N162B: Exam 2 (copy)
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
59 Terms
A patient sustains an electrical burn from a power socket. What does the nurse need to be aware of?
the iceberg effect
What is concerning about the iceberg effect?
The damaging effects inside the body can be more severe than the outside
When working on the house's electrical system, a patient sustains an electrical burn. What should the nurse assess the bones for?
fracture due to the voltage of the shock
What is a cardiac concern associated with electrical burns and what should the nurse do?
cardiac dysrhythmias
order a STAT EKG
What is a renal concern associated with electrical burns?
AKI due to massive muscle breakdown and the release of myoglobin which can clog the glomerulus and cause the AKI
In a chemical burn which is worse: alkaline or acid burn?
Alkaline because alkali burns continue to burn even after the agent is neutralized
Why are alkali burns difficult to manage?
they cause protein hydrolysis and liquefaction
A patient arrives to the ED with liver disease presenting like cirrhosis. Symptoms include pitting edema of the lower extremities. Why is this?
The liver is unable to make albumin. Albumin is:
the largest amount of protein in blood
responsible for keeping colloidal pressure within vasculature
What happens as a result of albumin levels decreasing in liver disease?
Fluid escapes out of the vasculature into the interstitial space causing edema
You are assigned a patient with cirrhosis. What education points must you make?
avoid things that can cause further damage such as alcohol ingestion
What is lactulose?
laxative
What condition can lactulose aid in that is associated with advanced cirrhosis?
hepatic encephalopathy
How does lactulose work in hepatic encephalopathy and advanced cirrhosis?
it will cause a decrease in ammonia levels due to it being excreted via the feces and the patient’s LOC will improve
What is a paracentesis?
a procedure performed on patients with ascites to tap fluids out of the peritoneal cavity
How does paracentesis help?
Patients can breathe easier since the liquid abdominal pressure that puts pressure against the diaphragm is gone
What is an important nursing consideration for paracentesis?
the patient must empty their bladder prior to initiating the procedure
What can cause ascites?
a patient may have liver disease and suffer from hepatic portal hypertension
What is neomycin and when is it used?
antibiotic used in patients with high ammonia and hepatic encephalopathy
How does neomycin work?
It affects ammonia producing bacteria in the gut, decreases the amount of ammonia produced and thus improves hepatic encephalopathy improving patient LOC
What are NANDAs for cirrhosis?
imbalanced nutrition: less than body requirements
fluid volume excess
ineffective breathing pattern
risk for injury
risk for acute confusion
disturbed body image
deficient knowledge
What is steatorrhea?
fatty, frothy, smelly stool due to increased amount of fat in the stool
associated with acute pancreatitis
pain worsens when lying supine
smell of food can stimulate pancreatic secretion
pain with alcohol consumption
How is Hepatitis A transmitted?
fecal oral route
What is proper education to give individuals who wish to prevent hepatitis A?
proper hand hygiene
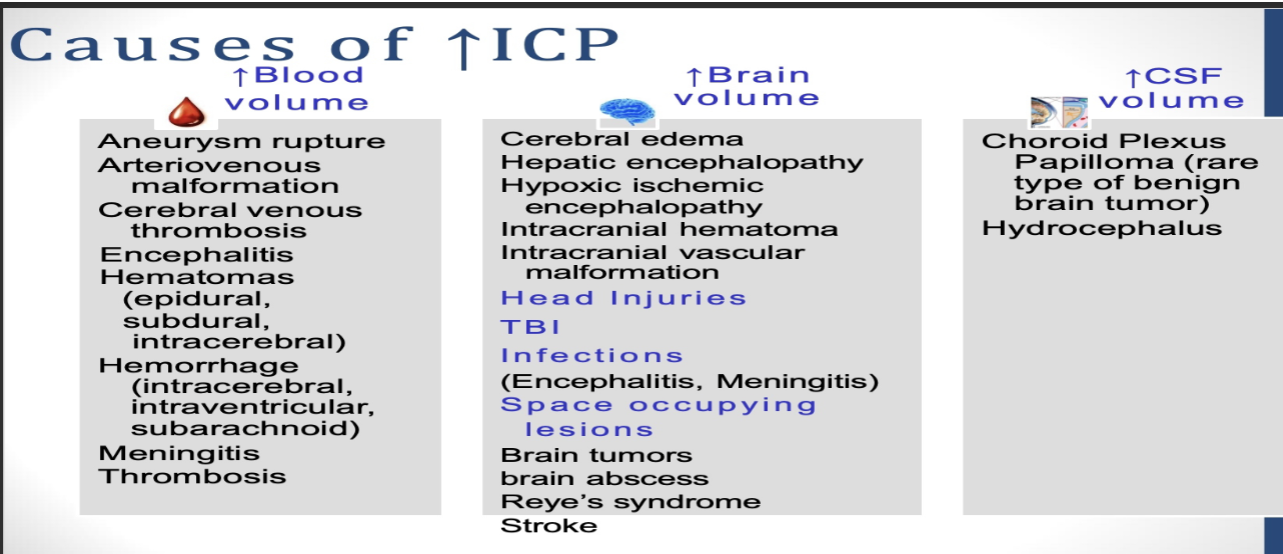
What are some causes of ICP?
What is an initial sign of increased ICP?
decreased LOC
You have a patient presenting with increased ICP. What would you educate your patient NOT to do?
valsava maneuver (make sure they do not get constipated)
buildup airway secretions (no coughing)
hip flexion
abdominal distention
lie supine (decreases cerebral drainage)
What are some presentations of ischemic stroke?
sudden onset of facial weakness
unilateral weakness (opposite side)
confusion
expressive aphasia
receptive aphasia
headache
nausea
visual disturbance
vertigo
numbness and tingling
What are some common presentations of hemorrhagic stroke?
gradual onset of symptoms
N/V
HTN
Confusion to altered LOC
headache
respiratory issues
What is a TIA?
stroke episode that lasts less than 24 hours but most last less than 1 hour
predictor of stroke
What are common presentations of basilar skull fractures?
raccoon eyes
battle sign
hemotympanum
halo sign
CSF otorrhea
CSF rhinorrhea
no neuro sx
What is the pathophysiology of multiple sclerosis?
CNS demyelination leaves sclerotic areas or plaques along with scarring
causes neuro weakness, spasticity, visual disturbances, and paresthesia
most prevalent further from equator due to low vitamin D
What test differentiates between a myasthenic crisis and a cholinergic crisis?
Tensilon test
uses edrophonium
myasthenic pt will improve
cholinergic pt will worsen
give atropine antidote
What is ALS?
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
rare progressive neuromuscular disease marked by loss of motor neurons
ASYMMETRIC
involves upper and lower motor neurons in spinal cord, brainstem, and cerebral cortex
What remains intact for ALS?
cognition
What is dementia?
loss of capacity to remember, think, or make judgments that interfere with daily tasks
manifestations occur gradually
Alzheimers
not normal aspect of aging
What is delirium?
state of confusion that develops over hours to days
decreased ability to focus, sustain, direct, and shift attention and awareness
caused by beeping, constant lights, noise, lack of human touch
What is the most common form of dementia?
Alzheimers
What are common triggers for delirium?
dehydration
dementia
electrolyte imbalance
emotional stress
disorder of lung or liver
infection
ICU
drugs
immobility
untreated pain
What are common interventions for delirium patients?
assess pt self-care needs
provide for all pt needs
provide reassurance
reorient pt to person, place, time, and event
use distraction for agitation
manage fever, pain, nausea, and sx
implement measures to sleep
What is an epidural hematoma?
bleeding into the space between the skull and dura mater
90% of adults have skull fractures
most commonly temporal bone which lacerates the middle meningeal artery
In an epidural hematoma, what can occur if the superior sagittal sinus tears?
venous epidural bleeding
What chain of events occurs with epidural hematomas?
immediate post-traumatic period of unconsciousness
lucid interval
rapid deterioration in LOC
sleepiness
confusion
obtundation
coma
death
What are characteristics of primary brain injury?
initial mechanical insult is to brain
primary injury is localized to the head
What are causes of a primary brain injury?
laceration
skull fracture
cerebral contusion
concussion
hematoma
diffuse axonal injury
damage to blood vessels
foreign object penetration
What are characteristics of a secondary brain injury?
the brain’s response to the initial injury
progressive insult that evolves following the primary injury
What is a chain reaction associated with secondary brain injuries?
inadequate CPP (cerebral perfusion pressure)
cerebral ischemia
ischemia cascade
cerebral infarction
What can secondary brain injuries result from?
hypotension
hypoxia
anemia
fever
What is a depressed skull fracture?
displacement of a comminuted skull fracture
frequently seen with other brain injuries
cerebral contusions
lacerations
What can cause a depressed skull fracture to become infected?
hair, dirt, and debris found in the wound
What is a TIA?
episode of stroke sx that lasts briefly
less than 24 hours but usually last less than 1 hour
What does a TIA tell you?
the patient is at high risk for a stroke
risk after TIA is 10-15% in 1st 3 months
urgent evaluation needs to be done since stroke and TIA share same etiology
What is the acronym assessment for a stroke?
Balance (sudden loss of balance?)
Eyes (lost vision in one or both eyes?)
Face (face look uneven?)
Arms (one arm hanging down?)
Speech (speech slurred? trouble speaking or confused?)
Time (call 911 now!)
What are the initial actions for a stroke?
ABC’s
provide O2 via NC
VS
cardiac monitor (anticipate EKG)
baseline neuro assessment
GCS, pupil check, mNIHSS
What is the most important information to receive from the patient or family of a suspected stroke patient?
initial time of symptom onset and time last known well
What is a hemorrhagic stroke?
sudden bleeding in the brain without trauma
headache often present
other sx depend on location of bleed
What causes hemorrhagic stroke?
HTN
amyloid angiopathy from age, metastatic disease, vascular malformations
What is the most common cause of subarachnoid hemorrhages?
aneurysms
What does the nurse need to monitor for TPA?
VS
neuro check
mNIHSS
q15m × 2hours
q30m × 6hours
q1hr x 16hours
What does the nurse need to observe when the patient is on TPA?
sudden headache
oozing from orifice
pain anywhere in the body (retroperitoneal)
sudden unconsciousness