Genetic lab techniques
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
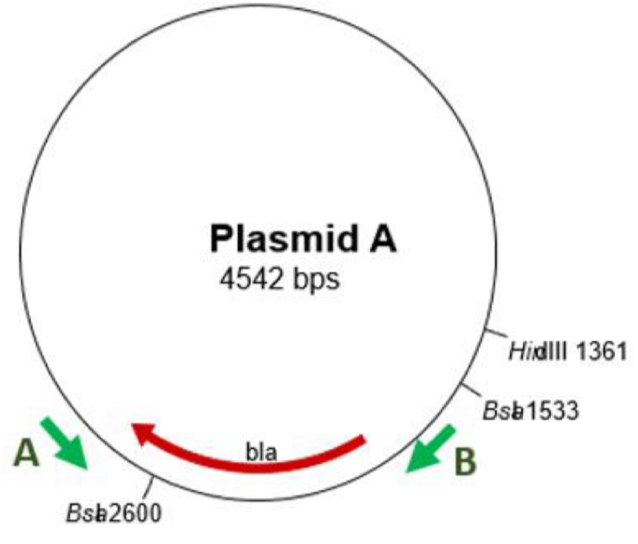
Cutting DNA
→ restriction digestion
DNA can be cut by restriction endonucleases that recognise specific sequences
Usually extracted from bacteria
Restriction maps say where different enzymes will cut
E.g. Bsa2600 = 2600 bp
Nucleic acid hybridisation Basics
→ two single stranded nucleic acids (DNA or RNA) are allowed to interact so that hybrids form
the DNA added is called a probe, and will only anneal to the corresponding sequence
Probes can be tagged with:
radioactivity
Fluorescence
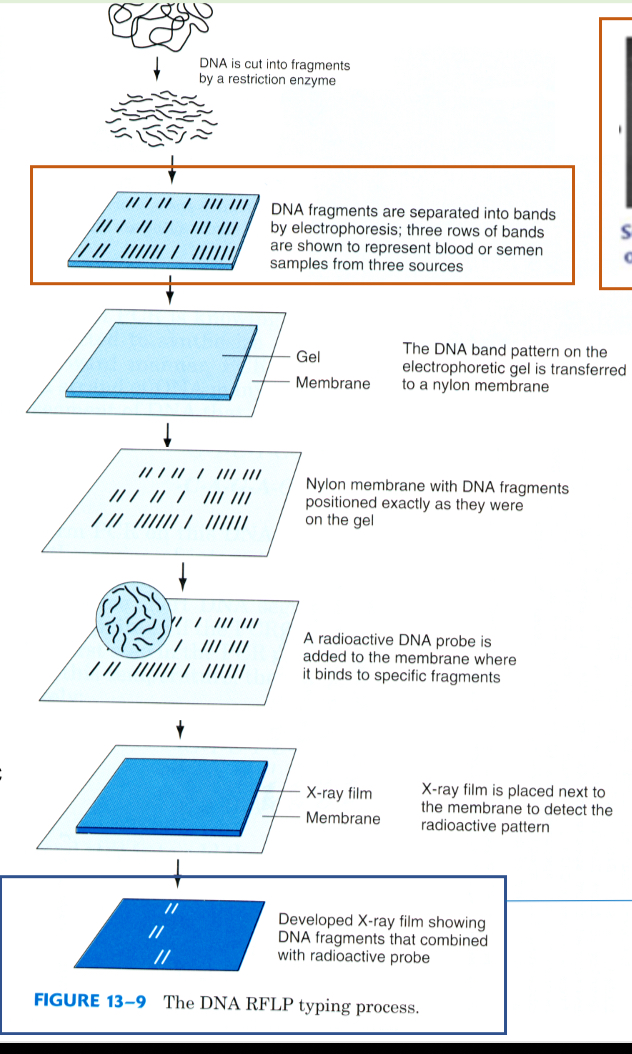
Nucleic acid hybridisation method
Extract DNA, cut using restriction enzymes
Separate by size using electrophoresis
Transfer DNA to a nylon membrane
Radioactive DNA probe added to membrane (binds to specific fragments)
Membrane onto photographic paper
Radioactivity transferred
*fluorescence is used more now
Detection of chromosome translocation FISH
→ fluorescent in-situ hybridisation
detecting prescience/absence of specific DNA sequences
Utilities short fluorescents labelled DNA probes
Used in genetic counselling, cancer etc
To identify chromosome translocations = where a segment from one chromosome is transferred to another
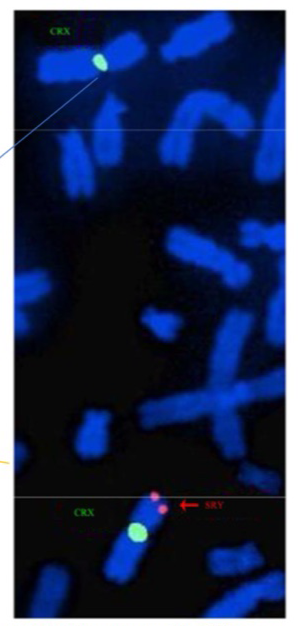
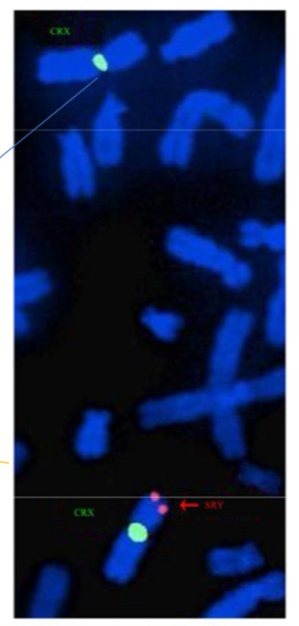
FISH example SRY
SRY = gene on Y chromosome that determines sex
green = probe for part of X
Orange = probe for SRY gene
Shows two X chromosomes in a male, with the SRY translocated onto it = present as male
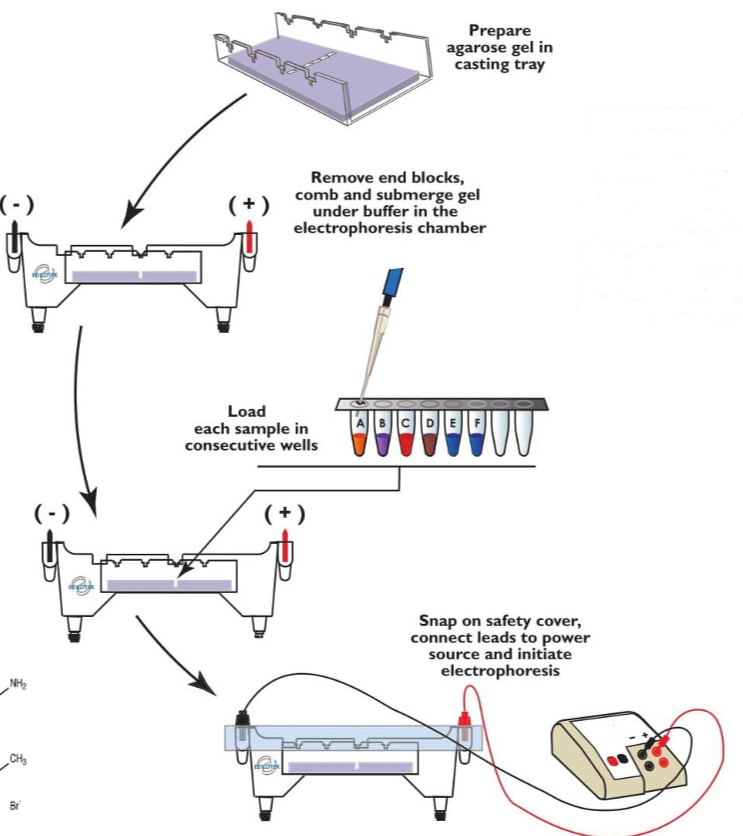
Gel electrophoresis
DNA fragments are separated into different lengths
DNA is negative so moves towards the positive electrode in a gel
Smaller fragments move faster through the gel
DNA binding dye added and detected using UV
Bands are seen and can identify no. Of base pairs in each band by how far they travel
Agarose = low resolution - large fragments
Polyacrylamide = high resolution - short fragments
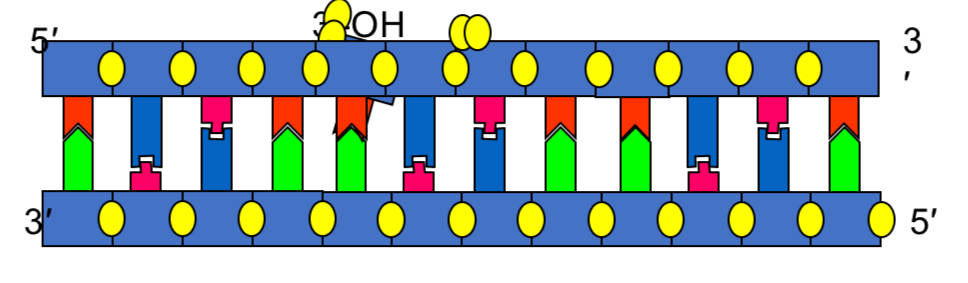
DNA synthesis in vivo ingredients
In vivo = organism
DNA polymerase
DNTPs
Template DNA
Primer
DNA synthesis in vitro ingredients
In vitro = test tube
DNA polymerase
DNTPs
Template DNA
Synthetic primer (oligonucleotides)
Buffer (Mg2+)
PCR basics and ingredients
→ used to amplify large quantities of a specific sequence of DNA from a small sample
each cycle doubles the amount - 30 cycles = 20 (index 30)
PCR products include the primers
template DNA
Primers (2)
DNTPs
Buffer Mg2+
Taq polymerase
PCR method
Desaturation = double DNA strand melts open 95*C
Annealing = (2) primers bind to DNA and polymerase attaches and starts copying about 50*C
Extension = DNA polymerase extends from annealed primer at 72*C
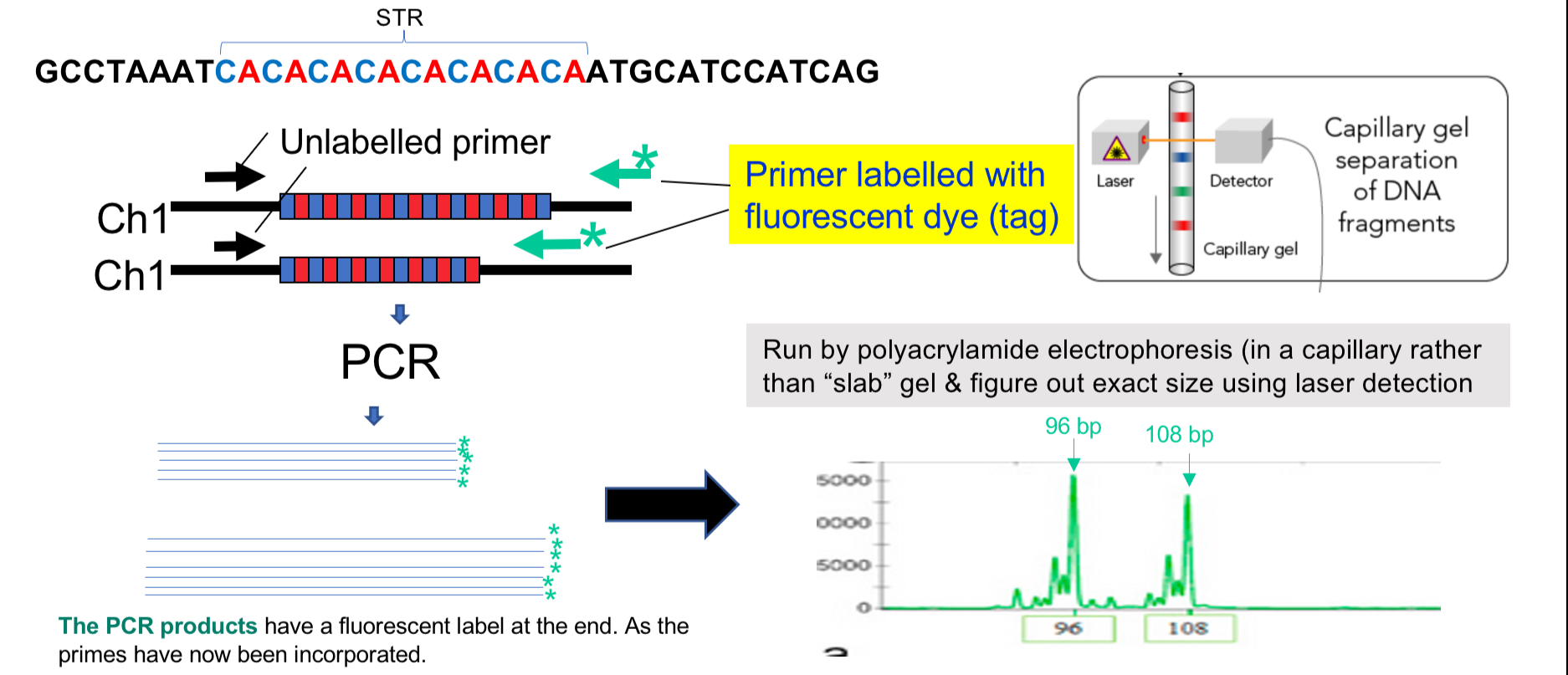
Amplification of STRs
STR = simple tandem repeats
Amplify STRs from small bits of DNA in crime scenes
2-6 base pairs of DNA
Higher mutation rate than most sequences
Uses PCR to amplify, but one primer is fluorescently labelled
Electrophoresis then takes place in a thin capillary with polyacrylamide
Lasers detect exact size
Transgenics
→ movement of DNA between species
genetic code is universal so expression is possible
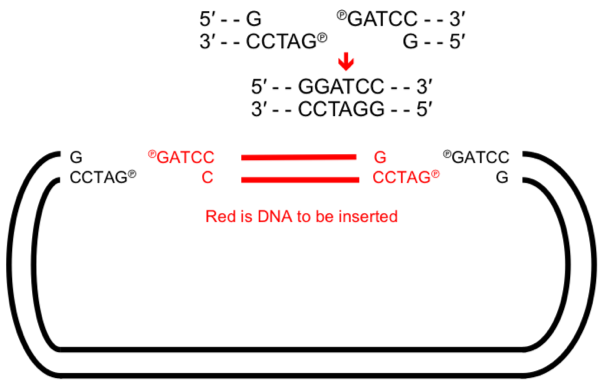
GM - molecular cloning
→ set of lab techniques that allow us to insert a fragment of foreign DNA into a vector to create RECOMBINANT DNA that is capable of replicating
Types of vectors:
plasmid - cloning of small fragments
Yeast artificial chromosome - large fragments
Strands joined together by DNA ligaments to form phosphodiester bonds
Amplifying recombinant DNA
Bacterial host- most common E.coli
Eukaryotic host = yeast
cleave DNA and create recombinant
Introduce into bacterial cell
Cell culture produces millions of bacteria
Many copies of purified plasmid isolated
Artificial plasmid purification
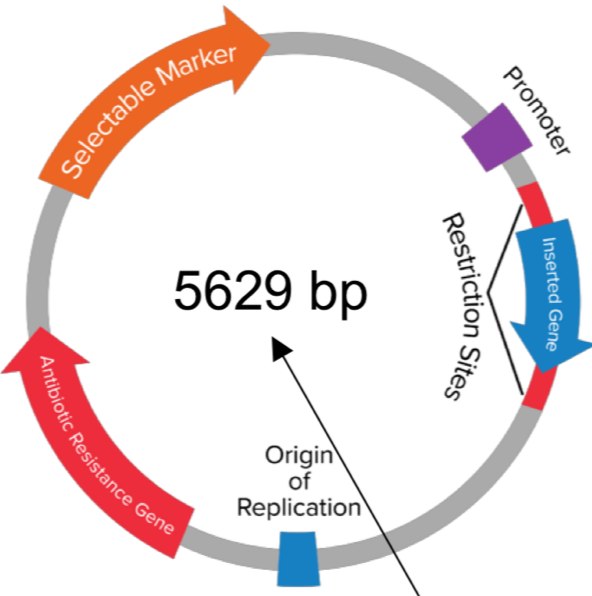
obtain an ‘origin of replicaion’ and a ‘cloning site’
Contain a ‘selectable marker’ (usually an antibiotic resistance gene)
Bacterial cells then exposed to an antibiotic = only those with plasmid survive
= purified
Artificial plasmid areas
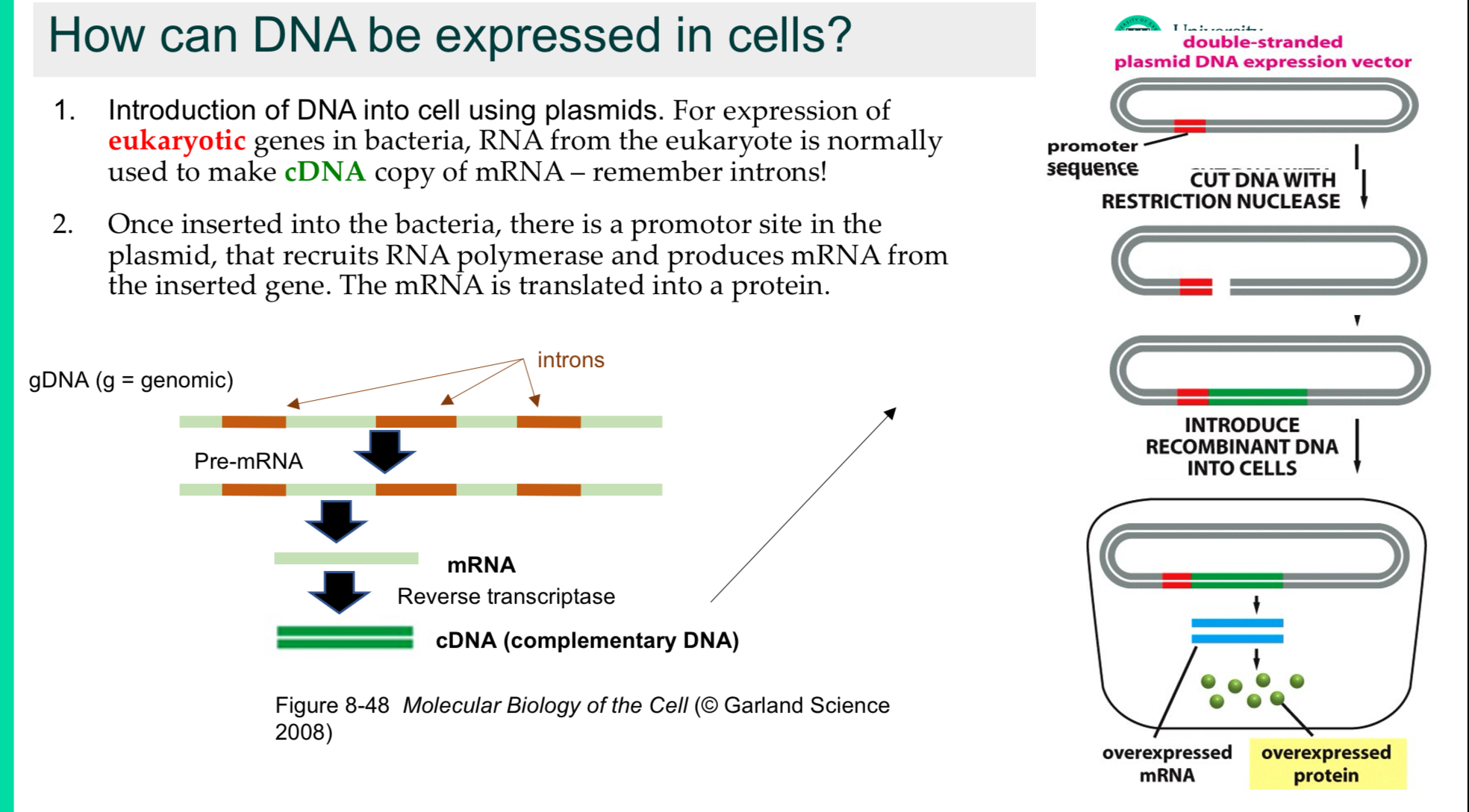
How can DNA be expressed in cells
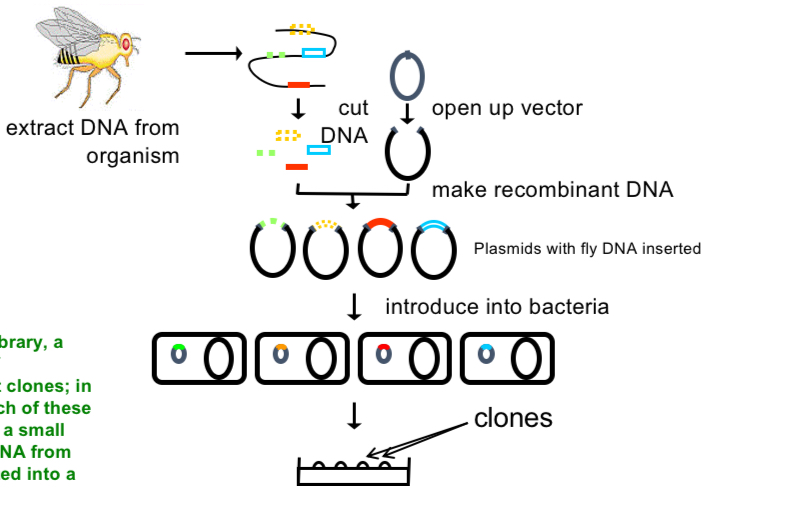
Gene library
→ collection of recombinant clones
E.g. each bacteria has a small part of DNA from the fly inserted into a plasmid
can then screen for clones containing genes of interest by DNA/RNA hybridisation or DNA sequencing
Sickle cell mutation though functional cloning
isolated mRNA from blood of SC patient
Used reverse transcriptase to make cDNA from mRNA
Insert cdNA into plasmids then transform bacteria to make a cDNA library
Used an antibody for haemoglobin to identify bacterial colonies containing the gene for haemoglobin (inserted into a plasmid)
Found that sickle cell haemoglobin is the result of a single base pair mutation