BIOL 3370 Chemical Synapses - Neurotransmitters
1/98
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts related to neurotransmitters and their functions, synthesis, and types based on the provided lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
99 Terms
What are ionotropic receptors?
Ligand-gated ion channels that cause direct graded potentials.
What are metabotropic receptors?
G-protein coupled receptors that can have modulatory effects on neurotransmitter functions.
May affect:
• Opening of ion channels
• Synthesis, release, degradation, and/or reuptake of neurotransmitter
• Number of receptors at synapse
What is the rate-limiting step in the synthesis of acetylcholine?
Choline acetyltransferase (ChAT, CAT).
What enzyme removes acetylcholine from the synapse?
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE).
What neurotransmitter is characterized by a combination of acetic acid and choline?
Acetylcholine.
Name two types of receptors for acetylcholine.
Nicotinic (nACh) receptors -ionotropic
Muscarinic (M) receptors -metabotropic
What role does serotonin play in the body?
Digestion, appetite, sleep, social behavior, and mood.
Which precursor is used to synthesize catecholamines?
Tyrosine.
What is the role of dopamine in the brain?
Reward and reinforcement, motivation, and motor control.
What are the two types of adrenergic receptors?
Alpha (α) and beta (β) receptors.
What function does glutamate have in the brain?
Main excitatory neurotransmitter, involved in learning, memory, and attention.
What characterizes GABA as a neurotransmitter?
It is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter of the brain.
Which neurotransmitter is derived from tryptophan?
Serotonin.
What is the primary site of melatonin synthesis?
The pineal gland.
What is the effect of caffeine on adenosine receptors?
Caffeine inhibits adenosine receptors, increasing alertness.
What is a significant function of endocannabinoids?
They play a role in motor control, learning, memory, and mood.
Where are endocannabinoids produced?
By enzymatic degradation of membrane lipids.
What neurotransmitter is the simplest amino acid?
Glycine.
What is the rate-limiting enzyme in the synthesis of GABA?
Glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD).
What neurotransmitter is primarily associated with the sympathetic response?
Epinephrine and norepinephrine.
What effect does norepinephrine have on cardiac muscle?
It's excitatory.
What effect does norepinephrine have on the smooth muscle of the respiratory tract?
It's inhibitory.
What neurotransmitter is involved in the body's arousal and wakefulness?
Histamine.
What are the transporters that remove dopamine from synapses?
Dopamine transporters (DAT), monoamine oxidase (MAO), and catechol O-methyltransferase (COMT).
What role does serotonin play in disorders like anxiety and depression?
Imbalances in serotonin levels are linked to these disorders.
What are the main roles of glycine?
Processing of motor and sensory information and acting as a co-agonist at NMDA receptors.
What is the function of ATP in neurotransmission?
It acts as a neurotransmitter as a nucleotide.
What are the removal mechanisms for neurotransmitters?
Transporters and enzymes such as monoamine oxidase.
What are the functions of endocannabinoids?
Regulate pain, appetite, and mood.
What neurotransmitter is associated with opioid peptides?
Endorphins and enkephalins.
Which neurotransmitter affects learning and memory and is primarily excitatory?
Glutamate.
Name a neurotransmitter that plays a role in sleep regulation.
Melatonin.
What effect does serotonin increase have?
It can lead to serotonin syndrome.
What role does GABA play in mood regulation?
It helps regulate brain activity and can affect mood.
What neurotransmitter is involved in pain regulation and mood?
Endocannabinoids.
What is the function of adenosine in the brain?
Acts as an inhibitory neurotransmitter promoting sleep.
What is the defining characteristic of imidazoleamines?
They are derived from the amino acid histidine.
What are glutamate receptors primarily responsible for?
Excitation of neurons.
How does the receptor type affect neurotransmitter response?
It determines if the neurotransmitter has excitatory or inhibitory effects.
What is the connection between dopamine and addiction?
Dopamine plays a role in reward pathways and can affect addiction behaviors.
What are the 3 Monoamines?
Catecholamines
Indolamines
Imidazoleamines
Describe the structure of Catecholamines and what are 3 examples
Catecholamines are characterized by a benzene ring with two hydroxyl groups and an ethyl side chain that connects to an amino group. Three examples include dopamine, norepinephrine, and epinephrine.
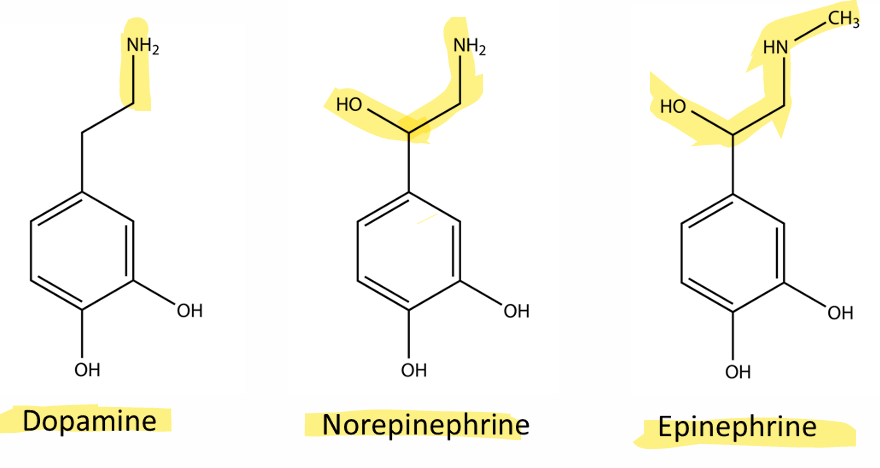
What is the rate-limiting step in synthesis for catecholamines
Tyrosine hydroxylase (TH)
What’s the removal mechanism for catecholamines
Transporters
Monoamine oxidase (MOA)
Catechol O-methyltransferase (COMT)
-these are all enzymes that are important in the metabolism of catecholamines and help regulate their levels in the synaptic cleft.
What is the removal mechanism for acetylcholine
Acetylcholinesterase (AChE)
What are the functions of Acetylcholine?
Skeletal muscle response
Autonomic response-especially parasympathetic
Memory
What is the receptor/s for catecholamines?
Dopamine (D)
In Catecholamines what is the function of Dopamine and what disease does it play a role in?
Reward & reinforcement
Motivation
Extrapyramidal motor control- which helps modulate movement rather than initiate it
It has a role in Parkinson's disease, schizophrenia, bipolar disease, etc.
In Catecholamines, Epinephrine & norepinephrine receptors are…?
Adrenergic (alpha and beta) receptors- these are metabotropic
In Catecholamines, what are Epinephrine & norepinephrine functions?
Sympathetic response- fight or flight response, can increase heartrate
Arousal & attention
Has some effects on mood
Plays role in ADHD and anxiety
Classified as an Indolamine, ___________ is derived from decarboxylated trpptophan with an added hydroxyl group
Serotonin
The ______ gland is the primary site of melatonin synthesis
pineal gland
Tryptophan is first converted to serotonin then acetylated and methylated to produce _________.
Melatonin
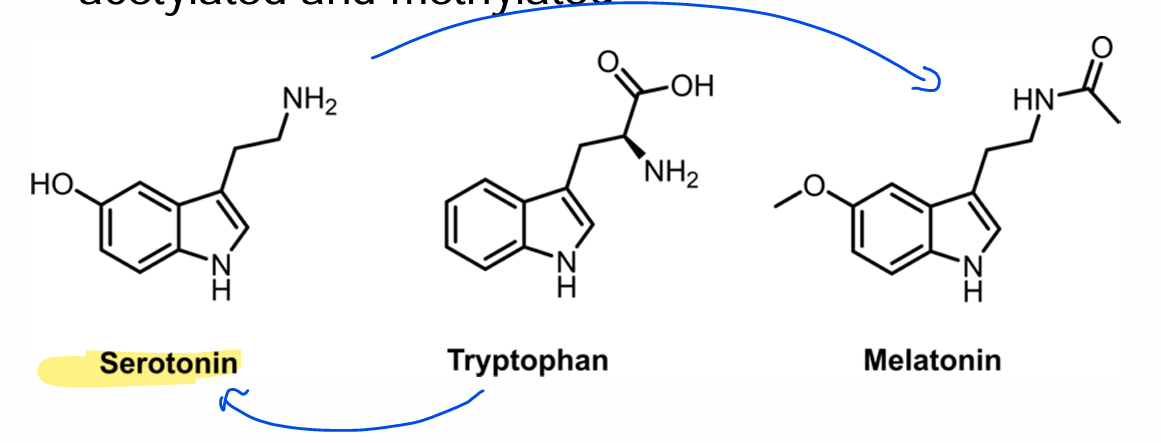
Classified as an Indolamine, what are the Serotonin receptors?
5-HT3 receptors – ionotropic
5-HT1,2,4,5,6 receptors - metabotropic
Classified as an Indolamine, what is the rate-limiting step in the synthesis of serotonin?
Tryptophan hydroxylase (TPH)
Classified as an Indolamine, what is the removal mechanism for Serotonin?
Transporters
Monoamine oxidase (MOA)
Classified as an Indolamine, what is the function of serotonin?
Digestion, appetite, sleep, social behavior, and mood
• Plays a role in depression, anxiety disorders, sleep disorders
Drugs that increase levels of serotonin (e.g., SSRI) can cause __________ _________
Serotonin Syndrome
causes confusion, rapid heart rate, high blood pressure, sweating, tremors, muscle rigidity, and seizures
Classified as an Indolamine, what are the Melatonin receptors?
MT receptors - metabotropic
Classified as an Indolamine, what is the rate-limiting step in the synthesis of melatonin?
Arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferase (AANAT)
Classified as an Indolamine, what is the removal mechanism for melatonin?
Unclear but its dispersed and broken down by the liver, acts similar to hormones
Classified as an Indolamine, what is the function of Melatonin?
Plays a role in circadian rhythms
Classified as an Imidazoleamine, ____________ is characterized by a single amino group connected to an imidazole ring by a ethyl chain
Histamine
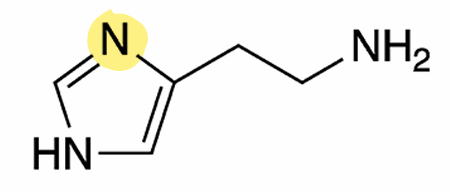
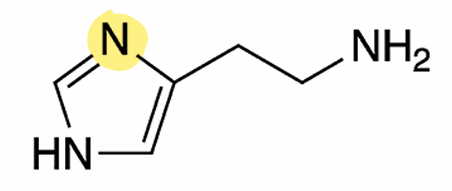
What is this molecule?
Histamine
Classified as an Imidazoleamine, what are the histamine receptors?
H receptors- metabotropic
Classified as an Imidazoleamine, what is the rate-limiting step in the synthesis of histamine?
Histamine decarboxylase (HDC)
Classified as an Imidazoleamine, what are the removal mechanisms of histamine?
Transporters (haven’t yet narrowed them all down)
Classified as an Imidazoleamine, what is the function of histamine
Wakefulness
Inflammatory response
____________ is thought to be the most important for brain function, and is the main excitatory neurotransmitter in the central nervous system.
Glutamate
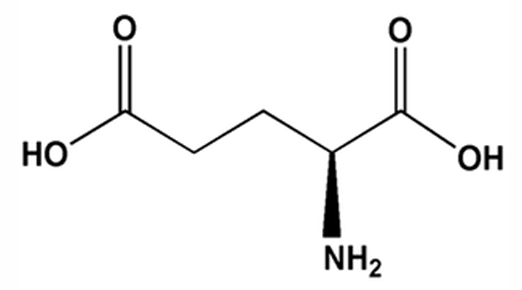
What amino acid is this image?
Glutamate
Classified as an amino acid, what are the glutamate receptors? (4 of them)
AMPA receptors- ionotropic
NMDA receptors-ionotropic
Kainate receptors- ionotropic
mGlu receptors- metabotropic
Classified as an amino acid, what is the rate-limiting step in synthesis of glutamate?
Glutaminase
Classified as an amino acid, what is the removal mechanism of glutamate?
Transporters (EAATs)
_______ metabolism can also be used to synthesize glutamate?
Glucose
Classified as an amino acid, what are the functions of glutamate?
Learning, memory, attention, mood regulation, and movement
Imbalances play a role in anxiety, ADHD, seizures, and neurodegenerative diseases
________ is a main inhibitory neurotransmitter of the brain.
GABA (γ-aminobutyric acid)
Classified as an Amino Acid, what are the GABA receptors?
• GABAA receptors – ionotropic
• GABAB receptors – metabotropic
Classified as an Amino Acid, what is the rate-limiting step in synthesis of GABA?
Glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD)
Classified as an Amino Acid, what is the removal mechanism for GABA?
Transporters (GATs)
Classified as an Amino Acid, what are the functions of GABA?
Regulation of brain activity, sleep, motor control, mood
Presynaptic inhibition of glutamatergic neurons
_______ is the main inhibitory neurotransmitter of the spinal cord
Glycine
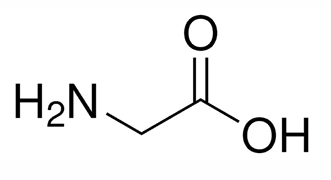
What amino acid is the image?
Glycine
Classified as an Amino Acid, what are the glycine receptors?
Glycine receptors- ionotropic
Classified as an Amino Acid, what is the rate-limiting step in synthesis of glycine?
Phosphoserine phosphatase (PSP)
Classified as an Amino Acids, what is the removal mechanism of glycine?
Glycine transporters
Classified as an Amino Acids, what is the function of glycine?
Processing of motor and sensory information coming and going to the peripheral nervous system
Interestingly, it also plays a role in excitatory neurotransmission as it is a co-agonist at NMDA receptors
Plays a role in synaptic plasticity, learning, and memory
____________ is a purine nucleoside composed of adenine attached to ribose
Adenosine
Adenosine (A) receptors are _________
metabotropic
_________acts as an inhibitory neuron in the brain promoting sleep and suppressing arousal
Adenosine
__________inhibits adenosine receptors increasing alertness
Caffeine
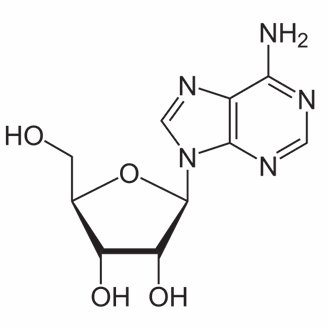
Identify the amino acid
Adenosine
_______________ are small, lipid-derived molecules that are produced by enzymatic degradation of membrane lipids
Endocannabinoids
What are 2 examples of endocannabinoids?
• Anandamide (AEA)
• 2-arachidonoyglycerol (2-AG)
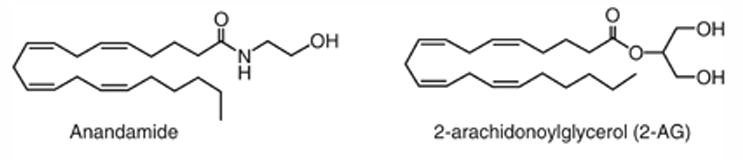
________________ are not stored in vesicles, production is stimulated by activation of G-protein-coupled receptors
Endocannabinoids
Endocannabinoids bind to ____________ receptors
cannabinoid
What are the 2 receptors of endocannabinoids? What role do they play? What are they responsible for?
• CB1 receptors – play a role in motor control, learning, memory, pain, appetite, mood
Responsible for the psychoactive effects of cannabis
• CB2 receptors – regulate inflammation and pain
mostly found in the spinal cord