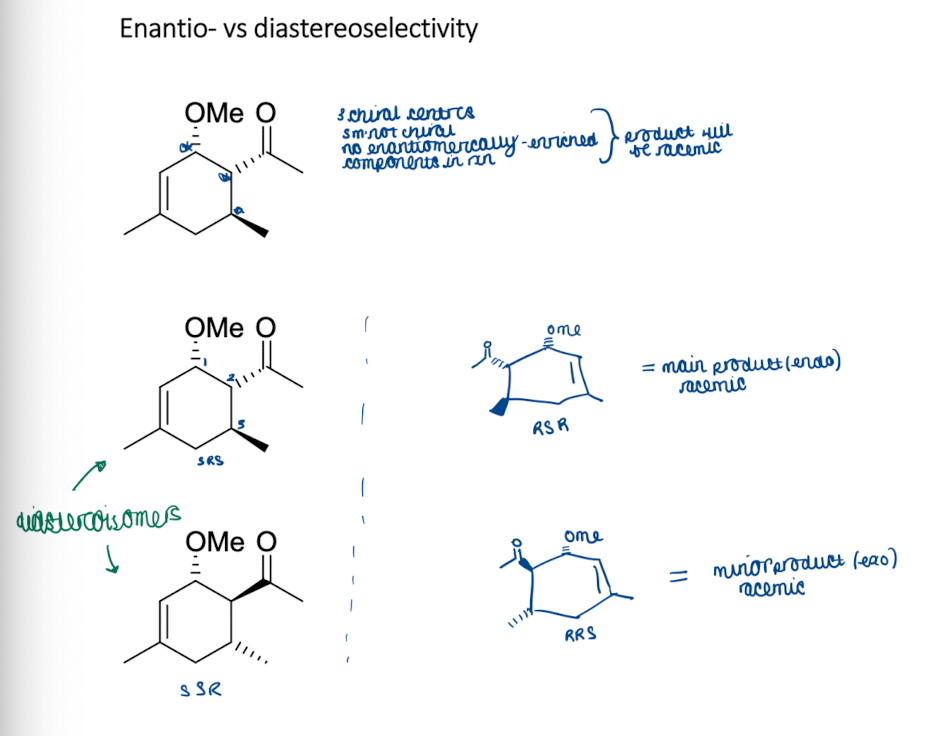
Show enantio- vs diasteroselectivity
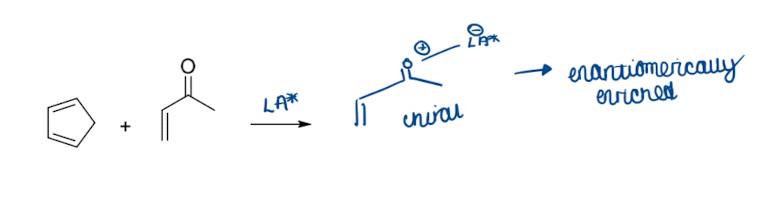
What is a trick to induce enantioselectivity in a DA reaction?
use a chiral lewis acid catalyst
What is photochemical cycloadditions in terms on DA reactions
[2+2] - thermally forbidden but allowed photochemically
![<p>[2+2] - thermally forbidden but allowed photochemically</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/5d5c6d8f-b9af-48e0-b25c-bdfce2d3e405.png)
Give an example of a cycloaddition - addition of 1,3-dipolar compounds
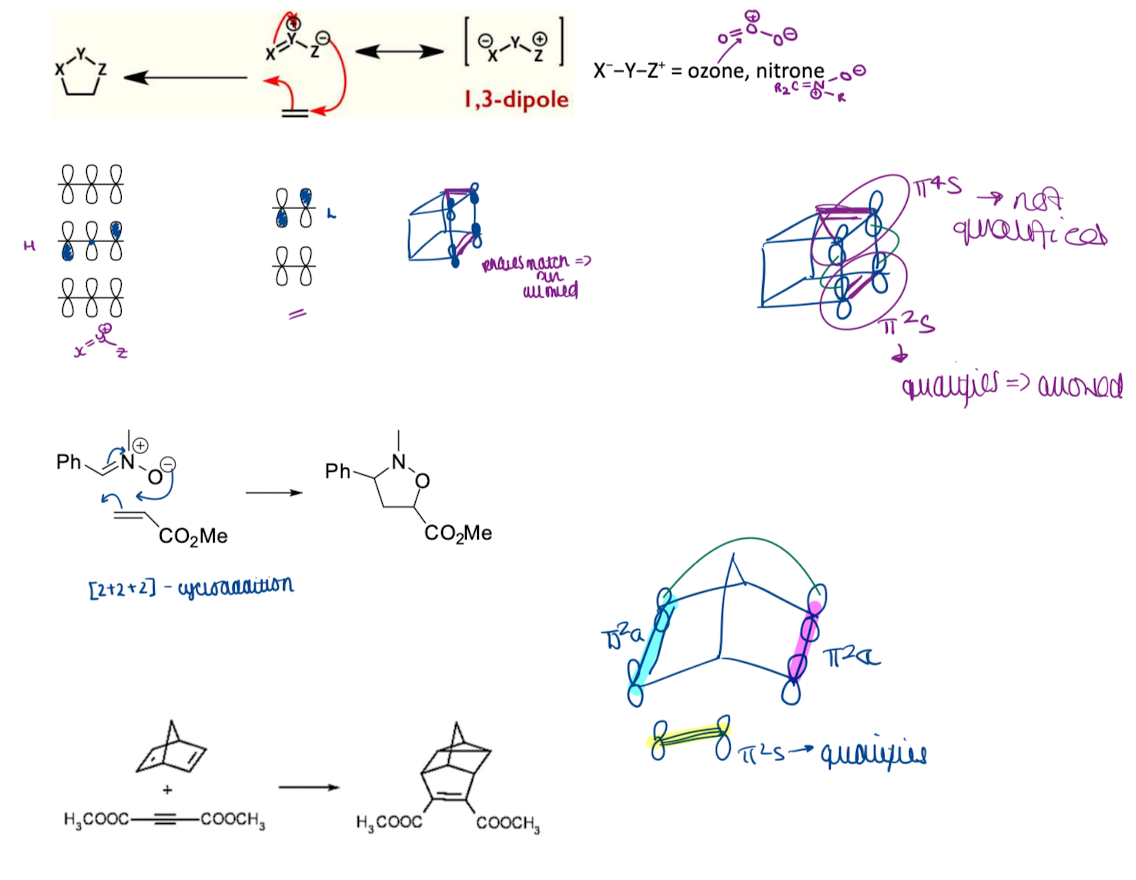
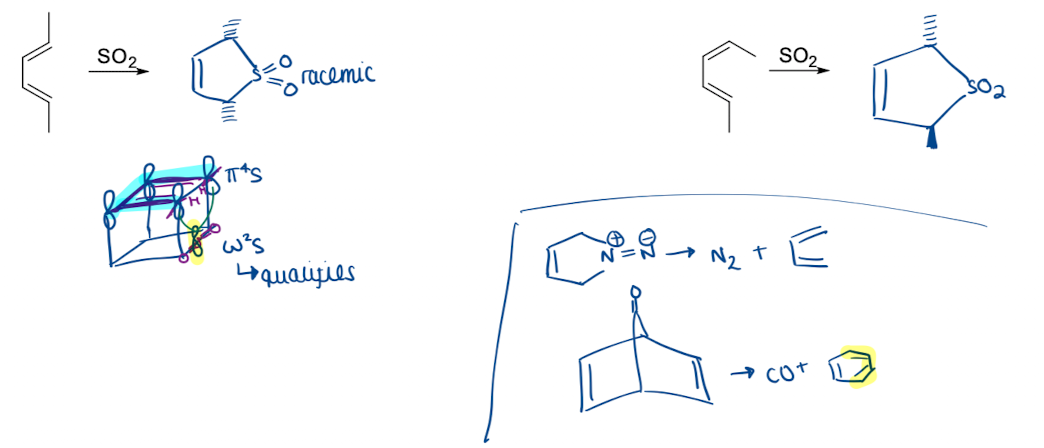
What is cheletropic reactions and show an example
cycloadditions (and reverse reactions) with two σ-bonds formed/broken to the same atom
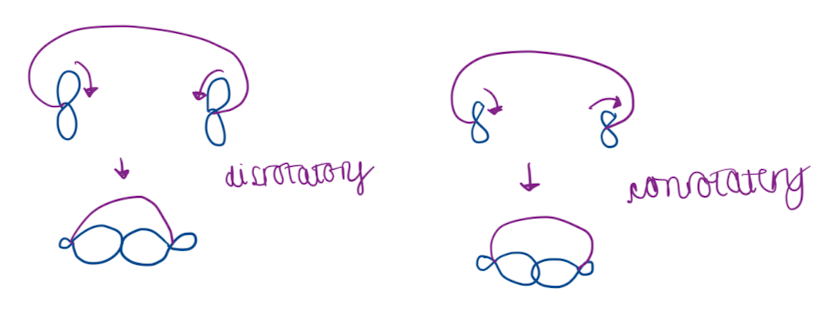
Draw a diagram to show conrotatory and disrotatory movement
all electrocyclisation are allowed (either con- or disrotatory) - but they may be geometrically constrained
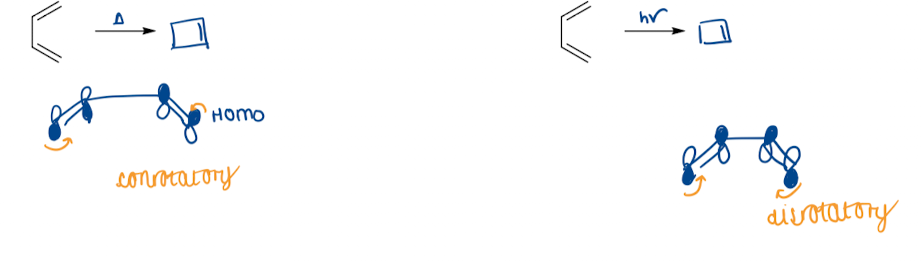
Show electrocyclisation in frontier MO treatment
use HOMO for thermal reactions
SOMO* for photochemical reactions
Show electrocyclisation in Woodward-Hoffman treatment
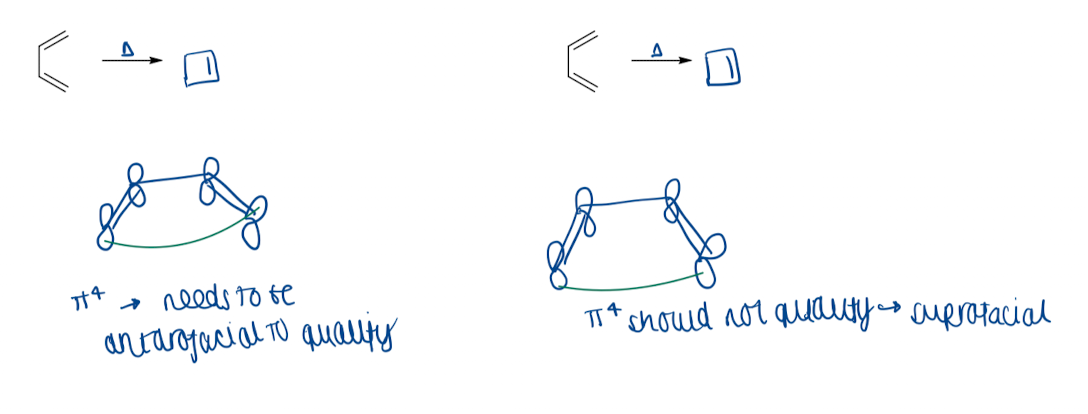
Show examples of stereoisomers in electrocyclisation
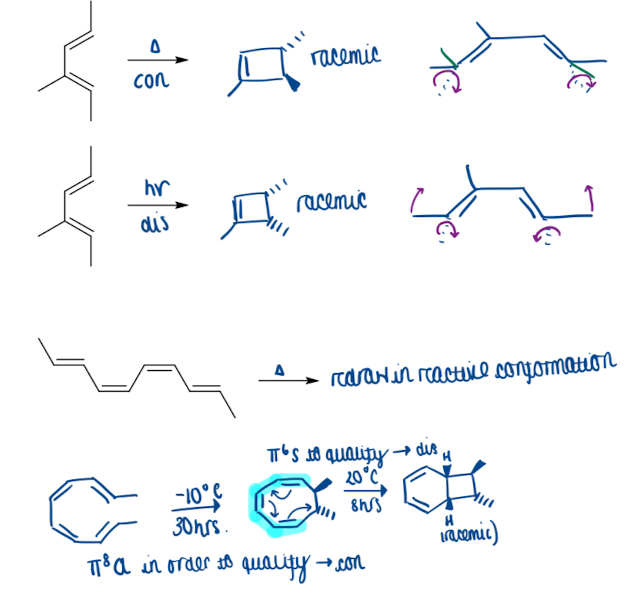
Show an example of the reversibility of electrocyclisation
direction of reactions depend on relative rate which difficult to predict
many rxn are reversible, equilibria rarely achieved
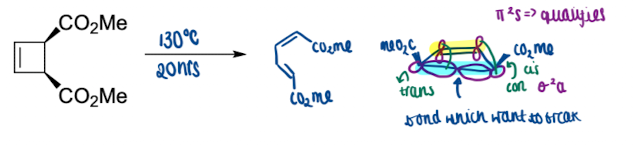
Give another example of electrocyclisation
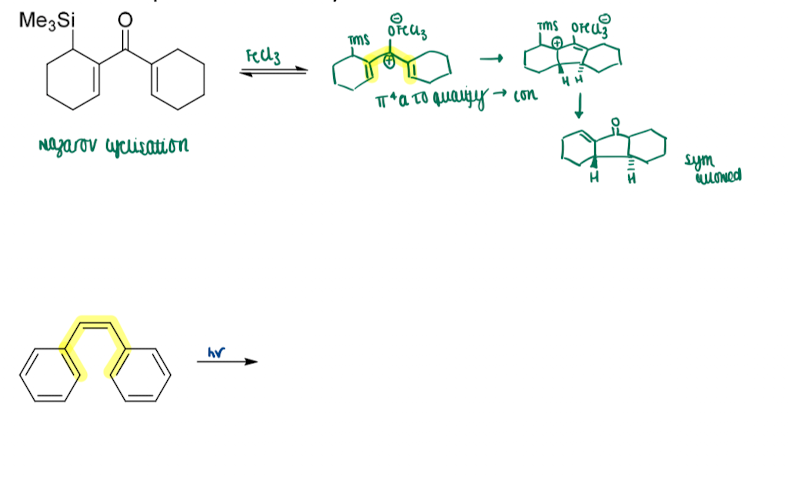
Define classification in sigmatropic rearrangements
migration of a sigma bond from one end of a π-system to the other
Give the rule for classification of sigmatropic rearrangements
[m,n]-sigmatropic rearrangement
![<p>[m,n]-sigmatropic rearrangement</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/066d643a-3acd-4131-838c-381035bf478d.png)
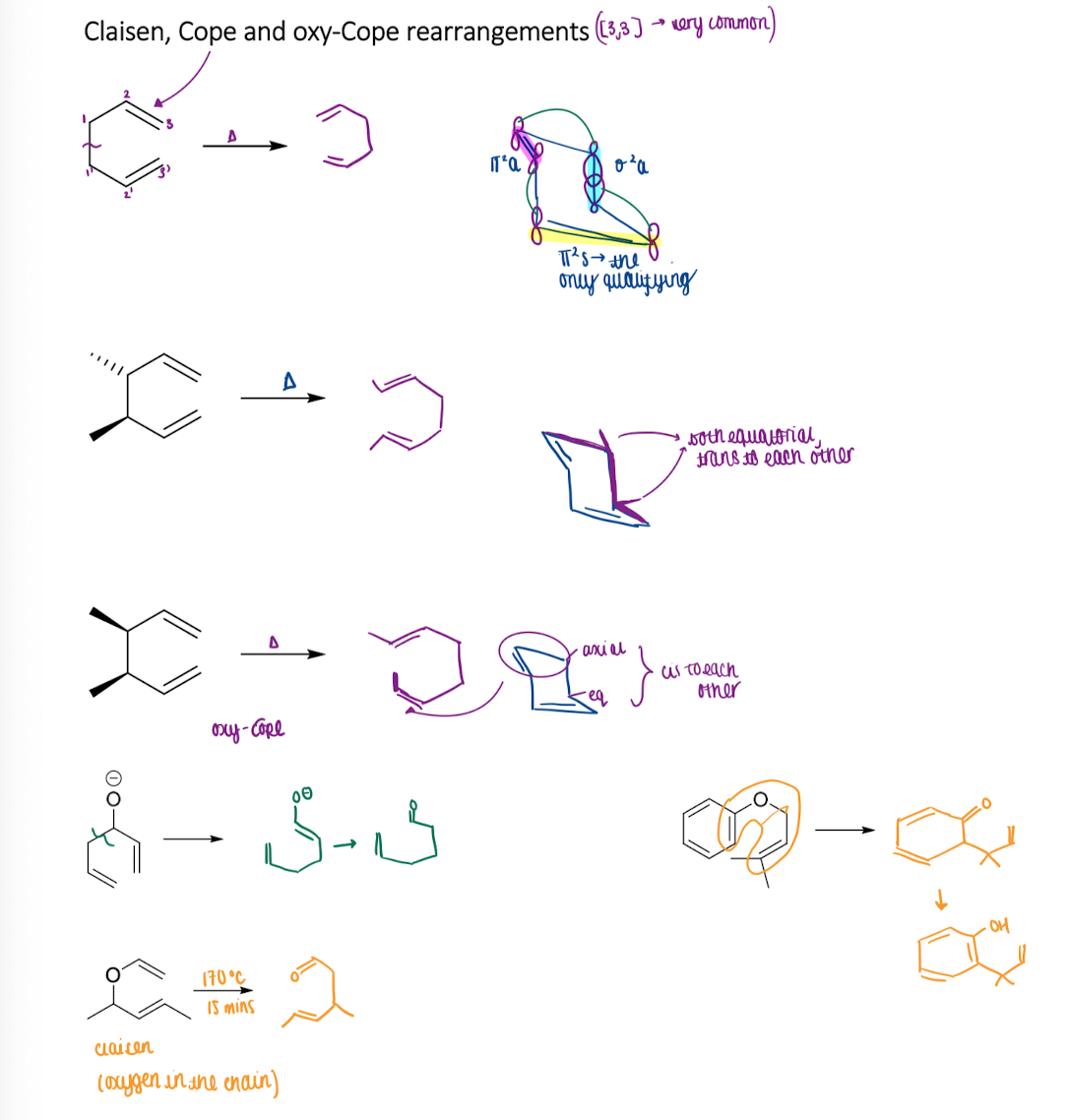
Sigmatropic rearrangement: Show examples of Claisen, Cope and oxy-Cope rearrangements
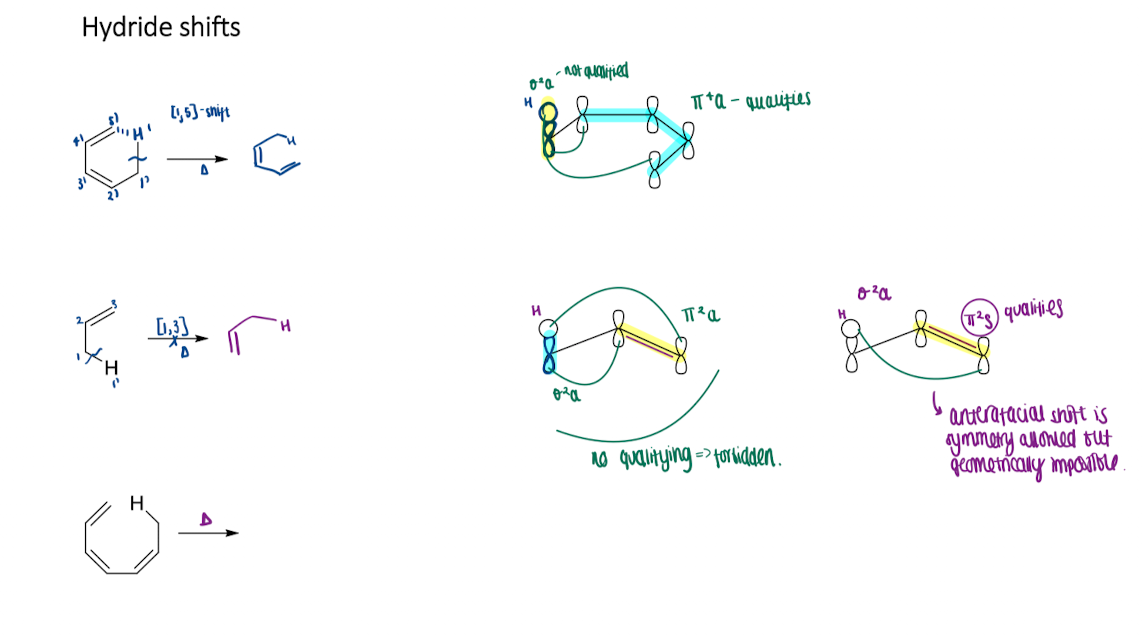
How hydride shift in sigmatropic rearrangements