Meiosis: Processes, Errors, and Genetic Diversity
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
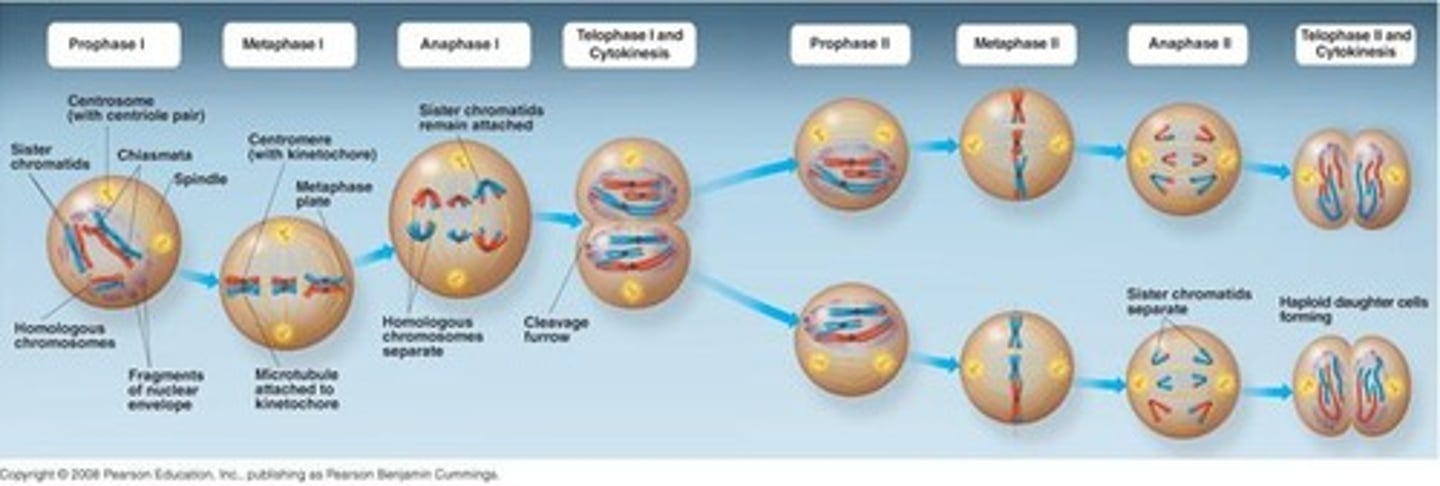
Meiosis
Cell division producing four genetically distinct daughter cells.
Gametes
Haploid cells formed during meiosis for reproduction.
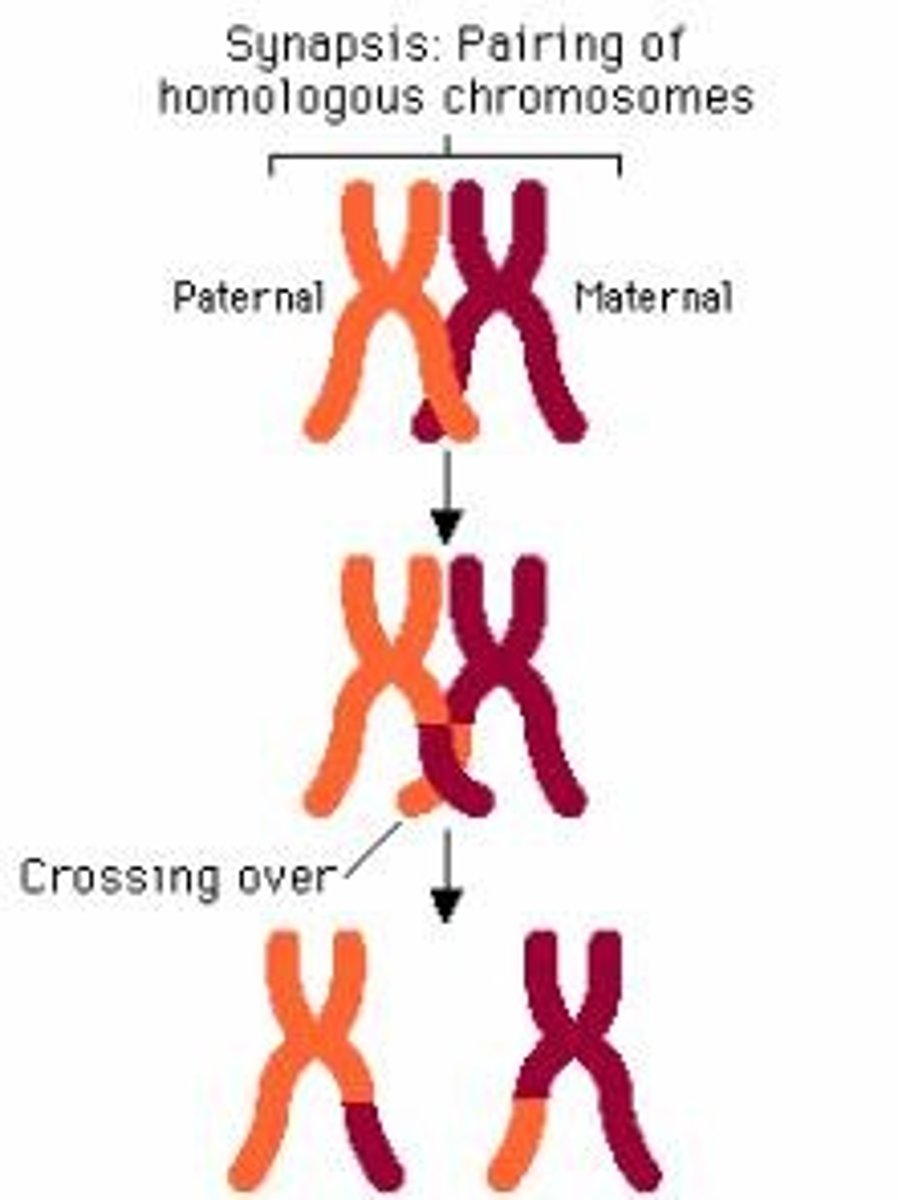
Crossing Over
Exchange of chromosomal segments between non-sister chromatids.
Independent Assortment
Random distribution of homologous chromosomes into daughter cells.
Nondisjunction
Failure of chromosomes to separate properly during cell division.
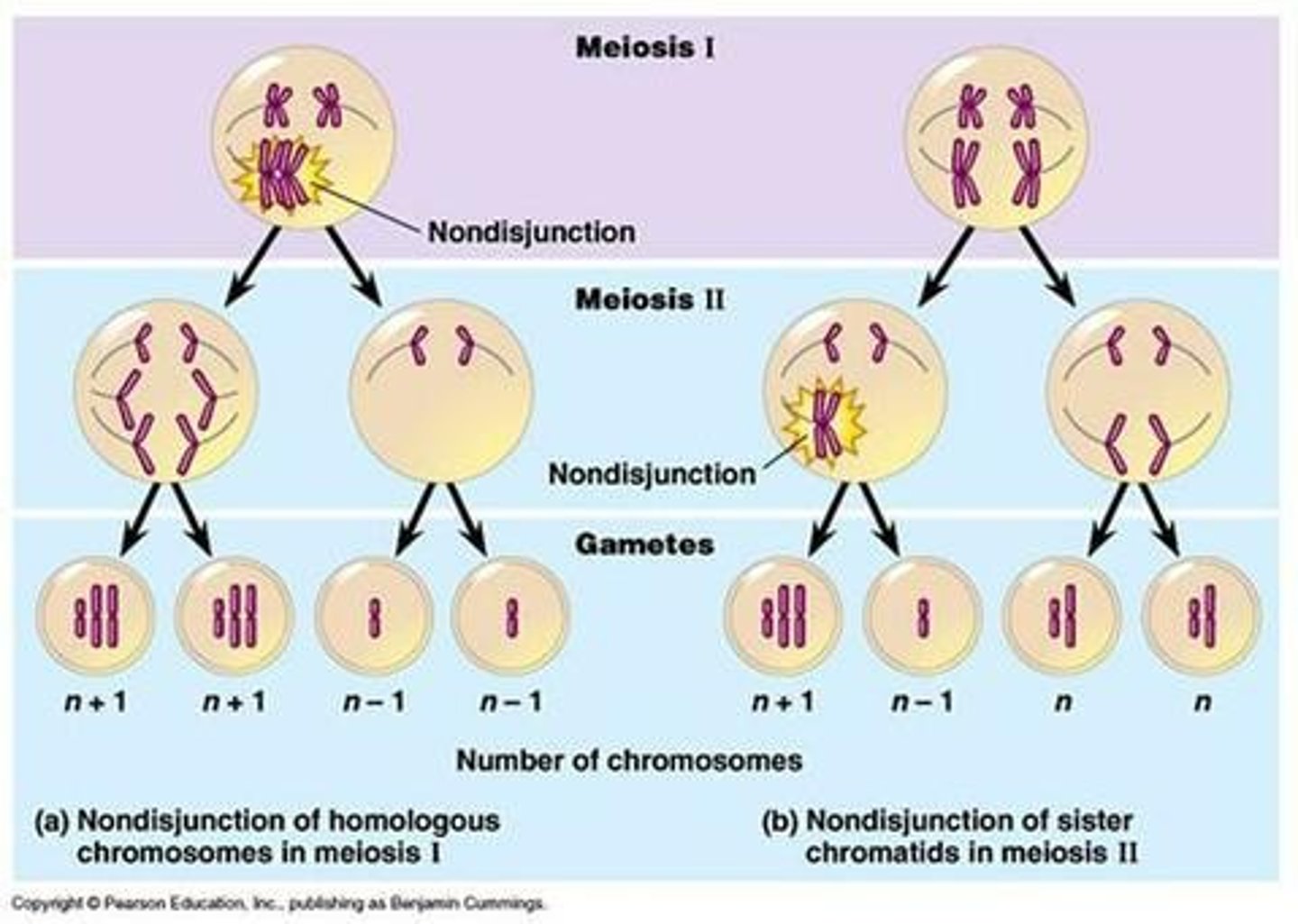
Aneuploidy
Abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell.
Monosomy
Loss of one chromosome from a pair.
Trisomy
Gain of an extra chromosome in addition to pairs.
Down Syndrome
Trisomy 21, caused by maternal nondisjunction.
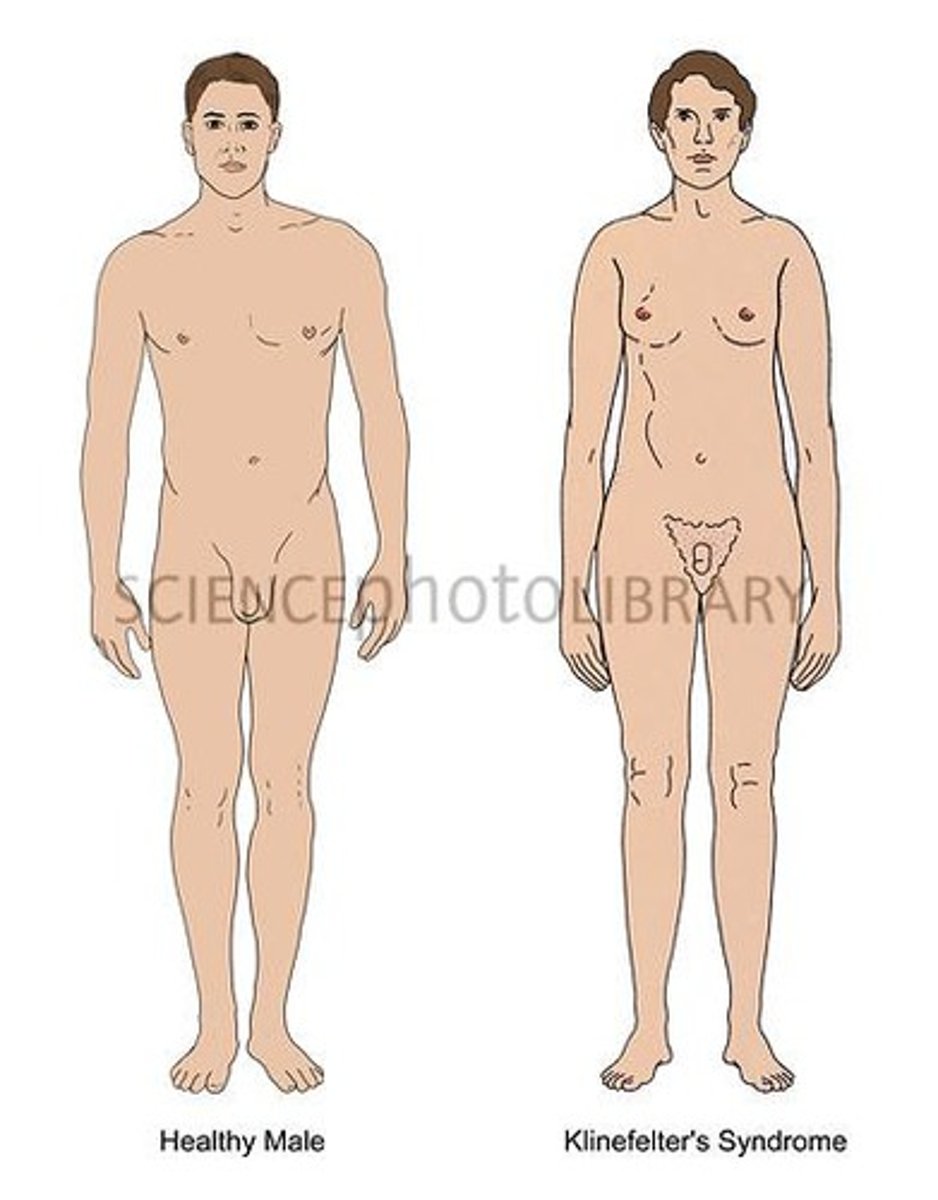
Klinefelter Syndrome
XXY condition, often due to paternal nondisjunction.
Jacob's Syndrome
47,XYY male, typically normal appearance and fertility.
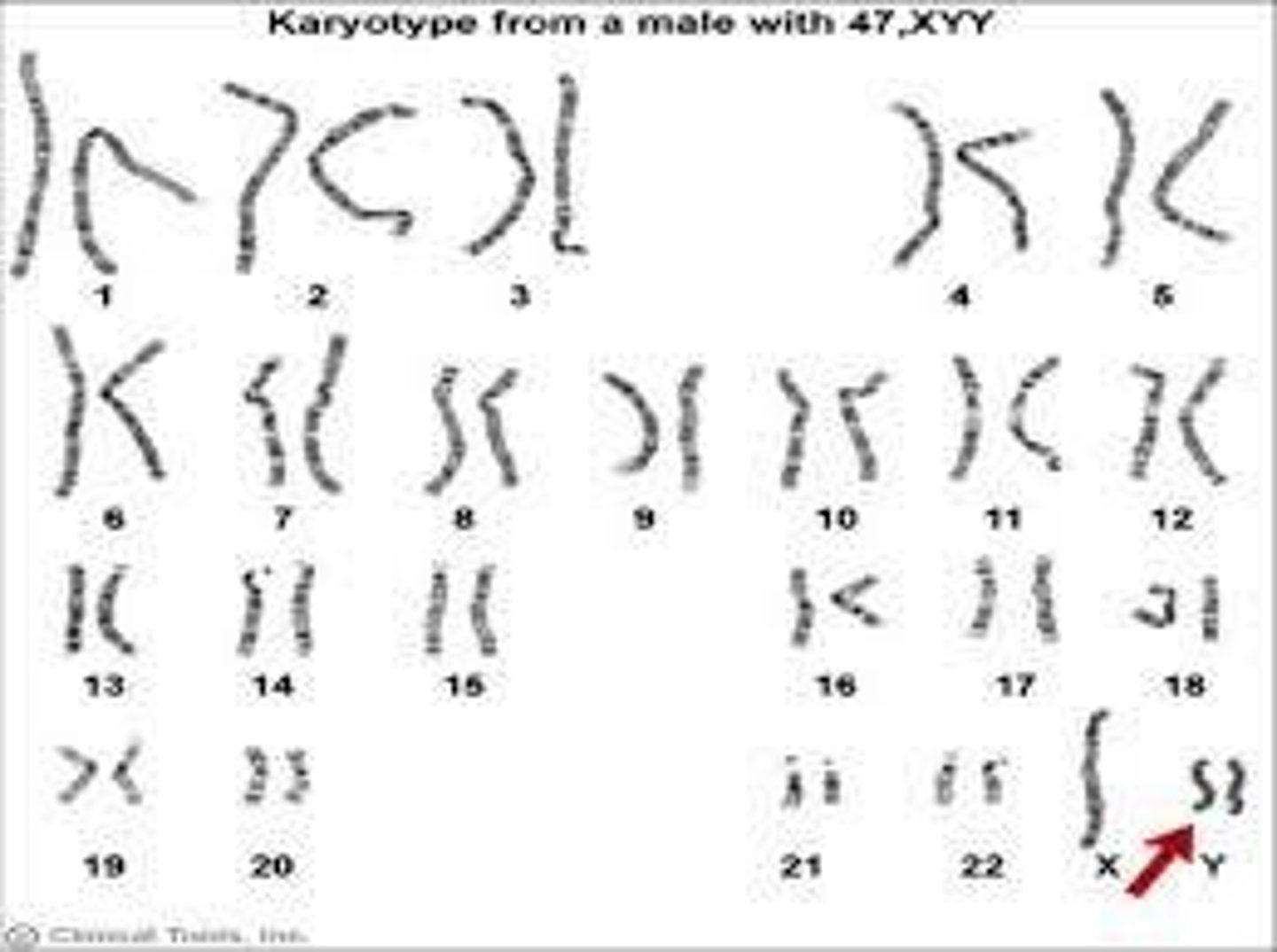
Karyotype
Display of all chromosomes in a somatic cell.
Sister Chromatids
Identical DNA molecules from a single DNA molecule.
Homologous Chromosomes
Pairs of chromosomes, one maternal and one paternal.
Genetic Recombination
Creation of new allele combinations through DNA exchange.
Prophase 1
Stage of meiosis where crossing over occurs.
Metaphase 1
Stage of meiosis where independent assortment occurs.
Metaphase 2
Second meiotic division stage with independent assortment.
Oocytes
Female gametes, more prone to meiosis errors.
Turner Syndrome
Monosomy of X chromosome, affects female development.
Fertilization
Union of sperm and egg, leading to genetic diversity.
Genetic Diversity Factors
Crossing over, independent assortment, and fertilization randomness.
Chromosomal Segments
Parts of chromosomes exchanged during crossing over.