Respiratory Distress
1/44
Earn XP
Description and Tags
WARNING: It's about to get Hectic
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
Respiratory Distress
A combination of the patient’s subjective sensation of dyspnea with physical signs indicating difficulty breathing
tachypnea and tachycardia, use of the accessory respiratory muscles, (sternocleidomastoid, sternoclavicular, and intercostals) nasal flaring, inability to speak normally, agitation or lethargy, depressed consciousness due to hypercapnia, and paradoxical abdominal wall movement
Physical Signs Associated with Dyspnea
Respiratory failure
The point at which the lungs and respiratory muscles cannot move enough air to adequately oxygenate and eliminate CO2 resulting in signs/symptoms of organ dysfunction (AMS, anxiety, confusion)
decreased pulse ox, CO2 capnography, decrease in O2 with increase in CO2 on ABG/VBG, decreasing pH
Finding suggestive of impending arrest
Do nothing (DNI), BiPAP, RSI, surgical airway (crike)
Choices in an impending arrest
reduces the work of breathing, improves pulmonary compliance, recruits alveoli, limited sedation needed, decreased intubation rates
Pros of BiPAP
Exacerbates air trapping (like in severe obstructive diseases), Barotrauma can lead to pneumos, anxiety, decreases CO and hypotension (increased intrathoracic pressure)
Cons of BiPAP
Rapid Sequence Intubation (RSI)
The use of a sedative and a paralytic to allow for a controlled, emergency intubation - make sure you use high flow before and after
Mallampati score
A score that determines how difficult it would be to place an emergency airway based on visualization on landmarks of the oropharynx (1 = you can see the tonsils, 4 = nothing)
LOOK (facial trauma, bleeding, large teeth/tongue, beard, moustache), Evaluate the 3-3-2 (incisor difference, hyoid mental distance, thyroid mouth distance), Mallampati score, Obstruction (epiglottitis, peritonsillar abscess, trauma), Neck mobility (if you can’t position the head)
Describe the LEMON score for airway difficulty
Vitals w/ pulse Ox, O2 supplementation, bilateral patent IV access (no fluids until volume status is assessed), EKG, defib pads, capnography, VBG/ABG
Shotgun orders for Respiratory Patients
Cardiac, pulmonary, neuro, ENT, + anything else pertinent
Physical exam for respiratory emergencies
Pulmonary (ventilatory/circulatory), Cardiac, Neuro, Toxin (CO, peripheral nerve blockage)
DDX for respiratory emergencies
CXR (2 views if possible), neck CT/Xray, chest CT, Chest CT with PE protocol (Angio). V/Q scan, DVT U/S, Brain CT/MRI
Imaging for a Respiratory emergency
ABG/VBG, CBC, Coagulation studies (INR, PT, PTT), CMP, Troponin, MAYBE D-dimer, urine tox, CO, hCG
Lab for a Respiratory emergency
COPD Exacerbation
A worsening of respiratory symptoms beyond normal day-to-day variation due to increased due to higher airway resistance and lung hyperinflation
Chronic and progressive dyspnea, cough, sputum production, minor hemoptysis is common
Hallmark symptoms of COPD Exacerbation
Irritants, tobacco smoke, air pollutants, bacteria, GERD
Common causes of COPD Exacerbation - trigger increase in inflammatory cells in the airways, lung interstitium, and alveoli
Supplemental O2, Nebulized B2 agonist and/or anticholinergic medications (albuterol and ipratropium), PO/IV steroids, maybe Abx (macrolides, TMP-SMX)
Treatment plan for COPD exacerbation in the ER
increased sputum volume, change in sputum color, fever, other suspicion for infection, consolidation on CXR
Indication for Abx in COPD exacerbation
improvement while in ED, ability to perform ADLs at home, Walk to life
Disposition on COPD exacerbation in the ER is due to
dyspnea, wheezing (unreliable), chest tightness, cough with Hx of asthma (new onset is rare), SOB, sputum production, fever, pulsus paradoxus (if severe)
Signs of Asthma Exacerbation - often due to pollen or weather changes
Status Asthmaticus
Acute severe asthma attack that does not improve with usual doses of inhaled bronchodilators and steroids
Supplemental O2 (watch the pulse ox, bipap for severe), Nebulized B2-agonist and/or anticholinergic agents (albuterol and ipratropium), PO/IV corticosteroids, maybe abx, IV Mg staticus asthmaticus, Ketamine (acute), Epi (if hella severe)
Emergent treatment of Asthma Exacerbation
improvement in the ED, ADLs, walk of life
Disposition of Asthma exacerbations depends on
Forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1), PEFR (CBC is not consistent enough)
What are the key objective measures in the severity of acute asthma?
Adult respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS)
A clinical syndrome of severe, rapid onset dyspnea, hypoxemia, and diffuse pulmonary infiltrates leading to respiratory failure
Severe sepsis syndrome, bacterial pneumonia, trauma, multiple transfusions, aspiration, drug OD
80+% of ARDS is caused by
unexplained bilateral opacities on CXR, respiratory failure w/o cardiac failure or volume overload, PaO2/Fio2 ratio under 300 mmHg with PEEP greater than 5 cm
Signs of ARDS
Exudative (protein rich flash edema - intubate), Proliferative, fibrotic
Stages of ARDS
treat the underlying, mechanical ventilation once patient fatigues (low tidal volume and adequate PEEP), fluid restriction and diuretics
Treatment plan for ARDS
Heart failure exacerbation
What is caused by either a worsening in cardiac function (decreased EF) or increase in circulating volume (decreased diuretic or increased intake)
Recent hx of chest pain (MI), SOB, DOE, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, cough, edema
In a heart failure exacerbation, what might patients present with
HTN, diabetes, valvular heart disease, old age, male sex, obesity
Risk factors for acute heart failure
pulmonary venous congestion, cardiomegaly, interstitial edema
CXR findings for acute heart failure
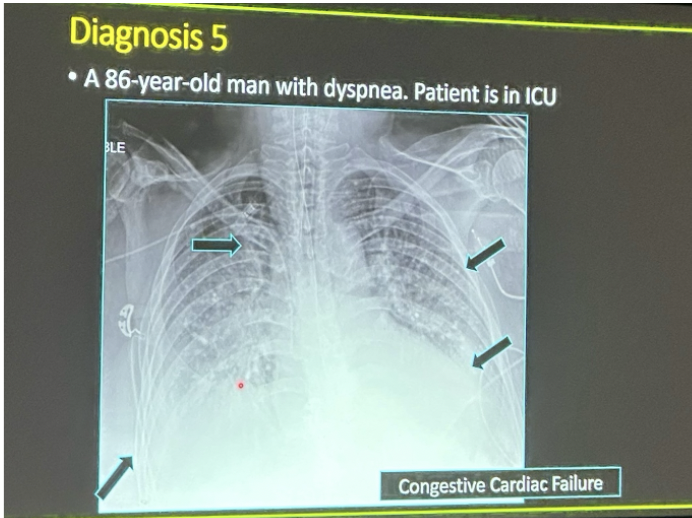
BiPAP, diuretics with strict I&Os (usually double the home dose IV style), maybe pacing/abortive therapy in the case of dysrhythmias
Treatment plan for HF exacerbations
improvement while in ED, ADLs, Walk of life, worsening cardiac function (use the chest pain eval)
When determining disposition of HF exacerbations, what should you look at?
Supplemental O2 (BiPAP or RSI to maybe push the FB into the right mainstem (last ditch effort)), if complete blocked, begin CPR, no blind sweeps
Treatment plan for FBA
Mild disease, (14% severe, 5% critical)
Of SARS-CoV-2 symptomatic patients 81% have
CVD, DM, HTN, chronic lung disease, hematologic malignancies, lung cancers, metastatic disease, CKD, obesity, smoking
Common comorbidities with SARS-COV-2
Cough, fever, myalgias, HA, dyspnea, sore throat, diarrhea, N/V; loss of smell/taste, abd pain, rhinorrhea (under <10%)
Common presentations of SARS-CoV-2 - worsen over 5-7 days
NAAT (Gold Standard)
Diagnostics for SARS-CoV-2
viral RNA in the blood, lymphopenia, thrombocytopenia, elevated LFTs, elevated lactate, elevated CRP, Ferritin, cytokines, and TNF-alpha, elevated D-dimer, elevated PT, elevated trop, elevated CPK, AKI
Lab abnormalities associated with worse SARS-CoV-2 outcomes
ABCs (O2, BiPAP, RSI, Crash airway if necessary), detailed I and Os, Paxlovid in under 5 days, Remdesivir under 7, convalescent plasma under 8, proper hydration, self proning, acetaminophen, cough suppressant
Treatment plan for SARS-CoV-2
immunocompromised, unvaxxed over 50, over 65, multiple comorbidities
Which SARS-CoV-2 patients are getting paxlovid (if symptoms under 5 days)?