exam
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
If Earth did not rotate, wind would cause the air to flow
perpendicular to the isobars
Which of the following describes the pressure gradient force?
it causes air to move from areas of higher to lower pressure
The Coriolis force is maximum at the poles, and zero at the equator.
True
The Northern Hemisphere’s midlatitude westerlies are midlatitude easterlies in the Southern Hemisphere, because of the opposite direction of the Coriolis force.
False
If there is no friction, the combined effect of the Coriolis force and the pressure gradient force produces
geostrophic winds parallel to the isobars in the upper troposphere
Assume the large black arrow in the diagram represents a Northern Hemisphere wind flowing parallel to the isobars, as a result of the two balanced forces x and y.
At which location in the above diagram would the lowest pressure be located?
C
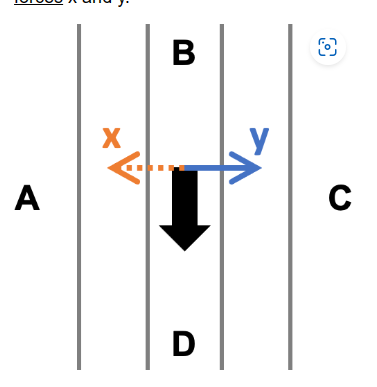
Assume the large black arrow in the diagram represents a Northern Hemisphere wind flowing parallel to the isobars, as a result of the two balanced forces x and y.
The dashed (orange) arrow x in the above diagram represents the pressure gradient force.
False
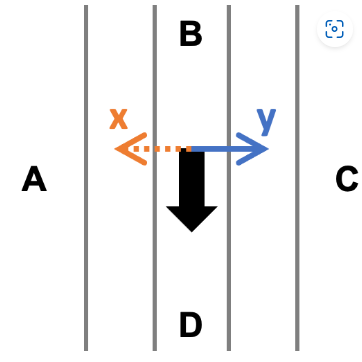
Friction slows the wind, creating an imbalance between the pressure gradient force and the Coriolis force, ultimately causing the wind to cross the isobars, toward the higher pressure.
False
Which of the following matches is incorrect relative to air circulation in the Northern Hemisphere?
cyclone = clockwise
Between approximately 20° to 35° north latitude and 20° to 35° south latitude are
high pressure zones (and therefore many of the world’s desert regions)
During the processes of melting and evaporation, water releases energy, while during condensation and freezing, water absorbs energy.
False
Specific humidity
Mass of water vapor per total mass of air
Relative humidity
Amount of water vapor in the air compared to the maximum amount of water vapor possible at a given temperature.
Absolute humidity
Mass water vapor per volume of air
Dewpoint
Temperature at which the air contains the maximum amount of water vapor possible.
Which of the moisture variables indicates how much water vapor is actually in the air, regardless of temperature, pressure, or volume?
Specific humidity
True
The moist adiabatic lapse rate is less than the dry adiabatic lapse rate because the heat released from condensation offsets some of the expansional cooling.
This scenario applies to the next 4 questions (questions 5–8): assume a saturated parcel of air with a temperature of 22°C is lifted adiabatically from the surface and remains saturated during its entire ascent. The environmental lapse rate (ELR) decreases 4°C/1000 m.
True or false? The dotted blue line B represents the dry adiabatic rate (DAR), and the solid green line C represents the moist adiabatic rate (MAR).
False
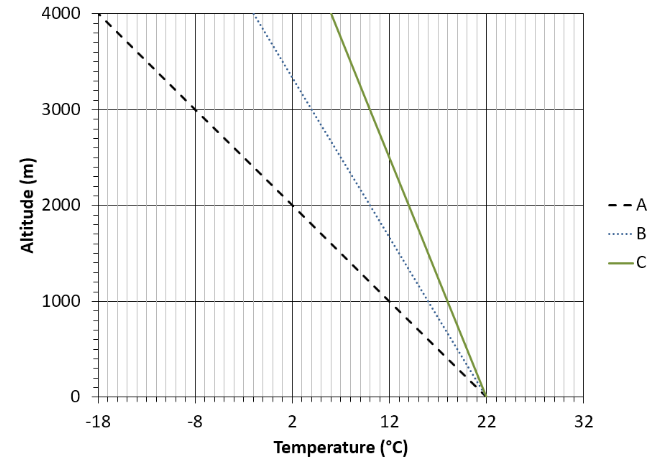
16 C
Same scenario again: a saturated parcel of air with a temperature of 22°C is lifted adiabatically from the surface and remains saturated during its entire ascent. The environmental lapse rate (ELR) decreases 4°C/1000 m.
What is the parcel's temperature at 1000 m?
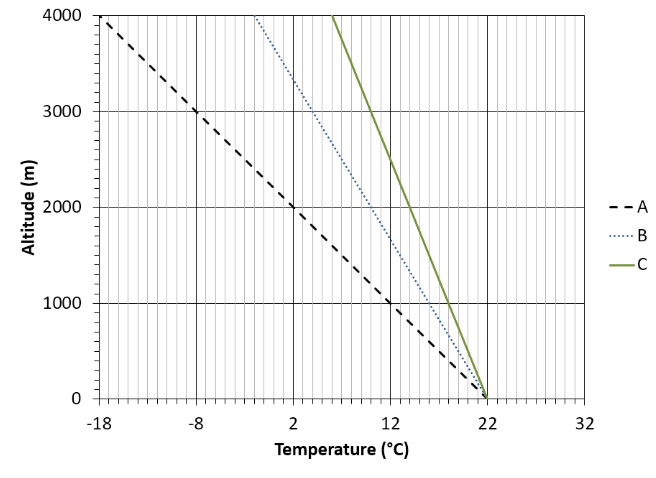
Still the same scenario: a saturated parcel of air with a temperature of 22°C is lifted adiabatically from the surface and remains saturated during its entire ascent. The environmental lapse rate (ELR) decreases 4°C/1000 m.
What is the environment's temperature at 1000 m?
18°C
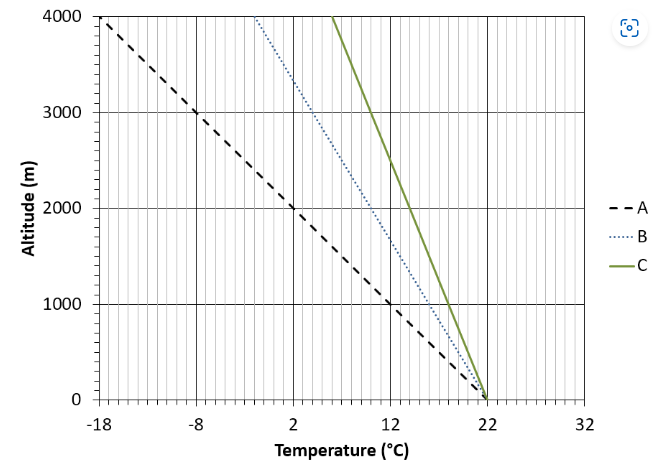
Same scenario one more time: a saturated parcel of air with a temperature of 22°C is lifted adiabatically from the surface and remains saturated during its entire ascent. The environmental lapse rate (ELR) decreases 4°C/1000 m.
Based on your answers to the previous two questions, which of the following best describes the stability of the atmosphere in this scenario?
Stable
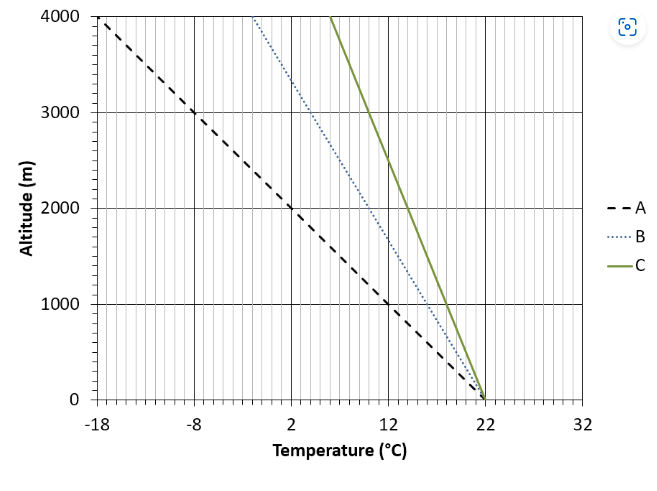
Specific humidity reaches 100%
All of the following apply to the altitude level at which clouds begin to form, except which one?
Which of the below cloud types best describes the cloud(s) shown in the above picture?
Altostratus
