3.4 Cognitive Development Across the Lifespan
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
Cognition
All the mental activities associated with thinking, knowing, remembering, and communicating
Schemas
A concept or framework that organizes and interprets information
Assimilation
Interpreting our new experiences in terms of our existing schemas
Accommodation
(1) in sensation and perception, the process by which the eye’s lens changes shape to focus images of near or far objects on the retina; (2) in developmental psychology, adapting our current schemas (understandings) to incorporate new information
Sensorimotor stage
In Piaget’s theory, the stage (from birth to nearly 2 years of age) at which infants know the world mostly in terms of their sensory impressions and motor activities
Object Permanence
The awareness that things continue to exist even when not perceived
Preoperational stage
In Piaget’s theory, the stage (from about 2 to 6 or 7 years of age) at which a child learns to use language but does not yet comprehend the mental operations of concrete logic
COnservation
The principle (which Piaget believed to be a part of concrete operational reasoning) that properties such as mass, volume, and number remain the same despite changes in the forms of objects
Egocentric
In Piaget’s theory, the preoperational child’s difficulty taking another’s point of view
Concrete Operational Stage
In Piaget’s theory, the stage of cognitive development (from about 7 to 11 years of age) at which children can perform the mental operations that enable them to think logically about concrete (actual, physical) events
Formal operational
In Piaget’s theory, the stage of cognitive development (normally beginning about age 12) at which people begin to think logically about abstract concepts
Paiget’s Stages of Cognitive Development (table)
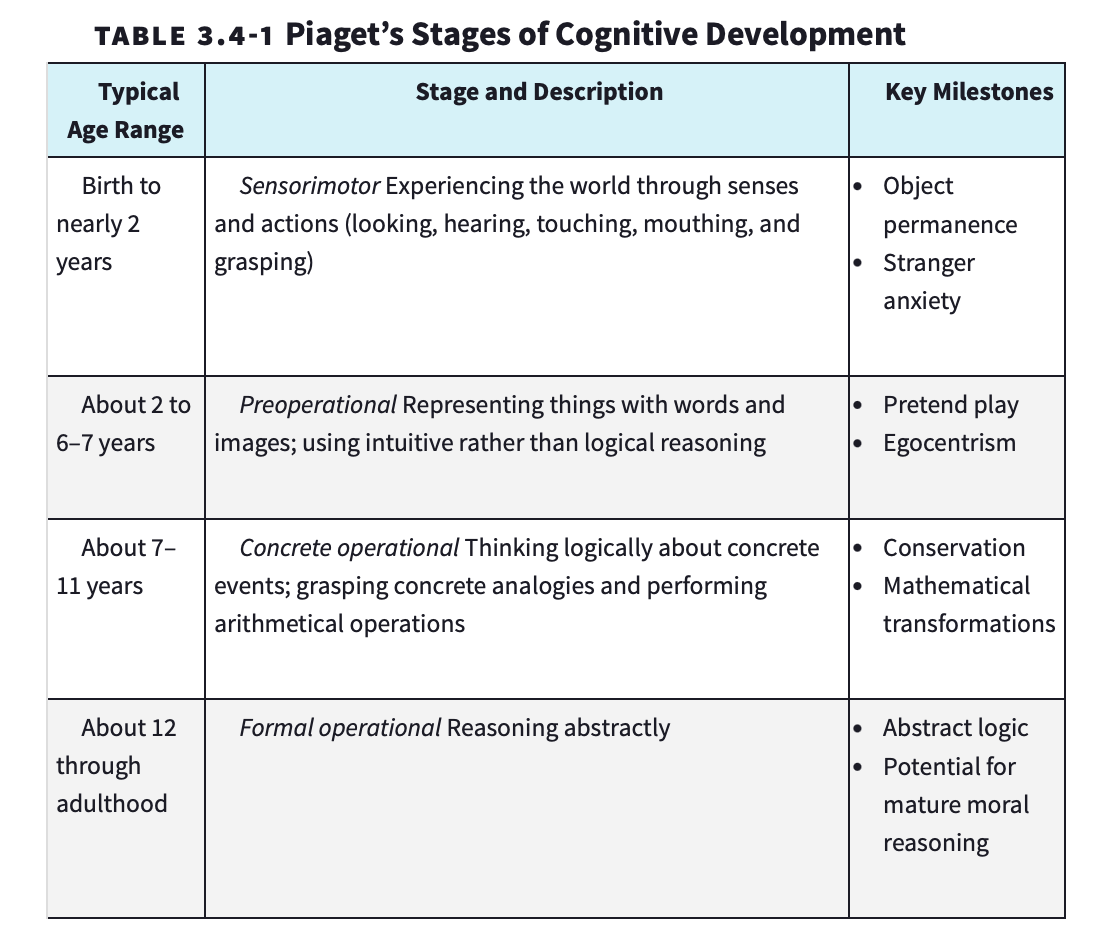
Sensorimother typical age range
Birth to nearly 2 years
Sensorimotor description
Experiencing the world through senses and actions (looking, hearing, touching, mouthing, and grasping)
Sensorimotor key milestones
Object permanence and stranger anxiety
Preoperational age range
About 2 to 6-7 years
Preoperational description
Representing things with words and images; using intuitive rather than logical reasoning
Preoperational
Pretend play and egocentricism
Concrete operational age range
About 7-11 years
Concrete operational description
Thinking logically about concrete events; grasping concrete analogies and performing arithmetical operations
Concrete operational key milestones
Conservation and mathematical transformations
Formal operational age range
About 12 through adulthood
Formal operational description
Reasoning abstractly
Formal operational key milestones
Abstract logic and potential for mature moral reasoning
Theory of mind
People’s ideas about their own and others’ mental states; about their feelings, perceptions, and thoughts, and the behaviors these might predict