NR442 -COMMUNITY HEALTH CMS (EXTRA BITS) questions and answers + rationales for student success
1/121
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
122 Terms
HOSPITAL INCIDENT COMMAND SYSTEM (HICS)
assists hospitals to improve their emergency management planning, response, and recovery capabilities for planned and unplanned events
DEPARTMENT OF HOMELAND SECURITY (DHS)
Mission of the DHS
prevent terrorism and enhance security
secure and manage U.S. borders
enforce and administer immigration laws
safeguard and secure cyberspace
ensure resilience to disasters
OFFICE OF EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT (OEM)
involves representatives from all official and unofficial agencies in:
developing the community disaster plan
developing scenarios to test the plan through drills
assessing the scope, intensity, and number of casualties once an incident has occurred in order to initiate the proper response
FEDERAL EMERGENCY MANAGEMENT AGENCY (FEMA)
FEMA's Mission
to support citizens and first responders to ensure that as a nation, everyone works together to build, sustain, and improve the capacity to prepare for, protect against, respond to, recover from, and mitigate all hazards
FEMA - RECOMMENDATIONS FOR BASIC DISASTER SUPPLY KIT
3 day supply of non-perishable food
3 day supply of water
- 1 gallon/per person/per day
portable, battery powered radio/television
with extra batteries
flashlight with extra batteries
first aid kit w/manual
sanitation/hygiene items
matches/waterproof container
whistle
kitchen accessories/utensils/can opener
photocopies of ID Cards/credit cards
cash/coins
medications
infant supplies (diapers, formula, bottle, etc)
warm clothes (if in a cold climate)
AMERICAN RED CROSS (ARC)
a nonprofit, humanitarian organization led by volunteers and guided by its Congressional Charter that provides relief to victims of disasters
SURVIVOR'S GUILT
when a person has feelings of guilt because they survived a life-threatening situation when others did not
a common reaction to traumatic events
a symptom of post traumatic stress disorder (PTSD)
PTSD - PREVENTION
During the incident, be aware of need for breaks, rest, adequate water, and nutrition
provide emotional support for those involved in the incident
encourage staff to support each other
debrief with others following the incident
encourage expression of feelings by all involved
use offered counseling resources
RISK MAP
geographic map of an area that is analyzed for the impact of a potential disaster on the population and buildings in the area that would be involved
examples
- an area in a flood plain
- area covered if a nuclear explosion would occur
- area involved in an explosion of an industrial site
DISASTER MANAGEMENT - DISASTER RESPONSE
assess extent of disaster
- how many people affected?
- how many injured/dead?
- how much fresh water/food available?
- what are areas of risk/sanitation concerns?
perform triage and direct those affected
coordinate evaluations/quarantines
RESOURCE MAP
geographic map that outlines the resources that would be available in or near the area affected by a potential disaster
examples
- potential shelter sites
- potential medical sources
- location of equipment that might be needed
MITIGATION
actions taken to reduce loss of life and property by lessening the impact of disasters
primary prevention = aimed at preventing the occurrence of a disaster or limiting consequences when the event cannot be prevented
NON-DISASTER STAGE
the period before the disaster occurs
ETHICAL PRINCIPLES IN COMMUNITY HEALTH NURSING
respect a client's right to autonomy
non-maleficence
beneficence
distributive justice
PREVENTIVE ACTIONS DURING THE NON-DISASTER STAGE
assessing communities to determine potential disaster hazards
developing disaster plans at local, state, and federal levels
conducting drills to test the plan
training volunteers and health care providers
providing educational programs of all kinds
AUTONOMY
respect a client's right to self-determination
individuals select actions that fulfill their goals
example
a client refusing chemotherapy
FIRST RESPONDERS
responsible for incident management at the local level
includes:
- police dept
- fire dept
- public health
- public works
- emergency medical services
NON-MALEFICENCE
do no harm
example
developing plans of care that include a system for monitoring/evaluating outcomes
GUIDELINES FOR EARLY DETECTION OF BIOCHEMICAL TERRORIST INCIDENTS
rapidly increasing disease incidence
unusual increase in the number of people seeking care
endemic disease rapidly emerging at an uncharacteristic time or in an unusual pattern
clusters of clients arriving from a single locale
large numbers of rapidly fatal cases
- clients who die within 72 hrs after admission
client who presents with disease that is relatively uncommon (i.e. pulmonary anthrax, smallpox, plague)
BENEFICENCE
do what is best
maximize benefits
example
assessing costs, risks, benefits when planning interventions
IN THE EVENT OF A BIOCHEMICAL INCIDENT - AGENCIES TO CALL INCLUDE...
CDC Bioterrorism Emergency Response
CDC Hospital Infections Program
U.S. Army Medical Research Institute of Infectious Diseases
DISTRIBUTIVE JUSTICE
fair allocation of resources in the community
example
determining eligibility for health care services based on income and fiscal resources
NATIONAL RESPONSE FRAMEWORK (NRF)
core operational plan for domestic incident management for an all-hazards response
describes best practices for managing incidents "that range from the serious but purely local, to large-scale terrorist attacks or catastrophic natural disasters"
CHARACTERISTICS OF DISASTERS
frequency
predictability
preventability
imminence
scope/number of casualties
intensity
DISASTER PLANNING PRINCIPLES
measures usually taken are not sufficient for major disasters
plans should be adjusted to people's needs
planning does not stop with the development of a written plan
lack of information causes inappropriate responses by community members
people should be able to respond with/without direction
plans should coordinate efforts of the entire community
plans should be linked to surrounding areas
plans should be general enough to cover all potential disaster events
CHARACTERISTICS OF DISASTERS - FREQUENCY
how often a disaster occurs
example
in the United States, there are 45 states/territories that have moderate to high risk for earthquakes and earthquakes have occurred in every region of the country
CONTINUOUS QUALITY IMPROVEMENT (CQI)
approach to quality management that emphasizes the organization and its processes and systems and uses objective data to analyze and improve processes
CHARACTERISTICS OF DISASTERS - PREDICTABILITY
relates to the ability to determine when and whether a disaster event will occur
examples
floods - predictions made by monitoring snowmelt
hurricanes - predictions based on system tracking
tornadoes - predictions based on weather conditions
CQI - EFFECTIVENESS
providing services to those who will benefit
CHARACTERISTICS OF DISASTERS - PREVENTABILITY/MITIGATION
assumes that all disasters are not inevitable and steps can be taken to prevent them
some disasters are not preventable, however, some disasters can be controlled
example
flood can be controlled by the building of dams/levees
CQI - TIMELINESS
reducing waits and harmful delays in providing/receiving care
CQI - CLIENT CENTERED
ensuring client values guide decision making
CQI - EQUITY
providing equal care without discriminating against gender, race, sexual orientation, or socioeconomic status
CQI - SAFETY
avoiding injuries to clients from the care intended to help
PRE-DISASTER STAGE
the time when the disaster is pending
CQI - EFFICIENCY
avoiding waste in supplies, ideas, or energies
CHARACTERISTICS OF DISASTERS - IMMINENCE
the speed of onset of an impending disaster and relates to the extent of forewarning possible and the anticipated duration of the incident
example
weather forecasters can tell when a hurricane may be developing days ahead of its expected arrival and can give the time of arrival, the general direction it will take, and an approximate location for its landing and forward movement
CHARACTERISTICS OF DISASTERS - SCOPE AND NUMBER OF CASUALTIES
scope
indicates range of its effect
scope is described in terms of both geographic area and number of individuals affected/injured/killed
CHARACTERISTICS OF DISASTERS - INTENSITY
characteristic describing the level of destruction and devastation of the disaster event
PNEUMOTHORAX - SYMPTOMS
deviated trachea
pain on affected site
unequal movement of chest during inhalation/exhalation
air hunger
tachycardia
shallow respirations
SCABIES - NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
pruritus may last up to 4 weeks after treatment
recurrence possible if inadequately treated
CHEST TUBE SYSTEM
first chamber
- drainage collection
second chamber
- water seal
third chamber
- suction control
- can be wet or dry
CUTANEOUS ANTHRAX
when anthrax spores get into the skin, usually through a cut or scrap
happens when a person handles infected animals or contaminated animal products (i.e. wool, hides, and hair)
most common form of anthrax
least dangerous
CHEST TUBE - INDICATIONS
drains fluid, air, or blood from the pleural space
CUTANEOUS ANTHRAX - NURSING CONSIDERATIONS
cutaneous anthrax is NOT contagious
all types of anthrax have the potential, if left untreated, to spread throughout the body and cause severe illness, and in some cases, death
CHEST TUBE - POSITIONING
TUBE TIP POSITION UP
- pneumothorax
TUBE TIP POSITION DOWN
- hemothorax
- plerual effusion
CUTANEOUS ANTHRAX - SIGNS/SYMPTOMS
small blisters/bumps
swelling around the sore
skin sores with a black center that appear on the face, neck, and arms
CHEST TUBE - DRAINAGE COLLECTION CHAMBER
chart the amount/color
report drainage amounts greater than 70 mL/hr to the provider
CUTANEOUS ANTHRAX - DIAGNOSIS
measure antibodies/toxin in the blood
Bacillus anthracis can be sampled from:
- blood
- skin lesion swab
- spinal fluid
- respiratory secretions
samples must be taken BEFORE initiating antibiotic therapy
CHEST TUBE - WATER SEAL CHAMBER
add sterile fluid up to 2 cm line
check every 2 hours
chamber must be kept upright and below chest tube insertion site
tidaling expected
lack of tidaling
- lung re-expansion or obstruction
continuous bubbling in water chamber indicates air leak
CUTANEOUS ANTHRAX - ANTIBIOTIC TREATMENT
ciprofloxacin
doxycycline
levofloxacin
CIPROFLOXACIN - CLIENT TEACHING
dairy products and antacids decrease absorption of this Rx.
this Rx can be taken with meals
increase fluid intake while taking this Rx
report unusual pain/inflammation and diarrhea symptoms
CIPROFLOXACIN - ADVERSE EFFECTS
achilles tendon rupture
GI discomfort (nausea/vomiting/diarrhea)
- take Rx with meals
suprainfection
- thrush
- vaginal yeast infection
phototoxicity (severe sunburn)
- avoid sun exposure
- wear protective clothing
DOXYCYCLINE - CLIENT TEACHING
take Rx on an empty stomach with full glass (8 oz) of water
avoid milk products and antacids while taking this Rx
this Rx decreases the effectiveness of oral contraceptives; alternative birth control needed
CHEST TUBE - SUCTION CONTROL CHAMBER
-20 cm H₂O common
continuous bubbling in suction control chamber is expected
DOXYCYCLINE - ADVERSE EFFECTS
GI discomfort
- nausea/vomiting
- cramping/diarrhea
- esophageal ulceration
tooth discoloration
- do not give to children under 8 years old
- do not give to pregnant women
hepatotoxicity
photosensitivity
- wear protective clothing
- use sunscreen
suprainfection
- pseudomembranous colitis
- yeast infections
CUTANEOUS ANTHRAX - ANTITOXIN TREATMENT
raxibacumab
obiltoxaximab
IV anthrax immune globulin
anthrax vaccine adsorbed (AVA)
SUCTION CONTROL - WET SUCTION
height of sterile fluid determines amount of suction transmitted to the pleural space
suction pressure is set by a regulator on the chest tube drainage device
suction results in continuous bubbling in the suction chamber
monitor fluid level and add fluid as needed to maintain prescribed suction level
SUCTION CONTROL - DRY SUCTION
when connected to wall suction, the regulator on the chest tube drainage system is set to manufacturer's recommendation
tidaling is expected in the water seal chamber
CHEST TUBE - RESPIRATION/FLUID PATTERNS
NEGATIVE PRESSURE/SPONTANEOUS RESPIRATION: Fluid will...
- rise with inspiration
- fall with expiration
POSITIVE PRESSURE/MECHANICAL RESPIRATION: Fluid will...
- rise with expiration
- fall with inspiration
CHEST TUBES - NURSING CARE
assess chest tube insertion site for erythema, pain, and crepitus
position patient in semi/high Fowler's position
obtain chest x-ray to verify tube placement
keep 2 hemostats, sterile water, occlusive dressing at the bedside
only clamp when ordered
do not strip/milk tubing
CHEST TUBE REMOVAL
tell patient to take a deep breath, exhale, and bear down (Valsalva maneuver)
apply sterile petroleum jelly gauze dressing over the chest tube site
CHEST TUBE COMPLICATIONS - ACCIDENTAL DISCONNECTION
if drainage system becomes compromised, place end of tube into sterile water (to maintain water seal)
if chest tube is accidentally removed, place occlusive dressing over insertion site - TAPED ONLY ON THREE SIDES
CHEST TUBE COMPLICATIONS - AIR LEAK
monitor the water seal chamber for continuous bubbling (which confirms air leak)
check all connections
tighten connection or replace drainage system
TENSION PNEUMOTHORAX
tracheal deviation
absent breath sounds on affected side
respiratory distress
asymmetry of chest
RESPIRATORY EMERGENCIES
pneumothorax
tension pneumothorax
hemothorax
flail chest
RESPIRATORY EMERGENCIES - PNEUMOTHORAX
lung collapse due to air in the pleural space
key symptom
- hyperresonance w/percussion
RESPIRATORY EMERGENCIES - TENSION PNEUMOTHORAX
air enters the pleural space during inspiration, but cannot exit during expiration
trapped air causes pressure on the heart and lungs
increased pressure compresses blood vessels and restricts venous return; decreases cardiac output
key symptom
- tracheal deviation
RESPIRATORY EMERGENCIES - HEMOTHORAX
blood accumulates in the pleural space
key symptom
- dull percussion
RESPIRATORY EMERGENCIES - FLAIL CHEST
chest wall expansion limited due to multiple fractured ribs
key symptom
- paradoxical chest wall movement
RESPIRATORY EMERGENCIES - TREATMENT
oxygen therapy
medications
- benzodiazepines (for anxiety)
- opioids (for pain)
chest tube insertion
CHEST TUBE - FUNCTIONS
drain fluid, blood, or air
re-establish negative pressure
facilitate lung expansion
restore normal intrapleural pressure
LUMBAR PUNCTURE
cerebral spinal fluid (CSF) sample is taken from the spinal canal for analysis
LUMBAR PUNCTURE - INDICATIONS
used to diagnose...
- multiple sclerosis
- syphilis
- meningitis
- infection in the CSF
LUMBAR PUNCTURE/PRE-PROCEDURE
have client void
position client in "cannonball" position on their side or have client stretch over table while sitting
LUMBAR PUNCTURE/POST-PROCEDURE
patient should lay flat for several hours
if dura puncture site does not heal, CSF may leak, resulting in headache
administer pain meds
encourage increased fluid intake
epidural blood patch can be used to seal off the hole
MENINGITIS
inflammation of the meninges (membrane around the brain/spinal cord)
viral meningitis is most common
bacterial meningitis is contagious, with high mortality rate
MENINGITIS - PREVENTION
immunizations help prevent bacterial meningitis
Hib vaccine is given to infants
- @ 2 months
- @ 6 months
- @ 1 to 1.5 years
MCV4 vaccine is given to students living in dorms
MENINGITIS - SIGNS/SYMPTOMS
headache
nuchal rigidity
photophobia
nausea/vomiting
positive Kernig's sign
positive Brudzinski's sign
fever
altered LOC
tachycardia
seizures
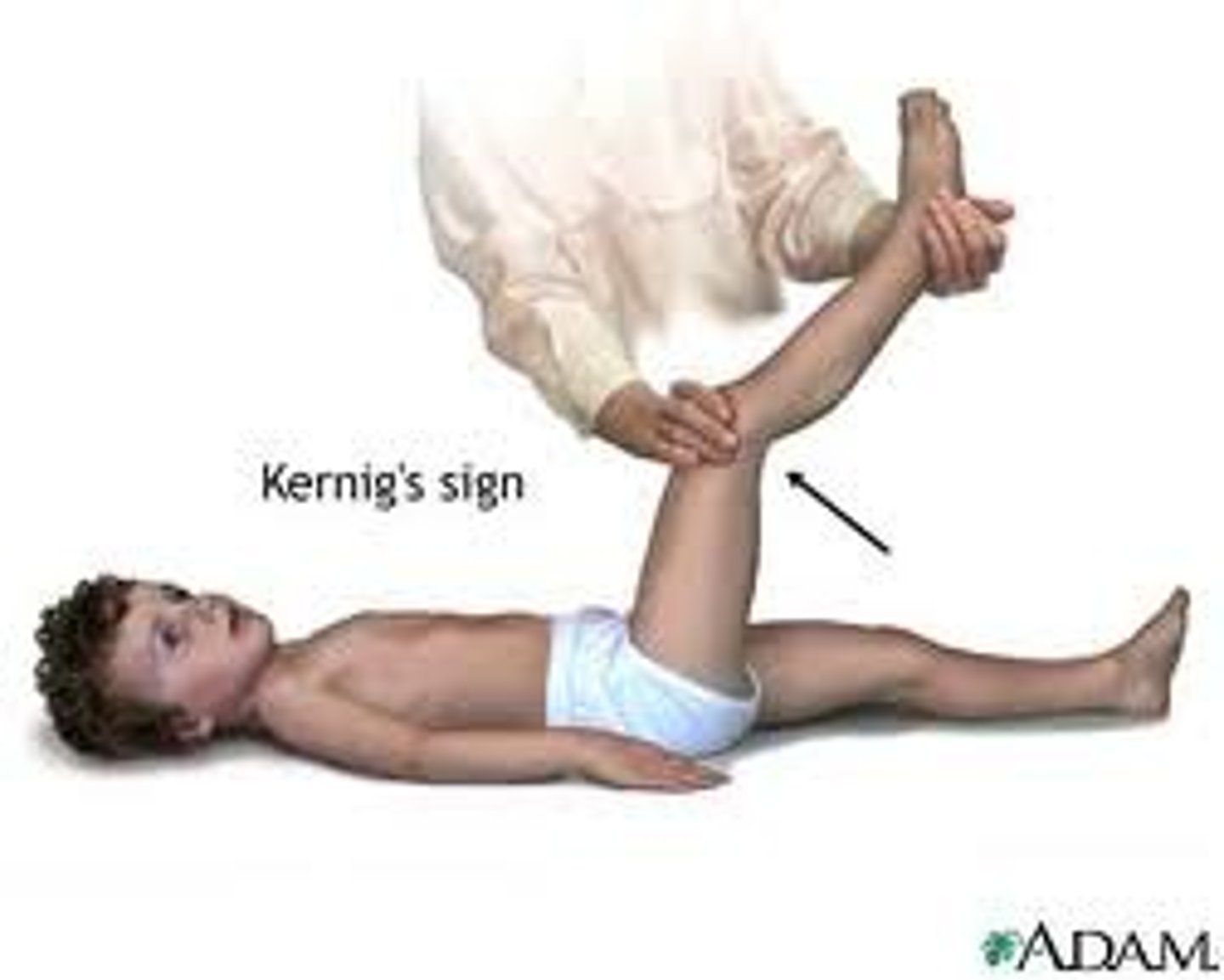
KERNIG'S SIGN
Severe stiffness of the hamstrings causes an inability to straighten the leg when the hip is flexed to 90 degrees.
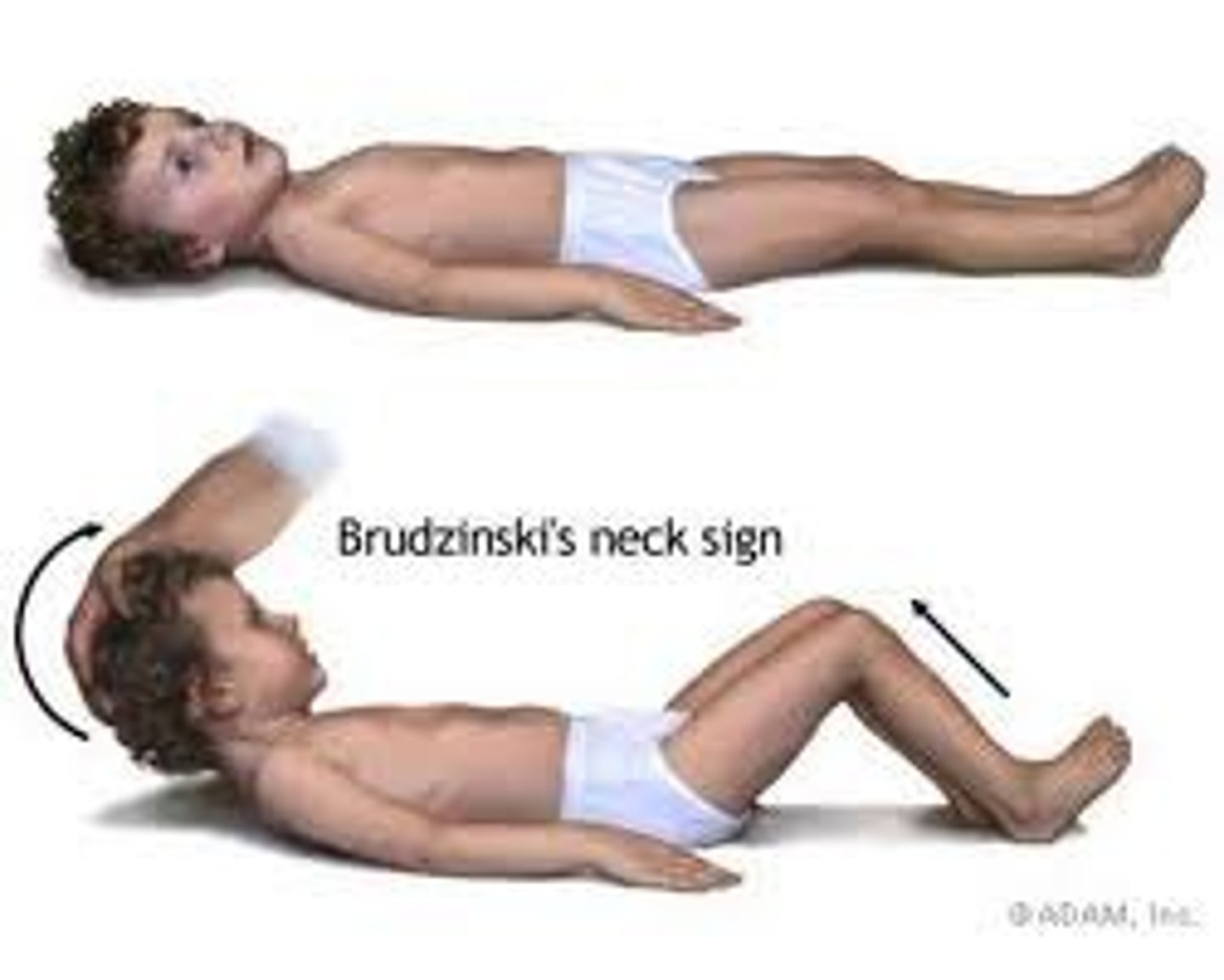
BRUDZINSKI'S SIGN
Severe neck stiffness causes a patient's hips and knees to flex when the neck is flexed.
MENINGITIS - DIAGNOSIS
CSF analysis
Bacterial
- cloudy CSF
- decreased glucose content
Viral
- clear CSF
both types will have elevated WBC and elevated protein
MENINGITIS - NURSING CARE
droplet precautions until antibiotics are administered for 24 hours (or per facility policy)
quiet room/low light
HOB @ 30 degrees
monitor for ICP
instruct patient to avoid coughing/sneezing
implement seizure precautions
MENINGITIS - MEDICATIONS
antibiotics
ceftriaxone or cefotaxime in combination with vancomycin
anticonvulsants
phenytoin
analgesics
acetaminophen
ibuprofen
prophylactic antibiotics (given to those in close contract with client). ABX include:
- ciprofloxacin
- rifampin
- ceftriaxone
MENINGITIS AND OPIOID MEDICATIONS - NURSING CONSIDERATION
non-opioid analgesics are preferred treatment for meningitis to avoid masking changes in level of consciousness
MENINGOCOCCAL VACCINE (MCV4)
initial dose between 11-12 years of age
booster dose at 16 years of age
MENINGITIS - COMPLICATIONS
Increased ICP
SIADH
Septic emboli
SCABIES
mite(s) penetrate the stratum corneum and deposit eggs
allergic reaction to eggs, feces, and mite parts occurs
transmission by direct physical contact
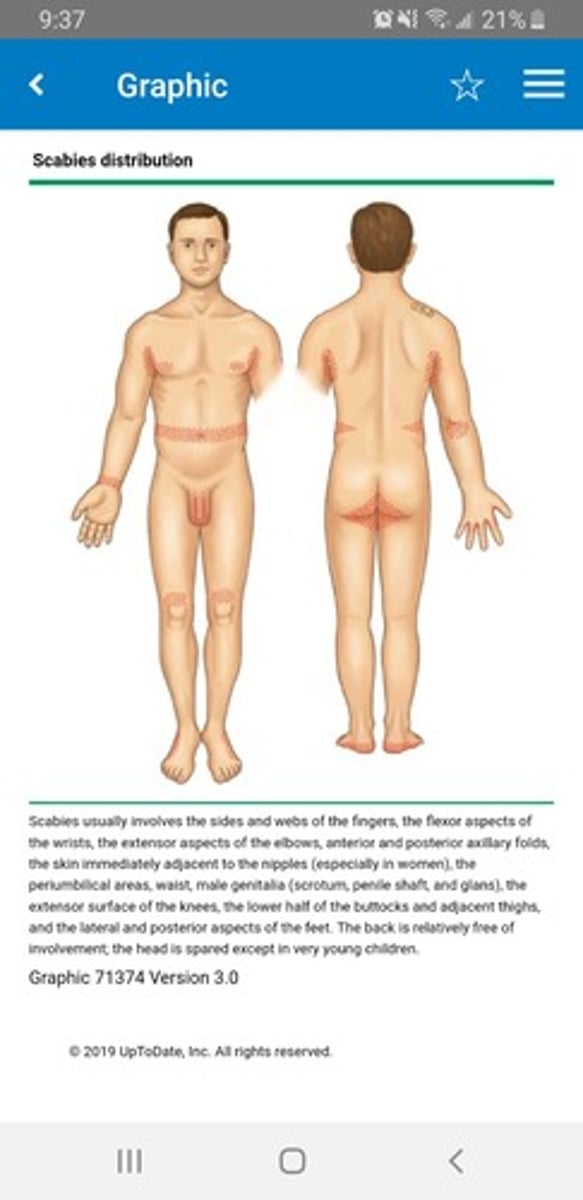
SCABIES - SIGNS/SYMPTOMS
severe itching, especially at night
usually not on the face
presence of burrows
- interdigital webs
- flexor surface of the wrists
- genitalia
- anterior axillary folds
erythematous papules with/without crusting
SCABIES - TREATMENT
5% permethrin cream
treat all family members/sexual partners
treat environment with plastic covering for 5 days
launder clothing/linen with bleach
antibiotics if secondary infections present
PPE - ORDER FOR PUTTING ON
gown
mask/respirator
goggles/face shield
gloves
(MEMORY TIP: from the bottom up, with hands above the head)
PPE - ORDER FOR TAKING OFF
gloves
goggles/face shield
gown
mask/respirator
(MEMORY TIP: these are in alphabetical order)
AIRBORNE PRECAUTIONS
smaller than 5 microns
measles
chickenpox (varicella)
disseminated varicella zoster (shingles)
pulmonary or laryngeal tuberculosis

AIRBORNE PRECAUTIONS - PROTECTIVE ACTIONS
Private room
NEGATIVE pressure airflow of at least 6 to 12 exchanges per hour via high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filtration
mask or respiratory protection device
N95 respirator (for TB)
DROPLET PRECAUTIONS
larger than 5 microns, within 3 feet of patient
requires surgical mask, proper hand hygiene and dedicated care equipment
DROPLET PRECAUTIONS - "SPIDERMAN"
S = Sepsis/Scarlet fever/Streptococcus pharyngitis
P = Parvovirus B19/Pneumonia/Pertussis
I = Influenza
D = Diptheria (pharyngeal)
E = Epiglottitis
R = Rubella
M = Mumps/Meningitis/Mycoplasma/Meningeal pneumonia
An = Adenovirus
DROPLET PRECAUTIONS - PROTECTIVE ACTIONS
Private room or cohort patients
mask or respirator required (depending on condition) (refer to agency policy)
CONTACT PRECAUTIONS
direct patient contact or environmental contact
requires gown & gloves
Colonization or infection with multidrug-resistant organisms such as VRE and MRSA, Clostridium difficile, shigella, and other enteric pathogens
major wound infections
herpes simplex
scabies
varicella zoster (disseminated)
respiratory syncytial virus in infants, young children, or immunocompromised adults
CONTACT PRECAUTIONS - "MRS WEE"
M = MDRO
R = respiratory infection
S = skin infections
W = wound infections
E = enteric (C. diff)
E = eye infection
CONTACT PRECAUTIONS - PROTECTIVE ACTIONS
Private room or cohort patients
gloves, gowns
Patients may leave their room for procedures or therapy if infectious material is contained or covered, placed in a clean gown, and if hands are cleaned