273 Exam 2
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
true labor
progressive dilation and effacement
regular contractions
pain usually starts in the back, radiates to abdomen
only diagnosed if cervical change is made!
false labor
lack of cervical change
irregular contractions
contractions mainly in front of abdomen
can relieve pain
Critical factors in labor: 1st 5 P’s
passageway (birth canal)
passenger (fetus)
powers (contractions)
position
psychological response
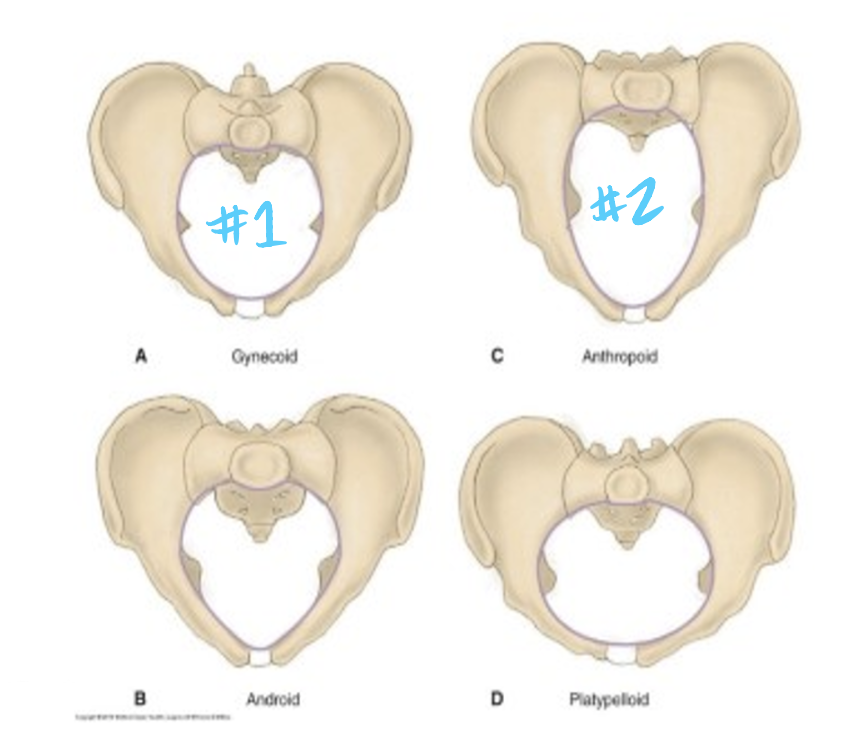
passageway
maternal (immovable) pelvis
gynecoid and anthropoid are best
soft tissues (cervix, pelvic floor, vagina)
cervix dilates and effaces
vaginal canal distends
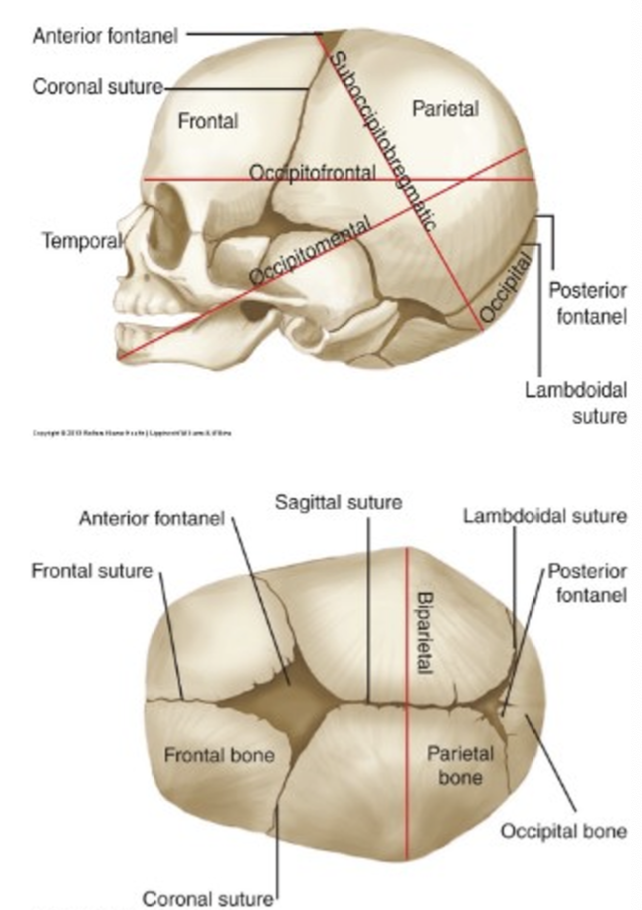
fetal head
face and cranial base are fixed
cranial vault, which has sutures, is moldable
fontanelle: intersection of sutures
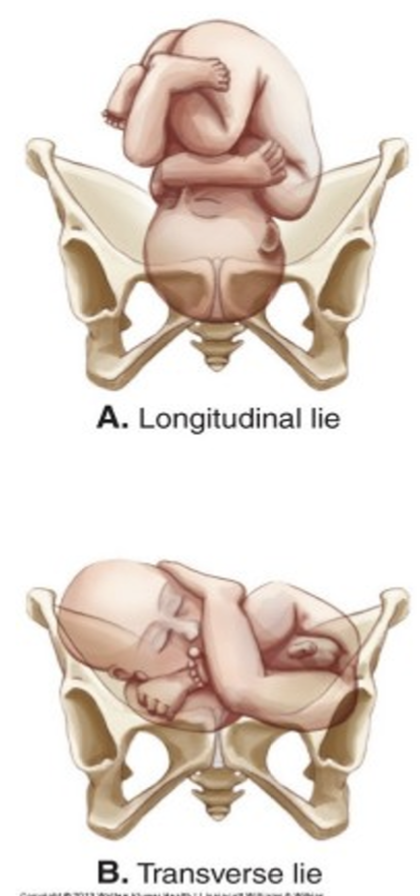
fetal lie
relationship of fetal spine to mother’s spine (cephalocaudal)
longitudinal - vertical (parallel to maternal spine)
cephalic
breech
transverse - horizontal
shoulder- always C/S
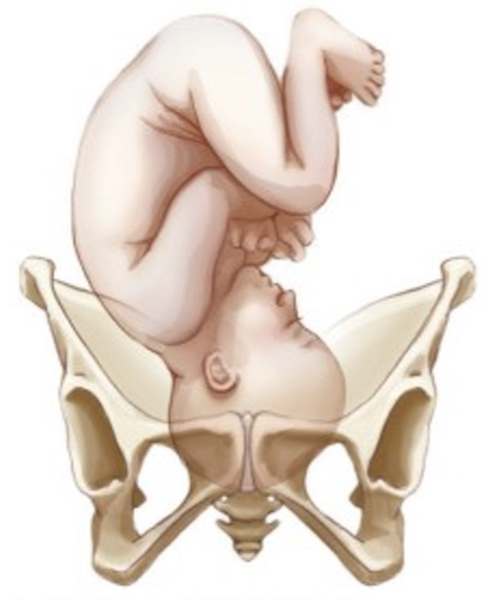
fetal attitude
relation of fetal body parts to one another
posture of fetus to conform to uterine cavity
normal- general flexion
head flexed, chin on chest
arms crossed over chest
legs flexed at knee, thighs on abdomen
abnormal- extension
fetal presentation
body part that enters the pelvis first
normal
cephalic presentation (AKA vertex)
occiput presenting, head flexed
powers
primary force (contractions)
uterine muscular contractions, which cause cervical change through effacement and dilation
laboring down (waiting 1-2 hrs once 2nd stage begins b/c easier and less energy)
secondary force (pushing)
pushing during 2nd stage once 10 cm dilated
coordinate with primary force
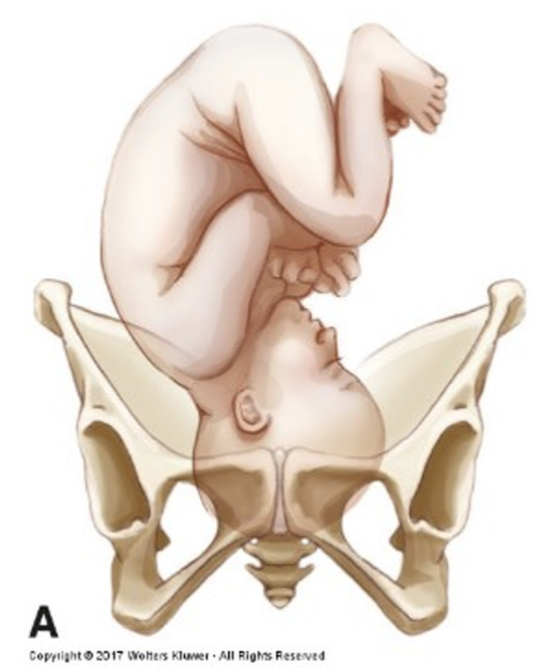
position (fetal)
engagement: when the fetal presenting part is even (station 0) with the ischial spine, this is the start of the cardinal movements of labor
extension: fetal head has to get underneath the pubic bone
LOA and ROA most favorable
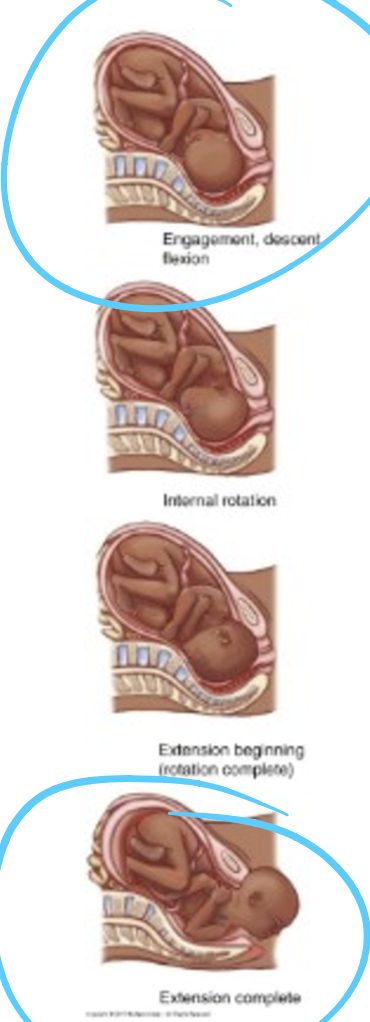
fetal malposition: occiput posterior (OP) maternal risks and clinical therapy
maternal risks
intense pain on small of back “back labor”
prolonged labor
increased risk of assisted vag delivery, perineal laceration, C/S
clinical therapy
hands/knees position to allow fetal rotation
vaginal or C/S
psychological factors in labor
birth experience factors
locus of control
pain/anxiety
labor support (doulas)
previous experience
preconceived ideas/expectations
readiness
cultural view
birth plan= wish list
maternal systemic responses to labor (CV, resp, GI)
CV
HR increases 10-20 bpm
BP increases during contractions
BP decreases with epidural
RESPIRATORY
oxygen demand increases at labor onset
GI
decreased motility and gastric emptying- N/V
sterile vaginal exam evaluates 6 things
dilation/effacement/station
dilation: 0-10 cm
effacement: 0-100% or 4-0 cm
station: -5 to +4
also evaluate:
fetal position (vertex vs. breech)
orientation (OA or OP)
membrane status
nursing care during admission: labor/fetal assessment (6)
uterine contractions
membranes/BOW
fetal movement
vaginal bleeding
EFM
SVE
nursing care during admission: maternal assessment (6)
VS
weight/weight gain
review prenatal record
psychosocial assessment
establish a positive relationship/rapport
patient education
3 ways to do EFM?
doppler
ultrasound
toco transducer
doppler or US
on baby’s back
assess fetal heart rate/tones
baseline/normal FHTs 110-160
variability
accelerations (15 beats x 15 sec)
decelerations
toco transducer
on fundus
assesses contractions
determines start, end, and interval contractions
cannot determine intensity
ask mom or palpate
what is a baseline?
10 min segment during non-event
exclude accels/decels
between UCs
reported as a single number in 5 bpm increments
normal is 110-160
possible influences on baseline changes (tachycardia >160)?
early sign of hypoxia
maternal medications, fever, dehydration
fetal anemia
possible influences on baseline changes (bradycardia <110)?
fetal hypoxia
maternal medications (analgesics)
maternal hypotension (position, epidural)
what is variability? what does it tell us?
how well is CNS functioning?
fluctuations in FHR around the baseline
exclude accels/decels
between UCs
NOT ASSESSED DURING AN “EVENT”
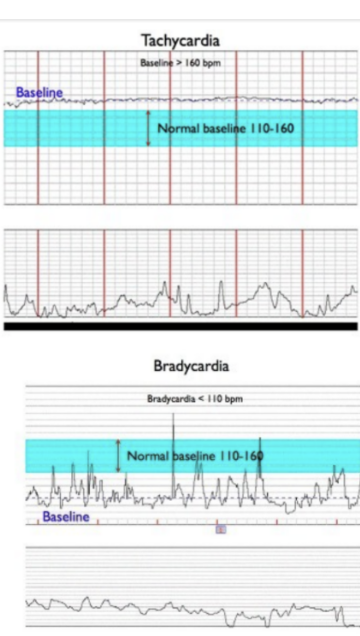
variability documentation
absent: undetectable or 0 bpm
minimal: 1-5 bpm
moderate: 6-25 bpm
marked: >25 bpm

what are accelerations?
an abrupt increase at least 15 bpm above baseline for at least 15 seconds, but less than 2 min
what may accelerations be associated with? what are they a sign of?
fetal movement
fetal well-being and adequate oxygenation
decelerations
onset
gradual
abrupt
shape
mirrors UC or V/W/U
relationship to UC
early, late, no relationship?
types of deceleration
early
late
variable
prolonged
internal monitoring: when are FSE and IUPC indicated? 4 criteria?
FSE: need instant, continuous recording. most accurate FHR tracing
IUPC: contraction intensity, uterine resting tone, very accurate timing
4 criteria
ROM
At least 2 cm
Presenting fetal part low enough to allow placement of the scalp electrode
Skilled practitioner available to insert spiral electrode
non-pharmacologic measures
labor support
water-birth/hydrotherapy
ambulation/position changes
birthing aids
massage
heat/cold
visualization
breathing techniques
pharmacologic measures
systemic analgesia
inhaled analgesics
regional analgesia/anesthesia
systemic analgesia
medications DO cross placenta
fetal respiratory depression
route: IV or IM, NOT PO
safety: dizzy, fall risk
not going to give if mom is delivering in next 4 hours because then the baby may be delivered w resp. depression
inhaled analgesics
50/50 nitrous oxide and oxygen “laughing gas”
safe- no FHR abnormalities
regional analgesia/anesthesia
local numbness
pain relief, NOT pressure relief
does NOT cross placenta
types:
epidural
spinal
spinal + epidural
pudenal block
epidural MOA
injection of local anesthetic and analgesic into epidural space
continuous block (catheter left in place)
epidural advantages
most report relief
pt is fully awake during labor and brith
can be given any time
dose can be adjusted during labor based on pt needs
DO NOT CROSS PLACENTA
epidural disadvantages
maternal hypotension
skilled personnel required to administer
costly- elective, insurance may not cover
onset may take 30 min
restricted in positions/movement during labor/birth
may increase duration of 2nd stage
epidural and spinal contraindications
local or systemic infection (sepsis)
coagulation disorders/plt count <100,000
severe anatomic abnormalities of the spine/back surgery
uncorrected hypovolemia
epidural expected findings
relief from pain, not pressure
epidural and spinal priority interventions
preload with IV fluid bolus
500-1000 ml wide open
monitor maternal vital signs, FHR
hypotension= corrective IV infusion prn
EFM
frequent bladder assessment
pruritis assessment
ensuring that mom avoids supine position to help minimize hypotension (HOB elevated or side lying)
assist with pushing
assess return of sensation prior to ambulation
epidural teachings
movement/position changes will be restricted during labor
might require straight or foley catheter
spinal block MOA
local anesthetic directly into spinal fluid in subarachnoid space
typically with C/S
spinal block advantages
immediate onset
smaller drug volume
can be given any time
spinal block disadvantages
high incidence of hypotension
short-acting (2-3 hrs)
one dose only
spinal headache= blood patch
pudenal block and local infiltration MOA
injected into pudenal nerves
SQ or IM
pudenal block and local infiltration advantages
absence of maternal hypotension
minimal medication used, none to fetus
pudenal block and local infiltration disadvantages
does not relieve contractions
pudenal block expected findings
provides pain relief in lower vagina, vulva, and perineum
pudenal block priority interventions
A pudendal block is used for the second stage of labor, an episiotomy, or an operative vaginal birth with outlet forceps or vacuum extractor.
It must be administered about 15 minutes before it would be needed to ensure its full effect.
pudenal block patient teachings
numbs the local area, does not relieve pain from contractions
no side effects
second stage comfort measures
Cool washcloths to face/neck
Pericare/change underpads
Encourage rest between contractions
Visualization techniques
Support her legs/head
Ice chips
Position changes
third stage comfort measures
Tremors common- heated blanket
Provide food and fluids- general diet
Encourage rest
Assist with perineal care, ambulation
To bathroom to void or straight cath
Icepack, peripad, peri bottle
Transfer to PP area when stable
signs of placental separation
gush of dark blood
“lengthening” cord protruding from vagina
firmly contracting uterus
bulge at perineum
rise in fundus (back into abdomen)
degrees of lacerations
1st: skin
2nd: muscles of perineal body
3rd: anal sphincter muscle
4th: anterior rectal wall
what is a VBAC?
vaginal birth after C/S
50-70% success
VBAC contraindications
prior classical uterine scar
myomectomy
inadequate staff/facility
cervical ripening
VBAC risks
uterine rupture
VBAC nursing considerations
fetal surveillance
documentation
readiness for emergent C/S
assisted vaginal delivery 4 criteria
ROM
10 cm
vertex and engaged
adequate pelvic size
assisted vaginal delivery indications
Prolonged second stage
Distressed FHR
Failure of presenting part to fully rotate and descend
Limited sensation and inability to push effectively due to anesthesia
Presumed fetal jeopardy or fetal distress
Maternal heart disease
Acute pulmonary edema
Intrapartum infection
Maternal fatigue
Infection
assisted vaginal delivery risks
perineal trauma (episiotomy, hematoma, etc.)
vacuum: bruising, swelling, hematoma
forceps: abrasions/marks, minor temporary facial nerve injury
C/S indications
breech/transverse
dystocia: doesn’t progress to full dilation
fetal distress
ECV unsuccessful
placenta previa
herpes lesions
C/S risks
infection
hemorrhage
fetal injury/tachypnea
C/S nursing care
pre-op: labs, history, anesthesia
post-op: lochia, breastfeeding, pain management, assess incision, catheters
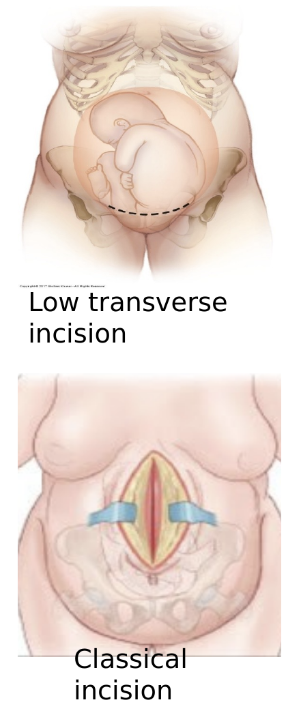
skin incision types
transverse (pfannenstiel)
vertical
skin and uterine incisions are not always in the same direction!!
uterine incision types
transverse-lower uterine segment
can have vaginal birth next time
classical-upper uterine segment
can’t have vaginal birth in the future due to risk of uterine rupture
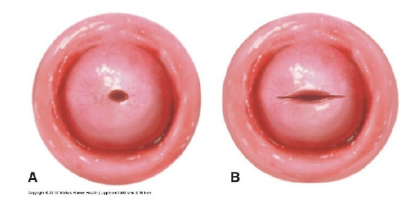
cervix adaptations
bruised
edematous
cervical os remains changed
back to normal in 6 weeks
vagina adaptations
mucous- edematous and relaxed after birth
thickens around 3 weeks
localized dryness
epithelium restored 6-8 weeks
perineum adaptations
hemorrhoids
edematous, bruising
possible lacerations
ovulation/menstruation adaptations
no breastfeeding= 6-11 weeks for ovulation, 7-9 weeks for menses
breastfeeding= depends on how much; 3-18 months
cardiovascular adaptations
Cardiac Output:
high first few days PP
normal by 3 months
Blood Volume:
drops rapidly after birth d/t blood loss
normal by 4 weeks
Pulse and BP:
40-60 bpm first 2 weeks PP
no big changes to BP, but observe for pre-eclampsia
Coagulation:
hypercoagulable state/risk for clotting (DVTs)
Cellular:
increased WBCs 4-6 days PP
urinary adaptations
GI adaptations
decreased peristalsis and fear leading to constipation
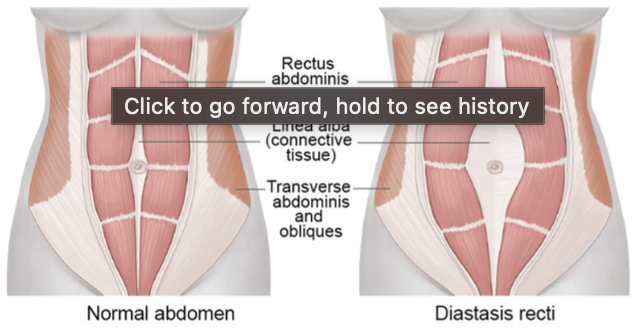
musculoskeletal adaptations
Some women have separation of rectus abdominal muscles
Changes in joints during pregnancy can cause feet to permanently increase 2 sizes
integumentary adaptations
hair loss- temporary
stretch marks
night sweats (getting rid of fluid)
breastfeeding adaptations
Pituitary gland stimulated to release:
Prolactin: synthesis and release of breast milk in the breast
Oxytocin: contraction of the smooth muscle in the uterus and around the alveoli cells in the breast
PP discomforts
Perineal discomfort
Promote good hygiene, wiping front to back
Peribottle
Ice for first 24 hours then warmth to help with circulation
Sitz bath
Hemorrhoidal discomfort
Topical ointments, preparation H, tucks pads
Abdominal incision if c-section
Afterpains - uterine contractions that occur when the uterus is involuting
More severe for multigravida becuase body is working harder to get back to pre-pregnancy state
Premedicate before breast feeding or pumping session
Immobility and muscle strain
Early ambulation
Decrease risk of DVTs
Safety first
Make sure they can bear weight on legs and not dizzy
Dangling
Assisting them the first few times
breast discomforts
Breast care
Plain water, no soap
Soap causes drying and difficult for baby to latch
Apply expressed breast milk for healing
Nipples: assess if erect, flat or inverted; erythema, bruising, cracked, fissured, bleeding
Breast engorgement
If breastfeeding: q 2-3 hour feeds
Non-breastfeeding mothers/weaning: lactation suppression efforts
Wear sports bra, tight bra, back to shower
Ice packs, ibuprofen
Rh and ABO incompatibility
Rho GAM at 28 weeks; PP within 72 hours; other at-risk events (car accident, invasive procedures)
type O mother with A, B, or AB fetus
less severe, no tx
male condom MOA
Thin sheath placed over an erect penis, blocking sperm
85% failure rate
instruct on proper use
Oral contraception (progestin only/minipill)
Pill containing only progestin that thickens cervical mucus to prevent sperm from penetrating
9% failure rate
Oral contraception (progestin only/minipill) teaching
can use while breastfeeding
must be taken with meticulous accuracy
IUSs MOA
T-shaped device inserted into uterus that releases copper, progesterone, or levonorgestrel
0.2% failure rate
No “user error”
IUSs teaching
Highly effective immediately after placement. May cause discomfort on insertion
vasectomy or tubal ligation MOA
Male:
Sealing, tying, or cutting the vas deferens
0.15% failure rate
Female:
Fallopian tubes are blocked to prevent conception
0.5% failure rate
vasectomy or tubal ligation teaching
permanent
lactational amenorrhea
98% effective
baby must be <6 months
no supplements/pacifiers: all infant nutrition from the breast (NOT pumping)
no menses
placenta purpose
acts as lungs and liver
provides O2 and nutrients
removes waste
umbilical cord purpose
2 arteries: transfer waste
1 vein transfers O2
shunts purpose
Ductus venosus
Blood bypasses liver into inferior vena cava
Foramen ovale
Blood flows from R atrium to L atrium
Ductus arteriosus
Blood bypasses lungs into descending aorta
APGAR
Appearance (skin color)
Pulse (heart rate)
Grimace (reflex irritability)
Activity (muscle tone)
Respirations (respiratory effort)
scored at 1, 5, and sometimes 10 min
8, 9, 10 - satisfactory adaptation
5, 6, 7 - required intervention
Below 5- requires resuscitation
rescore at 10 and 20 min
immediate newborn assessment
within first 2 hours
first assessment in birthing area
vital signs q30 min x2 hours in the immediate period
gestational age is determined using Ballard scale
physical maturity section within 2 hours
neuromuscular maturity section within 24 hours
newborn vital signs expected ranges
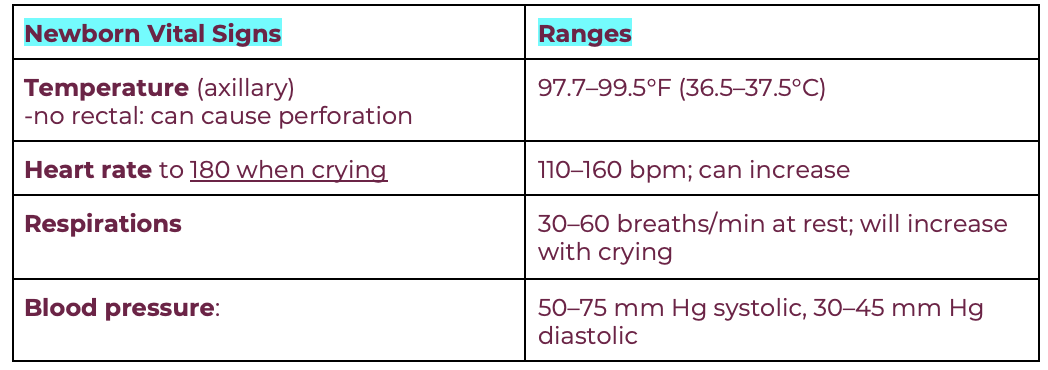
newborn measurements
weight: 5 lb 8 oz- 8 lb 14 oz
length: 17-22 in
HC: 13-15 in
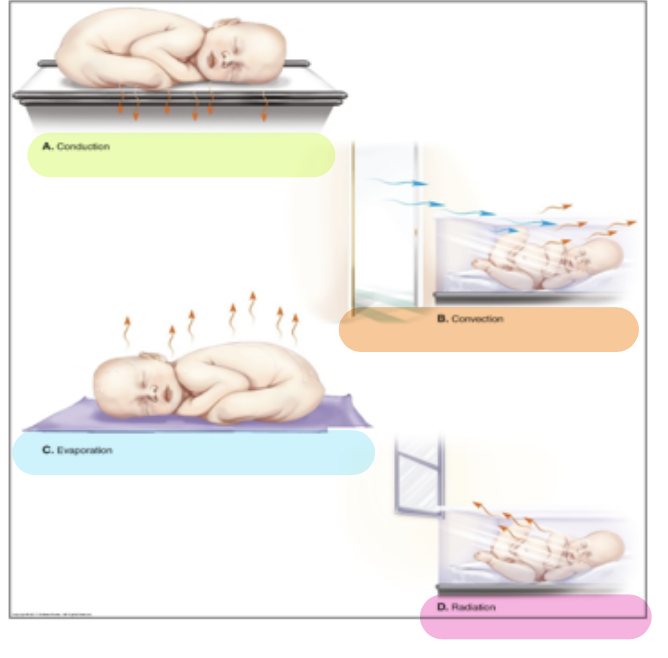
prevention of heat loss
Conduction: skin to skin; warm blanket on scale
Convection: keep newborns away from drafts
Evaporation: dry the newborn well
Radiation: keep away from cold objects (ex. windows)
vitamin K (phytonadione)
prevents hemorrhage
absence of gut bacteria at birth, cannot produce vit k
low prothrombin levels
IM in vastus lateralis
erythromycin eye ointment
prophylactic for opthalmia neonatorum from G or C
legally mandated
instilled into lower conjuntival sac, OU
may be delayed until 1 hour of life to facilitate bonding
expected lochia findings
rubra (days 1-3): red
serosa (days 3-10): pink/brown
alba (days 10-14): white/yellow
when should the fundus be midline (U/U)?
10-12 hours after delivery. should drop 1 cm below umbilicus (U/1) every day
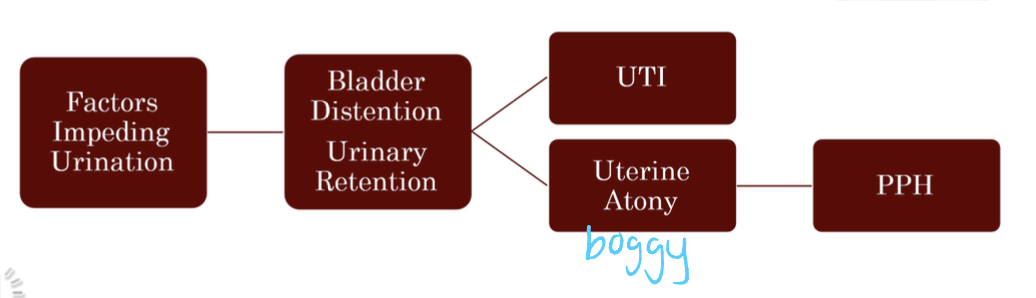
3 unexpected uterine involution findings
firm fundus, bright red trickling: laceration
boggy fundus, red flowing: uterine atony
boggy fundus, dark red and clots: retained placenta
expected RR, BP, HR, temp in PP
RR: 12-20
BP: falls first 2 days, increases days 3-7, back to pre-pregnancy by 6 weeks
HR: 40-80 bpm
Temp: low/afebrile