Bio Princ Exam 1
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Identify the atomic mass, # neutrons, # protons, # electrons
32.065, 16, 16, 16

What is the max number of electrons for each electron shell
2,8,8
Covalent bonds
electrons are shared
Ionic Bonds
give up or gain electrons
Hydrogen bond
interaction between the partial(+) charge of H and parrtial (-) charge of a more electrognegative atom (water)
Polar bonds
electrons are unequally shared by atoms (water)
Non-polar bonds
covalent bonds with equal sharing of electrons (methane)
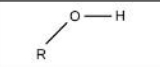
Hydroxyl
Identify the functional group
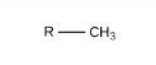
Methyl
Identify the functional group
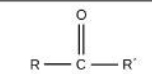
Carbonyl
Identify the functional group
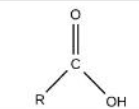
Carboxyl
Identify the functional group
Amino
What is this functional group
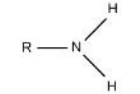
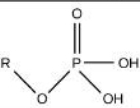
Phostphate
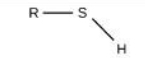
Identify the functional group
Sulfurhydryl
Identify the functional group
cohesion
H20 molecules stick together
adhesion
attractive force between H20 molecules and other charged molecules/surfaces
capillary action
water molecule move up tube because they're attracted to charged glass molecules
pH measures the concentration of what in a solution
Hydrogen ions
Acidic
high H+ ions in the solution (lowering pH)
Basic
lower H+ concentration in solution (raising pH/higher OH- concentration)
buffers
sustances that resist changes in pH by neutralizing acid/base
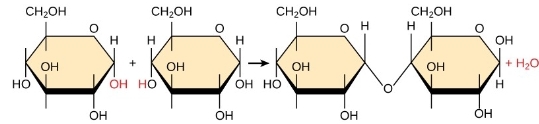
dehydration reaction
2 glucose molec are linked by covalent- glycosidic bond; H20 byproduct
hydrolysis
breaking polymers to monomers; H20 is a reactant
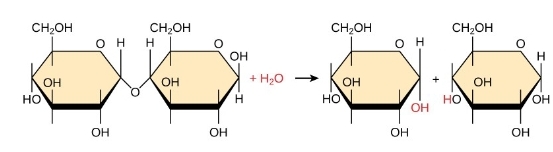
What are the monomers of carbs?
monosaccharides
What are the elements in carbs
CHO
What bond links monosaccharides
glycosidic bonds
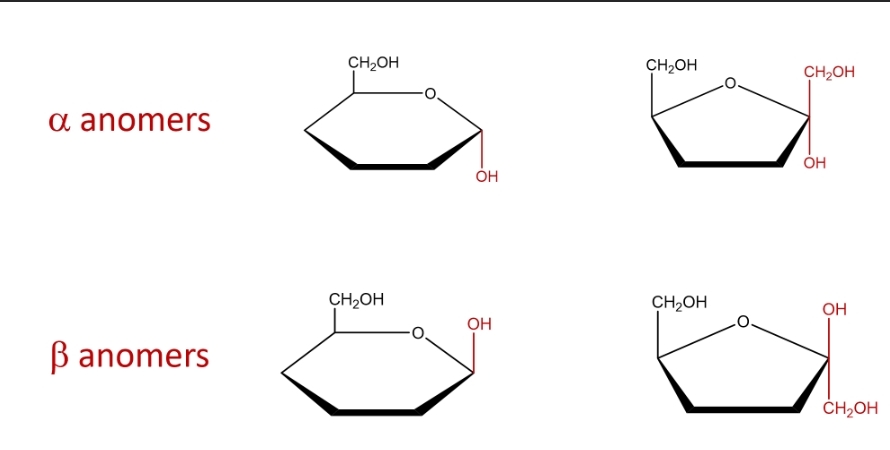
alpha vs. beta rings
alpha- hydroxyl group points down/ weaker
beta- hydroxyl group points up/ stronger
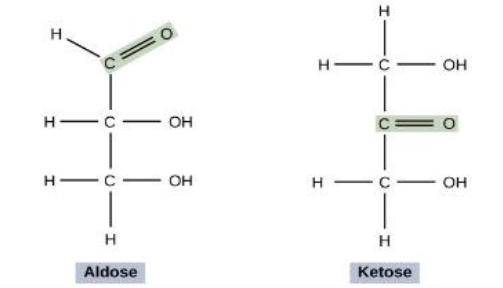
aldose vs. ketose
aldose is external/on the end
ketose is internal
alpha glycosidic bonds
forms coils, stores energy in C-C and C-H bonds, starch in plants, glycogen in animals
beta gycosidic bonds
form strong sheets, structure & support, cellulose in cell walls, chitin in animals & fungi
What elements are in nucleic acids?
CHONP
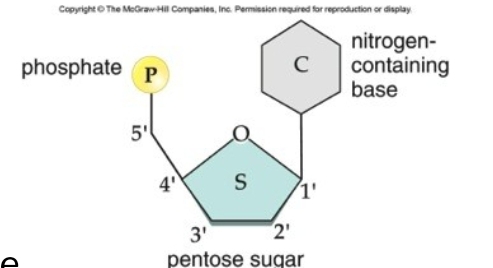
What are the monomers of nucleic acids and what are these monomers made of?
Nucleotides; nitrogenous base, pentose sugar (deoxyribose or ribose), phosphate group
DNA
stores genetic info, encodes info for protein assembly
RNA
reads DNA-encoded info to direct protein assembly
Pyrimidines vs. Purines
single ring; cytosine, thymine uracil
double ring; adenine guanine

how are nucleotides joined?
phosphodiester bonds- when phosphae group of 5’ carbon binds to hydroxyl group on 3’ carbon of other nucleotide
Which is DNA and which is RNA?
left- dna; right- rna
what elements make up proteins
CHONS
peptide bonds
bond between a carboxyl group and amino group
primary
unique sequence of aa is a polypeptide, beginning at N-terminus and ends at C-terminus
secondary
local folding of the polypeptide; a-helix and b-pleated sheets
tertiary
chain reactions between r-groups
quarternary
interactions between several polypeptide chains
molecular chaperones
proteins that facilitate protein folding upon sunthesis or after protein denatures
what chemicals make up lipids
CH
trigycerides
glycerol backbone+ 3 fatty acids
phospholipid
glycerol backbone+ 2 fatty acid chains+phosphate
hydrophilic
dissolve in water; polar and ionic compounds
hydrophobic
don’t dissolve in water; nonpolar
bicarbonate buffer system
carbonic acid partially dissociates into H+ and CO2
what is the only macromolecule that is nonpolar/hydrophobic
lipids
cell membrane
semi-permeable membrane that separates the inside of a cell and outside environment
cholesterol
embedded between phospholipids; keep memb fluid when cold and not too fluid when hot
phospholipids with _____ ____ ____ can pack more tightly; increase rigidity
saturated fatty acids
what temperature makes the memb more rigid
cold
simple diffusion
substance moves from a high to low concentration
what substances are transported through simple diffusion
gases, small lipids and small polar molecules
osmosis
diffusion of water across a memb; high water to low water
passive transport
does not require energy (high to low)
active transport
requires energy (low to high)
what substances are transported through active transport
ions and polar molecules
facilitated diffusion
move substances down their concentration gradients through integral transmembrane proteins
what substances are transported through facilitated diffusion
ions and small polar molecules
Na+ K+ pump
active transport example
bulk transport
import/export molecules that are too big to pass through pump; active
endocytosis
cells take in molecules
exocytosis
cells release molecules