BIO: 1.2 part 1
1/104
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
105 Terms
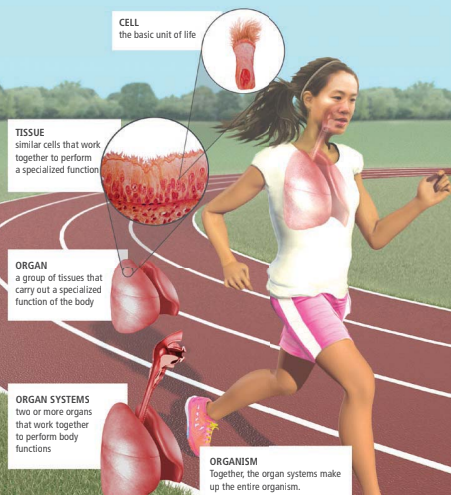
Cells
The basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms.
Cell Differentiation
The process by which a less specialized cell becomes a more specialized cell type, determined by gene expression.
Tissues
Groups of similar cells performing a specific function.
Epithelial Tissue
Covers body surfaces, lines cavities and organs
Connective Tissue
Supports, connects, and separates different types of tissues and organs
Muscle Tissue
Specialized for contraction to enable movement
Nervous Tissue
Found in the brain, spinal cord, and nerves
Organs
A collection of tissues joined in a structural unit to serve a common function.
Organ Systems
A group of organs that work together to perform one or more functions
Organism
An individual living thing, either unicellular or multicellular.
Circulatory System
Transports oxygen, nutrients, hormones, and waste
Heart
Pumps blood throughout the body.
Blood Vessels
Arteries, veins, and capillaries that transport blood.
Blood
Transports substances such as oxygen, nutrients, and waste products.
Lymph Nodes
Filter lymph and assist in immune function.
Digestive System
Breaks down food into smaller molecules, absorbs nutrients, eliminates undigested waste.
Mouth
Performs mechanical and chemical digestion.
Esophagus
Transports food from mouth to stomach.
Stomach
Stores and mixes food.
Small Intestine
Absorbs nutrients into the bloodstream.
Large Intestine
Absorbs water from undigested food.
Liver
Produces bile for fat digestion.
Pancreas
Produces enzymes for digestion.
Endocrine System
Produces hormones regulating growth, development, metabolism, reproduction, and mood.
Hypothalamus
Controls the pituitary gland.
Pituitary Gland
Known as the master gland
Thyroid Gland
Regulates metabolism.
Adrenal Glands
Control stress response.
Pancreas
Regulates blood sugar levels.
Ovaries/Testes
Produce sex hormones and gametes.
Excretory System
Filters waste from blood, regulates water and electrolyte balance, eliminates waste via urine and sweat.
Kidneys
Filter blood and produce urine.
Ureters
Transport urine from kidneys to bladder.
Bladder
Stores urine.
Urethra
Eliminates urine.
Skin
Removes waste through sweat.
Immune System
Protects the body against pathogens, foreign substances, and abnormal cells.
White Blood Cells
Fight infections.
Thymus
Matures T cells.
Spleen
Filters blood and stores white blood cells.
Lymph Nodes
Filter lymph fluid.
Integumentary System
Protects the body from injury, infection, and dehydration
Skin
Provides protection and sensation.
Hair
Provides insulation and protection.
Nails
Protect tips of fingers and toes.
Muscular System
Enables movement, maintains posture, generates heat.
Skeletal Muscles
Voluntary movement.
Smooth Muscles
Involuntary movement.
Cardiac Muscle
Heart contractions.
Nervous System
Receives and processes sensory information, controls actions, coordinates body functions.
Brain
Control center of the body.
Spinal Cord
Transmits signals between brain and body.
Nerves
Carry signals to and from the brain and spinal cord.
Reproductive System
Produces gametes, enables fertilization, and produces sex hormones.
Testes
Produce sperm.
Ovaries
Produce eggs.
Associated Ducts and Glands
Assist in gamete transport and secretion.
Respiratory System
Exchanges oxygen and carbon dioxide between the body and environment.
Nose
Filters air.
Trachea
Windpipe
Lungs
Perform gas exchange.
Skeletal System
Provides support, protection, enables movement, stores minerals, produces blood cells.
Bones
Provide support and protection.
Cartilage
Cushions joints.
Ligaments
Connect bones to bones.
Tendons
Connect muscles to bones.
Cell Membrane
A selectively permeable barrier separating the cell interior from the external environment
Cytoplasm
Gel-like substance containing organelles and cellular components.
Nucleus
Control center containing DNA.
Nuclear Envelope
Double membrane around the nucleus regulating molecule movement.
Ribosomes
Synthesize proteins from amino acids using mRNA instructions.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Network of membranes
Golgi Apparatus
Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for transport or secretion.
Mitochondria
Generate ATP through cellular respiration.
Lysosomes
Contain enzymes that break down cellular waste.
Cell Wall (Plants)
Rigid outer layer providing support and protection
Chloroplasts (Plants)
Perform photosynthesis, converting light energy into chemical energy.
Vacuole (Plants)
Stores water, nutrients, and waste
Cytoskeleton
Network of protein filaments providing structure, movement, and intracellular transport.
Prokaryotic Cells
Lack nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
Eukaryotic Cells
Contain nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
Homeostasis
The ability of an organism to maintain a stable internal environment despite external changes.
Nervous & Digestive Systems
Brain signals regulate enzyme secretion and muscle contractions
Cell Membrane
Controls movement of substances in and out, maintaining a stable internal environment.
Cell Wall
Provides structural support and protection for plant cells