Prolactin + multiple endocrine neoplasia
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What is the prolactin axis?
dopamine inhibits prolactin secretion and thyrotropin releasing hormone stimulates prolactin release
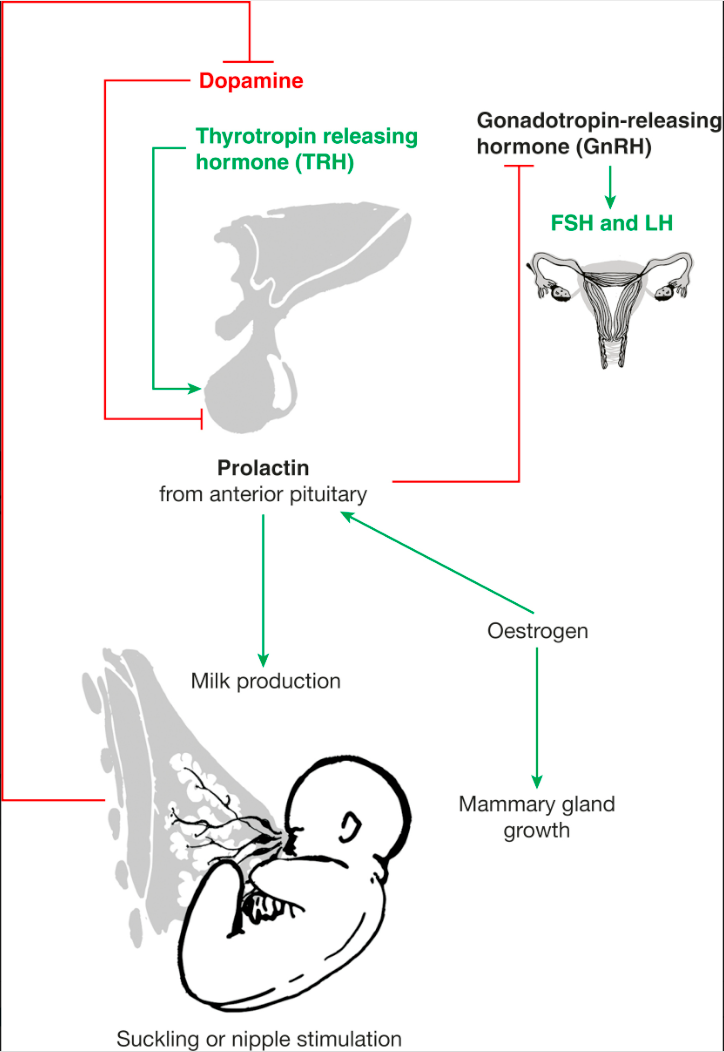
What stimulates prolactin?
nipple stimulation
thyrotropin-releasing hormone
elevated oestrogen during pregnancy
stress
sleep
What inhibits prolactin?
dopamine inhibits secretion of prolactin
progesterone inhibits effect of prolactin on breast tissue, hence why milk isn’t produced during pregnancy, but when progesterone levels fall after birth, prolactin can carry out it’s effects
What is the relevance of antipsychotics and prolactin?
Dopamine antagonists (e.g., antipsychotic medications) inhibit dopamine receptors, which can allow prolactin levels to rise, causing gynaecomastia (glandular breast tissue enlargement in males) and galactorrhea (breast milk production).
What are the actions of prolactin?
stimulates milk production
glandular breast tissue development
inhibits GnRH from hypothalamus→ inhibiting FSH/LH→ causing amenorrhoea
What are the actions of oxytocin?
oxytocin levels rise during pregnancy
oxytocin inhibits dopamine promoting prolactin production
stimulates uterine contraction
What is a prolactinoma?
benign pituitary adenoma secreting prolactin
How does hyperprolactinaemia present?
males- gynaecomastia, impotence loss of libido, galactorrhoea
females- amenorrhoea, galactorrhoea, infertility
How does hypothyroidism cause hyperprolactinaemia?
In hypothyroidism, low thyroid hormones mean reduced negative feedback on the hypothalamus, resulting in elevated thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH). This elevated TRH stimulates excessive prolactin release by the pituitary.
What can cause hyperprolactinaemia?
pregnancy
prolactinomas
hypothyroidism
dopamine antagonists
How is prolactinoma investigated?
bloods: high prolactin >5000mU/L
MRI pituitary
How is prolactinoma managed?
dopamine agonists, eg: cabergoline or bromocriptine
transsphenoidal surgery
What is a microprolactinoma?
<10mm on MRI
What is a macroprolactinoma?
<10mm MRI
What can cause hypoprolactinaemia?
Sheehan’s syndrome is a rare complication of postpartum haemorrhage, where the drop in circulating blood volume leads to avascular necrosis of the pituitary gland. Low blood pressure and reduced perfusion of the pituitary gland lead to ischaemia in the pituitary cells and cell death. It only affects the anterior pituitary gland. Hormones produced by the posterior pituitary (oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone) are spared
What is a multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome?
autosomal-dominant disorder causing endocrine glands to grow benign, malignant or noncancerous growths
What is MEN 1?
three P’s
parathyroid- hyperparathyroidism and raised calcium
pituitary
pancreas- insulinoma, gastrinoma )leading to peptic ulceration)
commonly presents with hypercalcaemia
What gene is affected in MEN 1?
MEN 1 on chromosome 11
What tissues are affected in MEN 2a?
parathyroid (however less than 20% get raised calcium)
pheochromocytoma
medullary thyroid cancer
What gene is affected in MEN 2a/b?
RET proto-oncogene on chromosome 10
What tissues are affected in MEN2b?
pheochromocytoma
medullary thyroid
Marfanoid habitus
neuromas
How is MEN 1 investigated?
screening of 1st/2nd degree relatives
full gut hormone screen, serum calcium, serum prolactin, genetic mutation
What is a Marfanoid habitus?
long limbs
arachnodactyly
high arched palate
hyperlaxity- increased flexibility of joints
crowded teeth
How is MEN managed?
genetic counselling and surgery to remove affected tissue