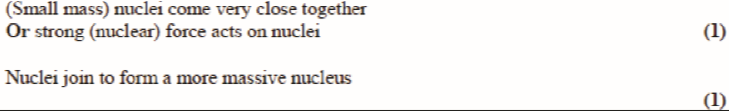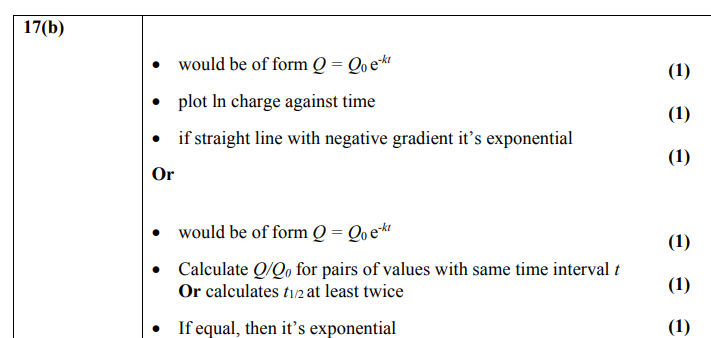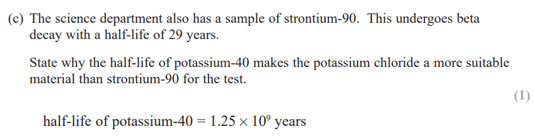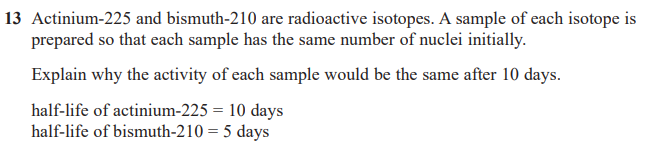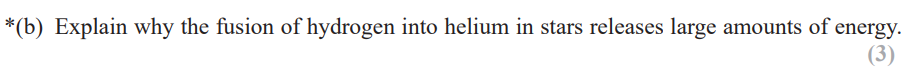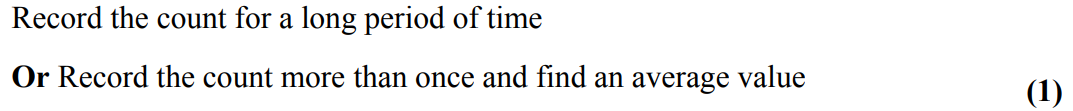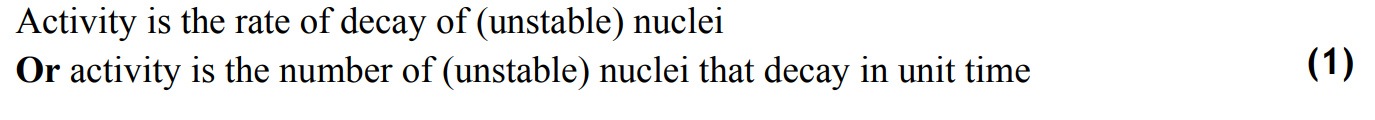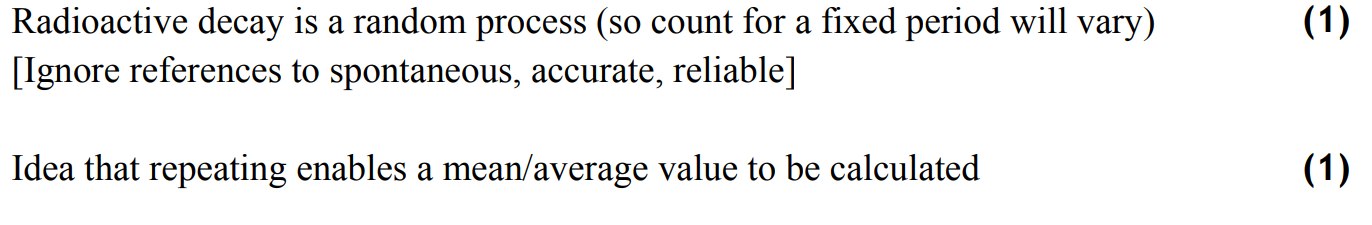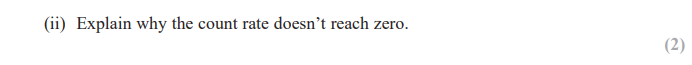Physics - Topic 11 - Nuclear Radiation
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
nuclear decay is spontaneous and random. what do these two terms mean?
random - cannot identify which atom/nucleus will be the next to decay
spontaneous - external factors cannot influence when a nucleus will decay (independent of external conditions)
what is the law of radioactive decay?
rate of decay is directly proportional to the number of unstable nuclei present.
A = ? (in terms of number of unstable nuclei present)
A = λN
A is the activity in Bq
λ is the decay constant, measured in s⁻¹ or min⁻¹
N is the number of unstable nucle, unitless
dN/dt = ?
dN/dt = -λN
λ = ?
λ = ln2/t1/2
A = ?, N = ?
A = A₀e-λt
N = N₀e-λt
write an equation for the nuclear decay of an unstable parent nuclide X into a daughter nuclide Y via alpha decay.
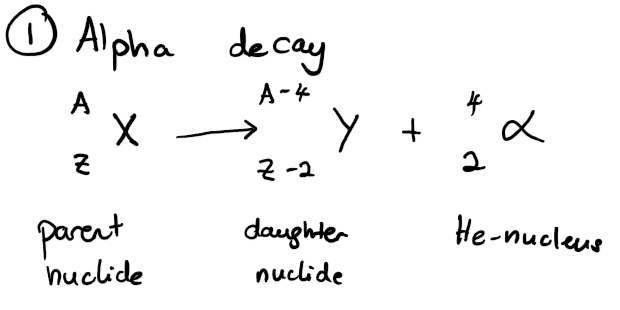
write an equation for the nuclear decay of an unstable parent nuclide X into a daughter nuclide Y via beta minus decay. write another equation to show which sub-atomic particle is being converted.
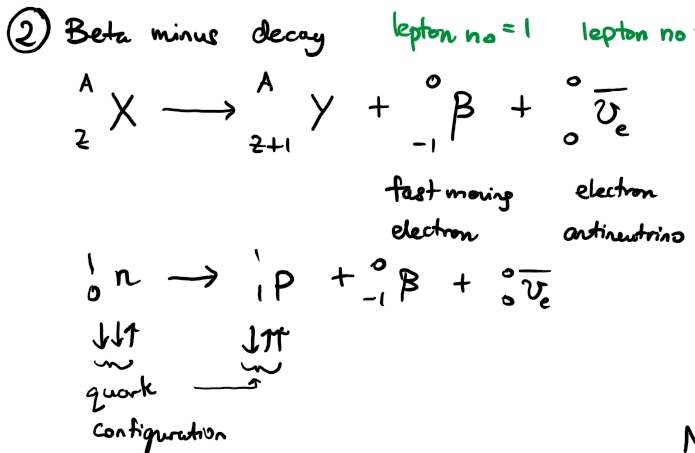
write an equation for the nuclear decay of an unstable parent nuclide X into a daughter nuclide Y via beta plus decay. write another equation to show which sub-atomic particle is being converted.
define nuclear binding energy and state its associated equation
nuclear binding energy is the energy needed to completely separate the individual nucleons in the nucleus
BE or ΔE = Δmc²
Δm is the mass deficit - calculated by finding initial mass - final mass
c is the speed of light in a vacuum
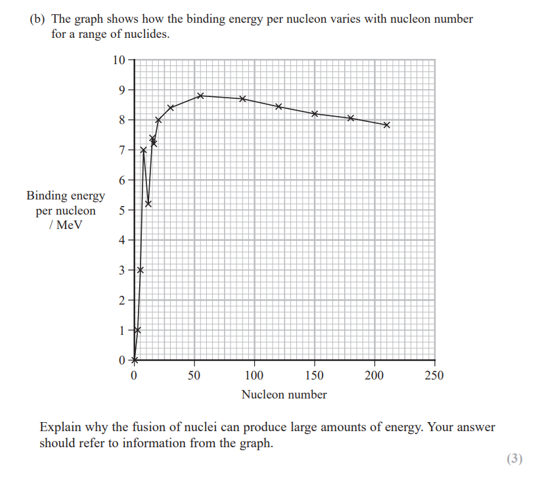
how do nuclear fusion and fission cause a change in binding energy per nucleon?
fusion - increase
fission - increase
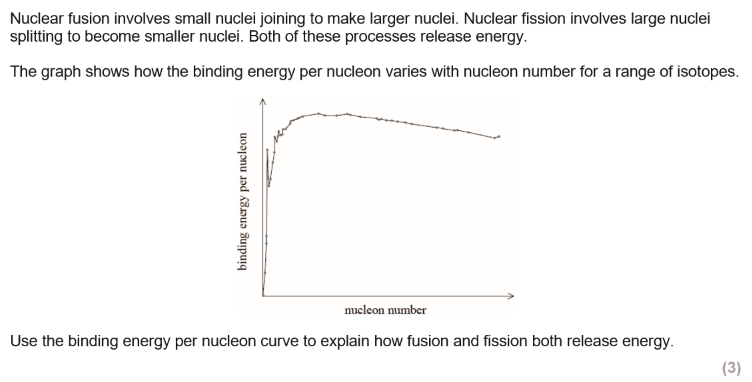
fusion involves an increase in binding energy (per nucleon) as the number of nucleons increases
fission involves as increase in binding energy (per nucleon) as the number of nucleons decreases
if binding energy per nucleon increases energy is released in the process

the rate of decay depends upon the number of unstable nuclei in the sample (A = λN)
radium has a large half-life, so unstable nuclei are present in the sample for a long time
when a nucleus decays there is a (small) decrease in mass Δm
energy is released according to ΔE = Δmc²
Δm is small but c is large, so a significant amount of energy is released
energy released by the decay becomes kinetic energy of the atoms in the sample (hence the sample is above the temperature of the surroundings)
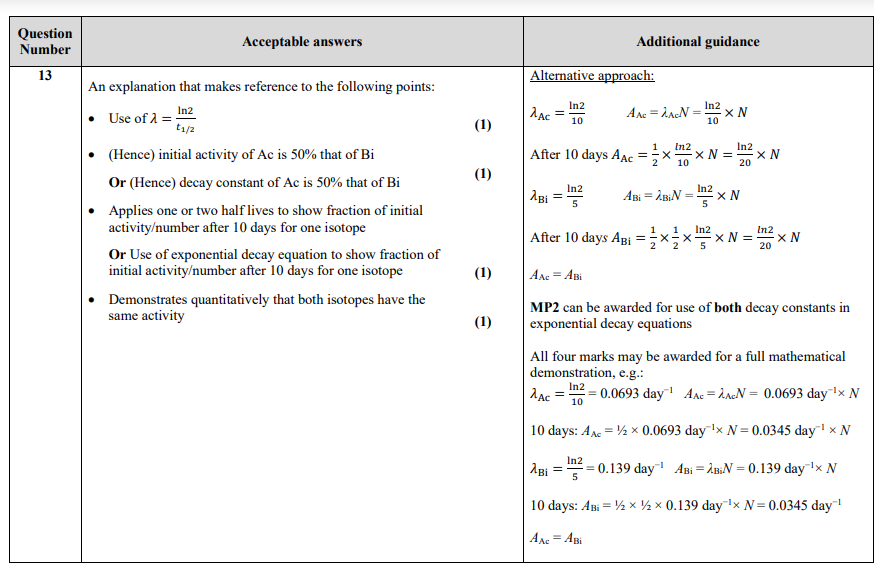
explain why the decay constant of an isotope can be determined even though nuclear decay is random. (2)
the probability of decay (in a specified time) may be determined
(probability may be applied accurately because) very larger numbers (of unstable nuclei) are involved
a radioactive source used in a school labaratory emits alpha and beta radiation.
describe how the percentage of activity due to beta radiation may be determined using a Geiger–Müller tube and ratemeter. (4)

the decay products of americium are unstable and undergo a series of further decays. the table shows the first three decays in this sequence.
a student says, “protactinium-233 emits beta particles when it decays, so by now the americium-241 source bought 34 years ago will be emitting a significant amount of beta radiation.”
discuss the student’s statement. (3)

what is nuclear fusion? what are the conditions for fusion and why? why is energy released during fusion?
nuclear fusion is when two smaller nuclei join together to form one larger nucleus
very high densities of matter are required to maintain the fusion reaction to ensure there are enough colliding protons undergoing fusion
very high temperatures are required as a massive amount of energy is needed to overcome the electrostatic force of repulsion between nuclei
energy is released during fusion because the larger nucleus has a much higher binding energy per nucleon (than the smaller nuclei)
what is nuclear fission? in what situations does it occur? why is energy released during fission?
nuclear fission is the splitting of a large nucleus into two daughter nuclei
it occurs in very large nuclei, which are unstable
energy is released during fission because the smaller daughter nuclei have a higher binding energy per nucleon
how do you calculate the binding energy per nucleon?
binding energy per nucleon = binding energy of nucleus ÷ number of nucleons in the nucleus
fill in the blanks: nuclei larger than ___ undergo ___ and nuclei smaller than ___ undergo ____
nuclei larger than iron undergo fission and nuclei smaller than iron undergo fusion
draw a table to show the relationship between the nature, penetration, ionising ability and range in different materials of nuclear radiations (alpha, beta and gamma)
what is the N/Z ratio? what are the comparative values of N and Z for small nuclei and large nuclei?
N/Z = ratio of number of neutrons to number of protons
small nuclei tend to have N = Z: when nuclei are small, strong nuclear force acts equally between all the nucleons and dominates over the electrostatic repulsion (between protons)
large nuclei have more neutrons than protons, N>Z: range of strong nuclear force is very short and smaller than size of nuclei, so more nucleons are needed to hold protons against electrostatic repulsion
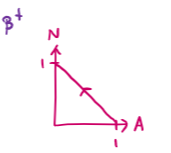
draw an N-Z plot for β+ decay
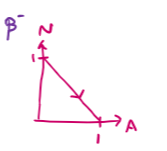
draw an N-Z plot for β- decay
draw an N-Z plot for α decay
core practical 15: describe an experiment to investigate the absorption of gamma radiation by lead
determine the thickness of six lead discs using a mx icrometer (or digital/vernier caliper)
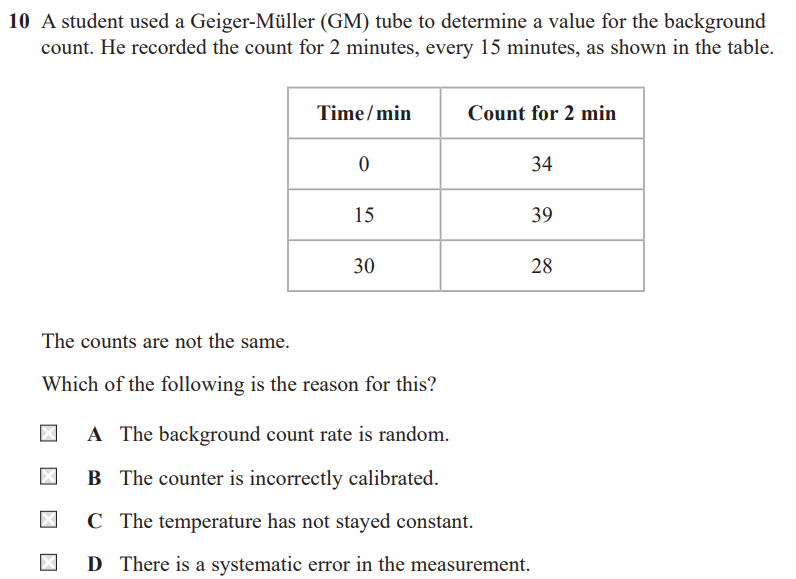
record background count for 5 minutes using a Geiger-Müller tube connected to a counter. repeat this and find the mean background count rate, which will be subtracted from subsequent count readings
place source in position and the count N0 with no lead discs in place is recorded
record the count N for several thicknesses x of lead by using the discs, either singly or in combination as absorbers
maintain a constant distance between source and G-M tube by marking positions of equipment with masking tape
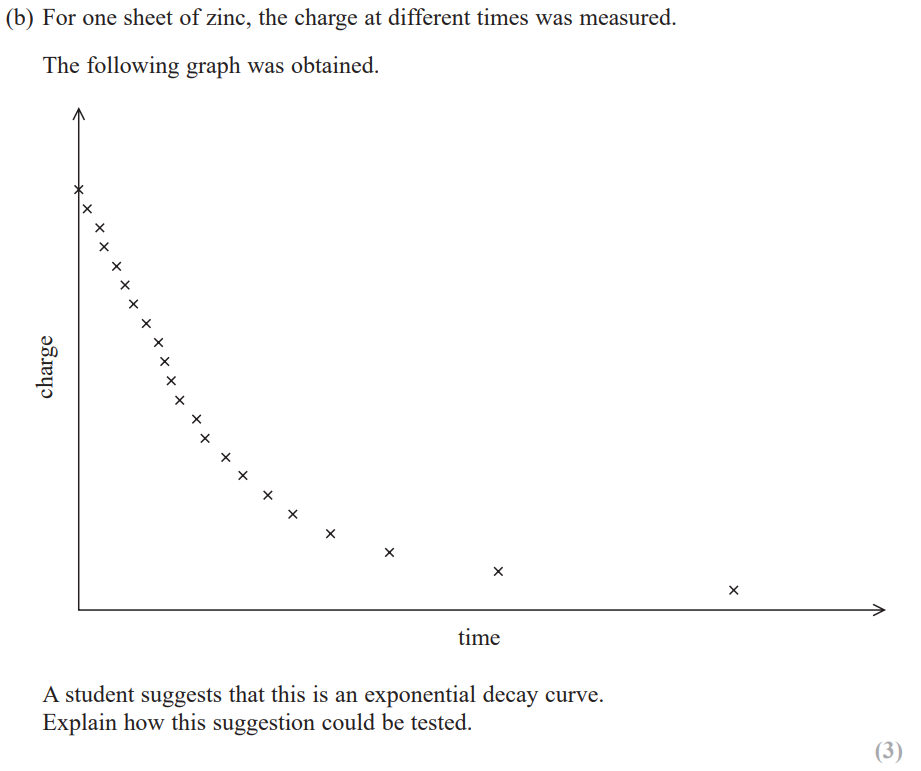
plot a graph of the count-rate N against absorber thickness x to test exponential relationship: N = N0e-μx where μ is the coefficient of absorption and is a constant
plot a graph of lnN against x which has equation
lnN = -μx + lnN0 which is in the form y = mx + c where -μ is the gradient and is a constant (and lnN0 is the y-intercept and is also a constant)
explain how the nuclear processes within the Sun are able to release energy. (3)
nuclear fusion
when hydrogen nuclei combine to form helium
there is a loss of mass
this mass loss is converted to energy (ΔE = Δmc²)
explain why sustainable fusion has not yet been achieved for the generation of electrical power. (4)

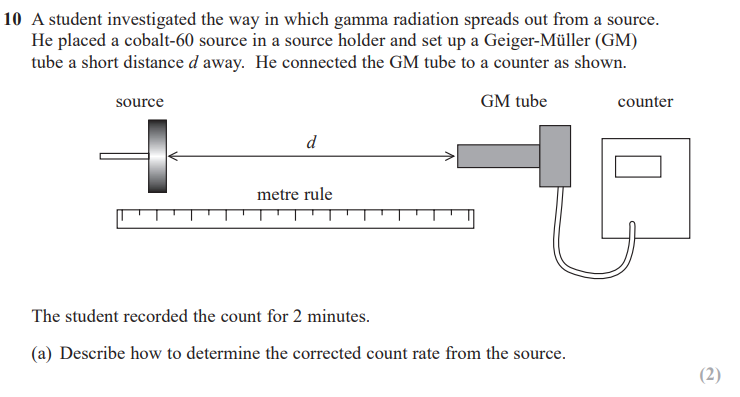
(remove the source and) record background count for specified time e.g. 2 minutes and subtract from count due to source
divide by time e.g. 2 to give a count rate





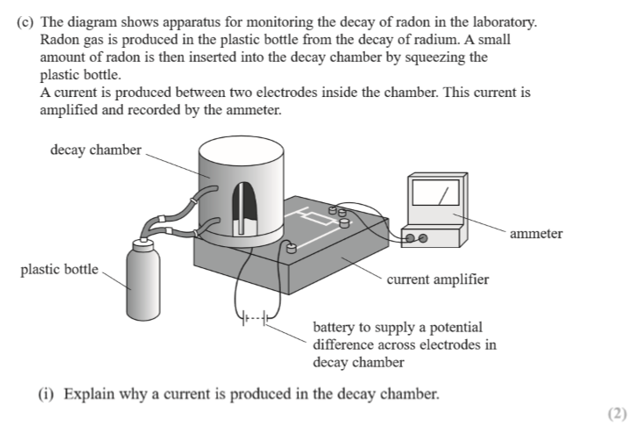


(potassium-40 has a much longer half-life than strontium-90)

state what is meant by binding energy. (2)
the energy equivalent to the mass deficit
when nucleons bind together to form an atomic nucleus
describe the process of nuclear fusion. (2)
specify two low mass nuclei come very close together