extracellular immunity
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
classification of parasites
protozoa
unicellular - amoebae, flagellates, ciliates, apicomplexa(sporozans)
can be intracellular or extraceullar but cause extracellular diseases
helminths
multicellular - nematodes(round worms), trematodes(flukes), cestodes(tapeworms)
ectoparasites
ticks, fleas, lice and mites
immune responses to parasites infections
most extracellular and too big for phagocytosis
thick coat, not penetrated by complement or T cell perforins
need to target weak spots e.g parasites digestive tract
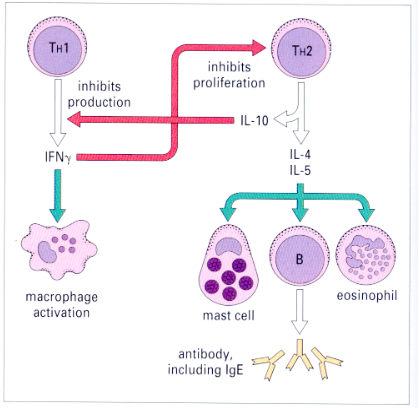
mainly Th2 driven immune responses
type 2 response at mucosal surfaces
worms cause damage to epithelial cells
release of alarmins from epithelial cells(e.g IL-33,IL-25)
together with parasite molecules, alarmins act on DCs in tissue and instruct them to promote Th2 response
meanwhile DCs take up and process helminth antigens for presentration on MHC class II
DCs migrate from tissue to lymph node and present antigen to CD4+ T cells
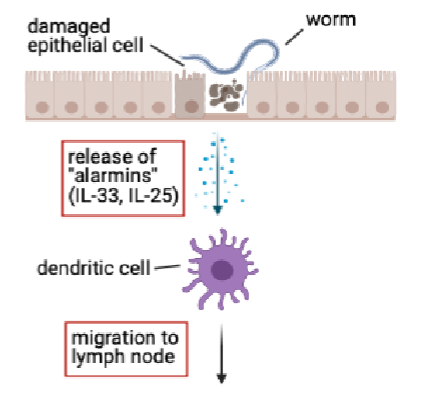
induction of Th2 response
antigen recognition leads to clonal expansion of T cells and idfferentiation towards Th2 lineage
signals recieved by DCs in infected tissue allow the to promote Th2 receptors
induction of Th2 response also requires IL-4
DCs don’t produce IL-4
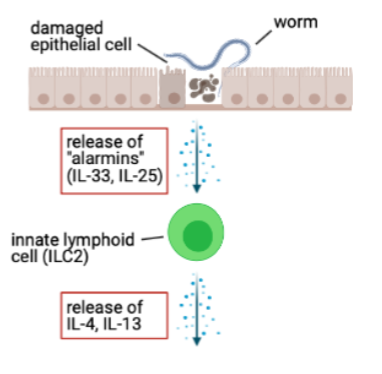
innate lymphoid cells support Th2 response
innate lymphoid cells(ILC) don’t express a TCR or BCR and don’t depend on recognition of specific antigen for activation
ILC can respond to alarmins by producing IL-13, IL-4
ILCs can respond within hrs
exact cytokines needed for Th2 differentiation
ILC-derived IL-4 supports differentiation of Th2 cells
ILC-derived IL-13 can promote migrationof DCs(dendritic cells) to lymph nodes
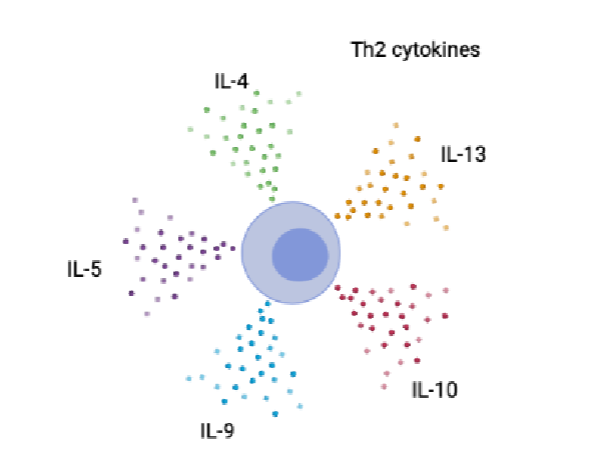
Th2 effector cytokines
IL- 10 = regulatory role, prevents excessive inflammation
B cell production of IgE
Th2-derived IL-4 mediates class switching to IgE or IgG1
IgE = mast cell degranulation, eosinophil antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC)
IgG1 = immune cell degradtion, enhanced phagocytosis, ADCC trapping of tissue migrating larvae by macrophages
effect of Th2 cytokines on intestinal epithelium g
goblet cell hyperplasia/ increased mucus production(worm expulsion)
lubrication in gut, reduces parasites ability to attach, traps parasite
increased production of resistin-like molecule - beta(RELM-beta)
specialised epithelial molecule that distrupts parasites nutrient uptake which affect its abilities
RELM beta inhibits ability of worms to feed on host tissues during infection → reduced fecundity
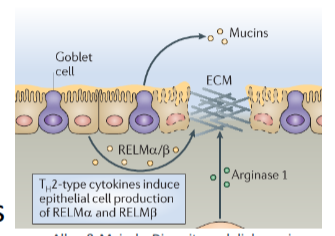
epithelial escalator and weep and sweep
Th2 cytokines and mast cell proteases increase fluid leakage across epithelium → weep
IL-13 drives increased intestinal muscle hypercontractility → sweep
IL-13 stimulates increased turnover → epithelial escalator
Th2 cytokines and mast cell proteases increase fluid leakage across epithelium. IL-13 drives increased intestinal muscle hypercontractility = weep and sweep
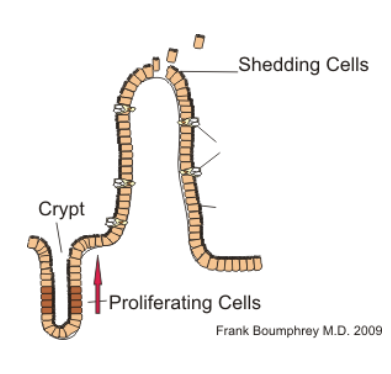
physiological host changes induced by anti-worm immunity
strong effects of anti-worm immune response on host gut physiology
does not kill worms
makes GI tract inhospitale for parasite
increases number of goblet cells = increased mucin secretion, increased intestinal mobility, increased water influx into intestinal lumen
helminth infections
promote antibodies and eosinophil and mast cell activities
choice towards Th2 response is driven by IL-4
Th2 cell cause alternative activation of macrophages and activate eosinophils and mast cells
Th2 cells promote a strong antibody response based on neutralising IgG and IgE
Th2 response is most effective to combat extracellular pathogens
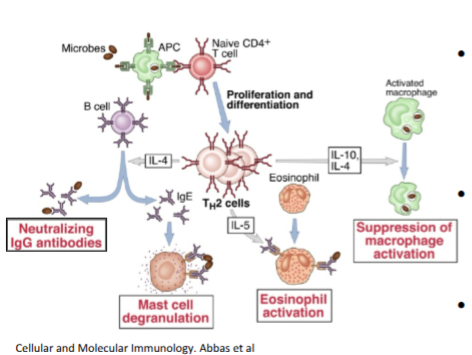
alternative activation of macrophages
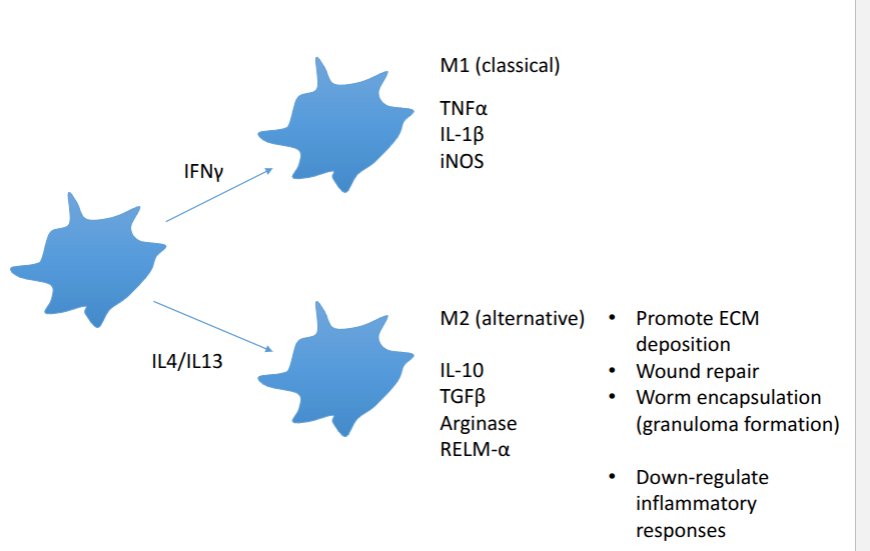
M2 macrophages = maintanence and repair
minimises damage where possible
traps and expels parasite
less about killing more about making a hostile environment and protecting the host
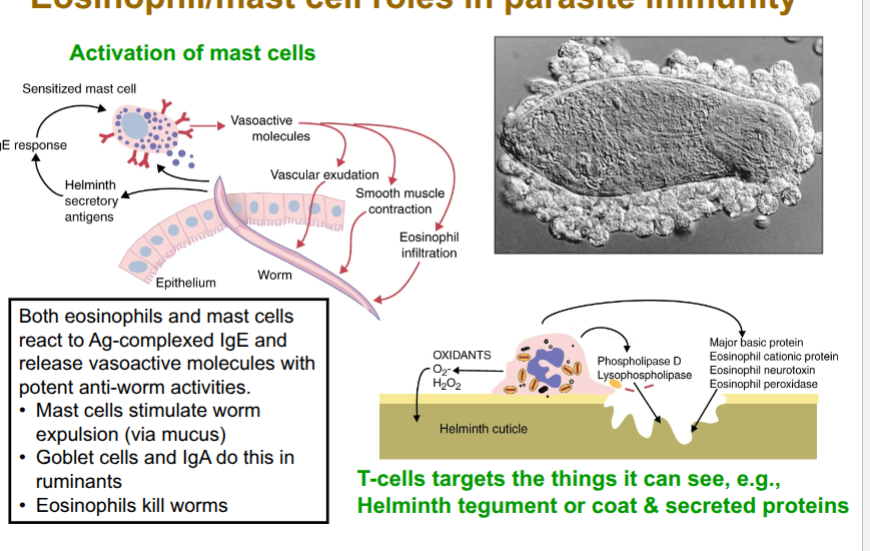
role of mast cells
early in response
sentinel function(produce cytokines to produce Th2 response)
produce alarmin, IL-33
initiation/amplification of Th2 response
later
expand and become activated in response to IL-9
express receptor for Fc region of IgE
mast cells degranulate when IgE bound to Fc receptors on mast cells surfacwe interacts when antigen
degranulation = release of antimicrobial or cytotoxic molecules from granules in cells(secretory vesicles)
release histamine, proteases, cytokunes
serine proteases directly toxic to helminths
mast cells protease opens tight junctions allowing fluid egress
role of eosinophils
IL-5 drives accumulation of eosinophils in blood(eosinophilia)
express high affinity receptor for Fc region of IgE (FcεRI)
IgE binds to surface of heminths. he FcεRI on eosinophils binds to the Fc
region of IgE. This causes the eosinophil to degranulate = destruction of helminth cuticle (ADCC).
eosinophils are bridge between adaptive and innate immunity via ADCC
eosinophil/mast cells oles in parasite immunity
how antibodies control extracellular infections
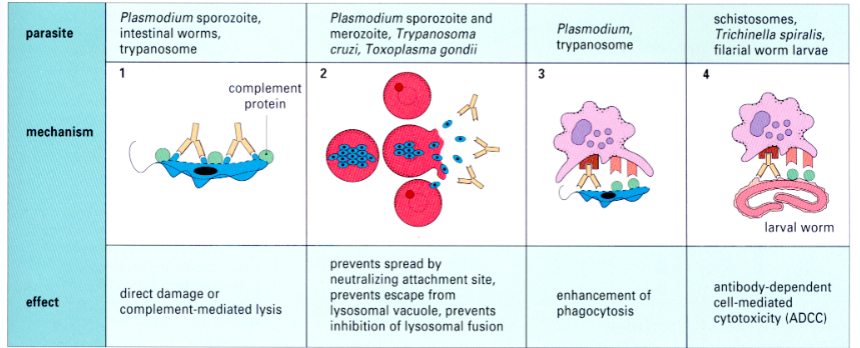
helminth evasion tactics
size - too large to be phagocytosed
thick extracellular coat
adsorbing host proteins - masking antigens
molecular mimicry - expressing antigens similar to host, trying to get recognised as self
anatomical seclusion
surface antigen shedding
interference with antigen presentation
immunosuppression
migration
production of enzymes (anti Ig/C5a)
Th2 cells promote neutralising antibodies
choice of Th2 response is driven by IL-4
Th2 cells suppress activation of macrophages
Th2 cells promote strong antibody response based on neutralising IgGs
Th2 response is most effective to combat extracellular pathogens
antibody mediated protection against extracellular bacteria
neutralises toxins
kill bacteria
opsonise bacteria
intracellular killing macrophages
essential protection for neonates