BIS 2C Seed Plants
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
22 Terms

What are the four synapomorphies of seed plants?
seeds, pollen, heterospory, and secondary growth

What trend in plant evolution is seen in seed plants regarding gametophytes?
gametophyte is reduced, retained on, and nourished by the sporophyte
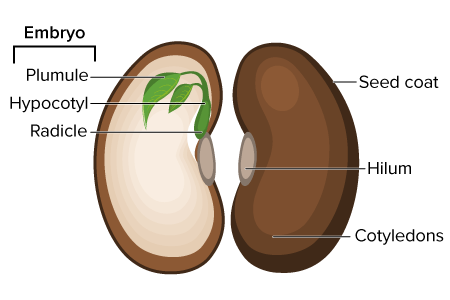
What does every seed contain?
embryo, nutritive tissue, protective seed coat
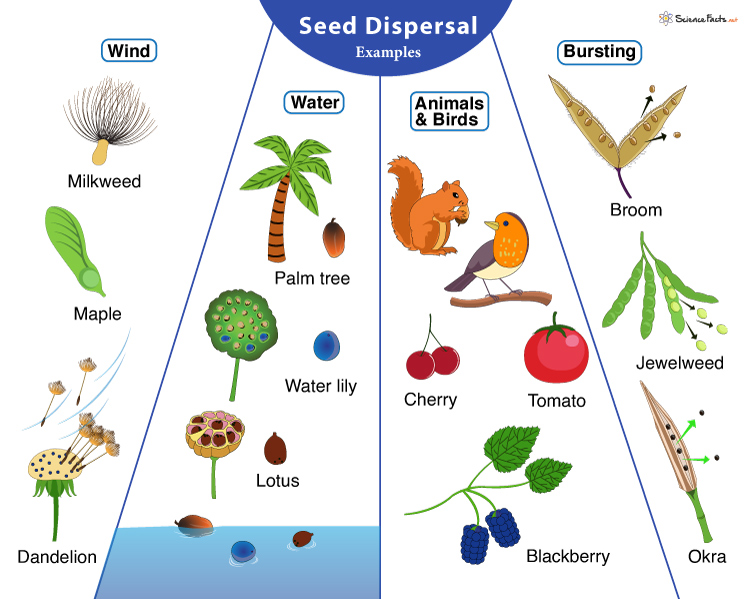
How are seeds dispersed?
wind, water, or animals

What’s the difference between seeds and fruits?
all seed plants make seeds; only angiosperms make fruits
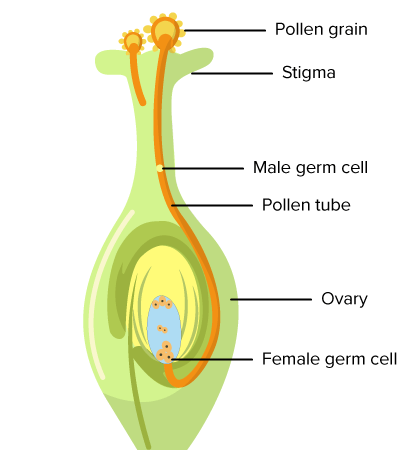
What replaced the antheridium in seed plants?
pollen; it delivers non-motile sperm via a pollen tube

What do seed plant spores develop into, and where?
gametophytes that develop inside the parent plant
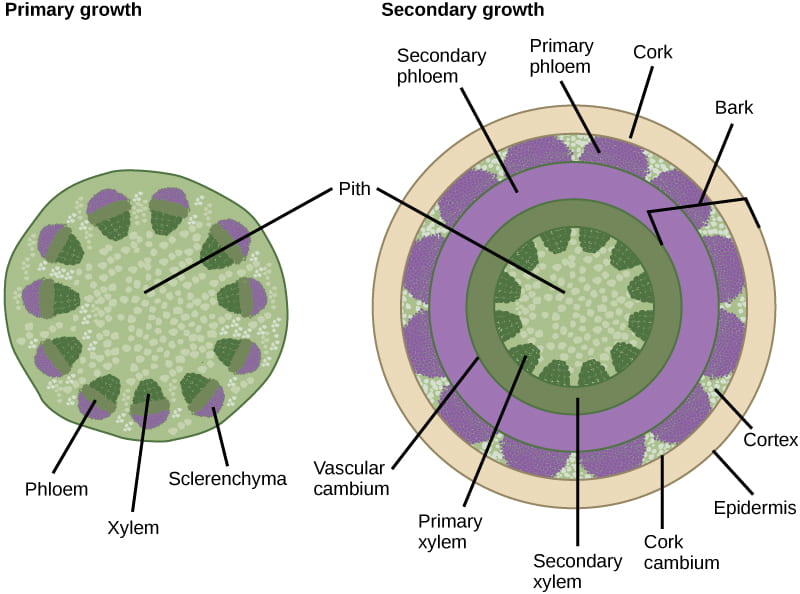
What does primary growth do?
adds length via apical meristems (SAM & RAM)
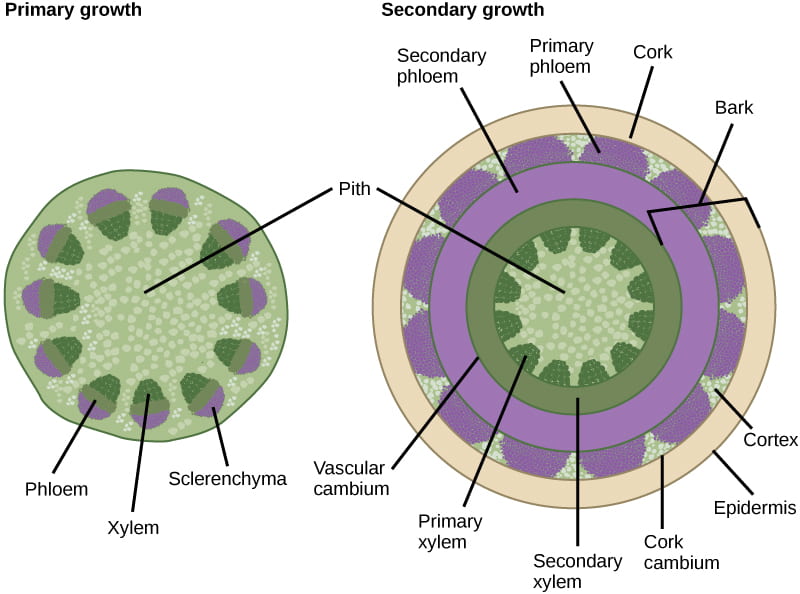
What does secondary growth do?
adds width via the bifacial vascular cambium (BVC)
What is the hormone auxin’s main role?
stimulates cell expansion and suppresses side growth (apical dominance)
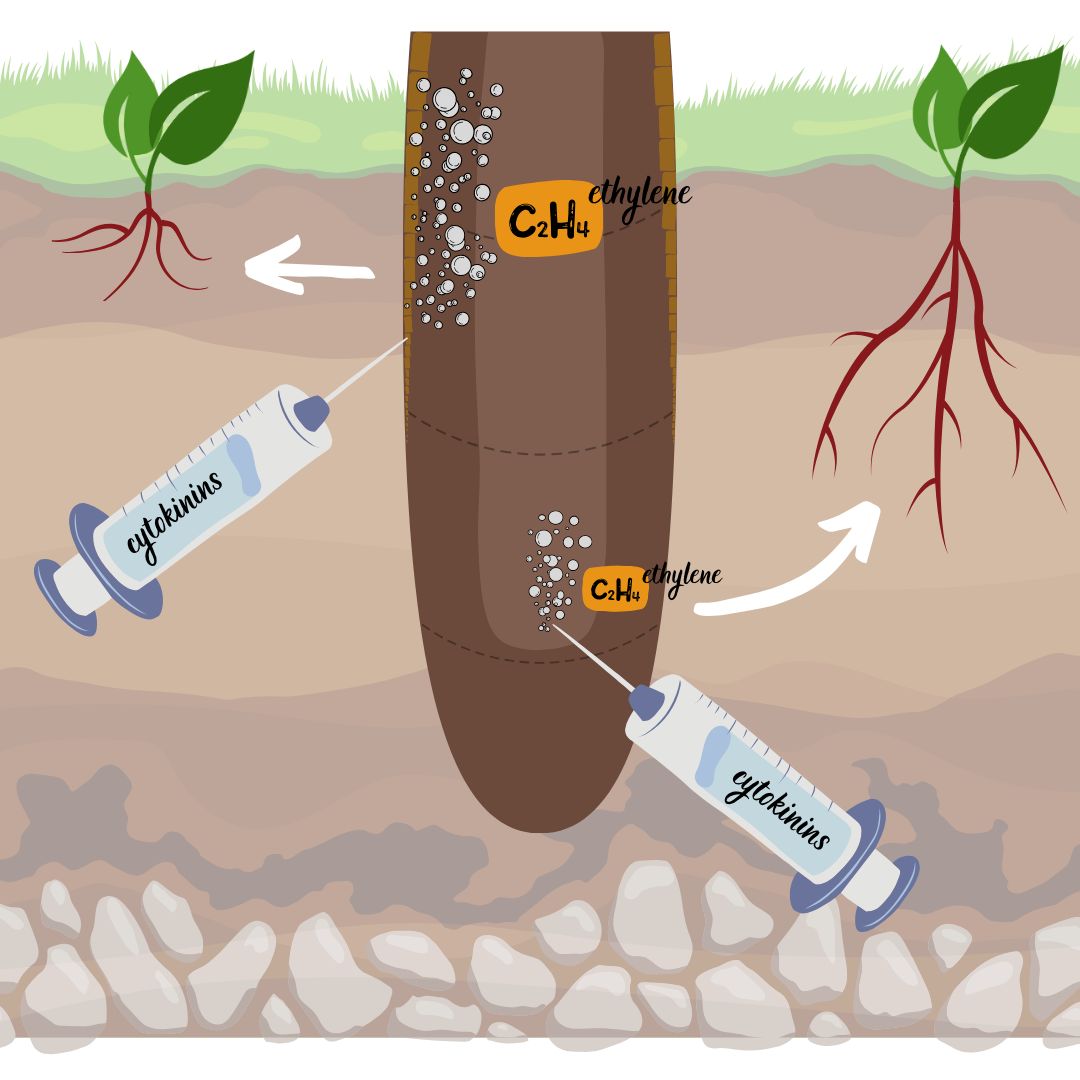
What is cytokinin’s role?
promotes axillary bud growth (branching)

How do auxin and cytokinin interact?
their balance regulates shoot and root growth
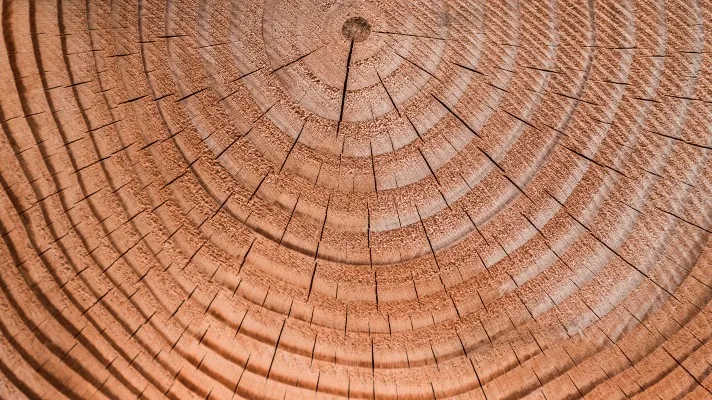

What forms wood?
secondary xylem (growth) produced by the vascular cambium
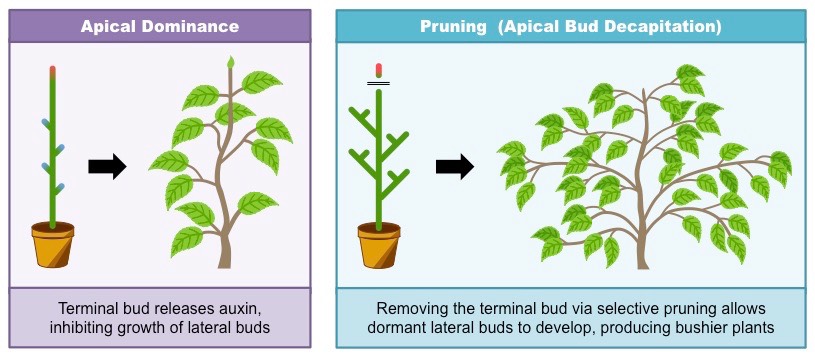
What is apical dominance?
auxin from the shoot tip suppresses side bud growth
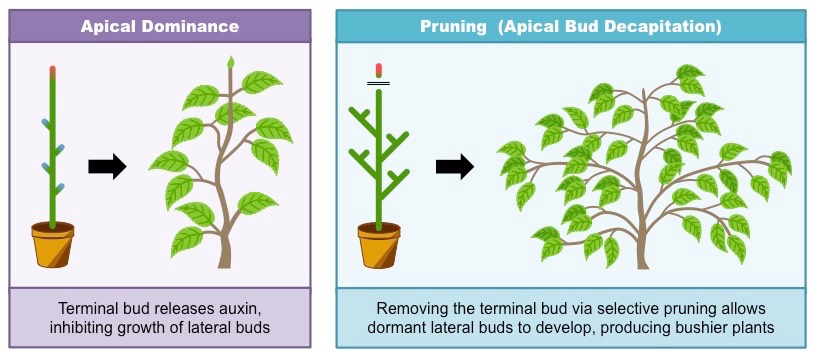
What happens when a plant is pruned?
the auxin source is removed = side buds grow = bushier plant
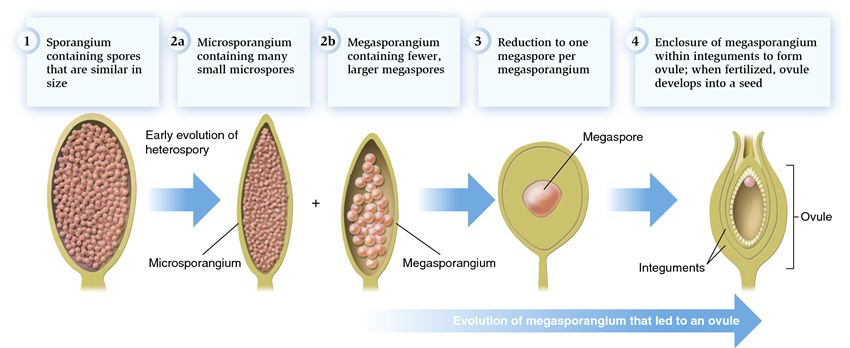
What are the major advantages of seeds?
protection, dormancy, and nutrient supply for the embryo
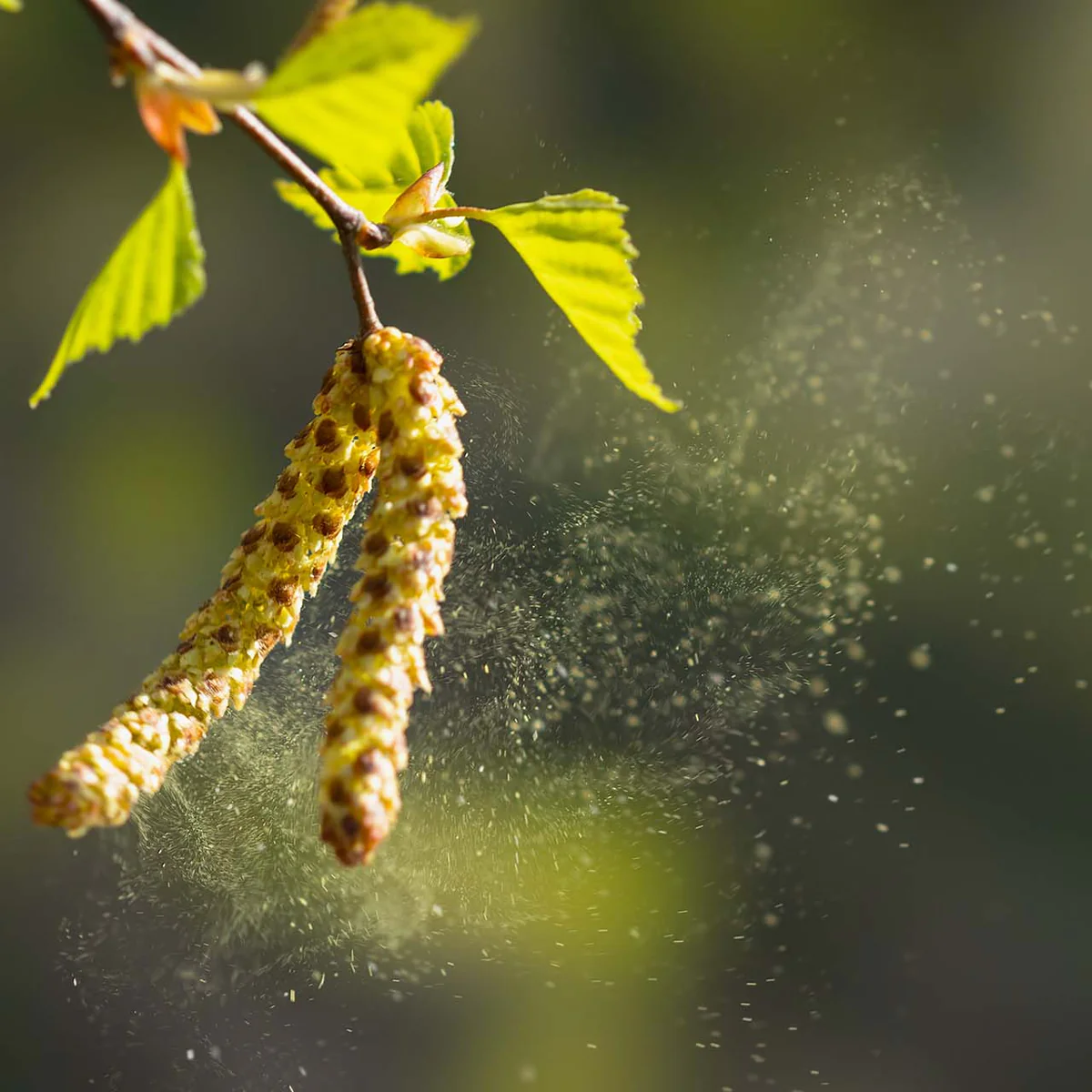

What is the major advantage of pollen?
fertilization without water; enables life on land
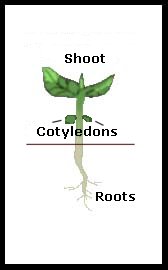
What do cotyledons do?
absorb or store nutrients for the developing embryo
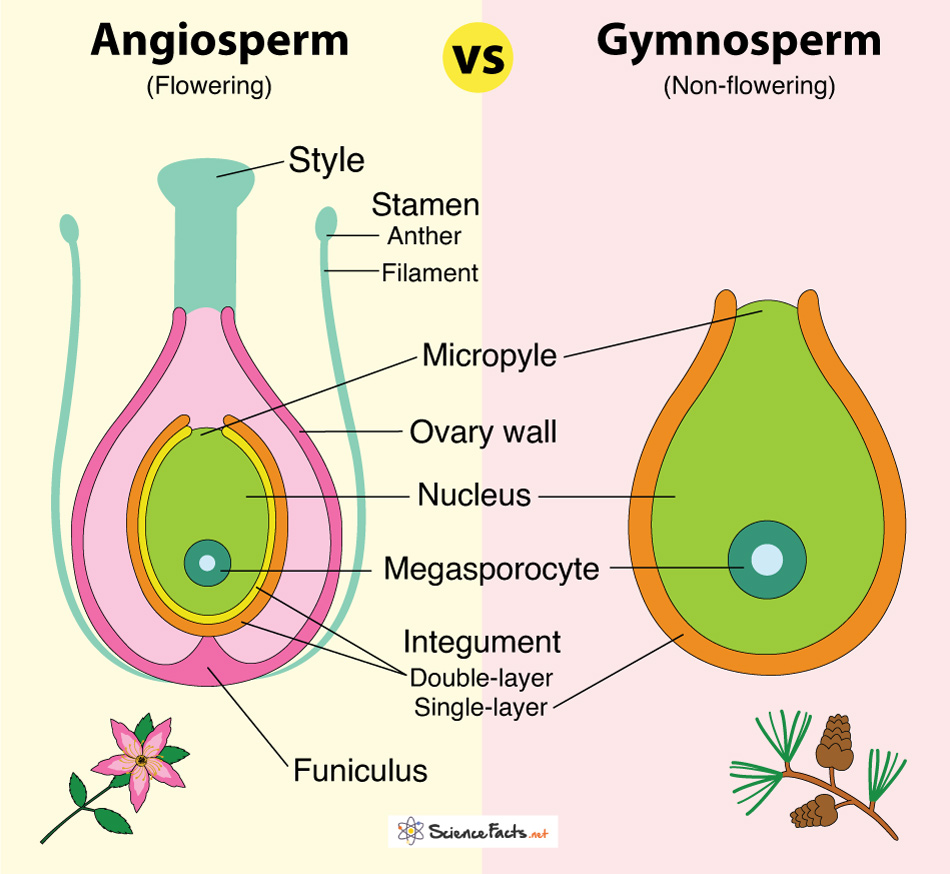
What distinguishes gymnosperms from angiosperms?
gymnosperms have naked seeds; angiosperms have seeds enclosed in fruit

What evolutionary trend occurs from mosses → ferns → seed plants?
gametophyte size decreases, protection increases, dependence on water decreases.
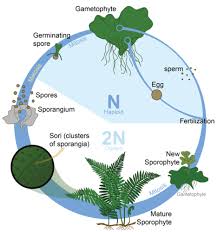
Where do seeds fit in the plant life cycle?
they are the fertilized ovule containing the next sporophyte generation
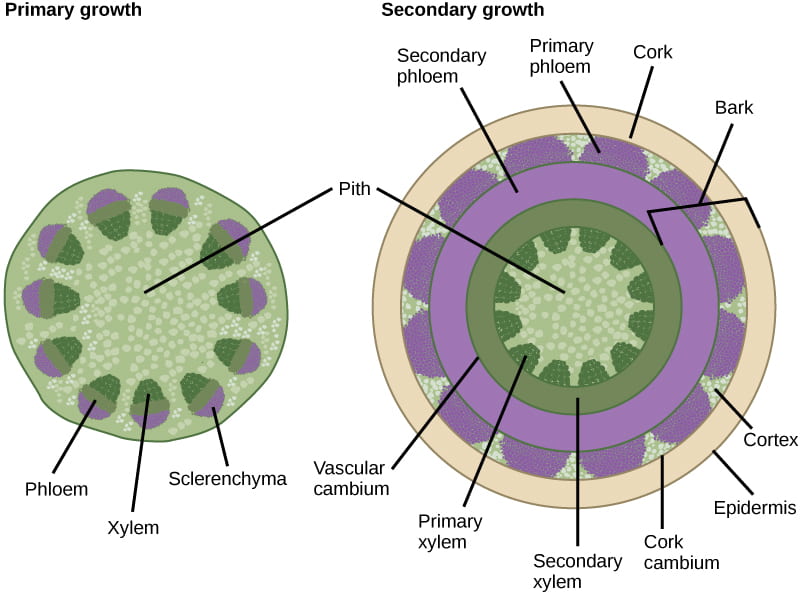
What do “primary vs. secondary” growth directions mean?
primary = up/down; Secondary = out/in