Virus, Bacteria, Immunity
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
what are most diseases caused by?
bacteria, viruses, protozoas
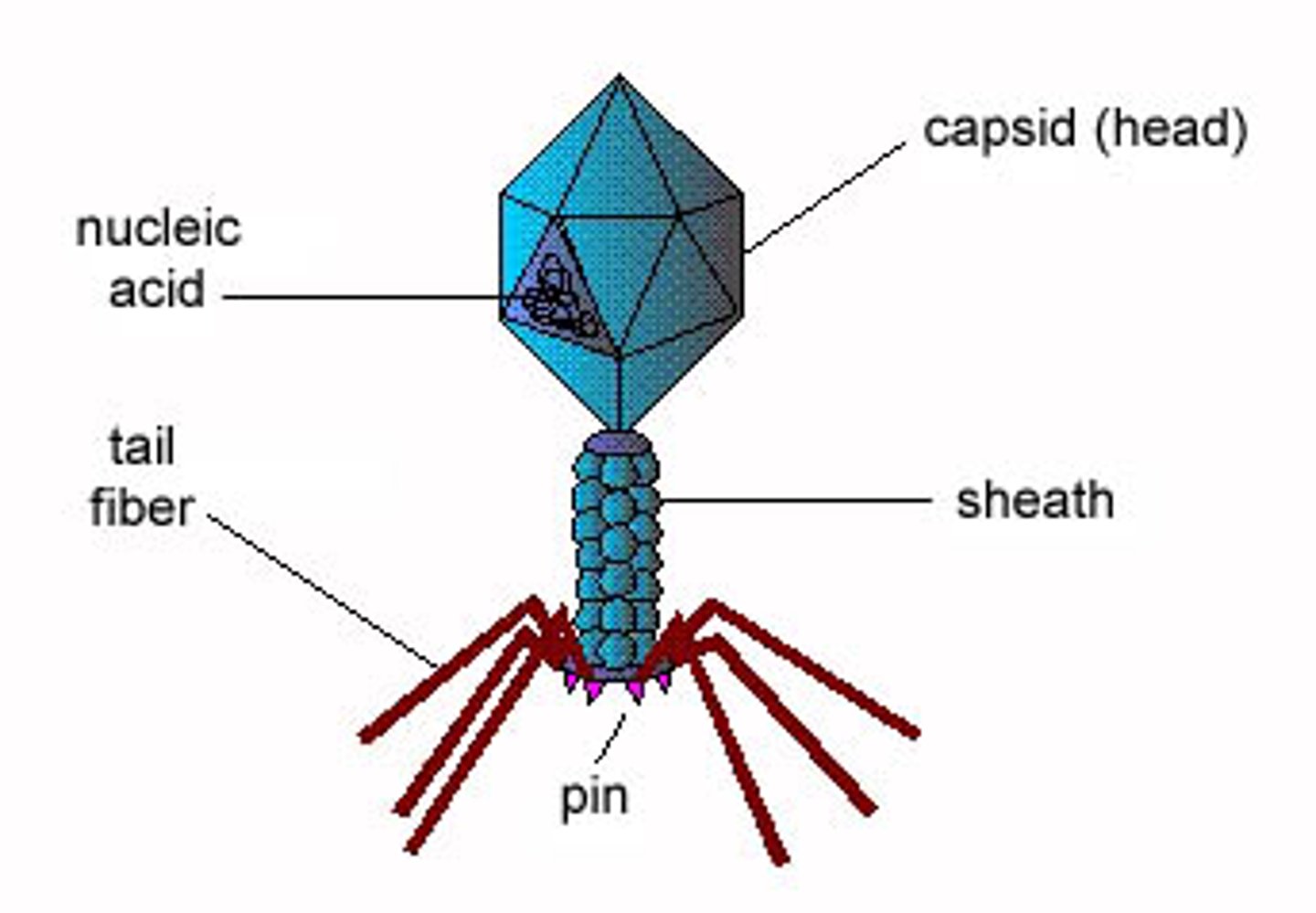
Bacteriophage (virus)
microscopic organisms that can infect hosts, like humans, plants or animals. They're a small piece of genetic information (DNA or RNA) inside of a protective shell (capsid). Some viruses also have an envelope. Viruses can't reproduce without a host
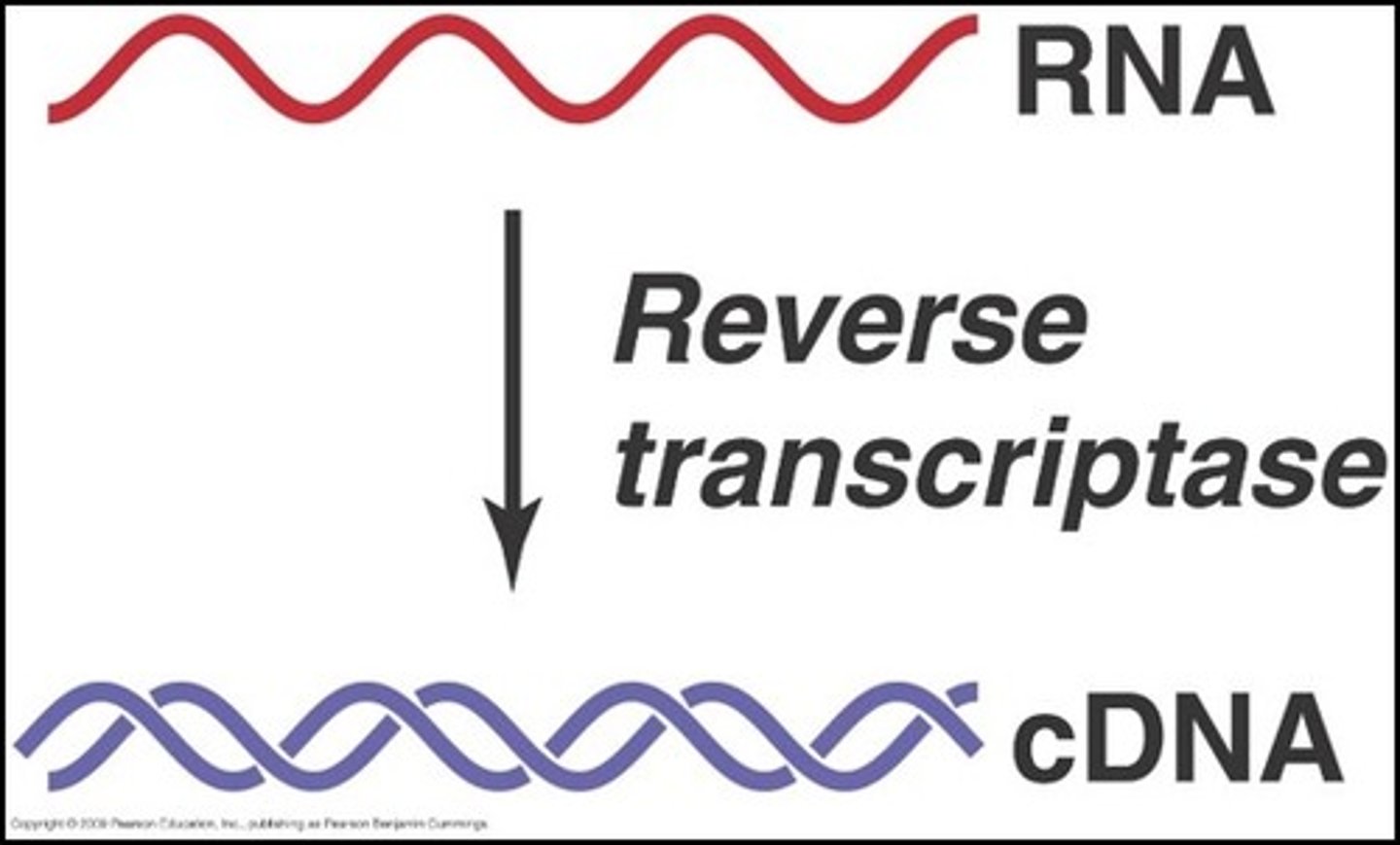
what type of viruses contain RNA? what is reverse transcript and why is it needed?
viruses that contian RNA: retroviruses
reverse transcript: turns RNA into DNA
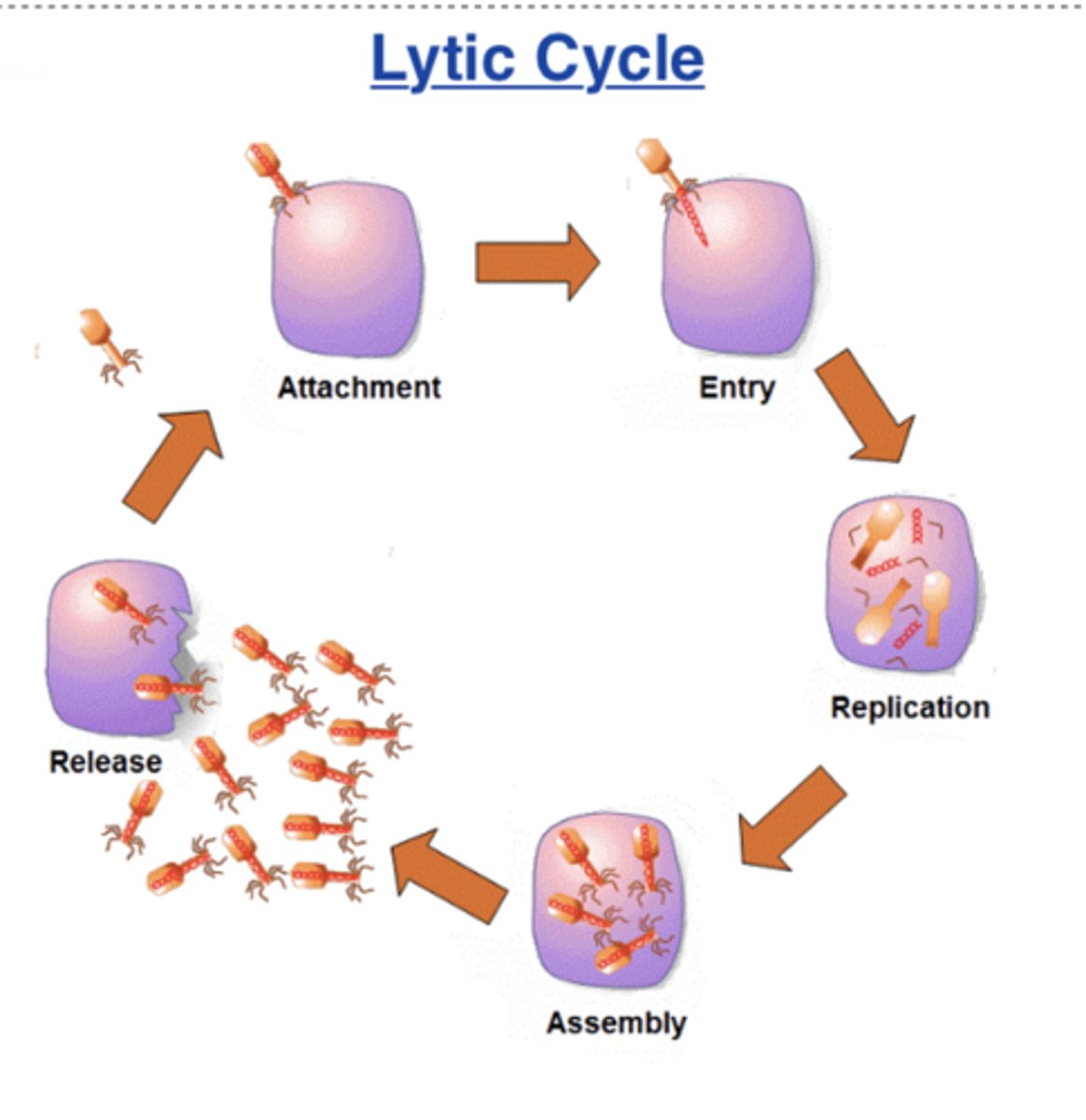
Describe the lytic cycle
1) attatchment
2) injection
3) cell take-over
4) assembly
5) cell lysis (burst)
FAST PACE AND PASSES (ebola, flu)
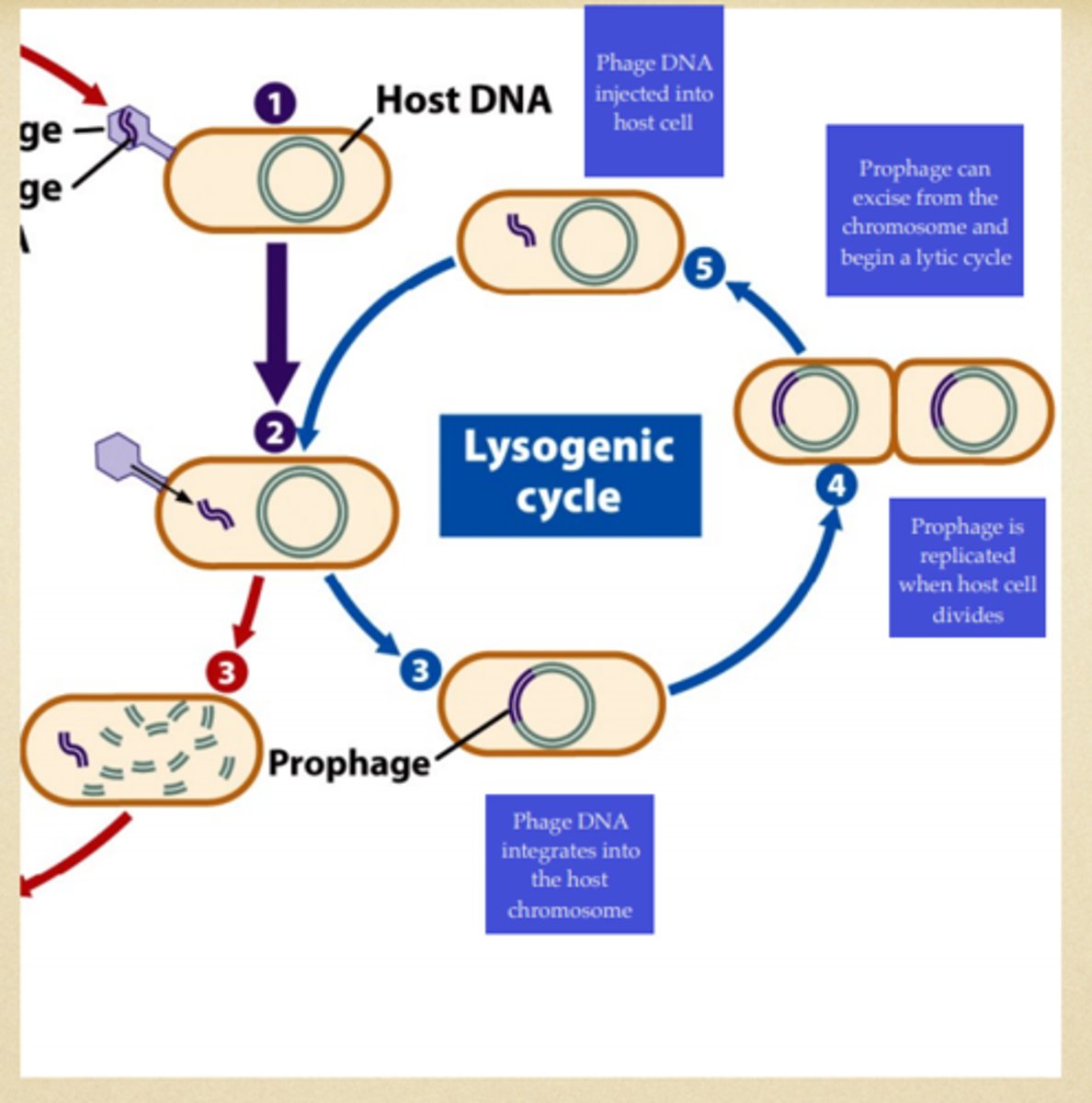
Describe the lysogenic cycle
1) attachment
2) injection
3) incorporation
4) replication
5) introduction (sometimes)
SLOW, DOESN’T PASS (HIV)
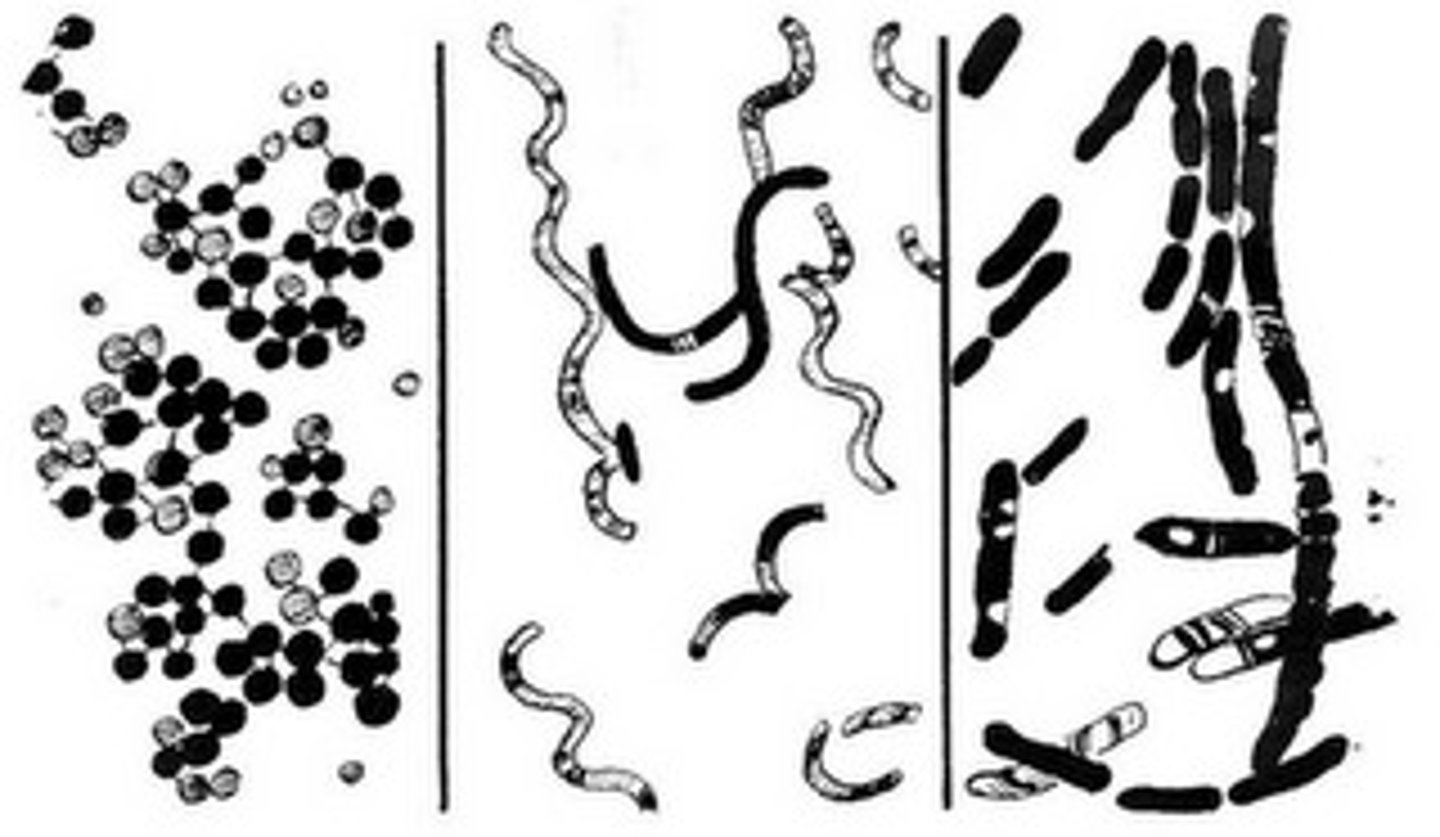
3 types of bacteria
-cocci (round shaped)
-bacilli (short and rod-shaped)
-spirilla (spiral, corkscrew shaped)
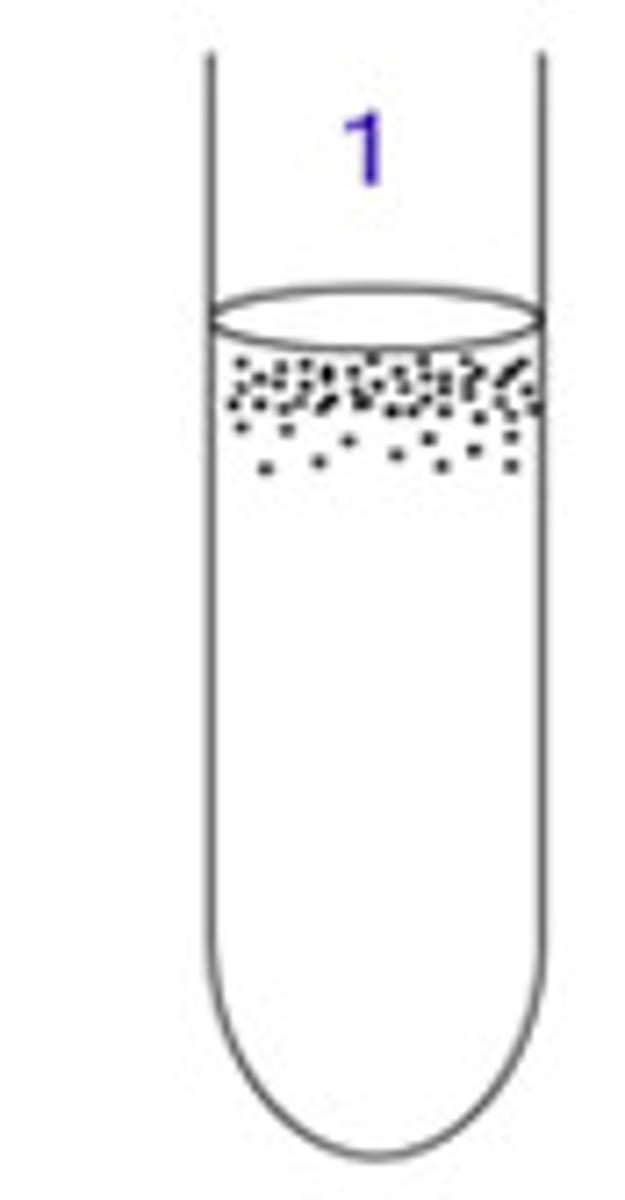
Obligate aerobe
requires oxygen
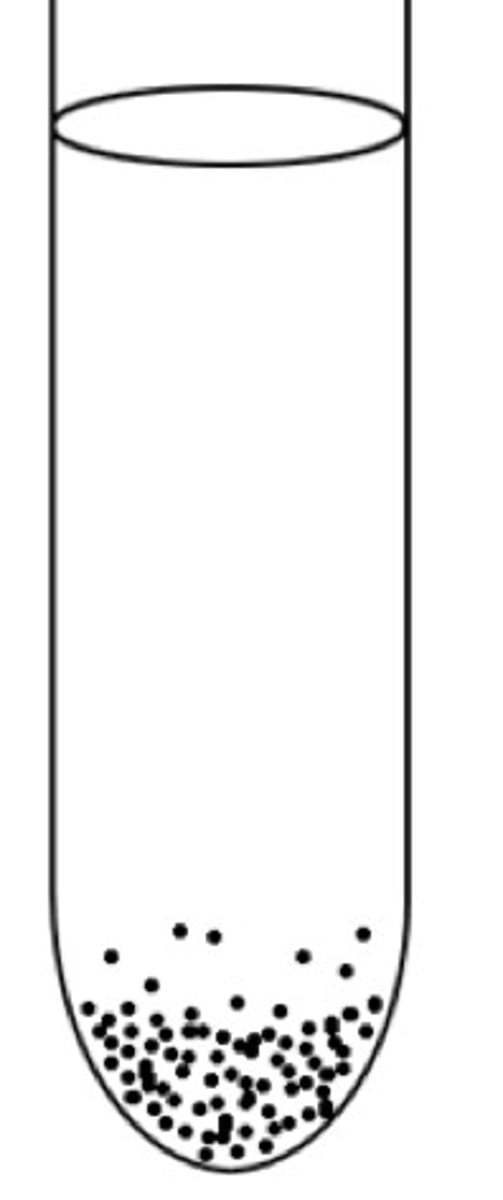
obligate anaerobe
Cannot survive in the presence of oxygen
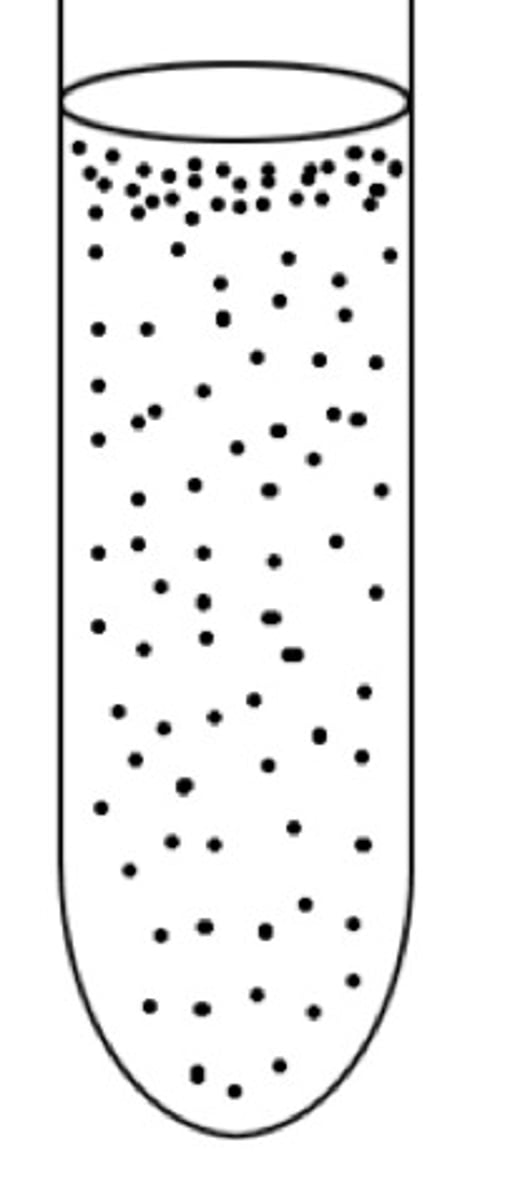
Facultative anaerobe
organism that can survive with or without oxygen
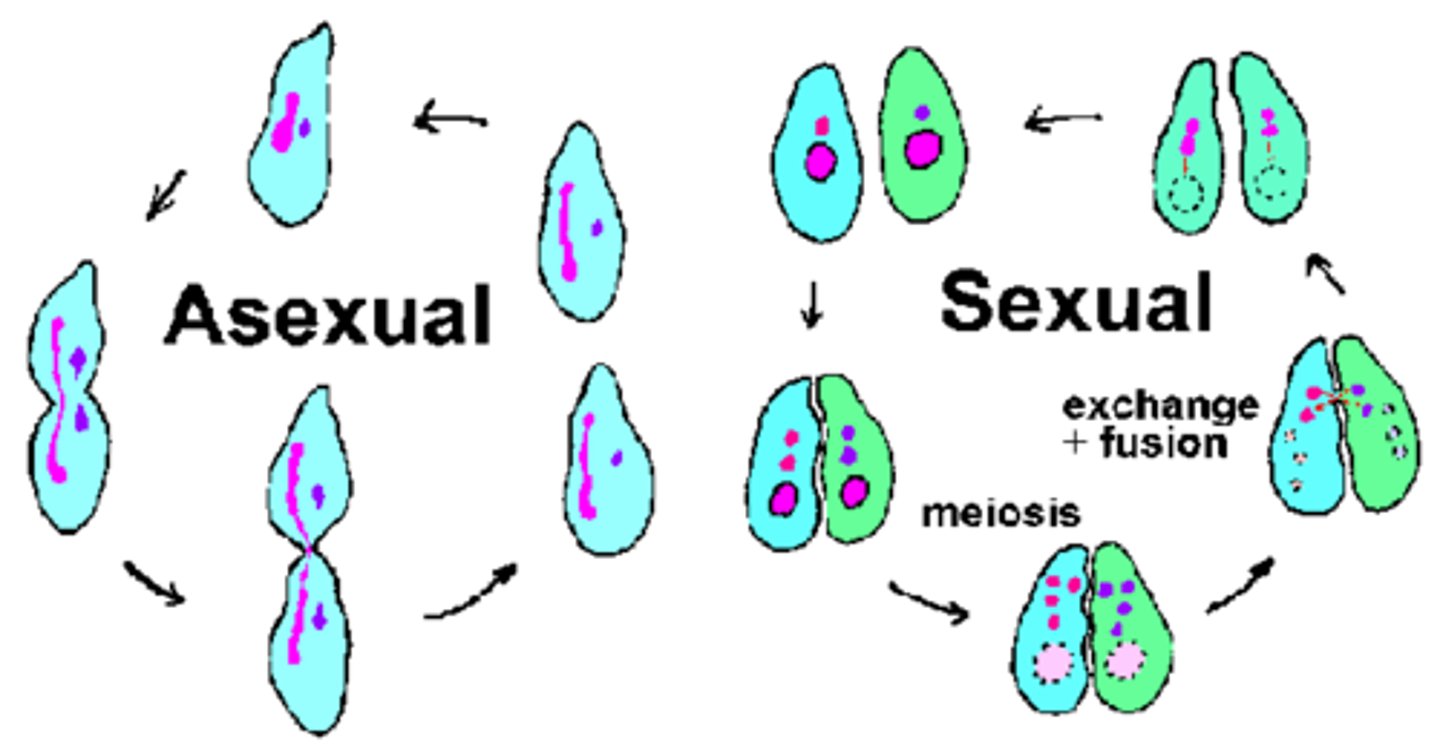
How do bacteria usually reproduce?
Binary fission: asexual
Conjugation: sexual
Endospore formation: hibernation
What are 3 ways bacteria is helpful to humans?
1) aids digestion
2) protects against infection
3) fermentation
When should antibiotics be used, and how can we prevent misuse?
-used to destroy or inhibit growth of bacteria
-we can prevent misuse by using only when needed
who developed the first vaccine?
Edward Jenner- did it by using cowpox to provide immunity to smallpox

What did Pasteur and Koch do?
Pasteur: pasteurization to kill disease causing agents in food and beverages
Koch: linked a specific microorganism to a specfic disease (namely anthrax)

what is the first line of defense?
physical and chemical barriers that keep pathogens out (skin, mucus)
What is the second line of defense?
inflamation: swelling, redness, heat
complement: proteins punch holes in pathogens
fever: raises body temp to slow down pathogens
memory cells
long lasting cells that "remember" a pathogen
effector cells
short-lived cells that take effect immediately against the antigen and any pathogens producing that antigen
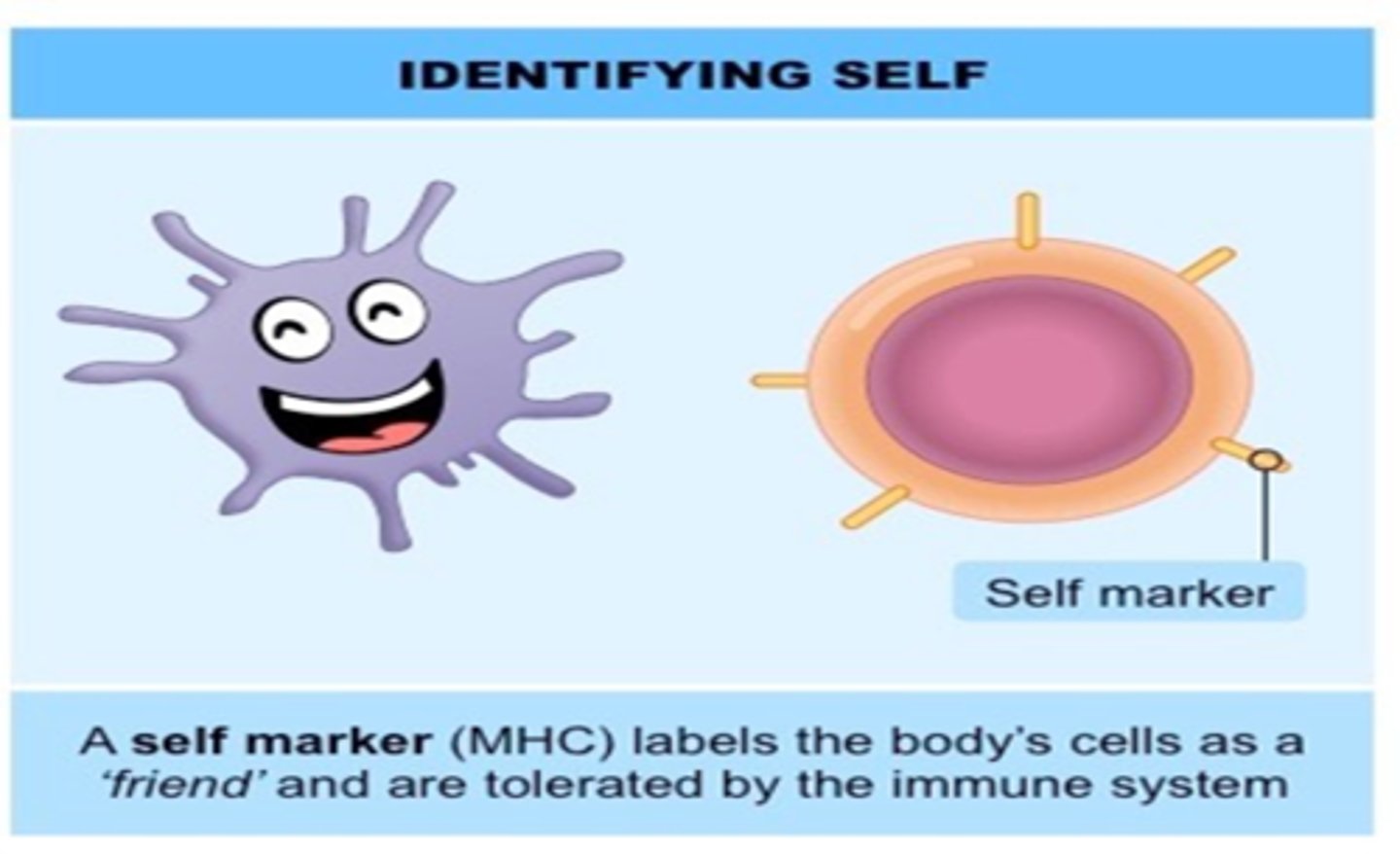
MHC marker
a self-recognition protein on a body cell
Antigen-presenting cells (APCs)
Cells that present antigens to T cells.

active immunity
A form of acquired immunity in which the body produces its own antibodies against disease-causing antigens
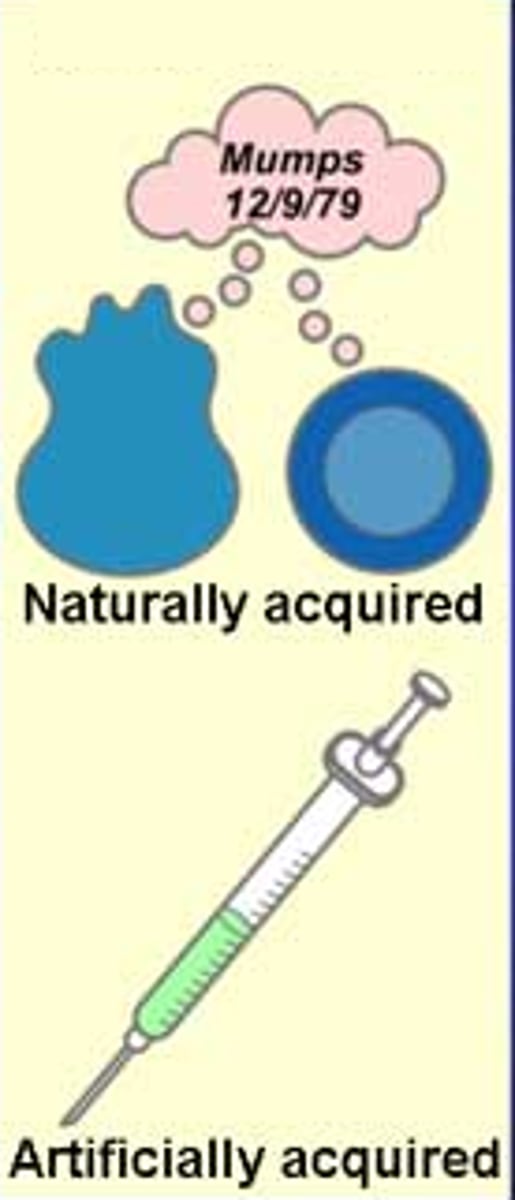
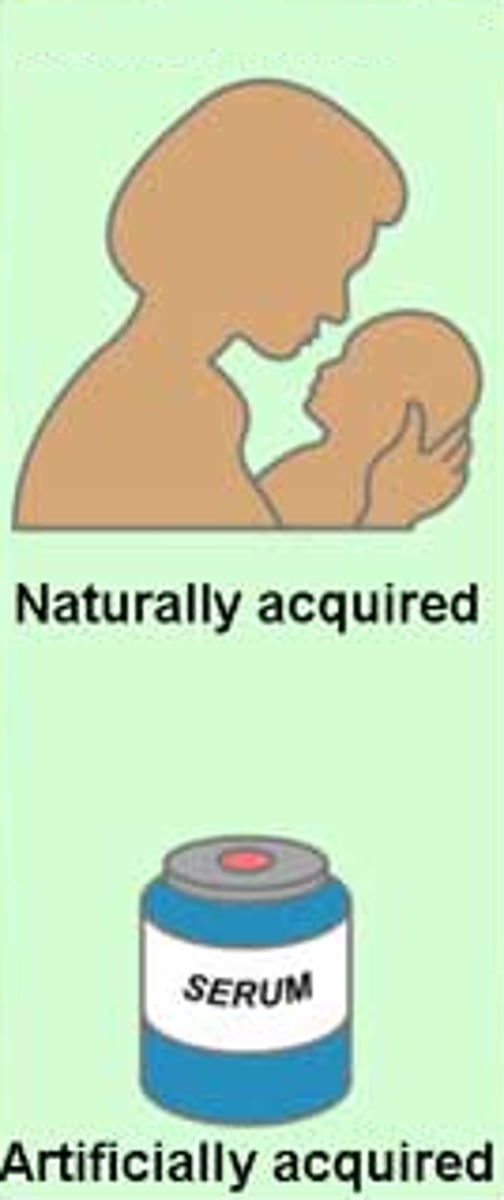
passive immunity
the short-term immunity that results from the introduction of antibodies from another person or animal.
vaccine
substance prepared from killed or weakened pathogens and introduced into a body to produce immunity
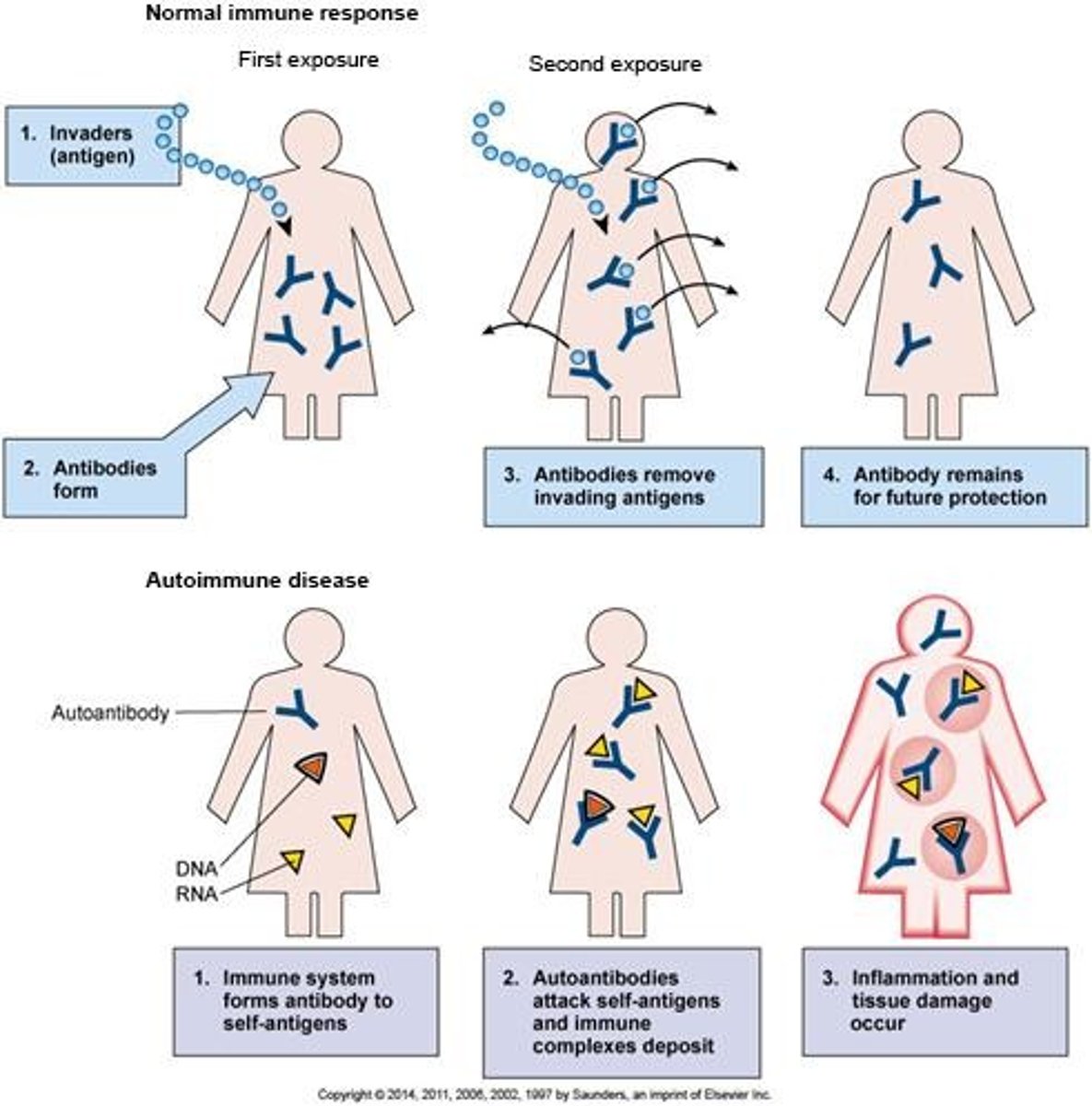
Autoimmune Disorders
Immune system attacks body's own tissues (diabetes, lupus)
How do viruses reproduce?
they invade and take over host cells
Which diseases are caused by bacteria?
tuberculosis and step throat