MICR 200 Chapter 17: Adaptive Immunity part 1
1/126
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
127 Terms
innate immunity
Immunity
1 of 2 branches of immunity. Characteristics:
- First responders
- Nonspecific defenses
- Recognizes pathogens by predetermined patterns, such as with TLRs
adaptive immunity
Immunity
1 of 2 branches of immunity. Characteristics:
- Second responders
- Specific defenses
- Clears infection
- Develops memory of each pathogen as its encountered
- Aka "acquired immunity"
adaptive immunity
Immunity
1 of 2 branches of immunity. Contain specific defenses.
acquired immunity
Immunity
Also called adaptive immunity.
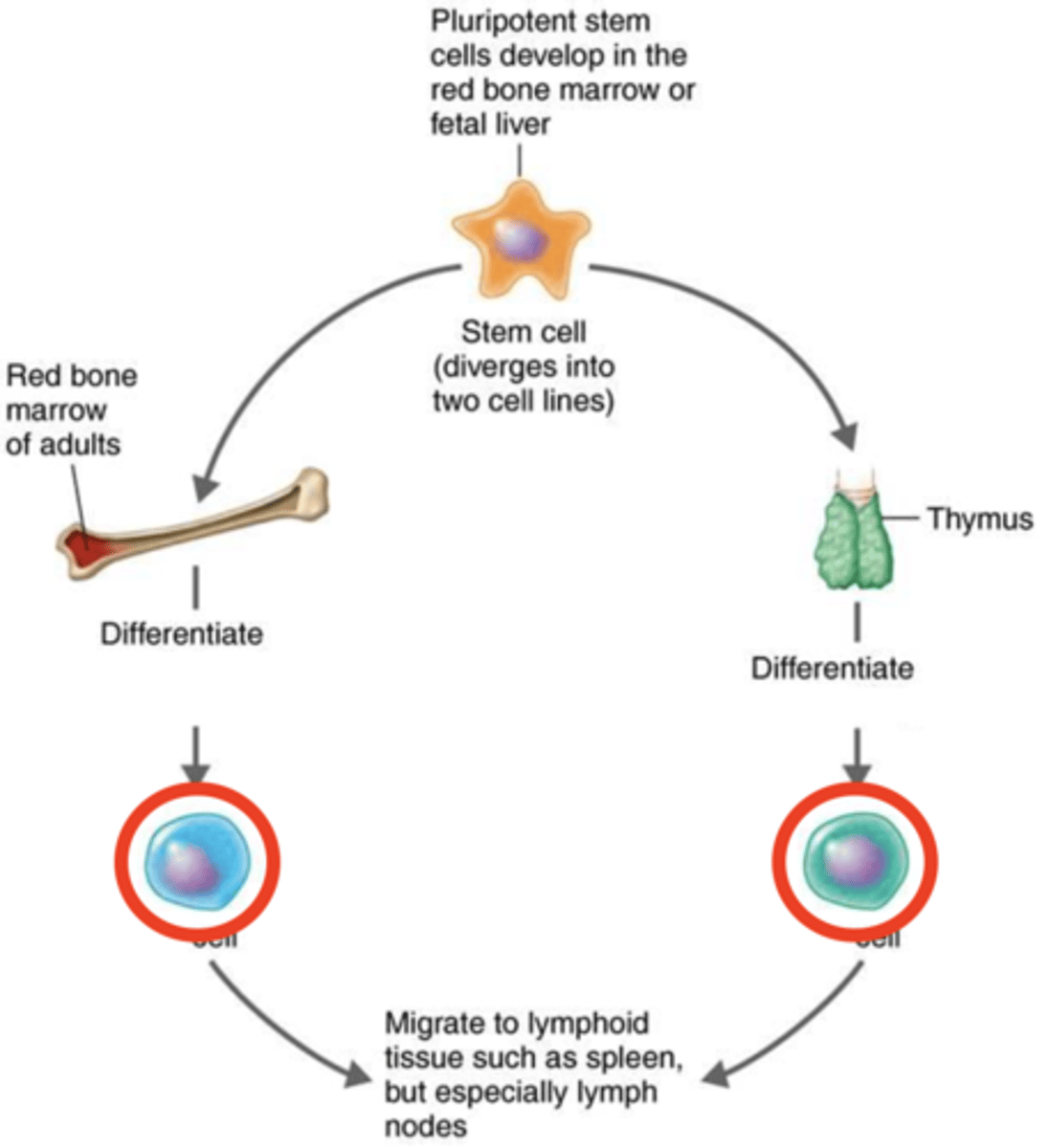
stem cells
Immunity
Cells that can differentiate into different types of cells such as into B cells and T cells
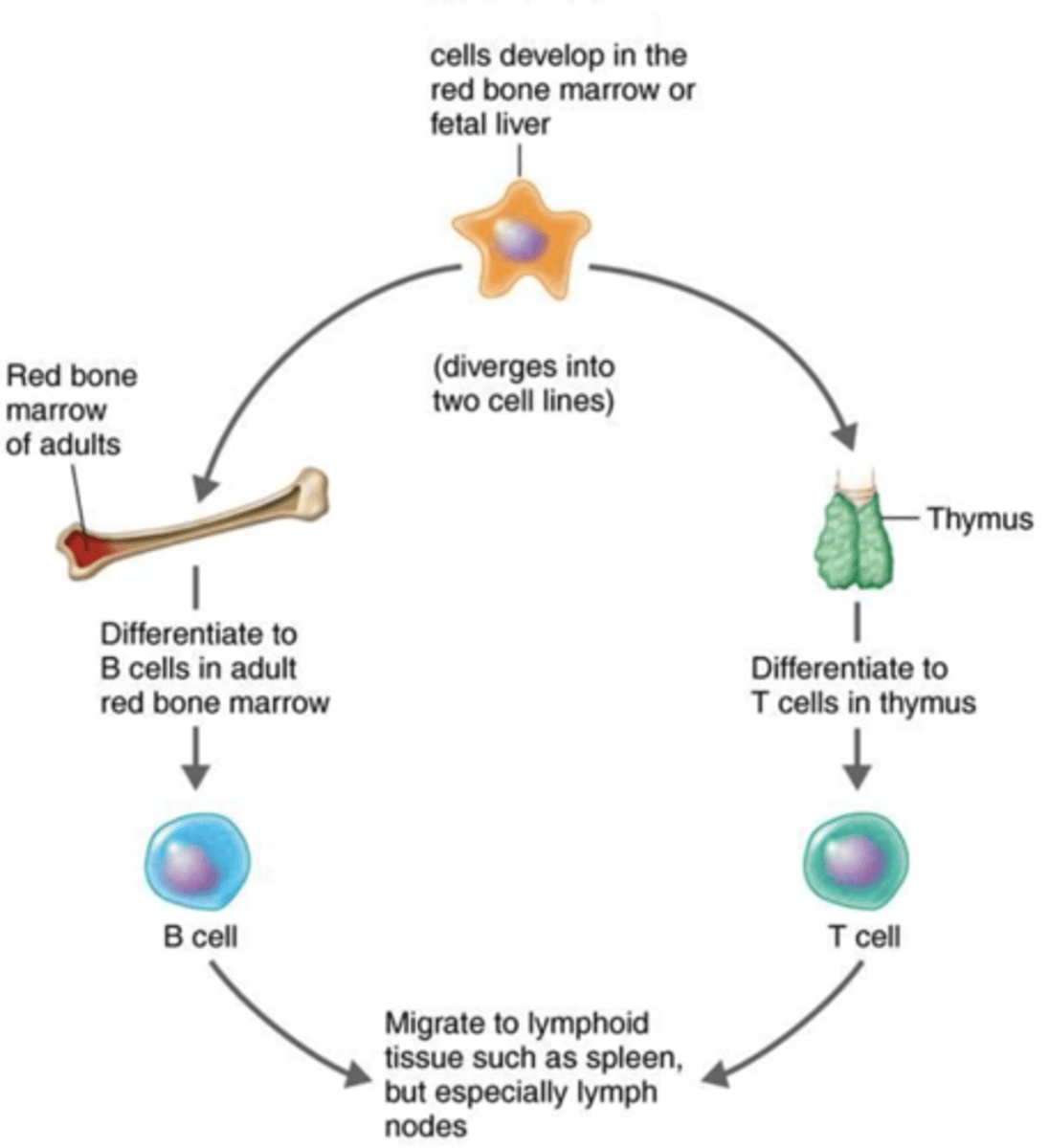
T cells, B cells
Adaptive immunity
Once mature, these lymphocytes migrate to lymphoid organs such as to the lymph nodes to perform their specific functions
adaptive immunity
Immunity
2 different branches:
1. Humoral immunity
2. Cellular immunity
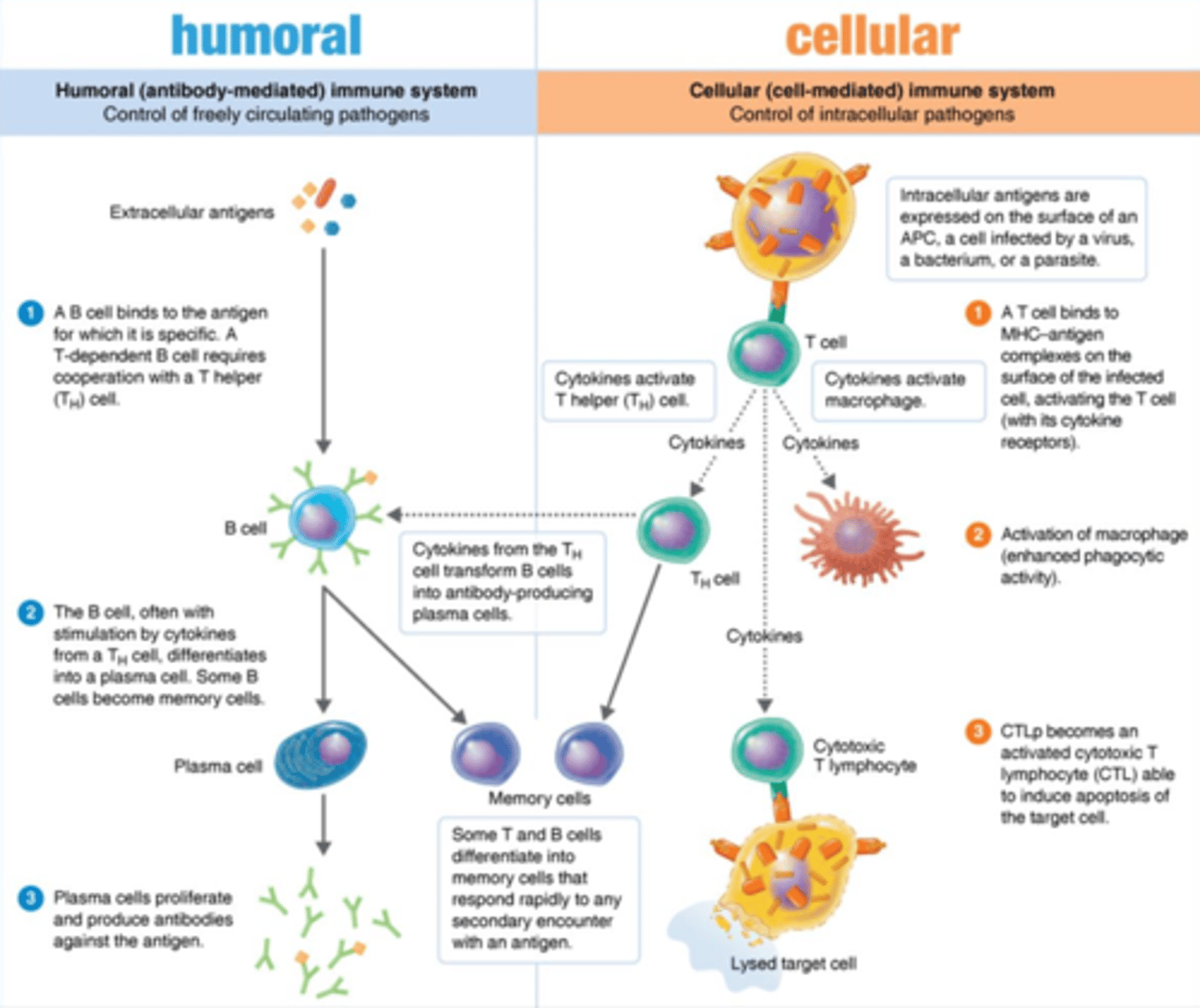
humoral immunity
Adaptive immunity
Branch that includes:
1. B cells
2. Plasma cells
3. Memory B cells
4. Antibodies
cellular immunity
Adaptive immunity
Branch that includes:
1. T cells
2. T helper cells (Th1, Th2)
3. Cytotoxic T cells (CTLs)
humoral immunity
Adaptive immunity
Branch that targets pathogens in circulation or outside the cell
cellular immunity
Adaptive immunity
Branch that destroys pathogens inside the cell
false
Cellular immunity
True or false?
Intracellular antigens are exposed to antibodies
yes
Cellular immunity
Yes or no?
Do some infected cells need to be detected and killed to clear some infections?
antigens
Adaptive immunity
- Proteins or polysaccharides recognized by the immune system
- Usually components of invading microbes or foreign substances
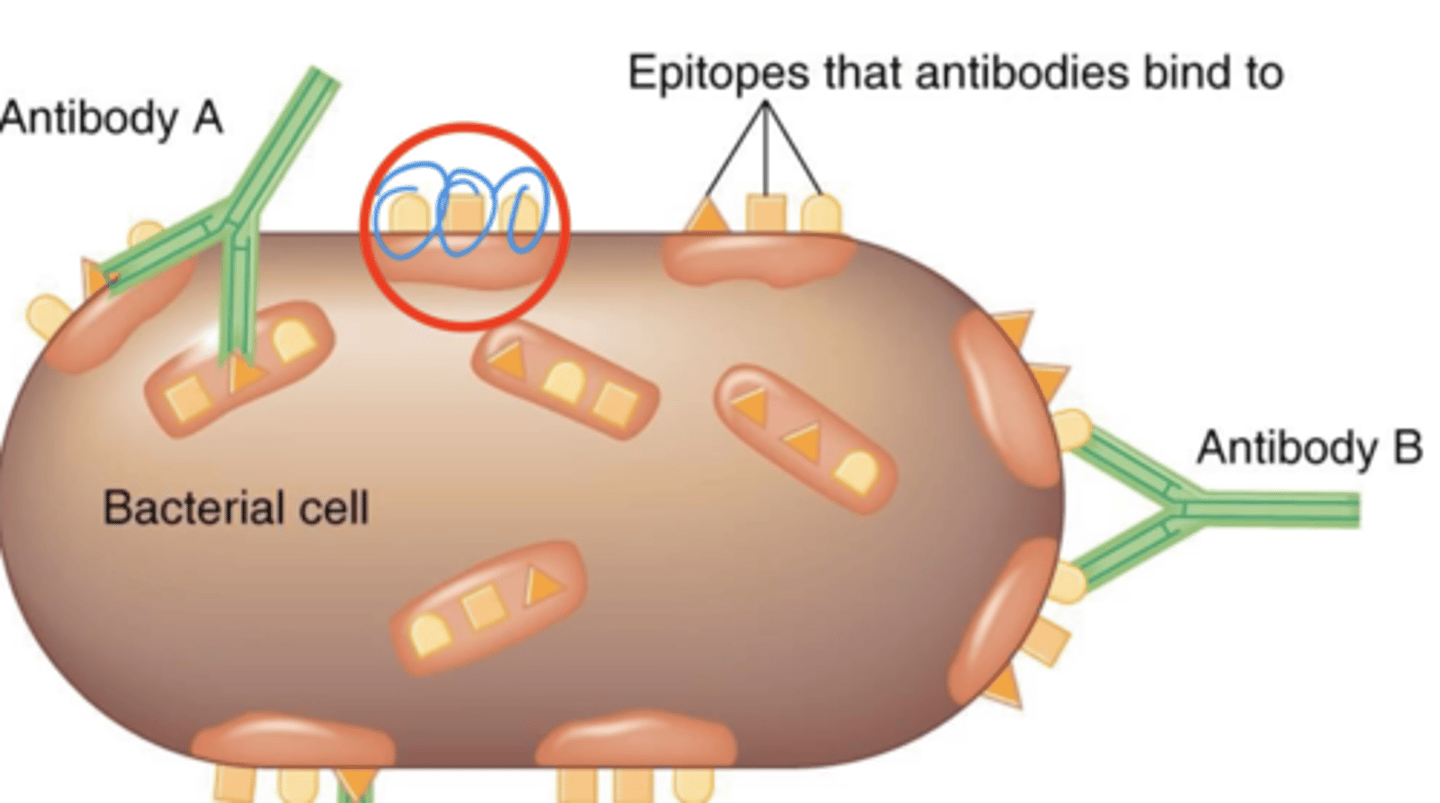
epitope
Adaptive immunity
- Subset of a particular type of antigen
- Where an antibody, T cell receptor (TCR), or B cell receptor (BCR) binds
- Aka antigenic determinants
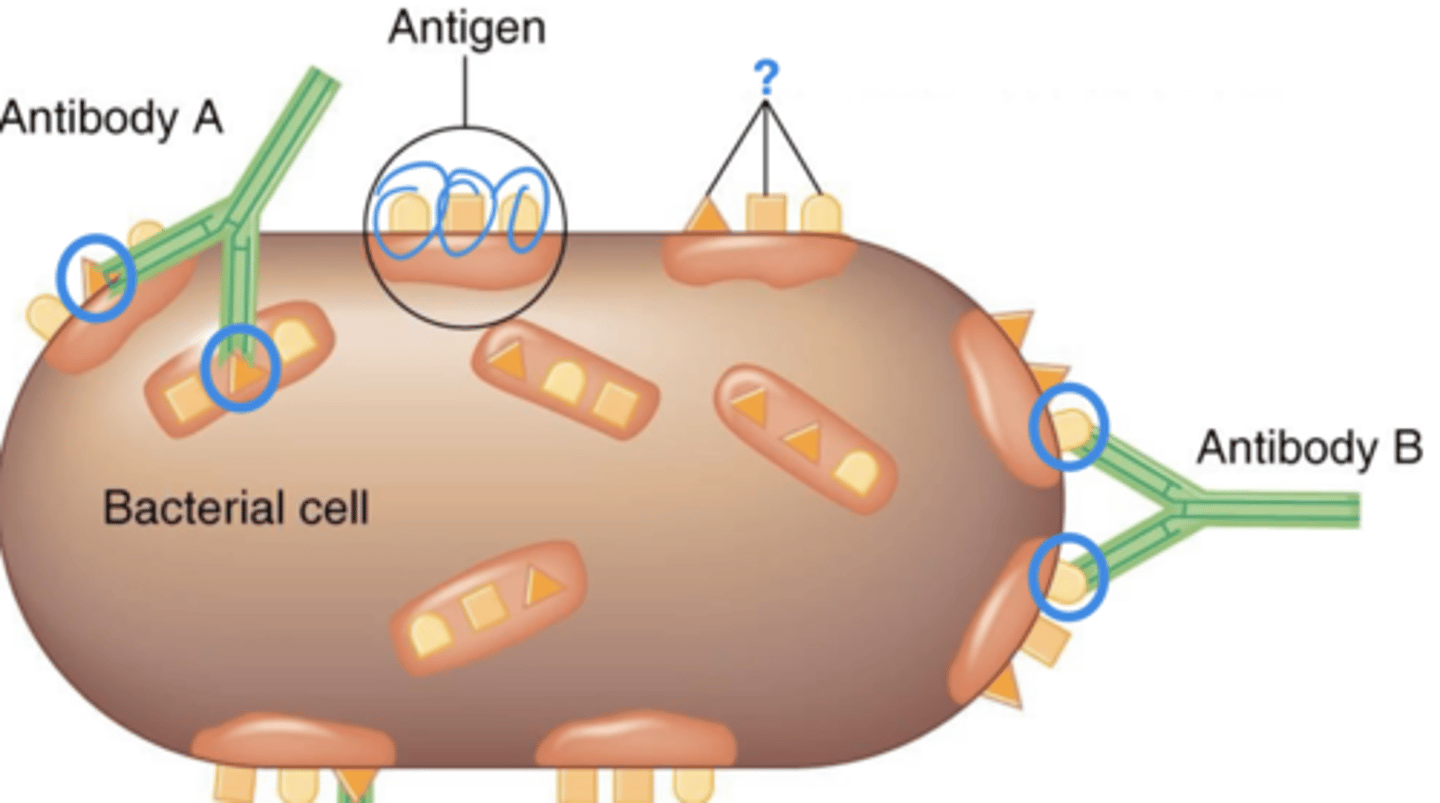
antigenic determinants
Adaptive immunity
Also called epitopes
antibodies
Humoral immunity
- Immunoglobulins (Ig) that bind to antigens
- Major effector molecules of humoral immunity
- Major components:
1. Structures
2. 5 classes
3. 5 effects of binding
proteins
Which macromolecules are globulins, such as in antibodies?
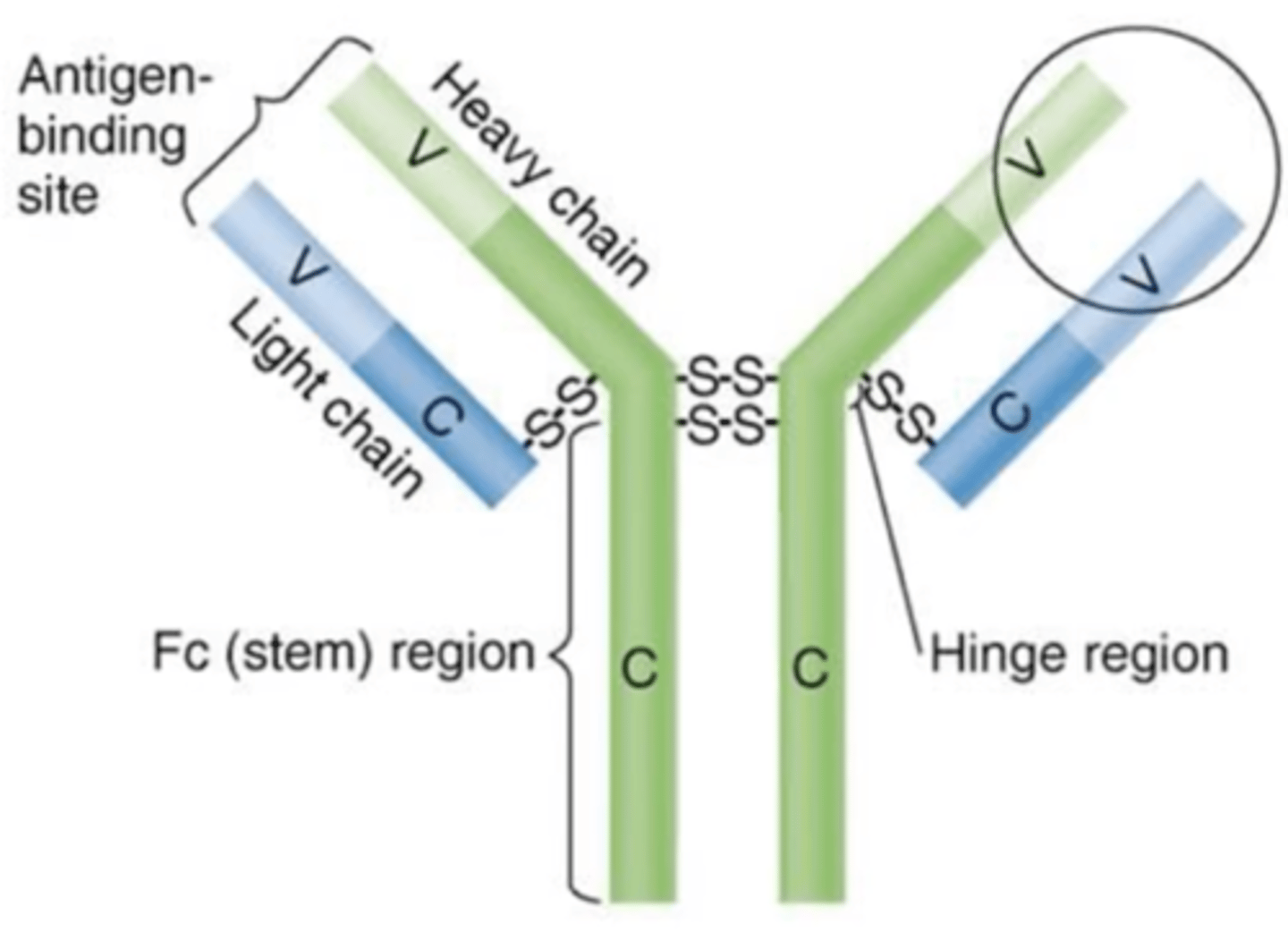
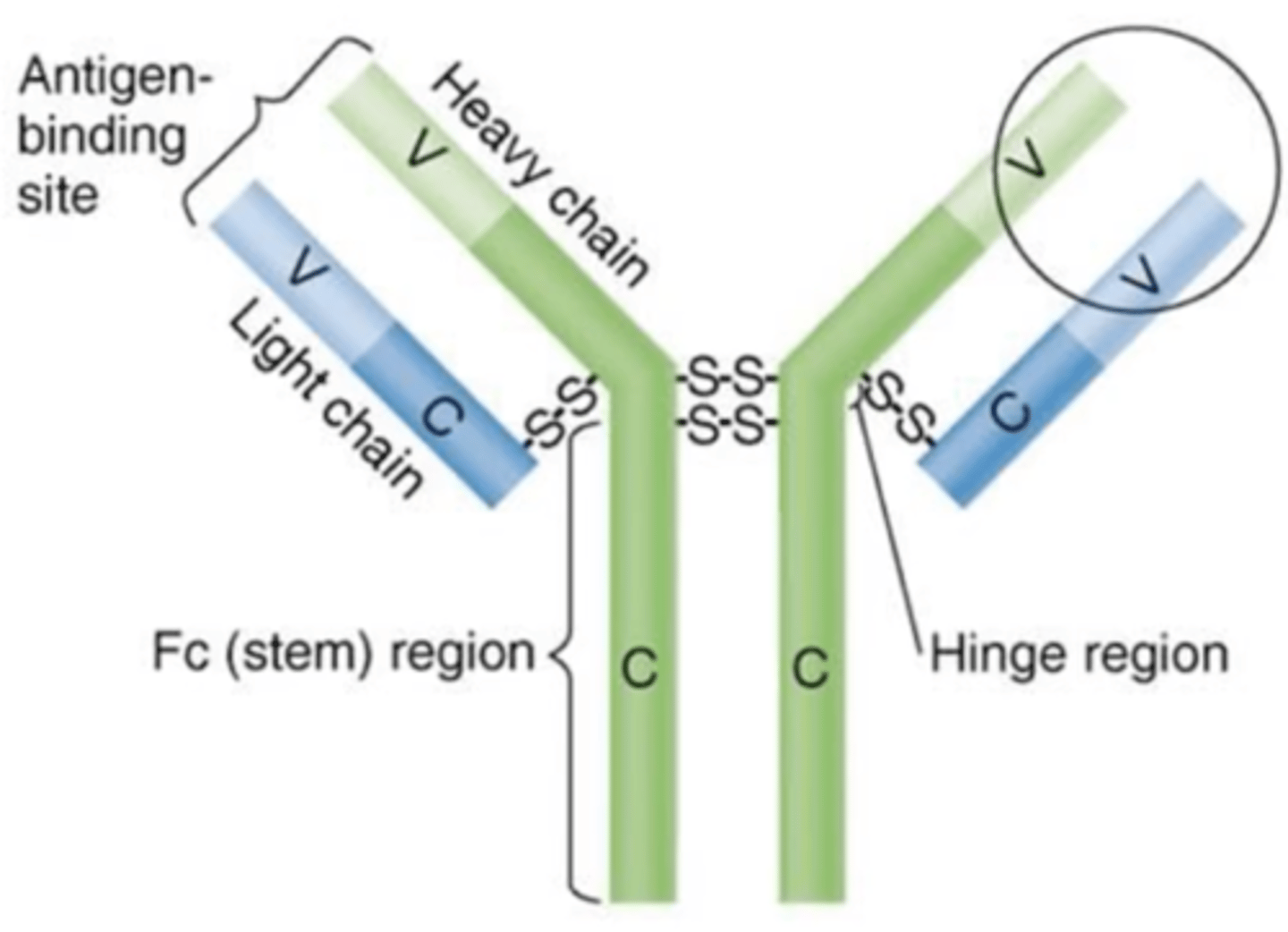
immunoglobulin
Antibody structure
What does Ig (antibody) stand for?

light, heavy, disulfide
Antibody structure
Fill in the blank:
Antibodies contain 2 identical __________ and __________ chains that are joined by __________ bonds.
light chains
Antibody structure
Which structures are these?
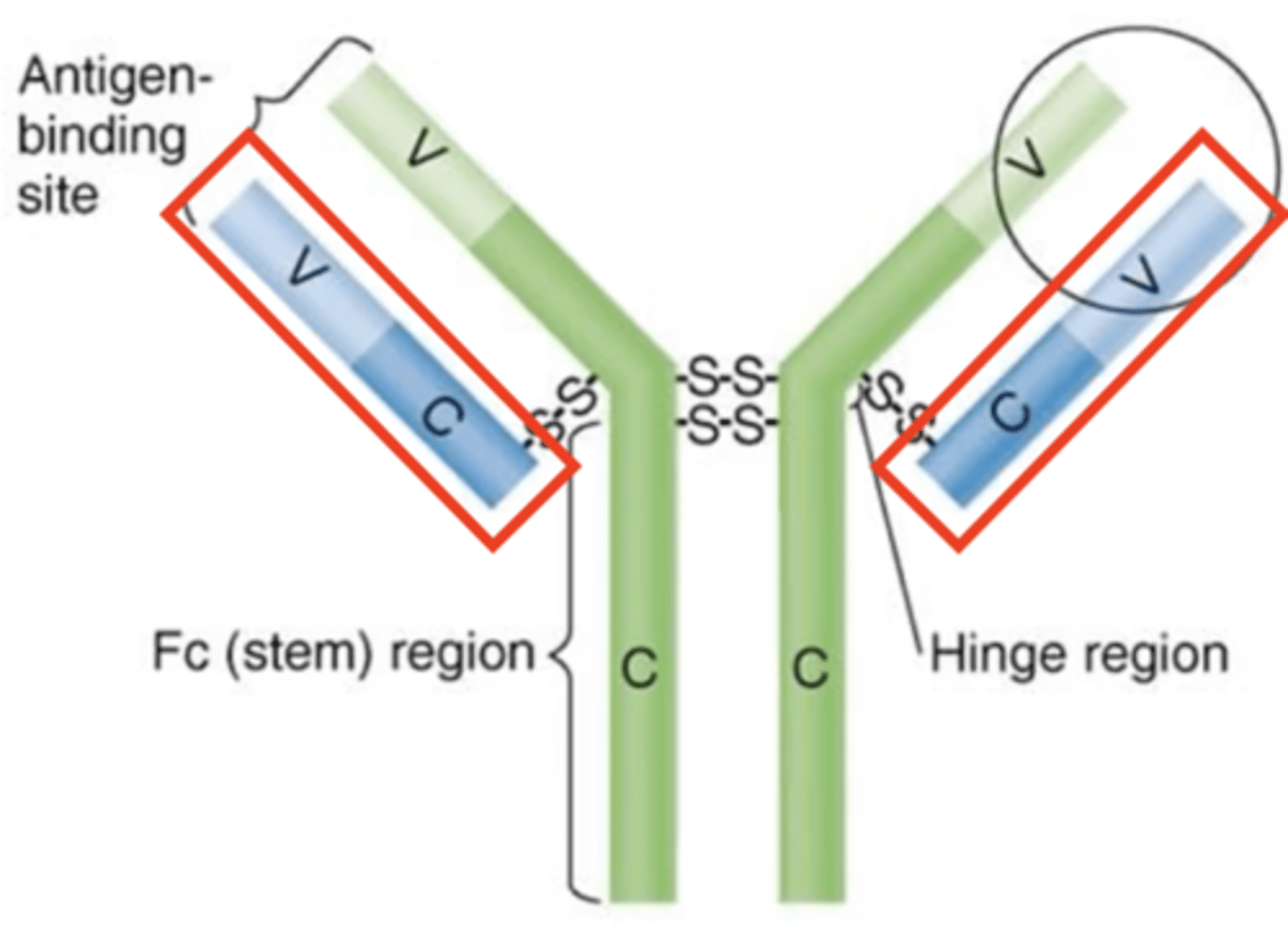
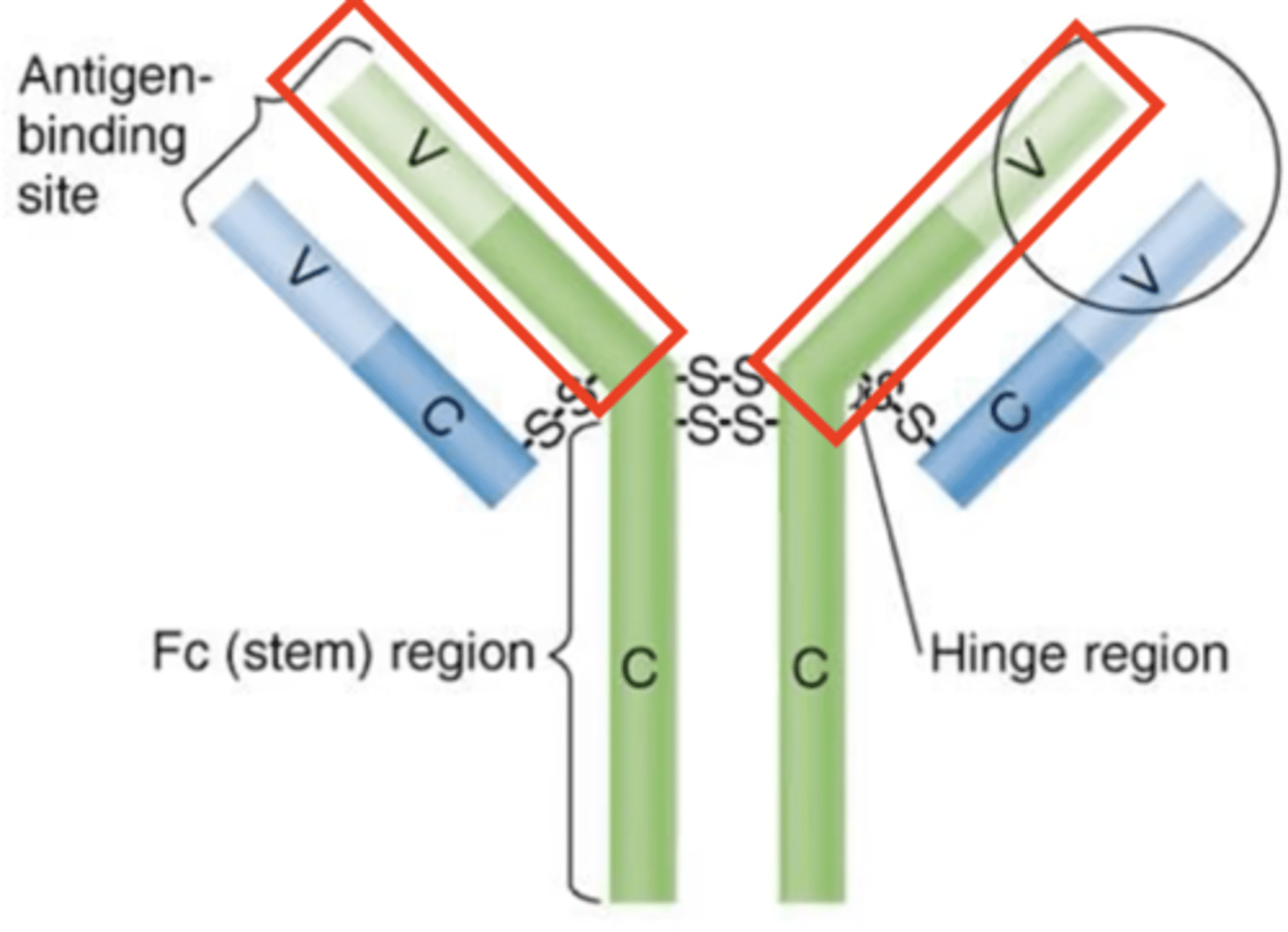
heavy chains
Antibody structure
Which structures are these?
disulfide bonds
Antibody structure
Which structures are these?
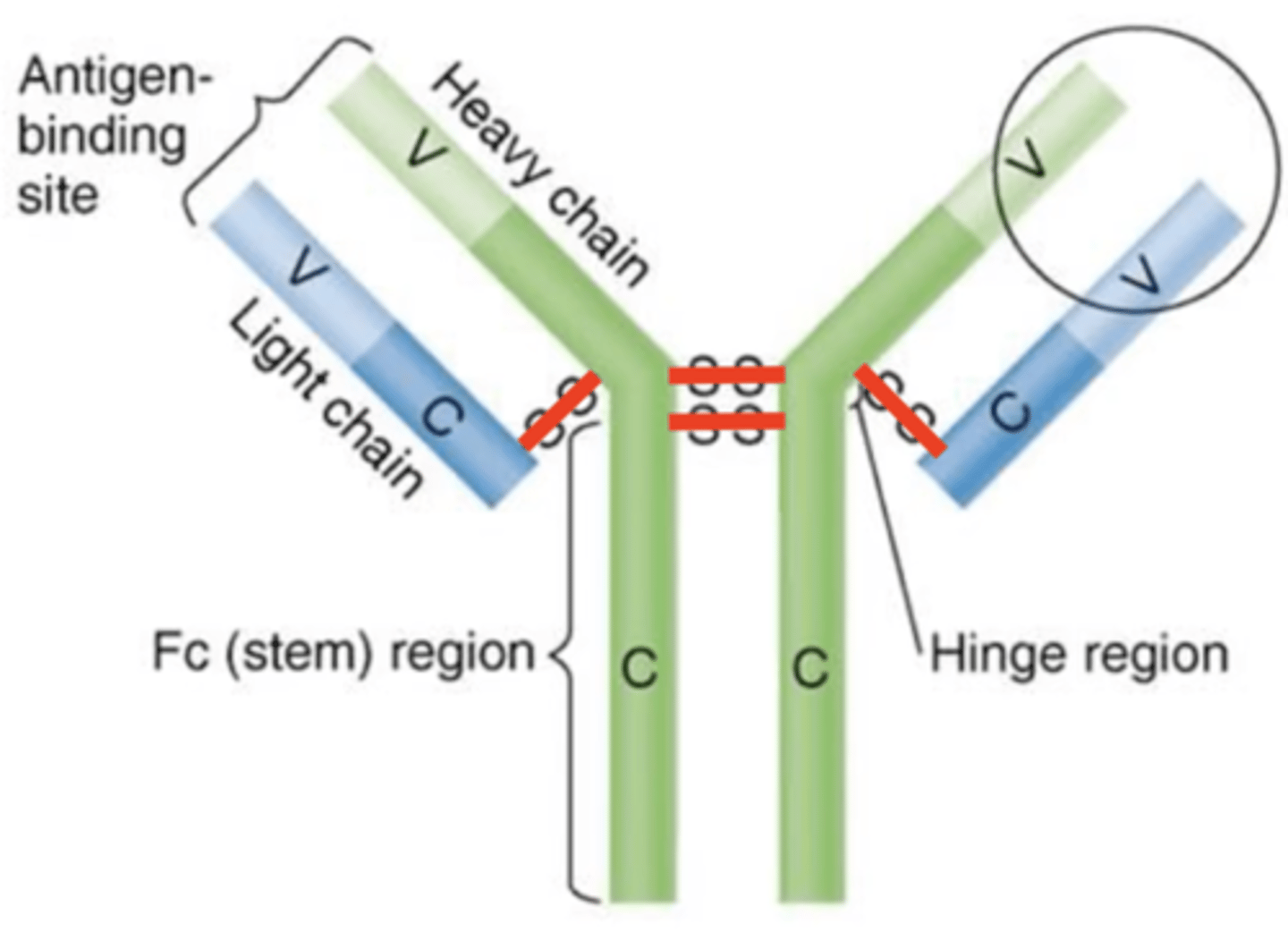
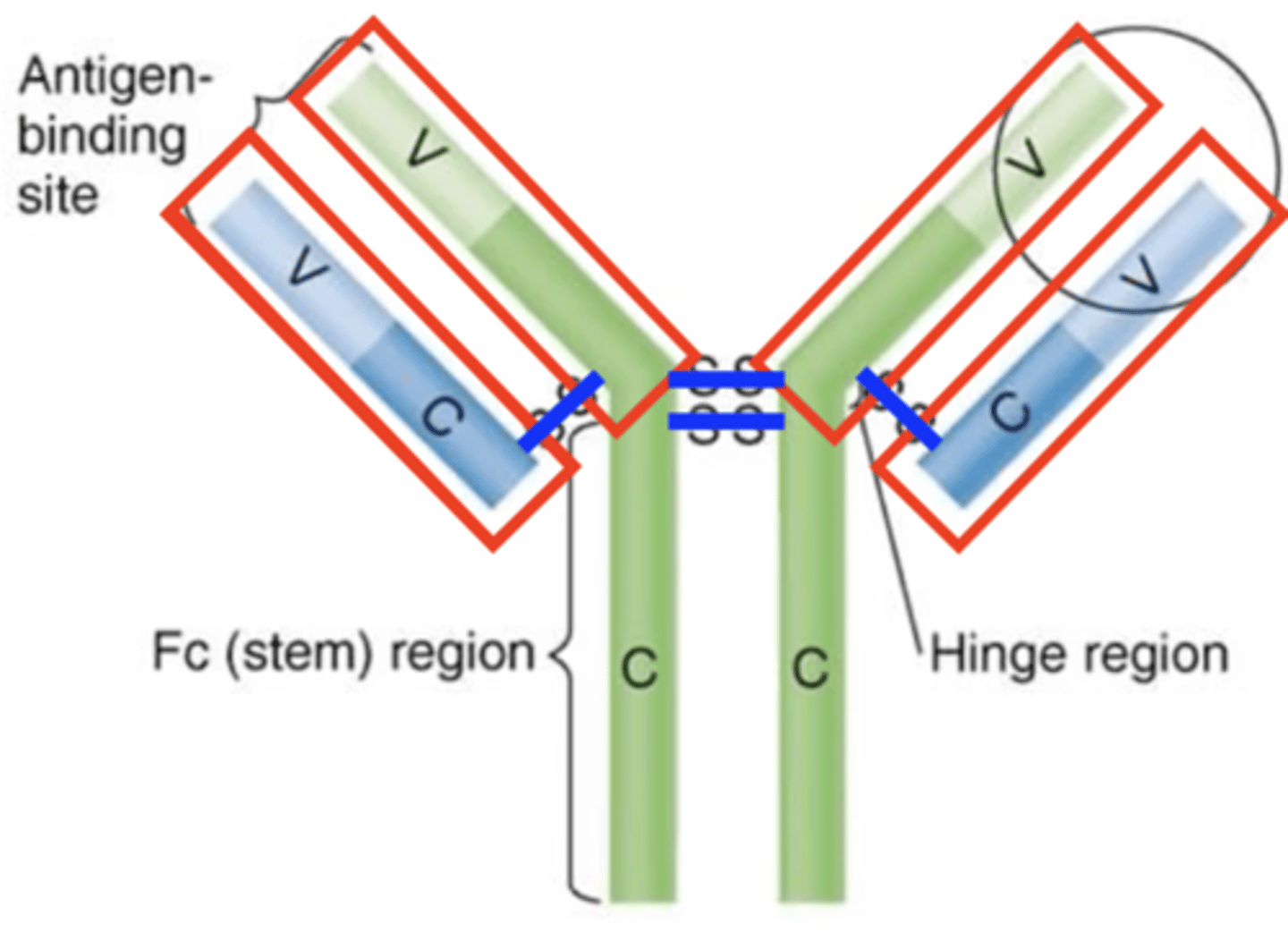
Fab region
Antibody structure
Which structures are these?
variable (V) regions
Antibody structure
- Ends of Fab regions
- Contain antigen-binding sites that bind to epitopes
antigen-binding sites
Antibody structure
- Ends of variable (V) regions
- Bind to epitopes
epitope
Antibody structure
- Antigen subunit
- Part of an antigen that binds to an antibody's antigen binding site
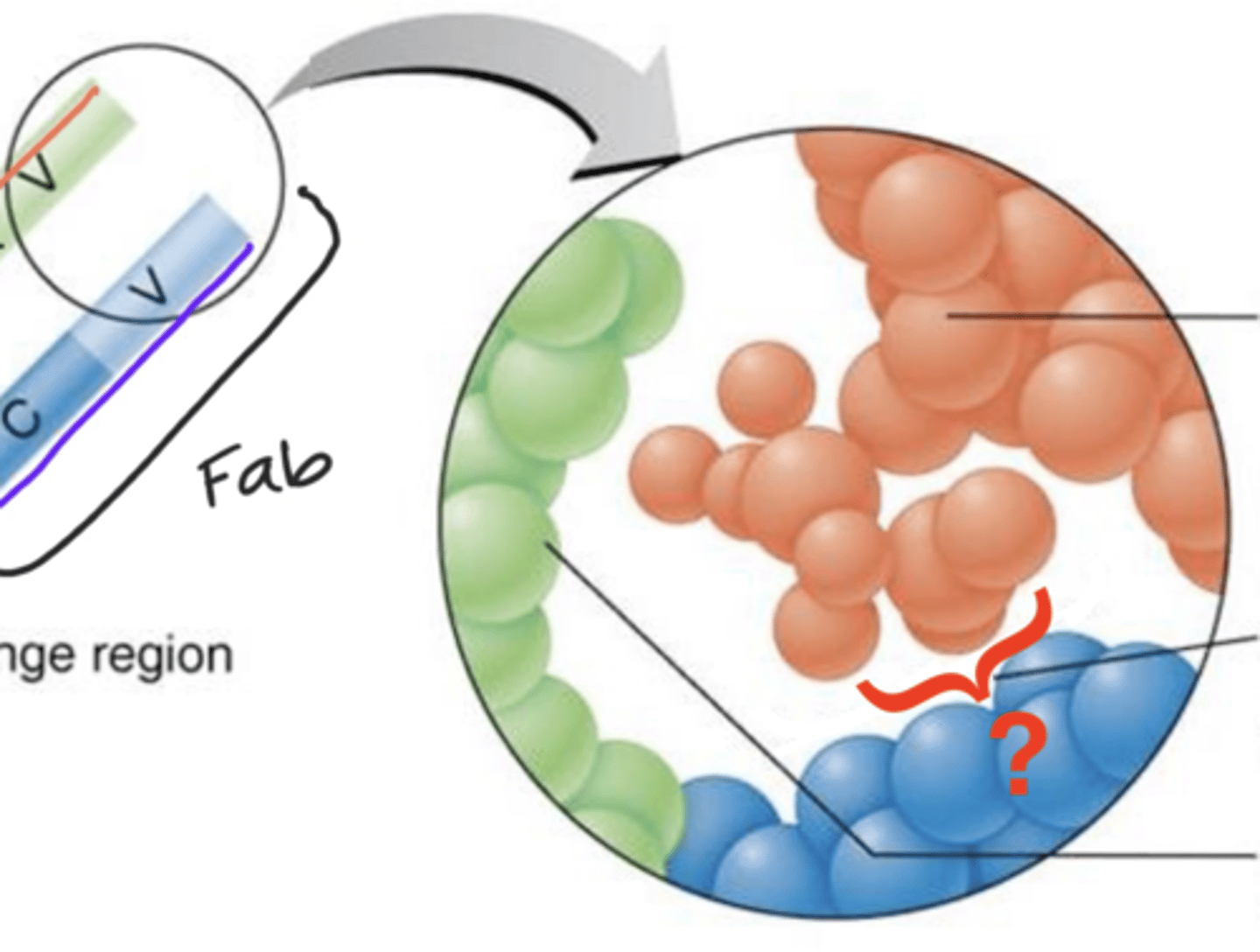
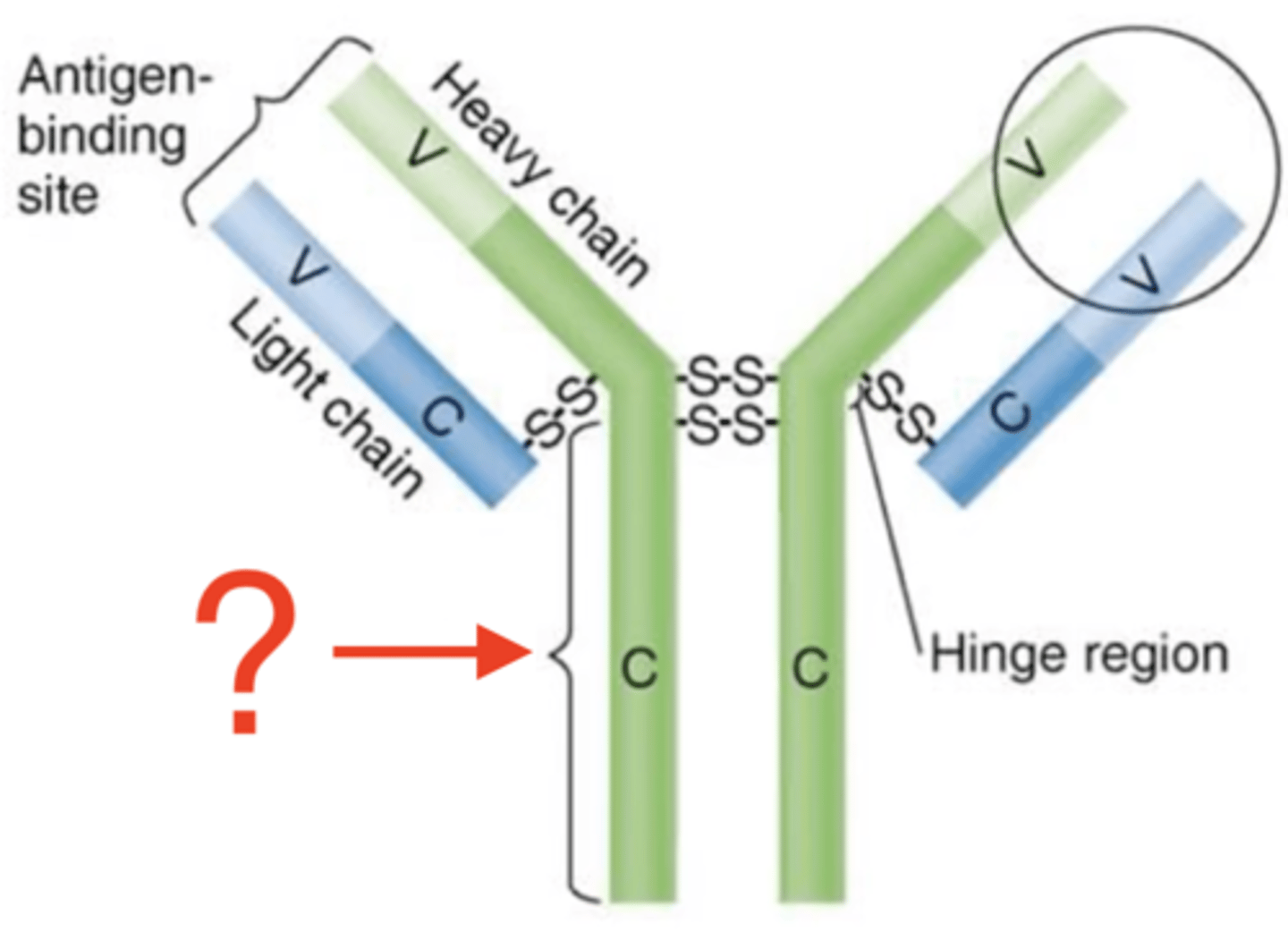
constant (C)
Antibody structure
- Includes heavy chains and Fc regions
- Some bind to receptors
- Structure is determined by 1 of 5 antibody classes
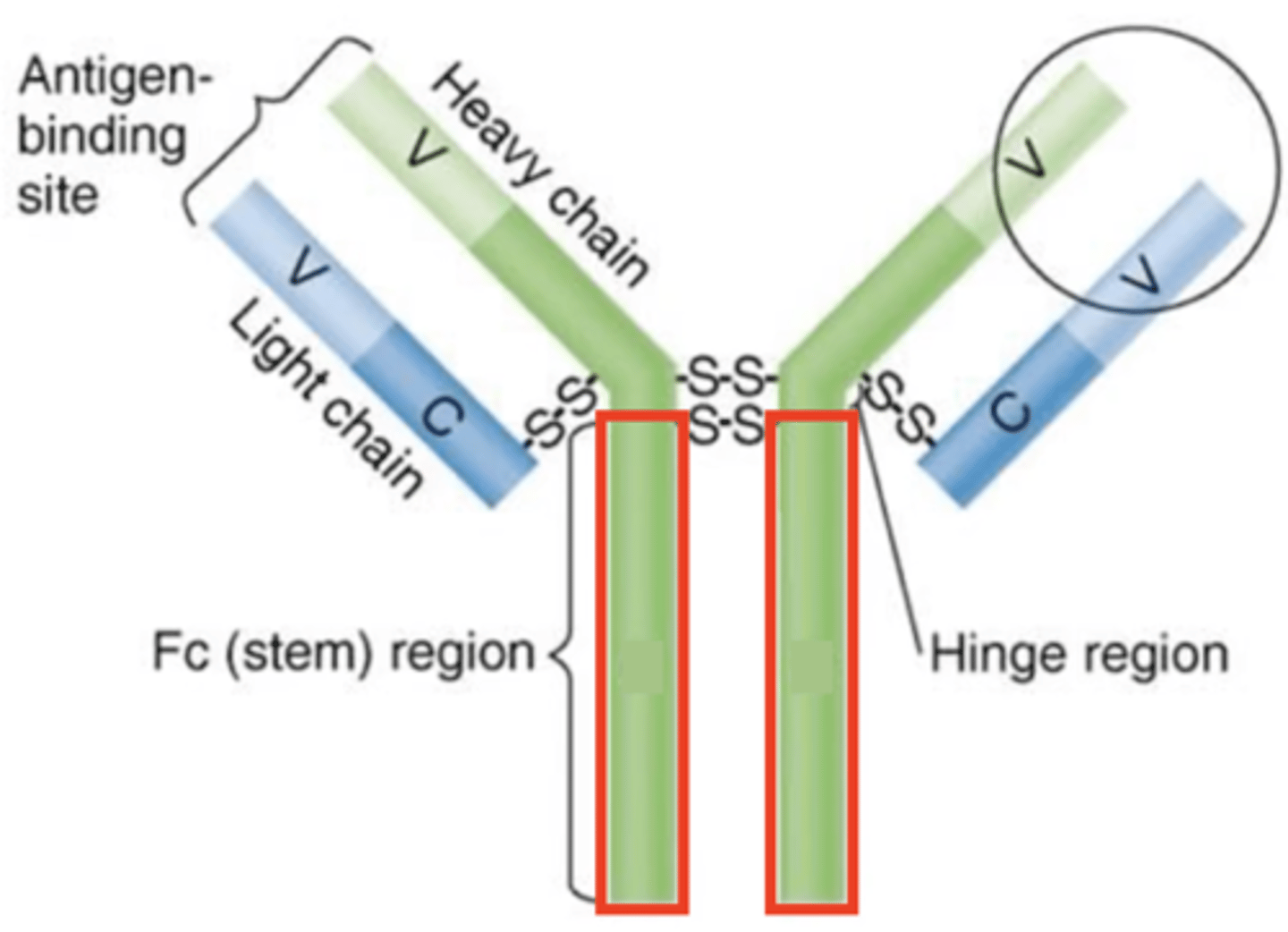
Fc regions
Antibody structure
- Tail ends of constant (C) regions
- Some bind to receptors
- Determined by 1 of 5 antibody classes
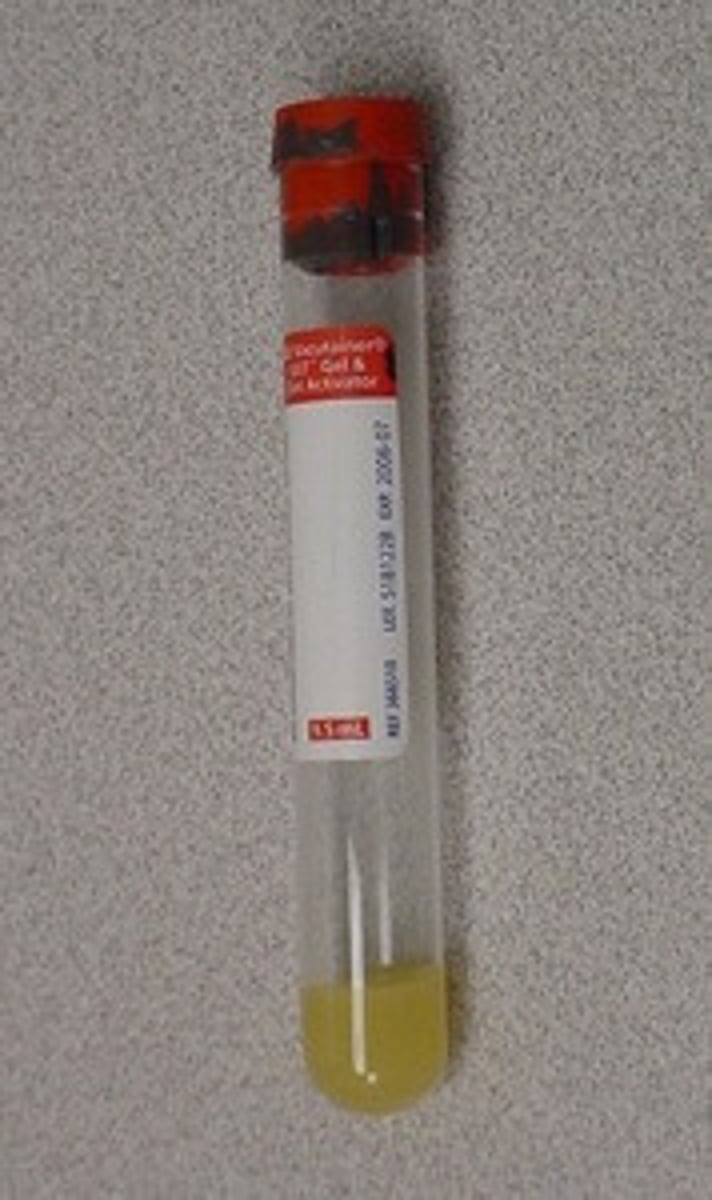
serum
Antibody production
- Blood plasma minus erythrocytes and fibrinogen
- Part of blood that contains antibodies

IgG
Antibody class
- Monomers
- 80% of serum antibodies
- In blood, lymph, intestines
- Cross the placenta
- Trigger complements
- Enhance phagocytosis
- Neutralize toxins and viruses
- Half-life = 23 days

2
Antibody class
How many antigen-binding sites do IgG antibodies have?
IgG
Antibody class
Which is the only antibody class that can cross the placenta to protect fetuses and newborns that do not produce their own?

IgM
Antibody class
- Pentamers
- 5-10% of serum antibodies
- In blood, lymph, B cells
- Involved in complement activation
- Involved in agglutination
- First antibodies produced in response to infection
- Half-life = 5 days
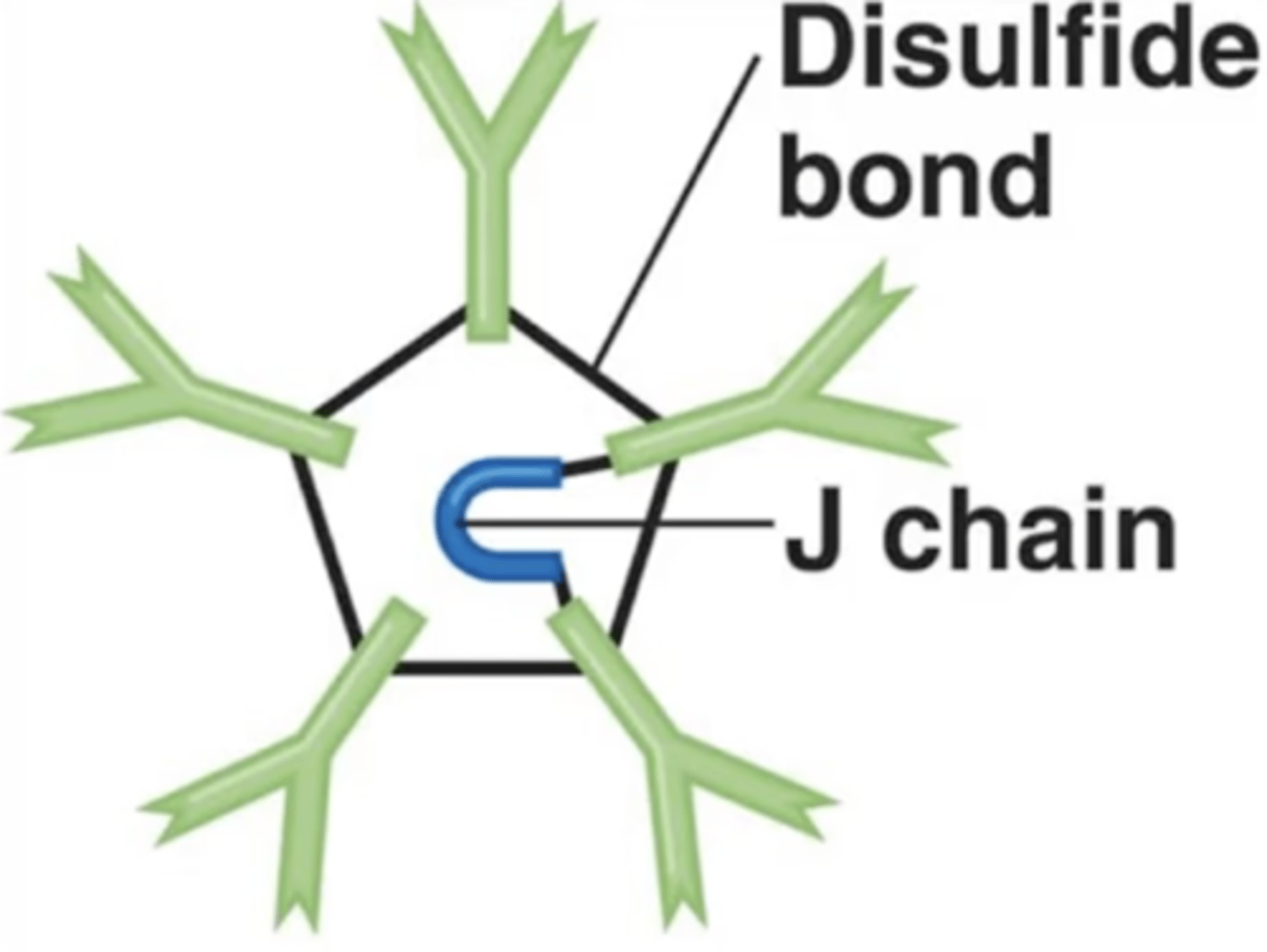
IgM
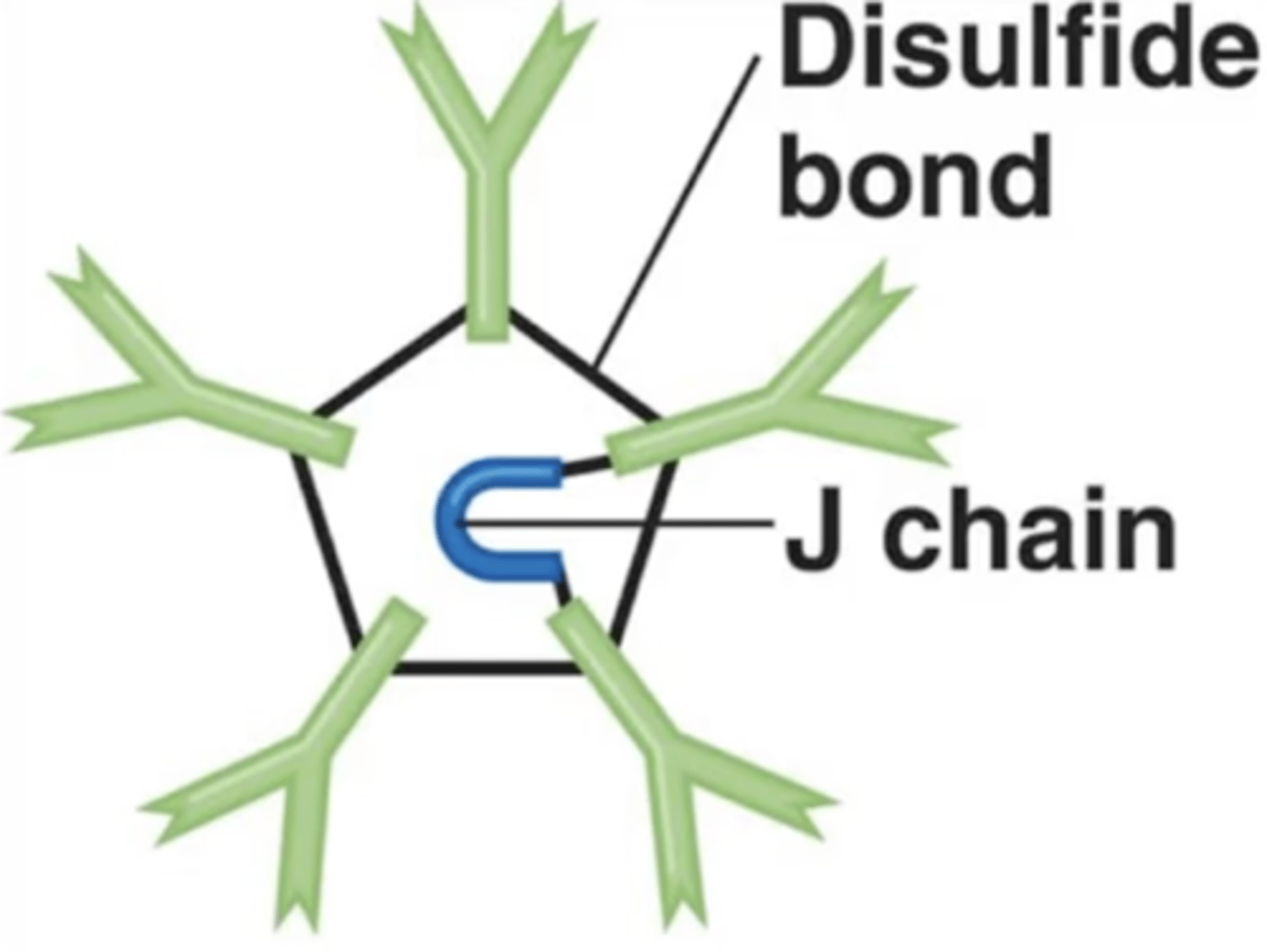
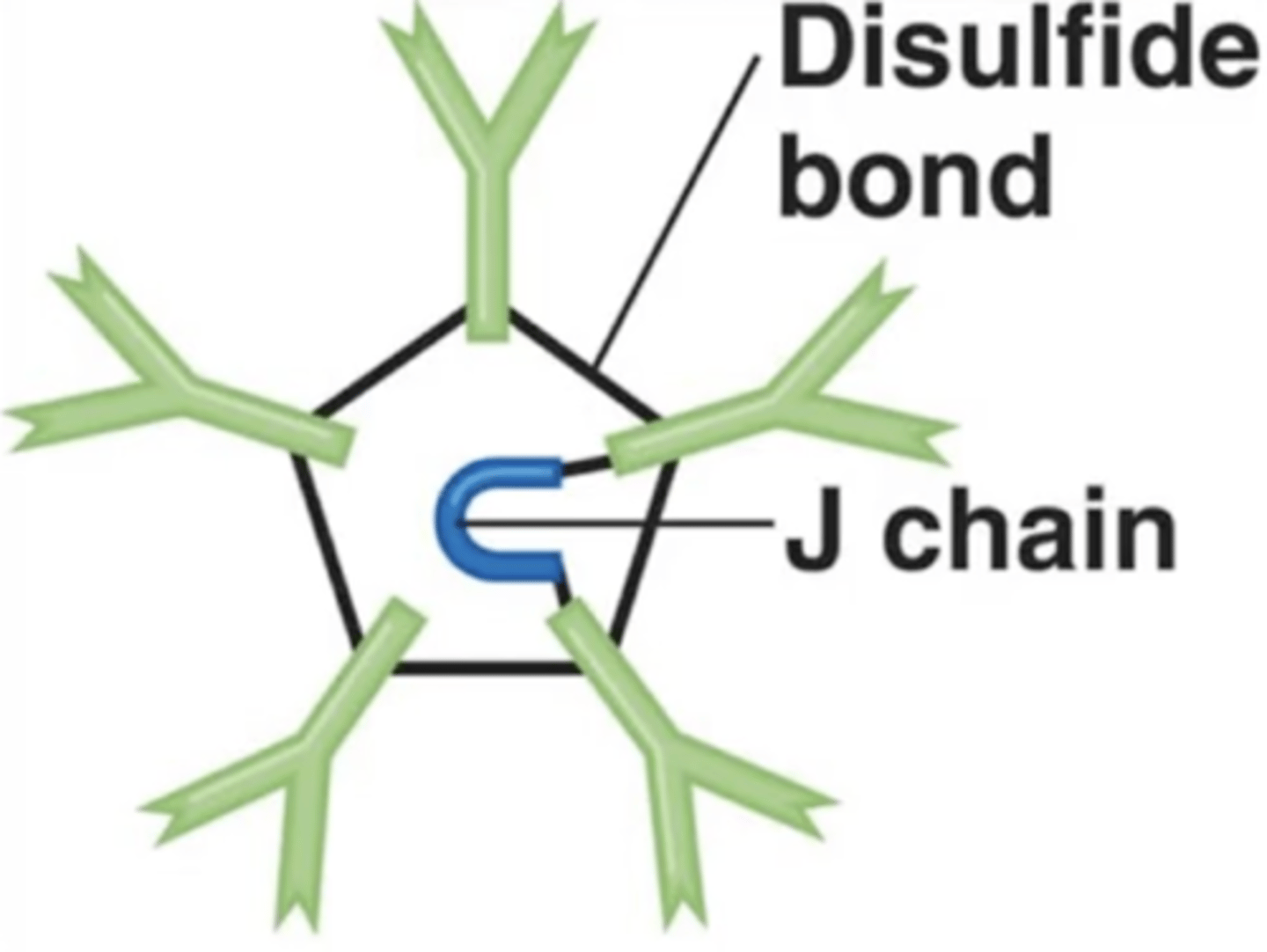
Antibody class
Which antibody class is this?
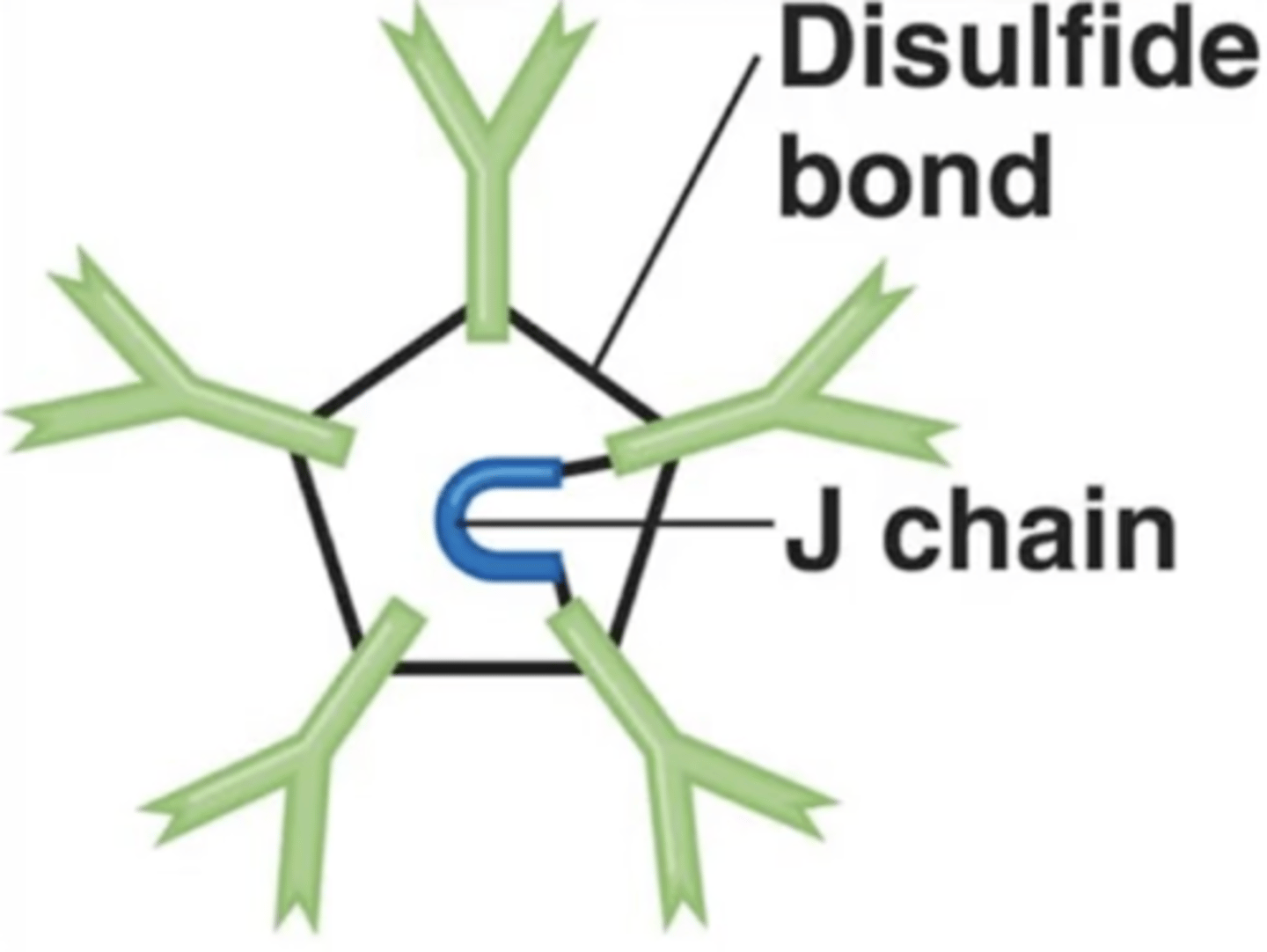
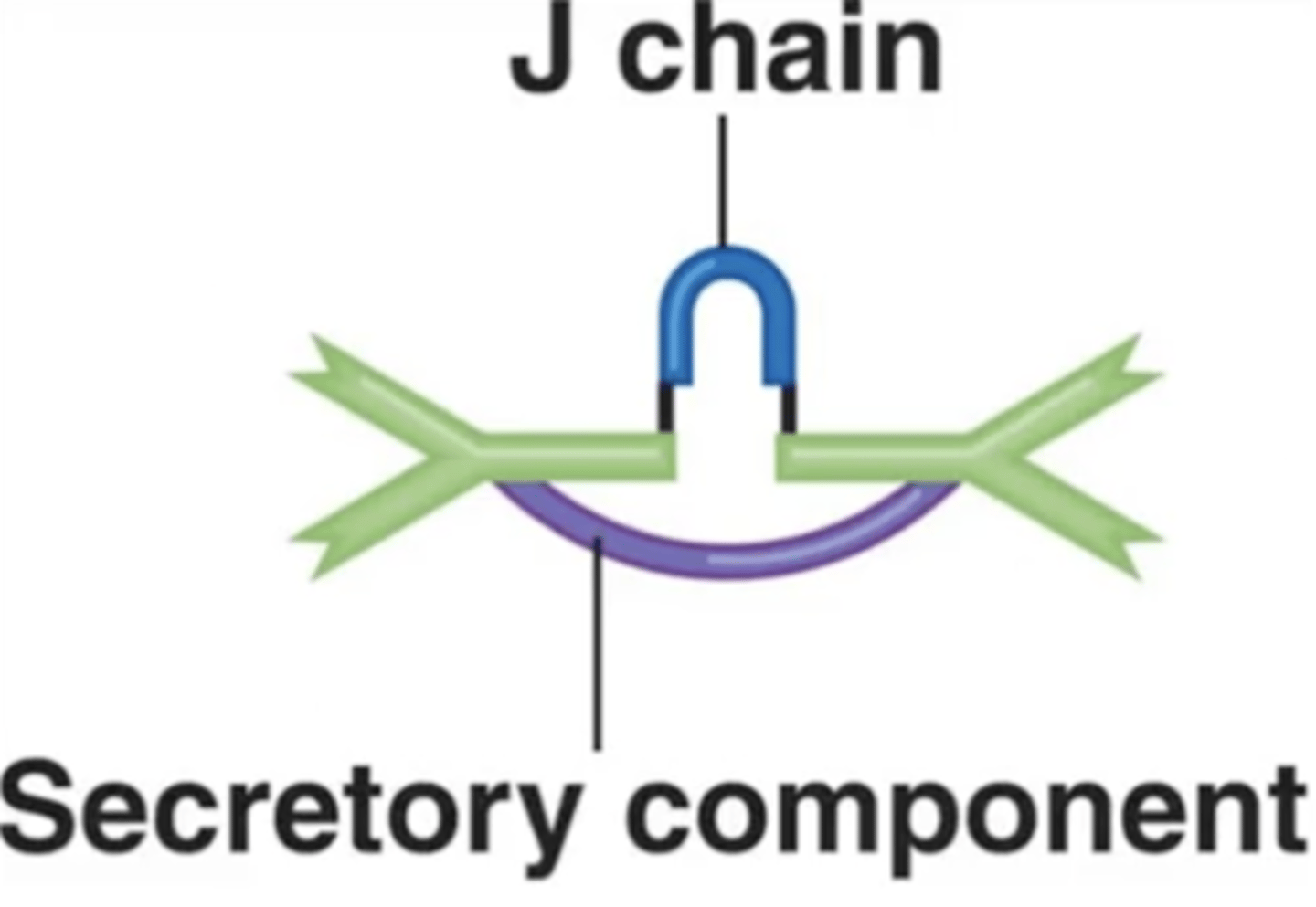
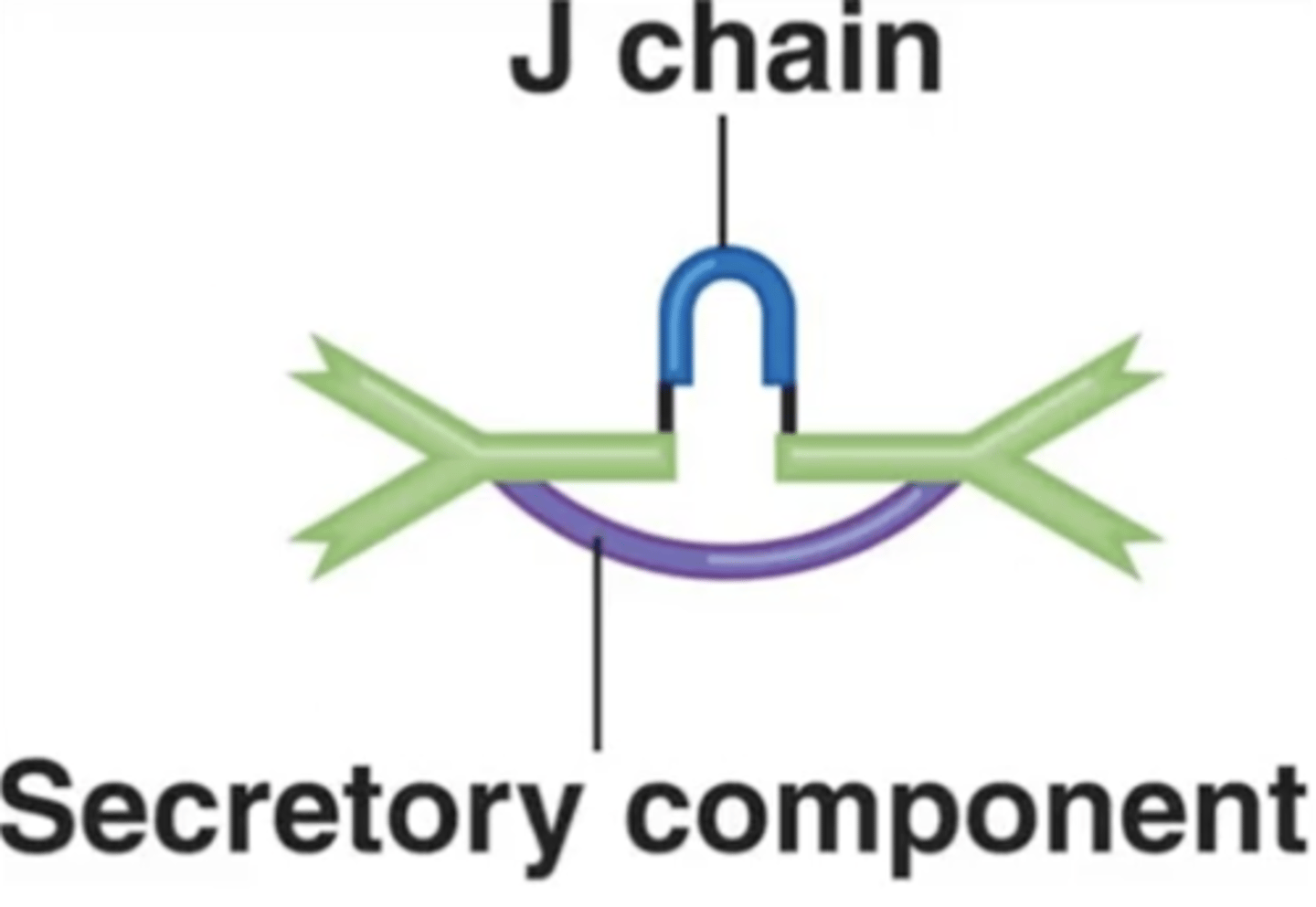
J chains
Antibody class
Polypeptides that hold together monomers on IgM and IgA antibodies
10
Antibody class
How many antigen-binding sites do IgM antibodies have?
IgM, agglutinate
Antibody class
Fill in the blank:
_____ are the first antibodies released to _______________, or "clump," viruses and bacteria because they can bind to many antigens.
IgM
Antibody class
Which is the first antibody class produced in response to an infection?
IgM
Antibody class
Contains pentamers, which are 5 monomers held together by a polypeptide called a J chain.
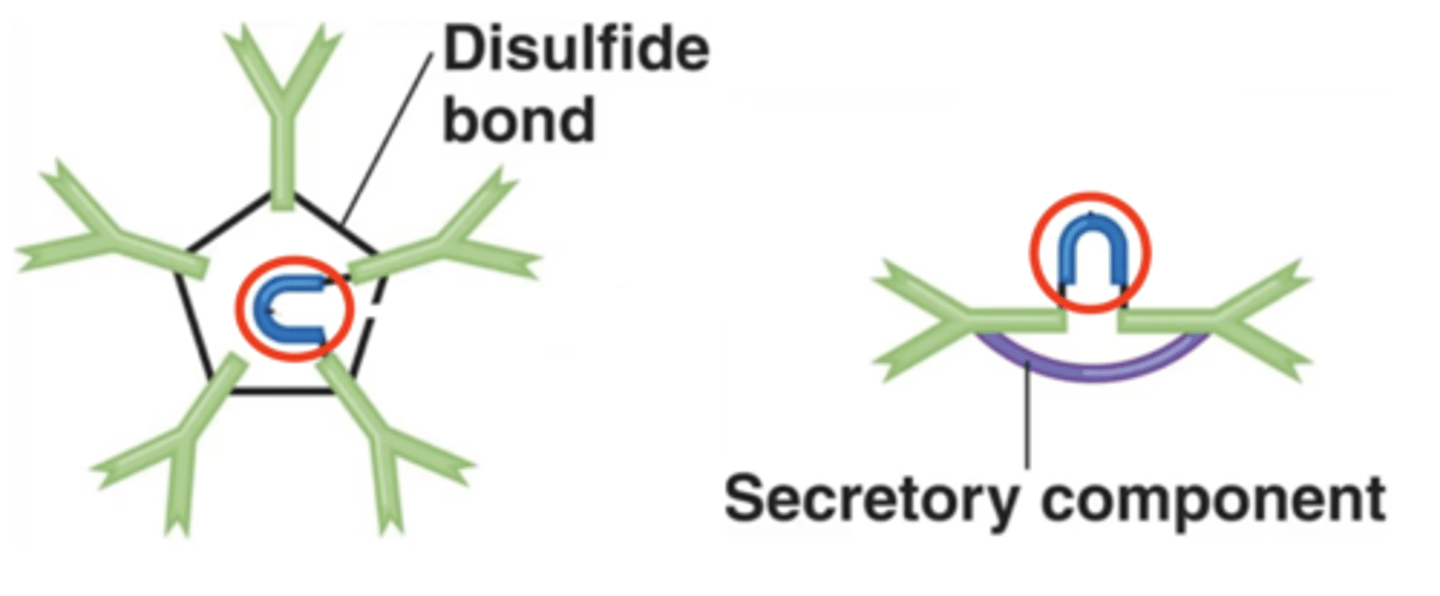
IgA
Antibody class
- Monomers when in serum
- Dimers when in secretions
- 10-15% of serum antibodies
- Prevent microbes from attaching to mucous membranes
- Involved in neutralization
- Half-life = 6 days
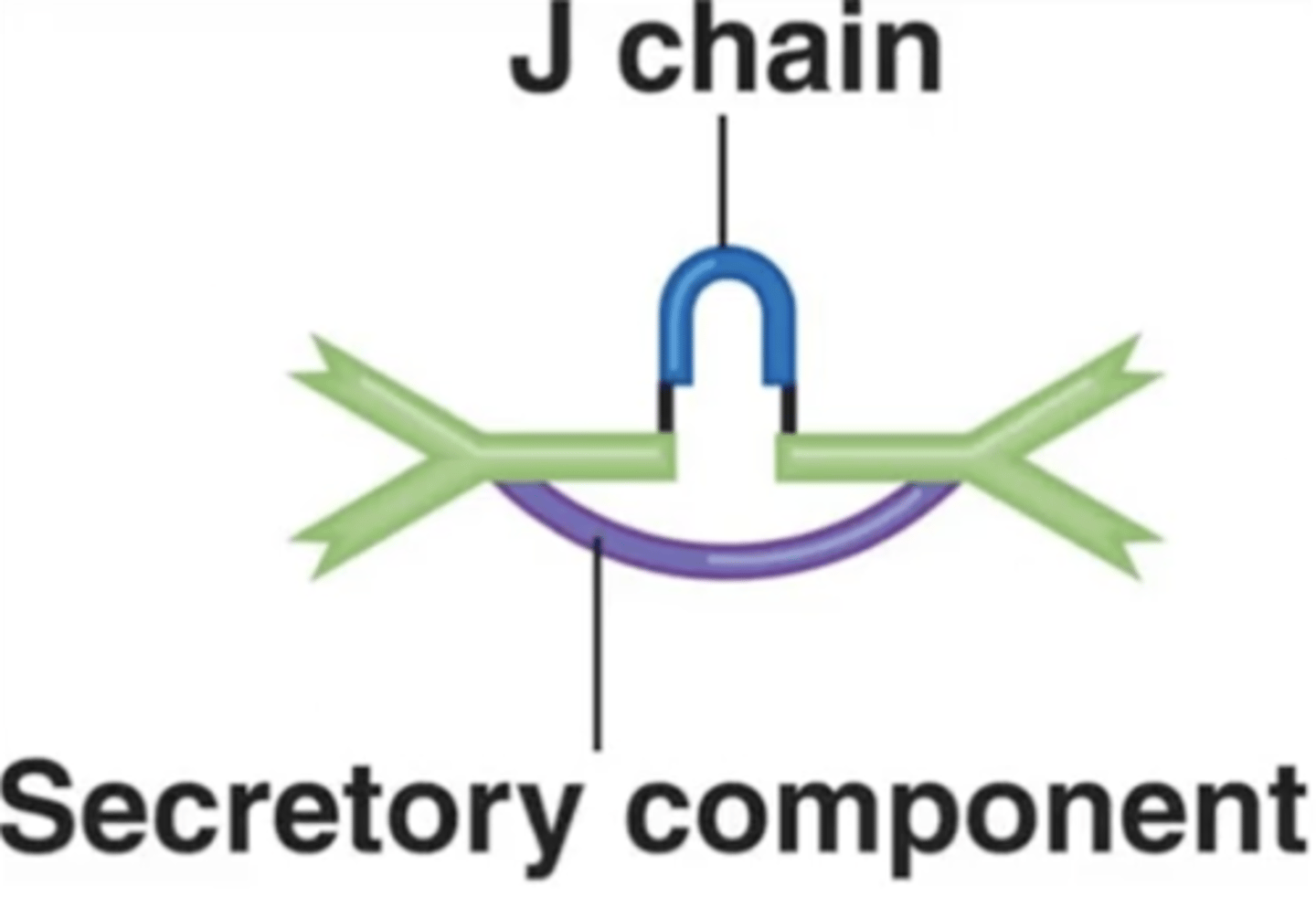
IgA
Antibody class
Which antibody class is this?
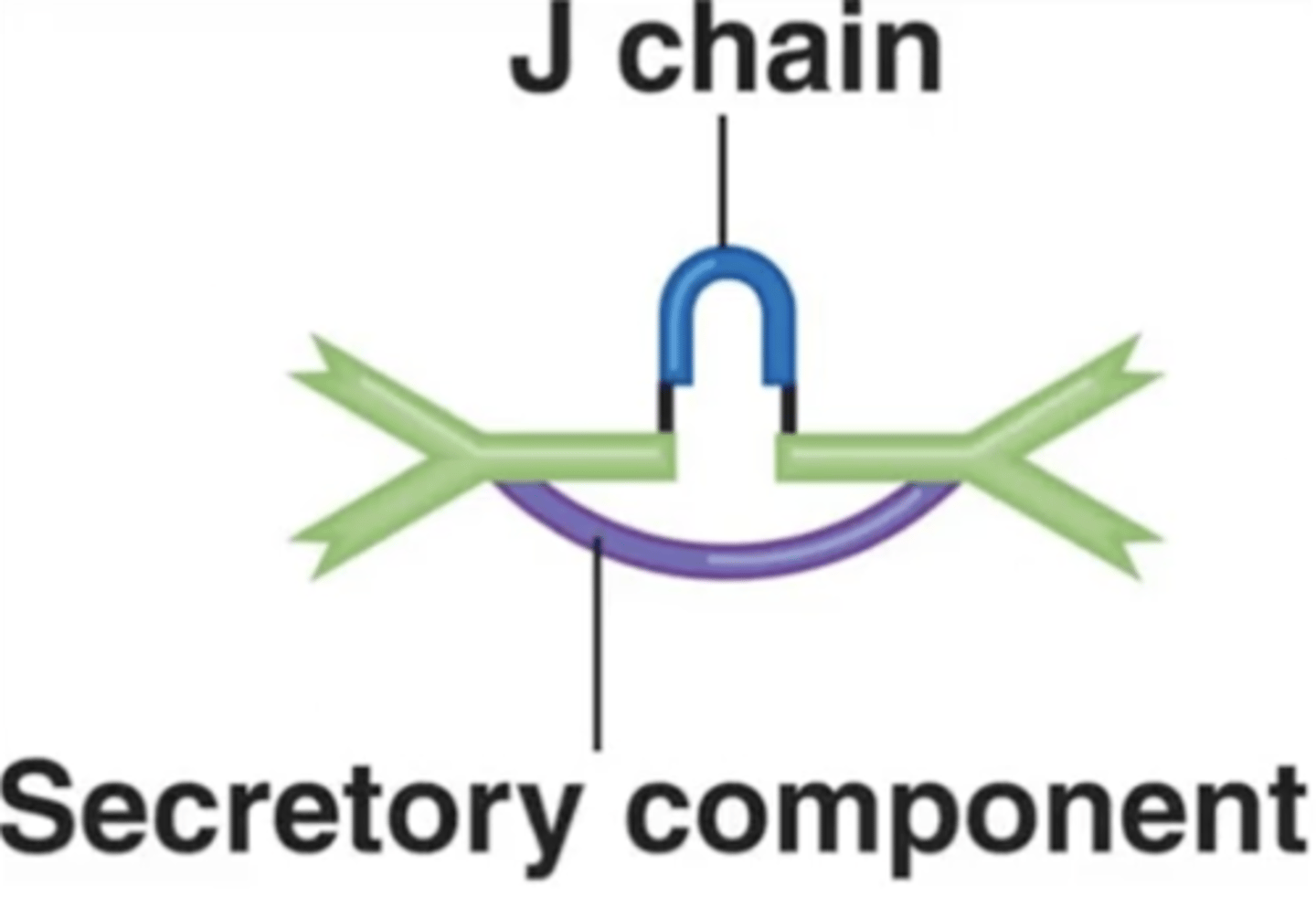
J chain
Antibody class
Which structure is this?
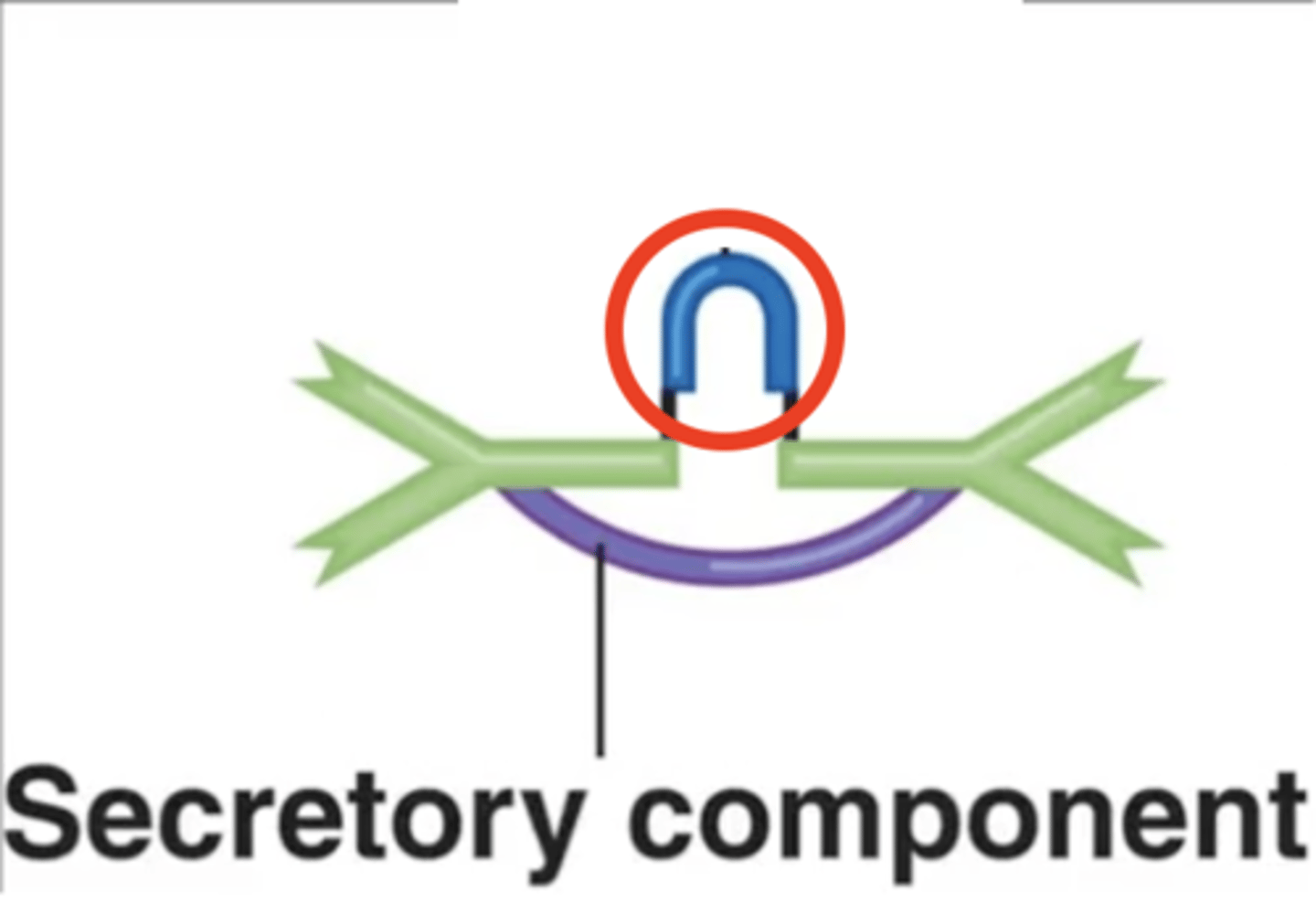
IgM, IgA
Antibody class
Fill in the blank:
J chains hold together certain antibodies' monomers such as on _____ and _____ antibodies.
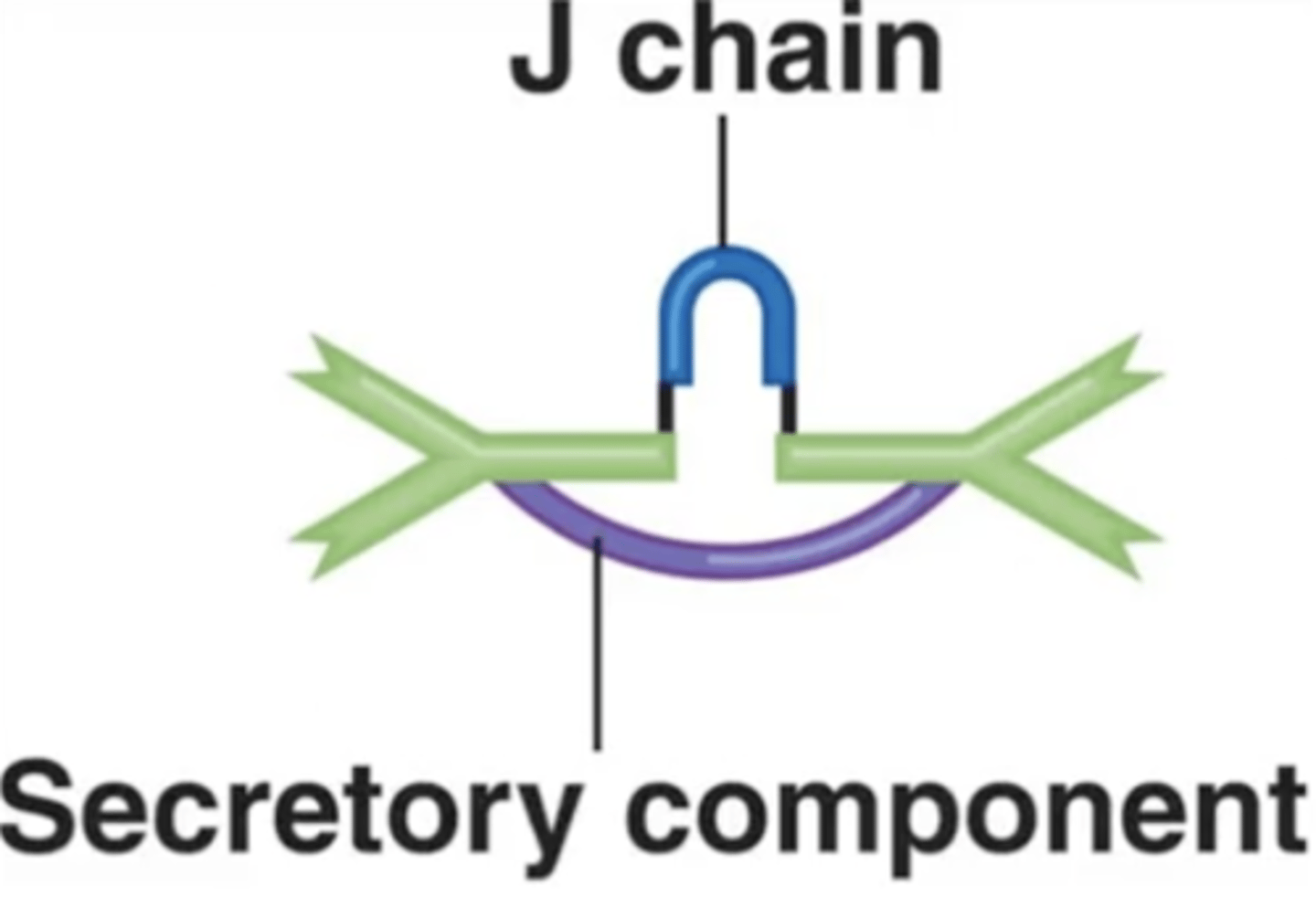
IgM, IgA
Antibody class
Which antibody class(es) has/have J chains to hold together their monomers?
monomers
Antibody class
What are IgA antibodies when in serum?
dimers
Antibody class
What are IgA antibodies when in secretions?
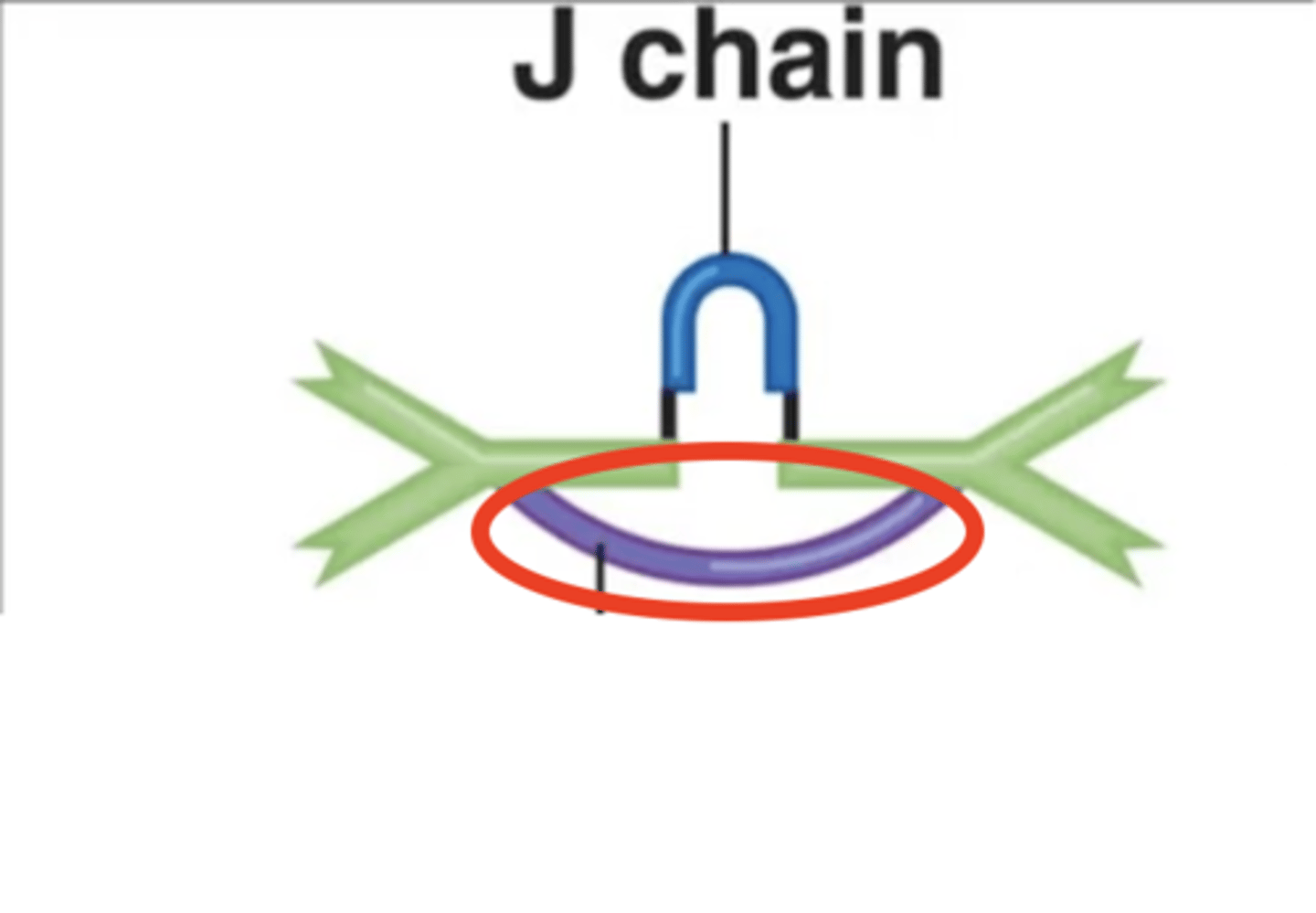
secretory component
Antibody class
- Holds together an IgA antibody's 2 monomers
- Helps prevent microbial attachment to mucous membranes
- Only on IgA antibodies under normal conditions
IgA
Antibody class
Found in secretions such as tears, mucous, saliva, and breast milk through which they can be transferred from mother to newborn for protection
4
Antibody class
How many antigen-binding sites do IgA antibodies have when in secretions?
2
Antibody class
How many antigen-binding sites do IgA antibodies have when in serum?
IgE
Antibody class
- Monomers
- 0.002% of serum antibodies
- On eosinophils, mast cells, basophils, blood
- When on mast cells or basophils, cause release of histamine; cause allergies
- Involved in antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) against parasites
- When on eosinophils, cause release of perforin and lytic enzymes
- Half-life = 2 days

eosinophils, mast cells, basophils, blood
Antibody class
Where are IgE antibodies found?

release of histamine
Antibody class
What happens when an IgE antibody links a mast cell or basophil with an antigen?

release of perforin and lytic enzymes
Antibody class
What happens when an IgE antibody links an eosinophil with an antigen

IgE
Antibody class
Which antibody class is involved in the lysis of parasitic worms?

2
Antibody class
How many antigen-binding sites do IgE antibodies have?
IgD
Antibody class
- Monomers
- 0.02% of serum antibodies
- In blood, lymph, on B cells
- No known well-defined function
- Assists B cells in immune response
- Half-life 3 days

IgD
Antibody class
Which antibody class(es) has/have no known well-defined function, but assists B cells in the immune response?

2
Antibody class
How many antigen-binding sites do IgD antibodies have?
IgG, IgE, IgD
Antibody class
Under normal conditions, which antibody class(es) is/are monomers?

agglutination, neutralization, activation of complements, opsonization, antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC)
Antibody effects of binding
What are the 5 antibody effects of binding?
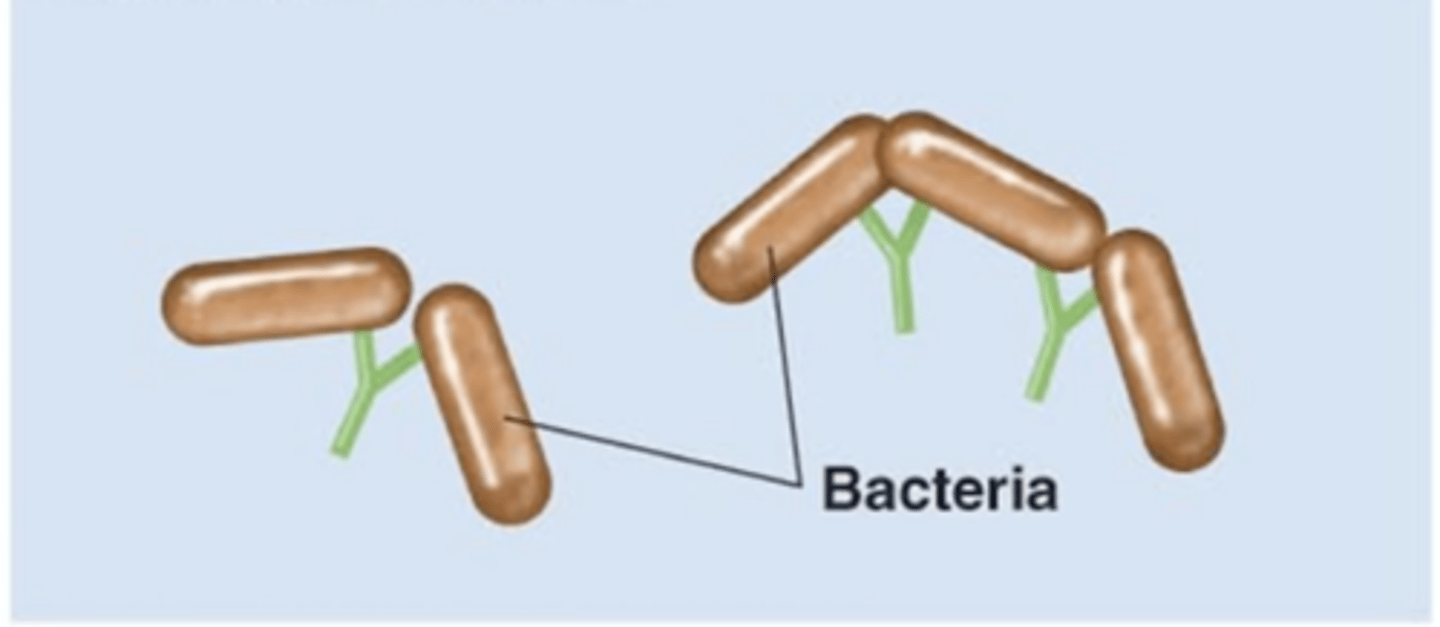
agglutination
Antibody effects of binding
- 1 of 5 effects
- Antibodies bind to and "clump" pathogens
- Helps immobilize pathogens
- Helps decrease the number of pathogens to be "dealt with"
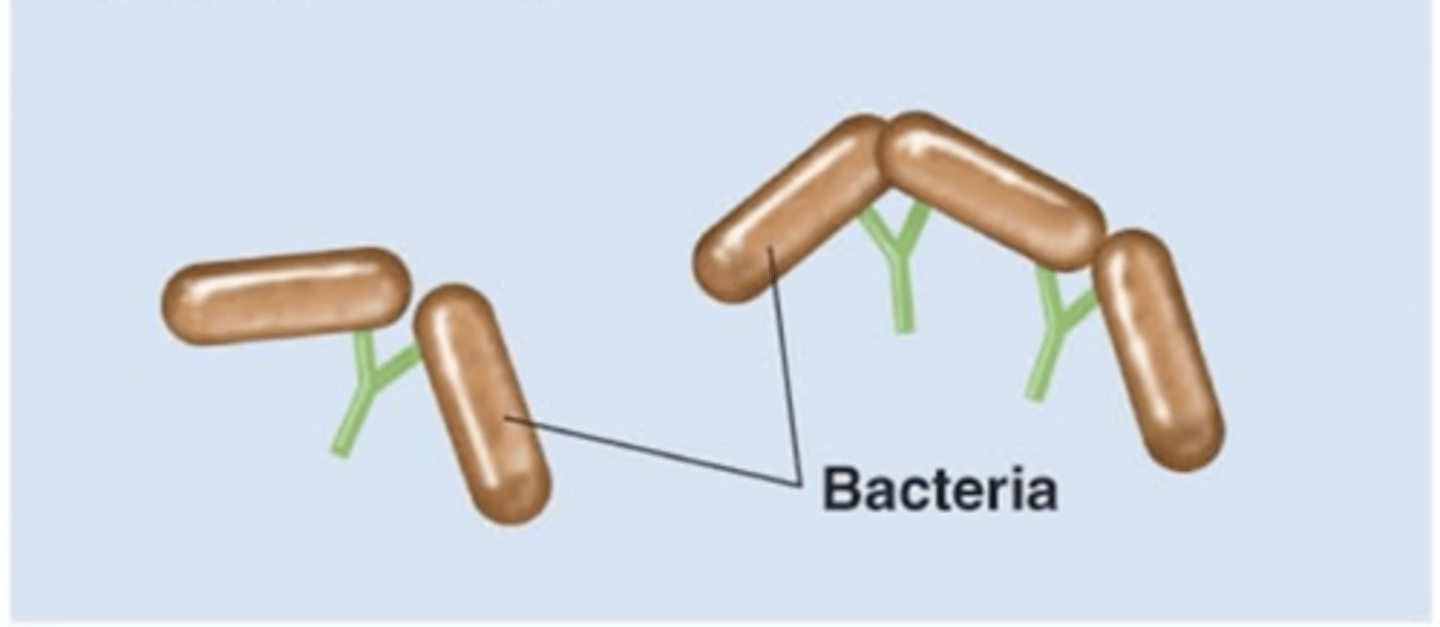
IgG, IgM
Antibody effects of binding
Which antibody class(es) is/are involved in agglutination?
neutralization
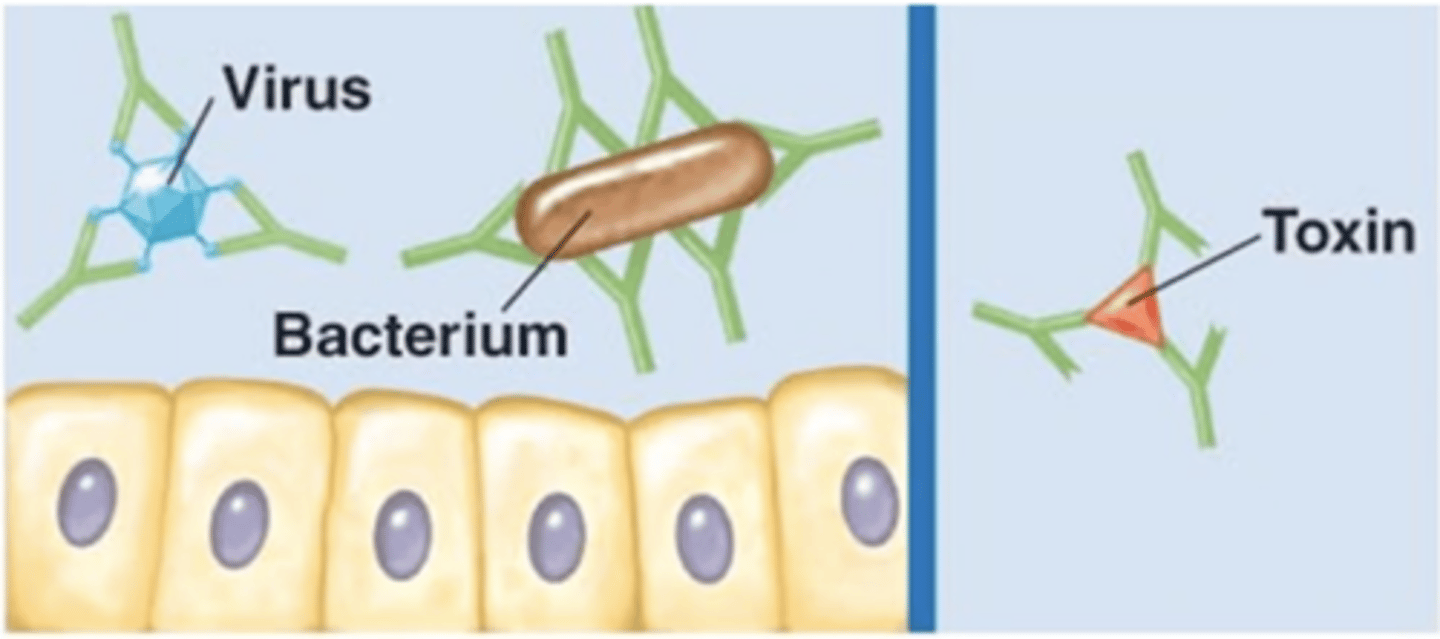
Antibody effects of binding
- 1 of 5 effects
- Antibodies bind and completely cover the surface of a virus, bacterium, or toxin
- Prevent attachment and entry into the host cell
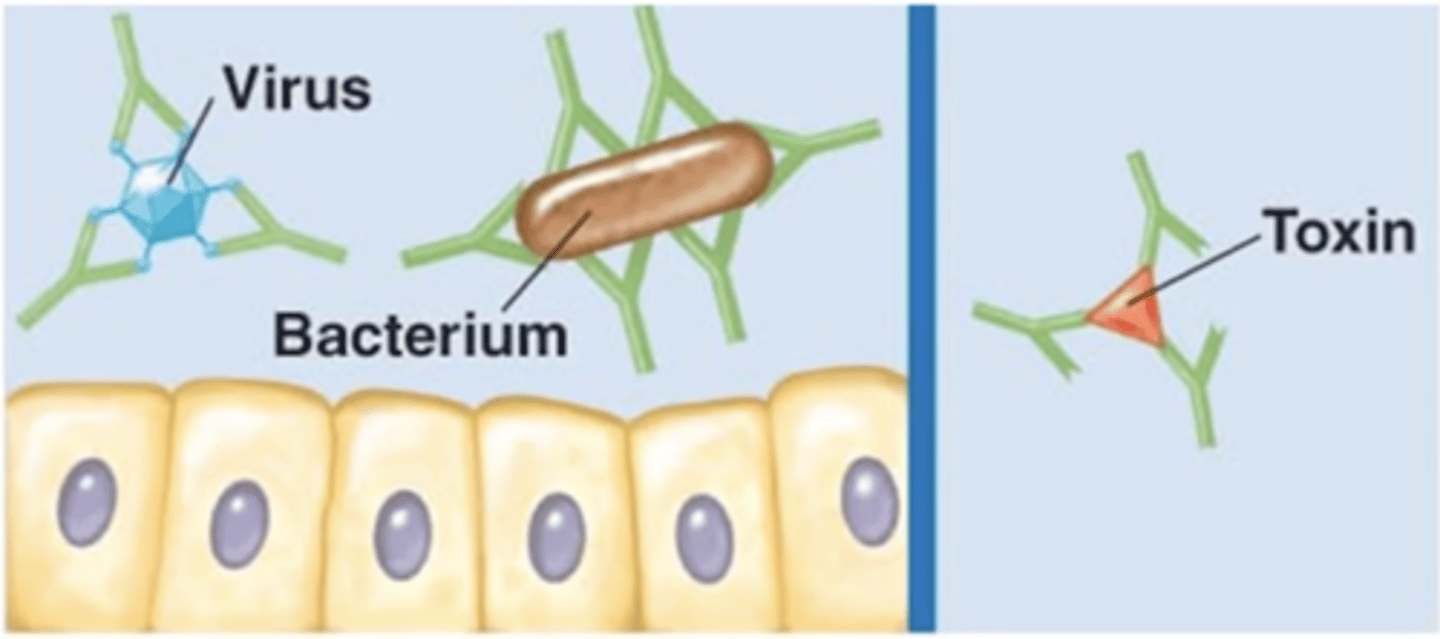
IgG, IgA
Antibody effects of binding
Which antibody class(es) is/are involved in neutralization?
activation of complements (classical pathway)
Antibody effects of binding
- 1 of 5 effects
- IgGs/IgMs attach to a bacterium
- IgGs/IgMs attach to C1
- Antigen-antibody complex initiates pathway
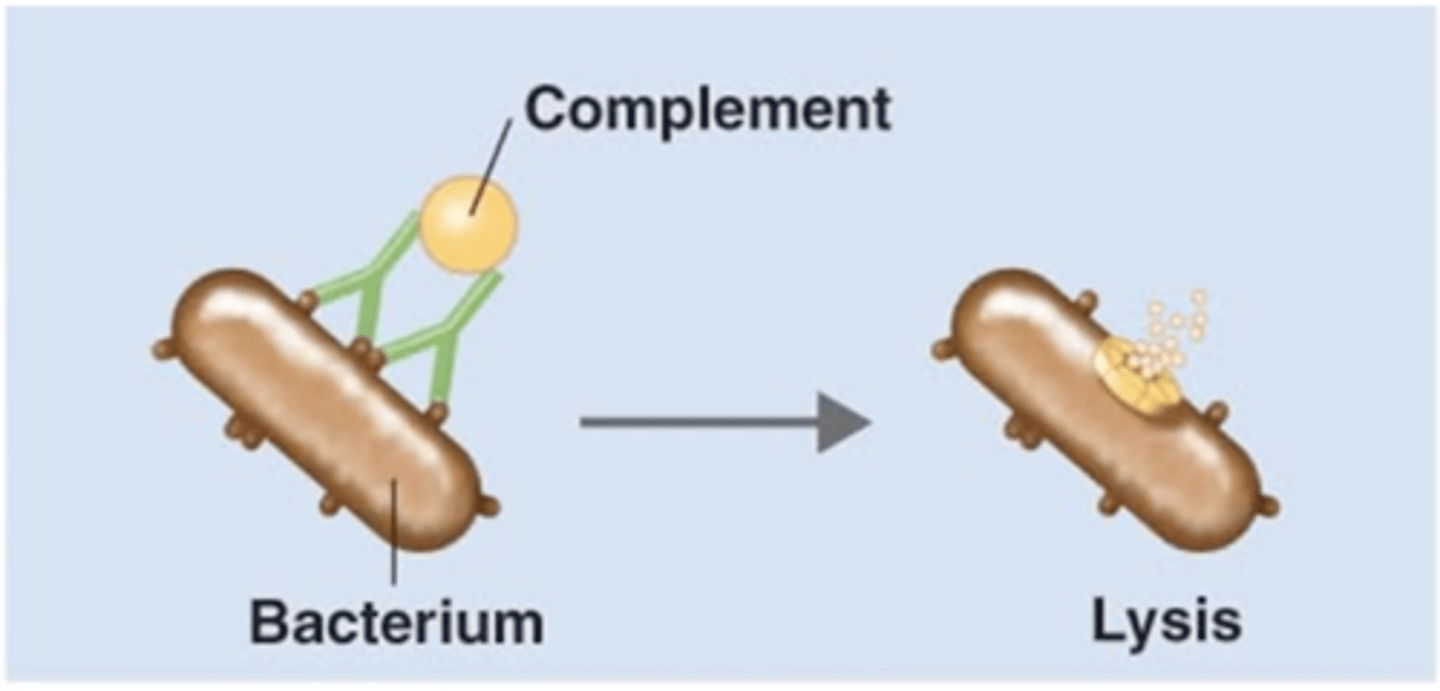
IgG, IgM
Antibody effects of binding
Which antibody class(es) is/are involved in initiating activation of complements (classical pathway)?
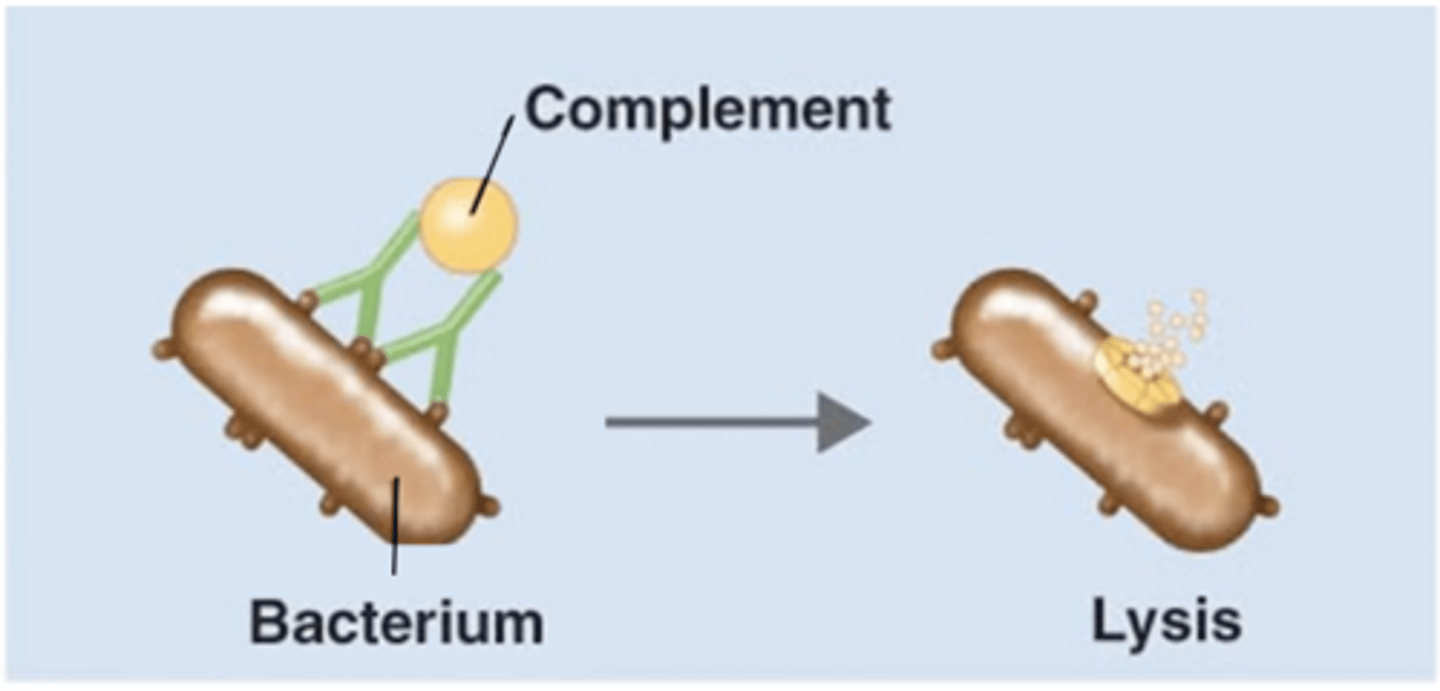
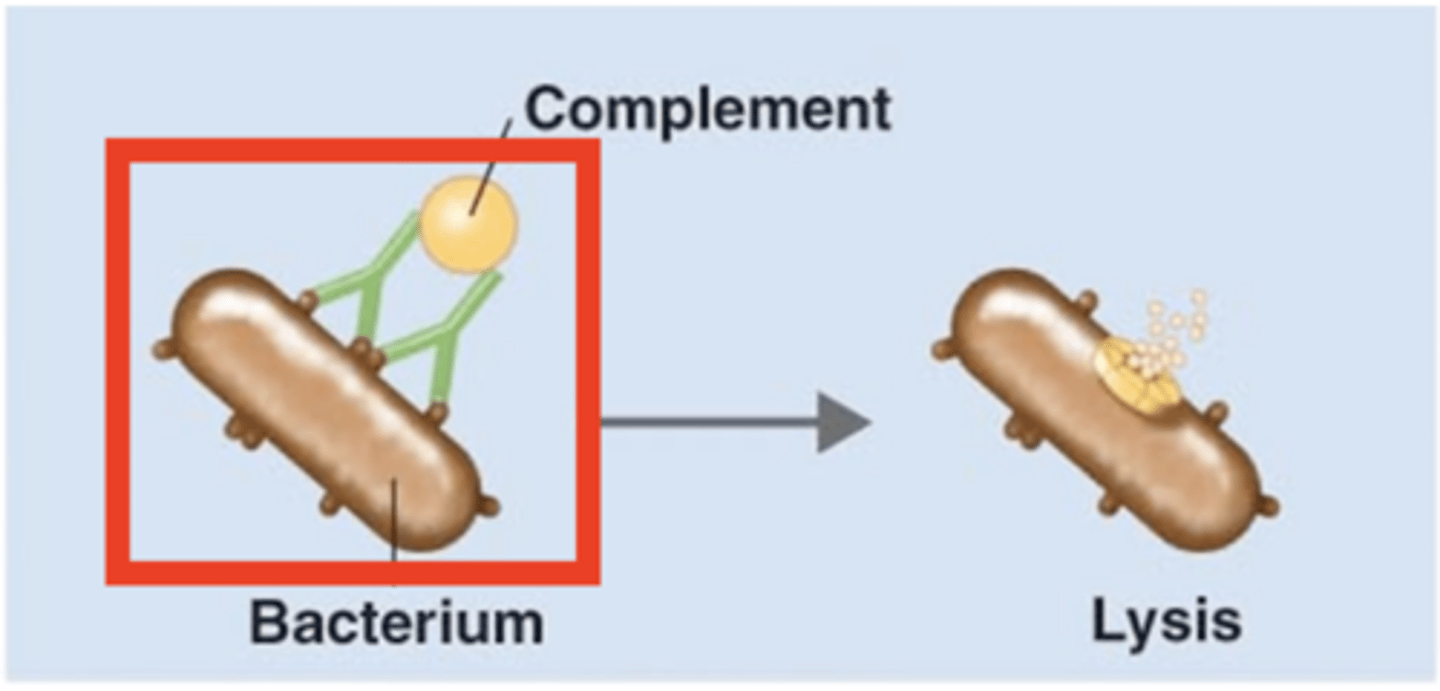
antigen-antibody complex
Antibody effects of binding
Which structure is this?
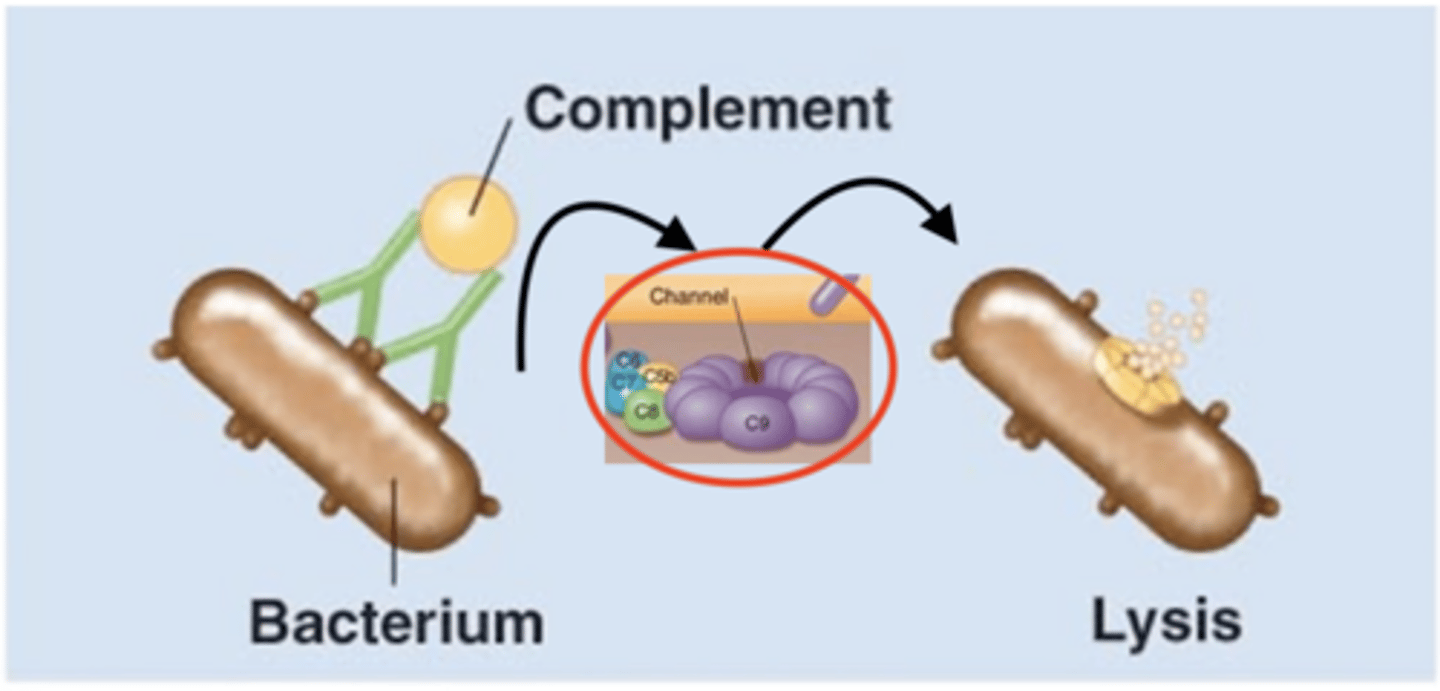
membrane attack complex (MAC), plasma membrane, cytolysis
Antibody effects of binding
Fill in the blank:
1. IgGs and/or IGMs activate C1
2. IgGs and/or IgMs initiate classical pathway of complement activation
3. C5b combines with C6, C7, C8, and multiple C9 to form a ____________________ in target bacterium's ____________________
4. __________ of bacterium results
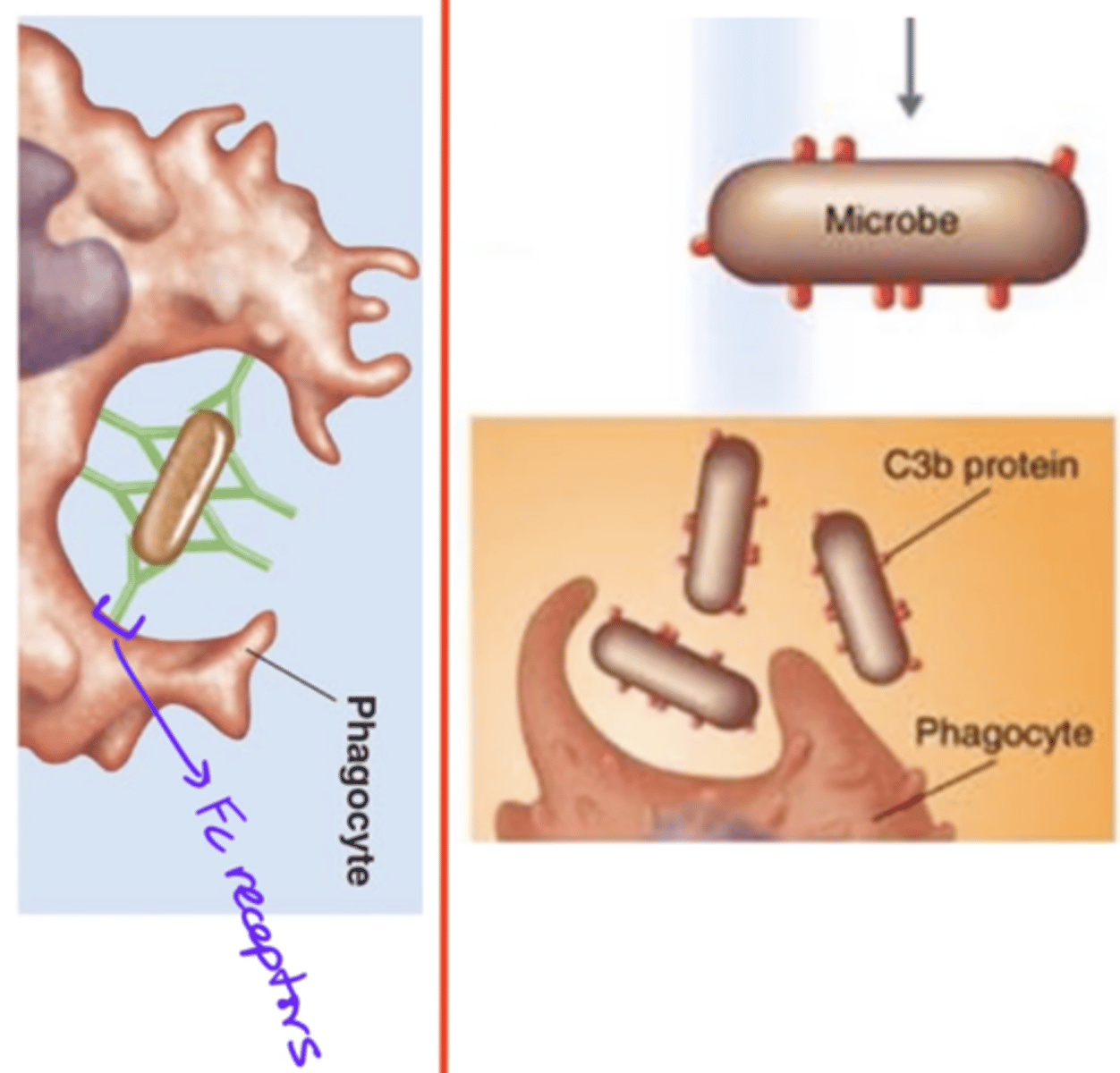
opsonization
Antibody effects of binding
- 1 of 5 effects
- IgGs act as opsonins
- IgGs' Fc regions bind to phagocyte's Fc receptors
- Enhances phagocyte's access to pathogen
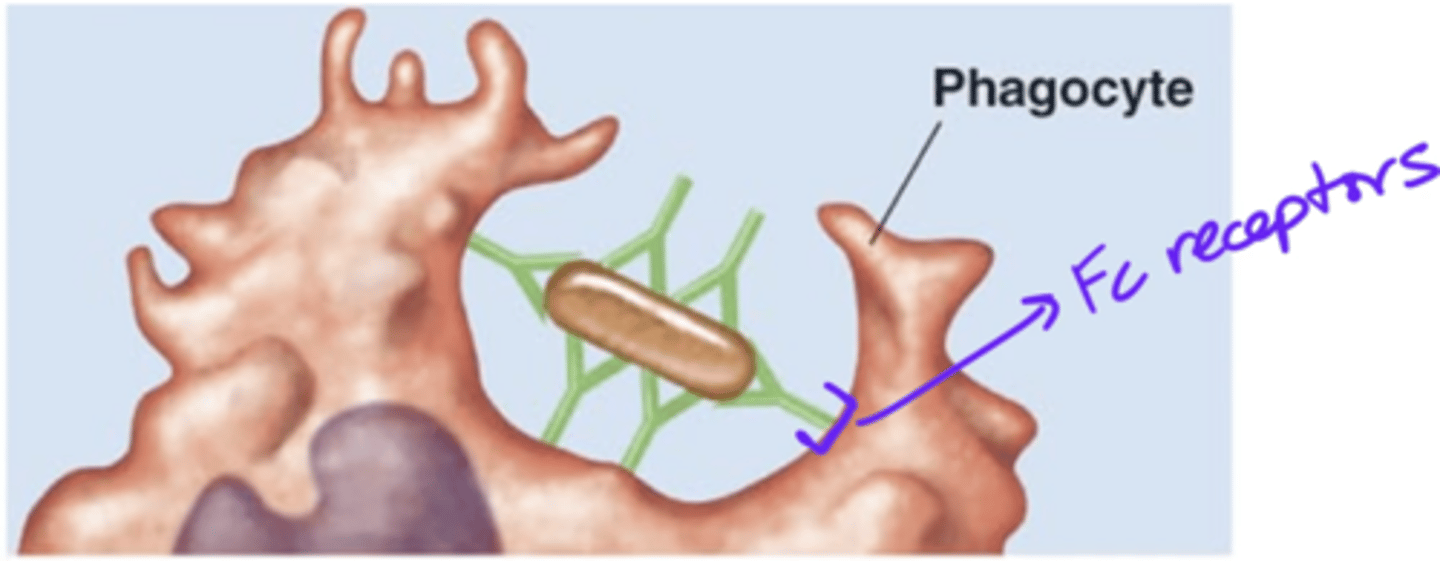
IgG
Antibody effects of binding
Which antibody class(es) is/are involved in opsonization?
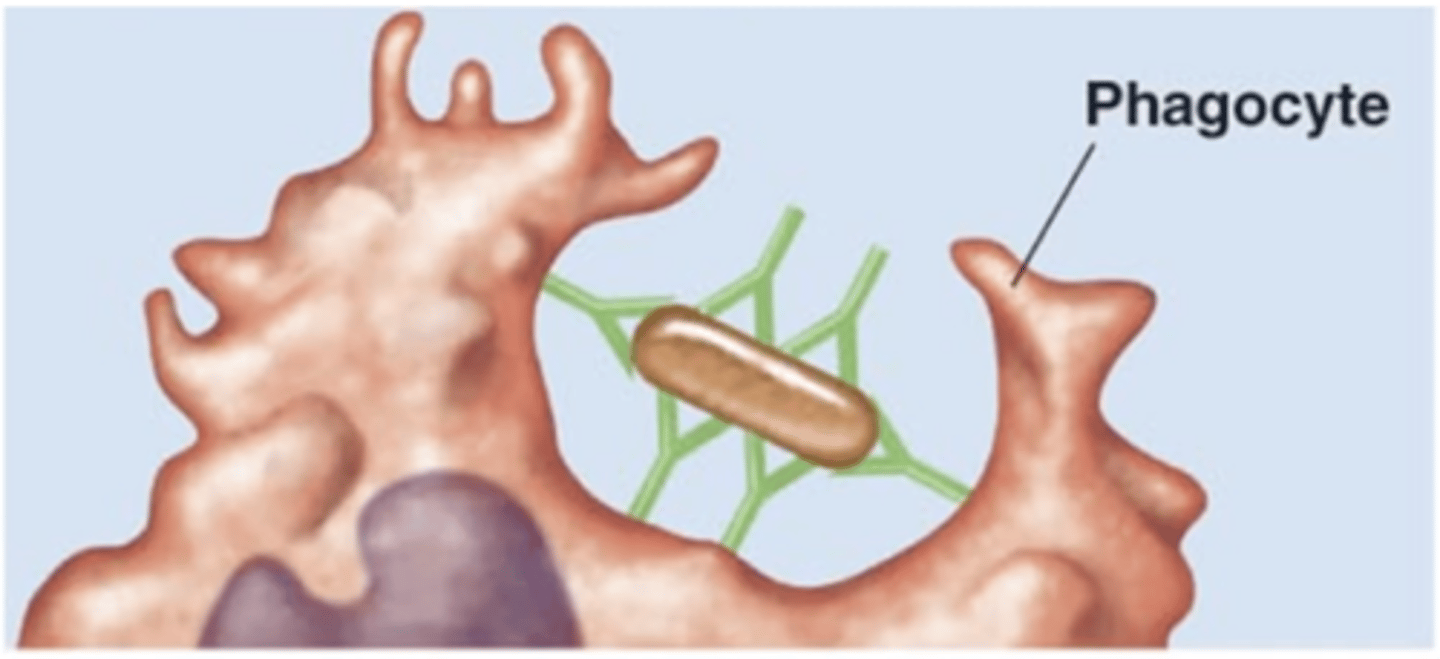
opsonins
Antibody effects of binding
- Proteins that code for a pathogen
- These bind pathogen to a phagocyte's receptors
- These enhance phagocyte's access to pathogen
- E.g., IgG, C3b
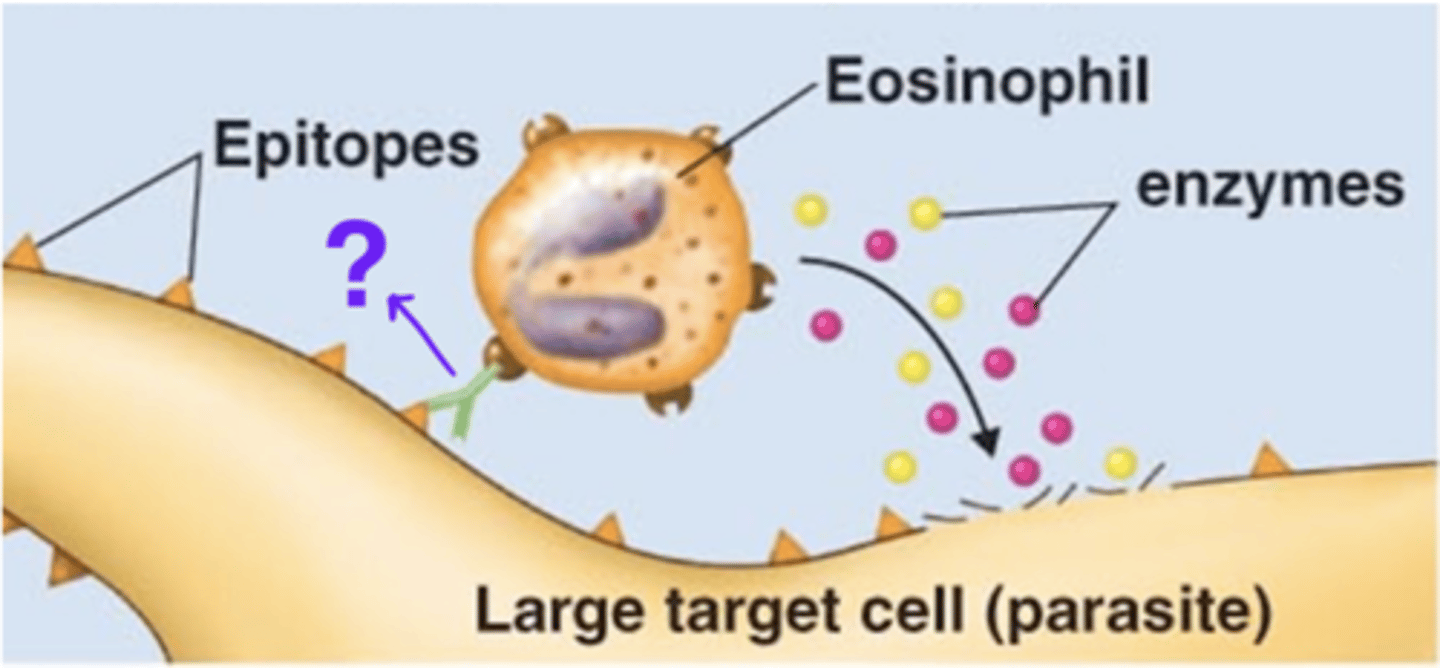
antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC)
Antibody effects of binding
- 1 of 5 effects
- IgE's Fab region binds to an epitope on a parasite
- Eosinophil binds to the IgE's Fc region
- Eosinophil releases perforin and lytic enzymes
- Perforin and lytic enzymes target and destroy cell membrane of parasite
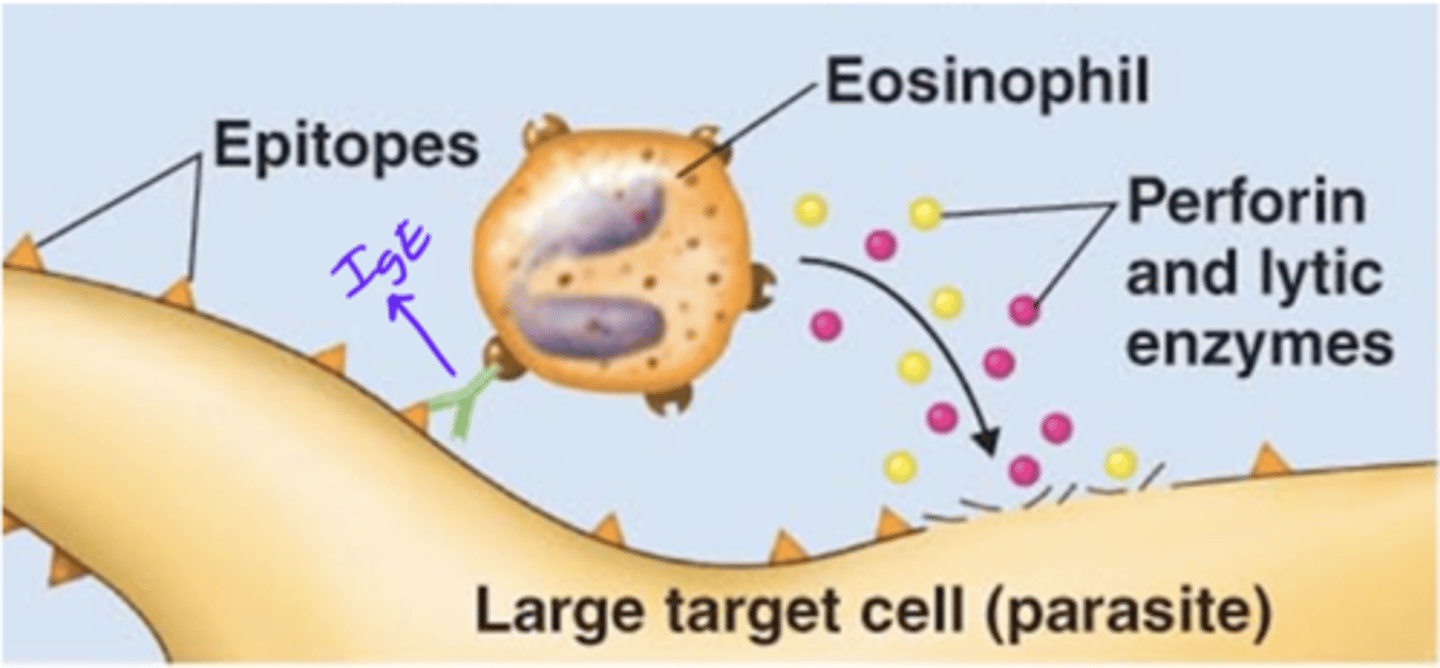
IgE
Antibody class
Which antibody class(es) is/are involved in antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC)?
perforin, lytic enzymes
Antibody effects of binding
Enzymes released by eosinophils that target and destroy cell membranes of parasites
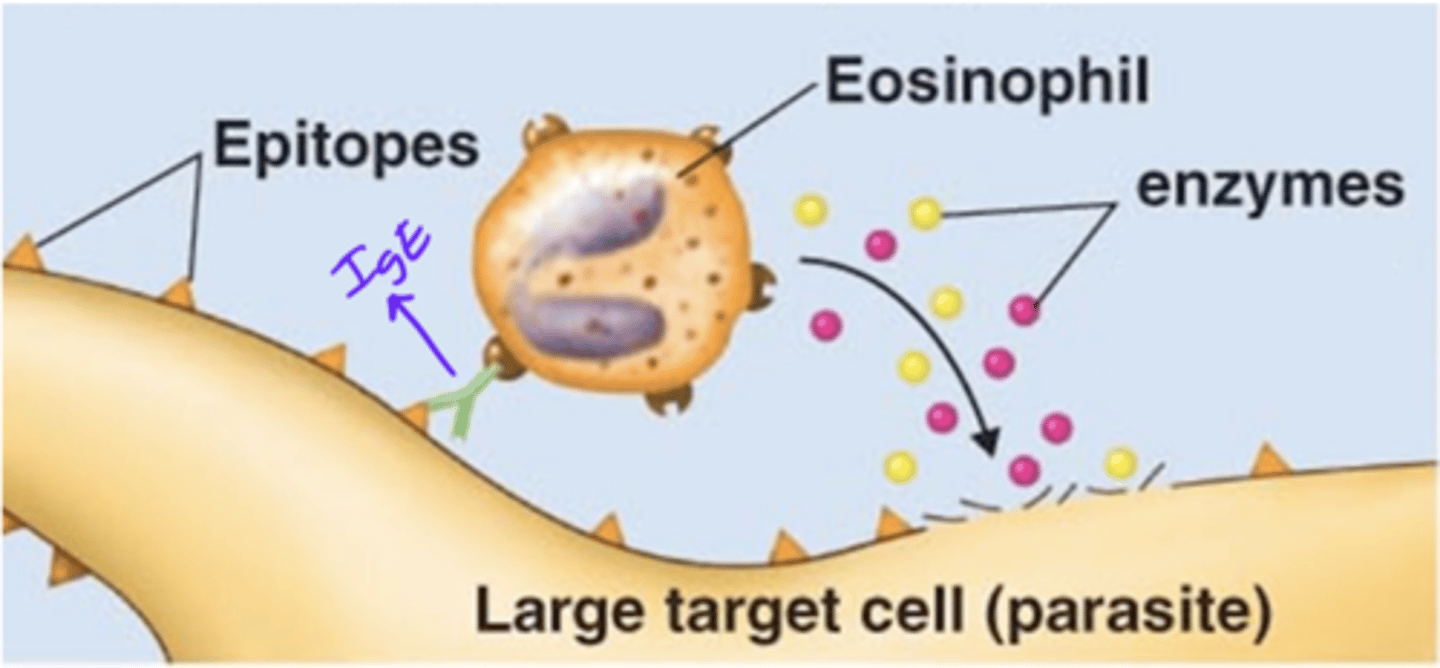
IgE, epitope, eosinophil's, perforin, lytic
Antibody effects of binding
Fill in the blank:
- During antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), a(n) _____ antibody's Fab region binds to a(n) __________ on a parasite.
- The antibody's Fc region binds to a(n) _________________________ Fc receptor.
- The leukocyte releases __________ and __________ enzymes that lyse target parasite.
macrophages, natural killer (NK) cells
Antibody effects of binding
In addition to eosinophils, what other leukocytes can cause destruction of parasites?
major histocompatability complexes (MHCs)
Immunity
- Receptors on the surfaces of all cells except for erythrocytes
- Help differentiate between "self" and "non-self"
- Help reject "foreign" tissue
- Aka human leukocyte antigens (HLA)
human leukocyte antigen (HLA)
Immunity
Also called a major histocompatibility complex (MHC)
major histocompatability complexes (MHCs)
Immunity
Receptors found on the surfaces of all cells except for erythrocytes. Include:
1. Class I
2. Class II
MHC-I
Immunity
- 1 of 2 classes of major histocompatibility complexes (MHCs)
- Markers display unique characteristics of "self" molecules that bind to CD8
- Markers are on all cells except for erythrocytes
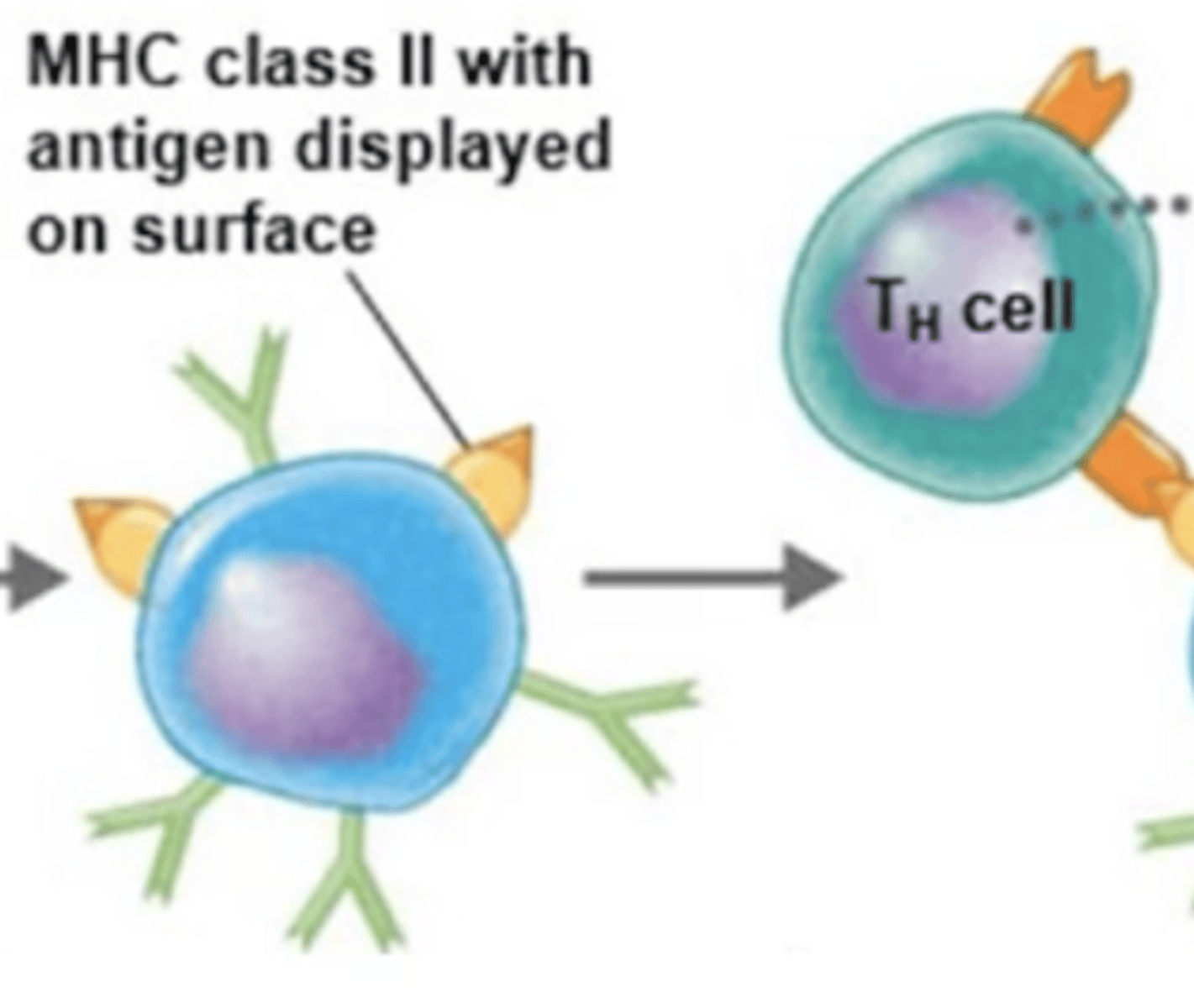
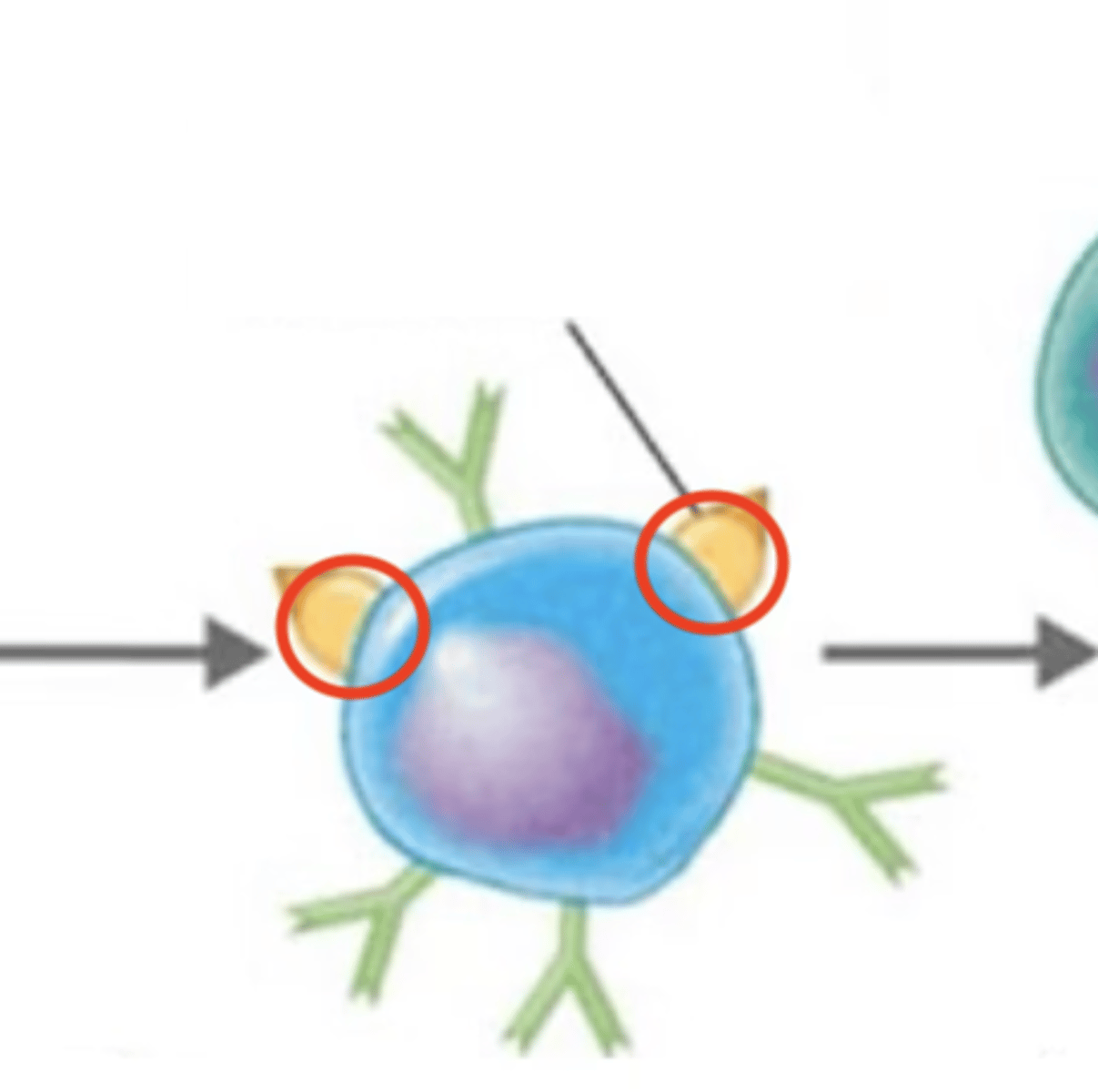
MHC-II
Immunity
- 1 of 2 classes of major histocompatibility complexes (MHC)
- Markers are on the surfaces of antigen-presenting cells (dendritic cells, macrophages, B cells)
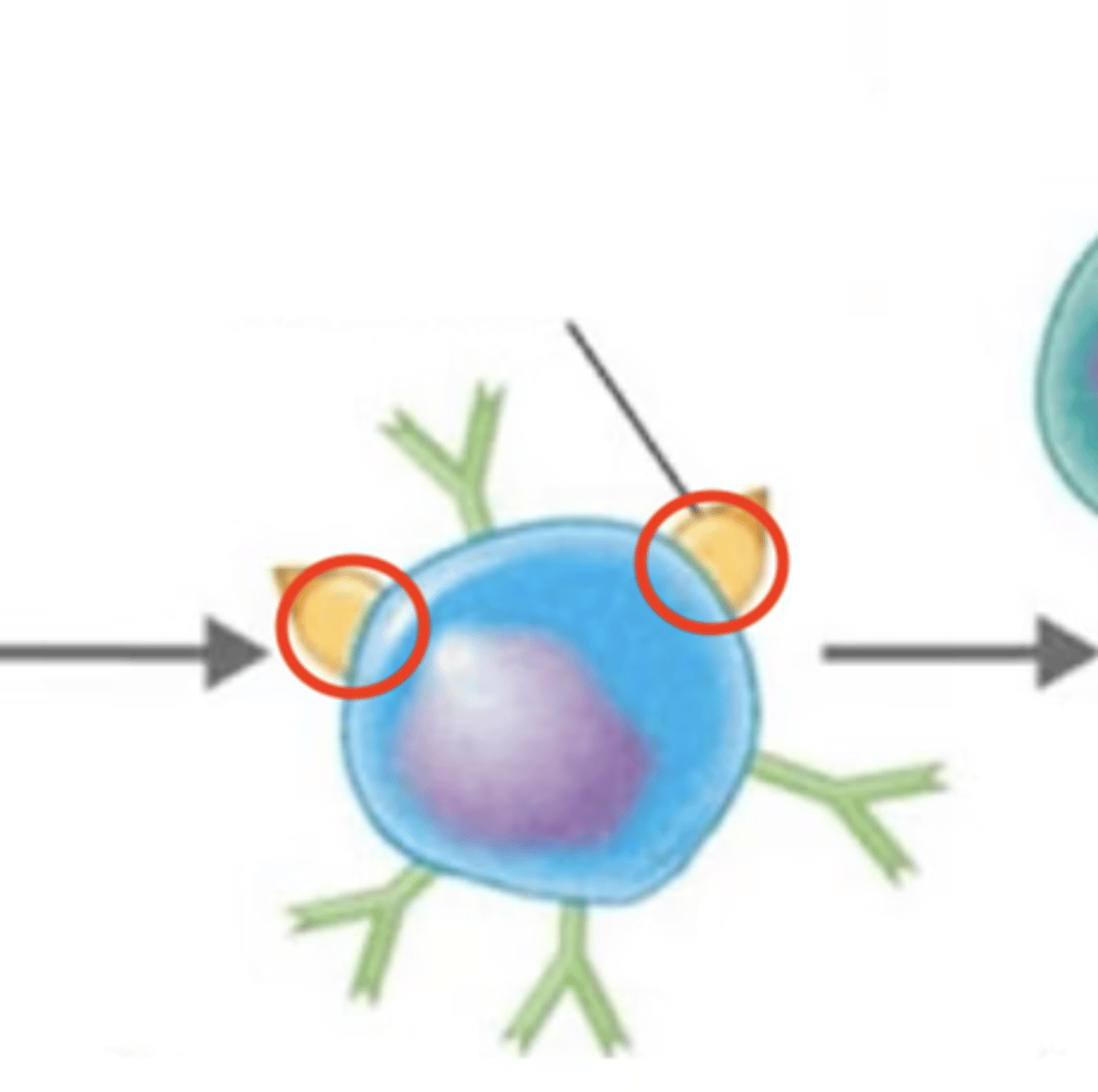
dendritic cells, macrophages, B cells
Adaptive immunity
MHC-II are found on the surfaces of antigen-presenting cells (APCs), which are?
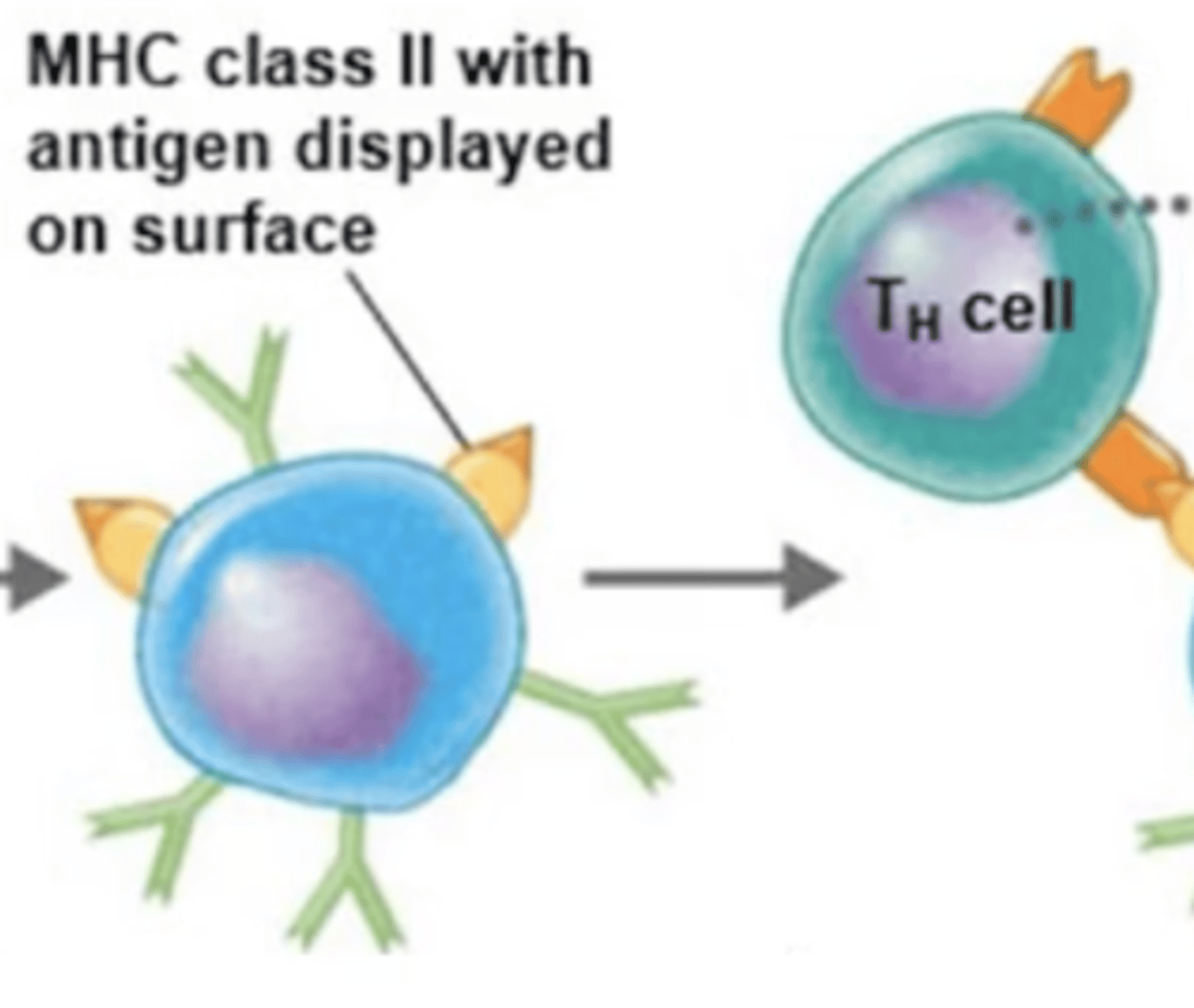
MHC-II
Adaptive immunity
Antigen-presenting cells (APCs), such as dendritic cells, macrophages, and B cells have these receptors on their surfaces
T-independent, T-dependent
B cell activation
Fill in the blank:
2 types of B cell-activating antigens:
1. ____________________ antigens
2. ____________________ antigens
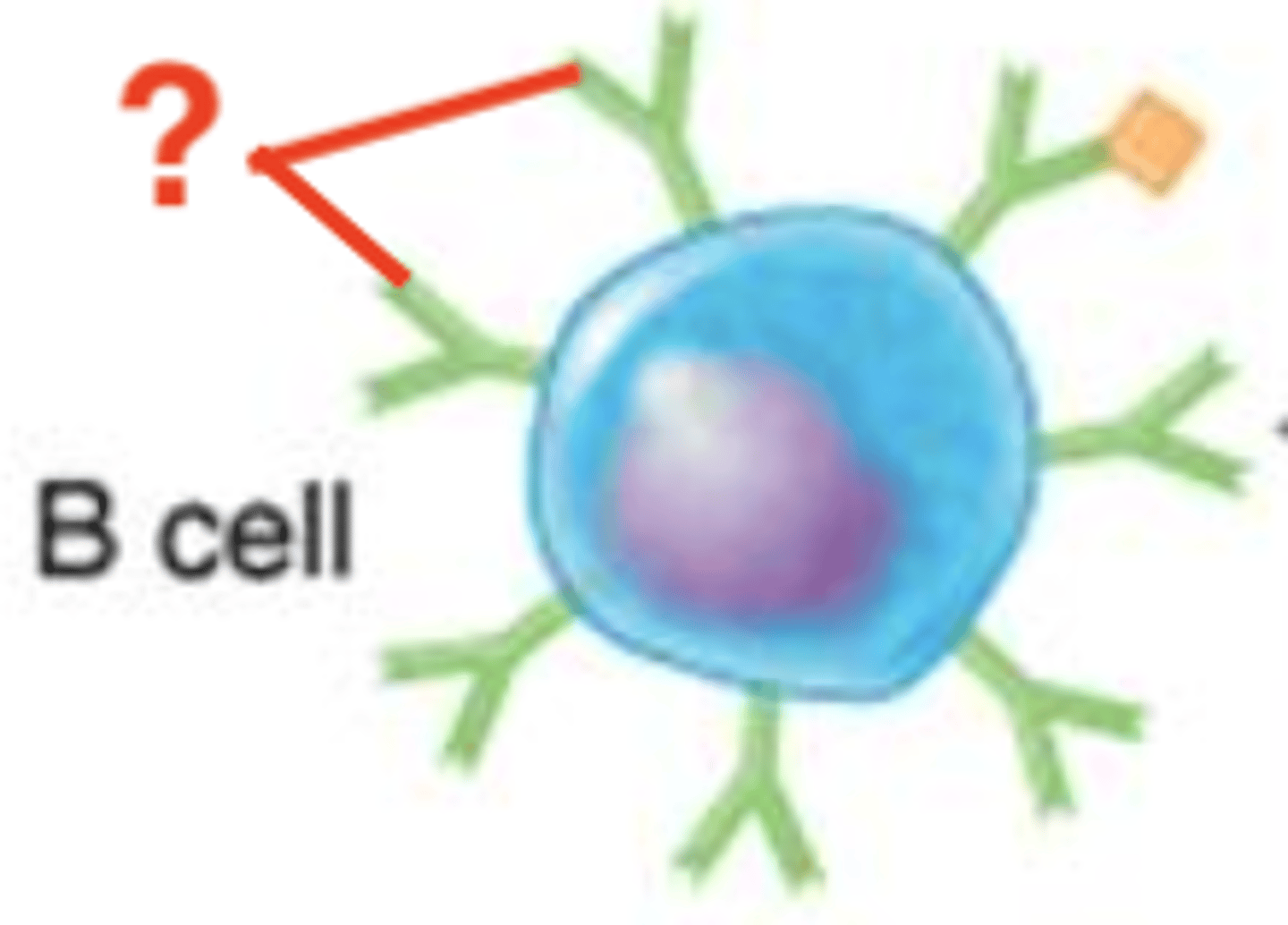
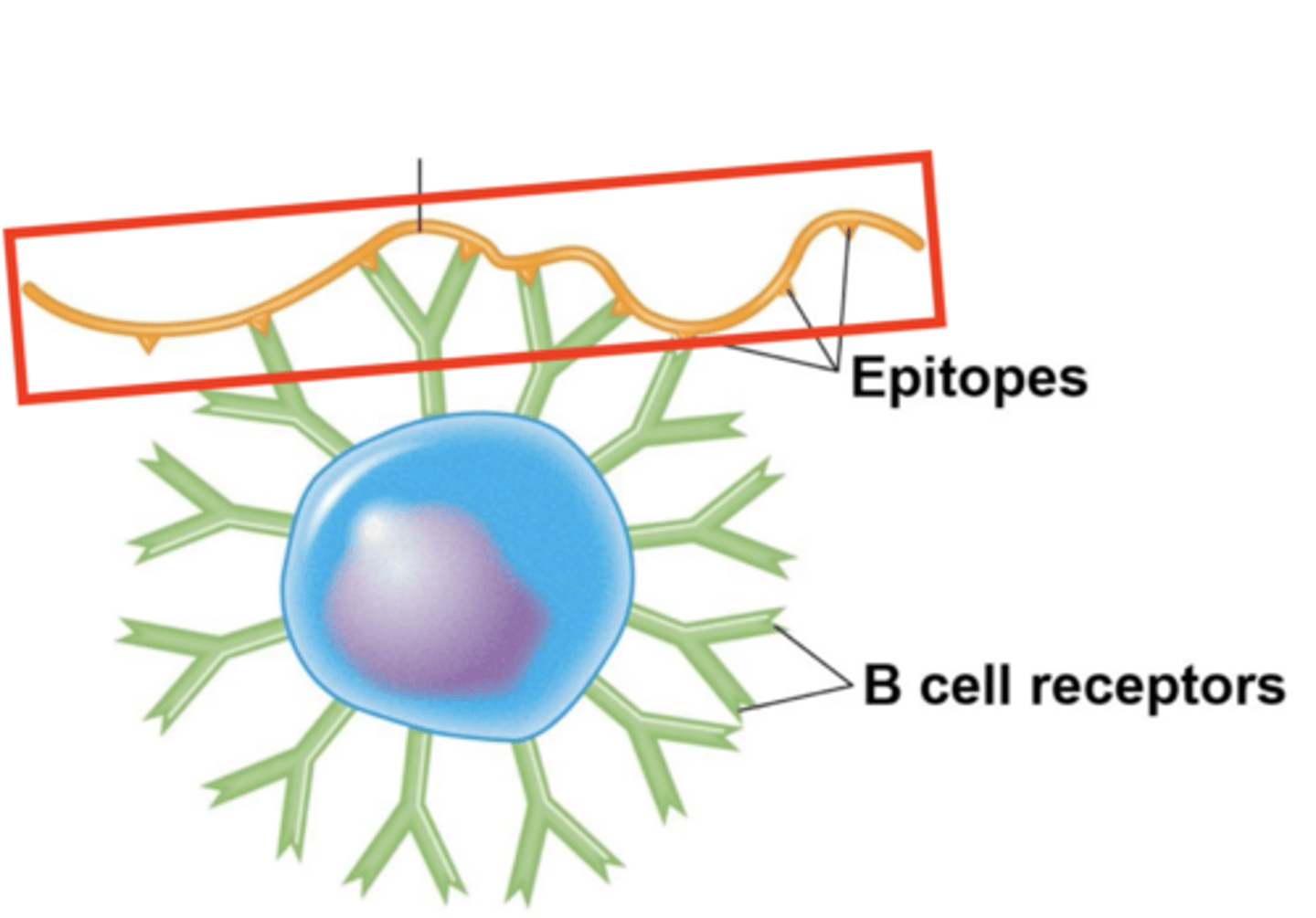
B cell receptors (BCRs)
B cell activation
Which structures are these? Include Fab regions
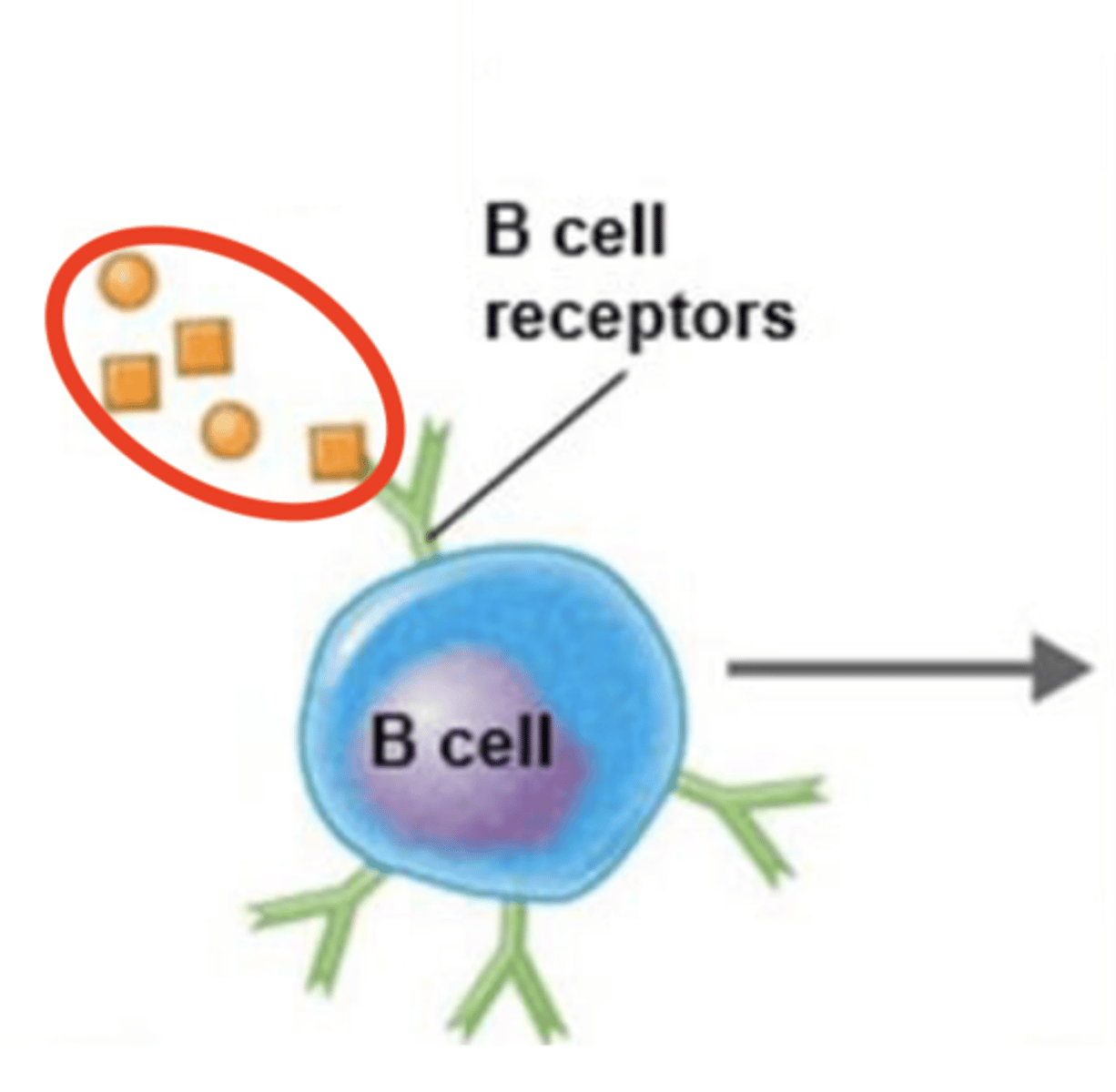
T-independent antigens
- 1 of 2 types of B-cell-activating antigens
- Large polysaccharides
- Have repeating structures/subunits
- Epitopes bind to multiple B cell receptors (BCRs)
- T cells are not needed to activate B cell
- Produce no memory
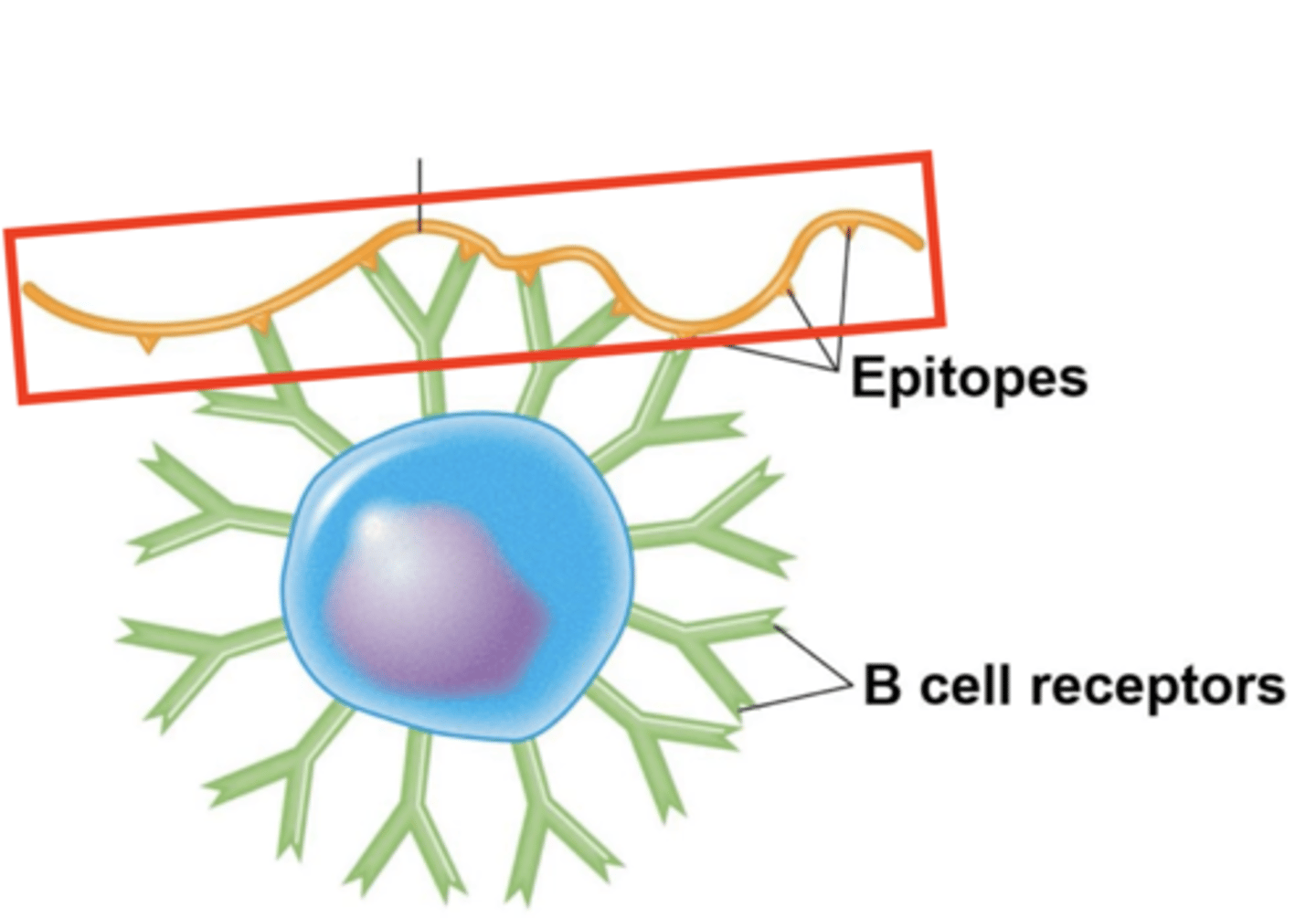
BCRs, epitopes, plasma cells
B cell activation against T-independent antigen
Fill in the blank:
- Multiple Fabs, or "_____," bind to multiple T-independent antigen __________.
- B cell will activate and differentiate into _______________.
plasma cells
B cell activation against T-independent antigen
What do activated B cells differentiate into against a T-independent antigen?
produce antibodies
B cell activation against T-independent antigen
- Multiple BCRs bind to multiple T-independent antigen epitopes.
- B cell will activate and differentiate into plasma cells
- What do the plasma cells do?
T-dependent antigens
B cell activation
- 1 of 2 types of B-cell-activating antigens
- Mostly proteins
- Have respective markers on the surfaces of antigen-presenting cells (APC)
- T cells need to recognize them as "foreign" and secrete cytokines to activate B cells
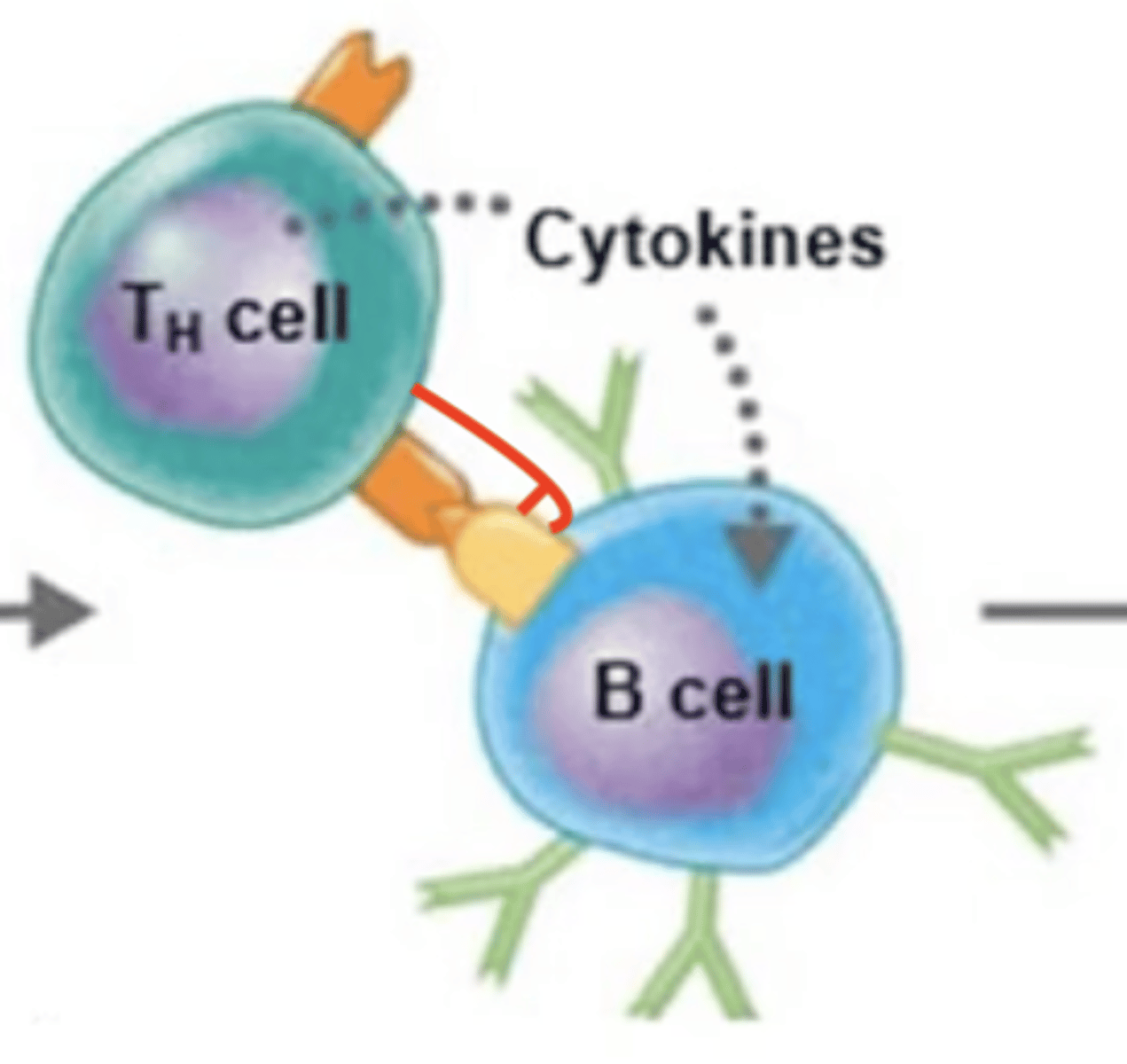
BCR binds to extracellular antigen.
B cell activation against T-dependent antigen
Fill in the blank:
1.
2. Extracellular antigen enters B cell via endocytosis.
3. Intracellular antigen is digested into antigen fragments = processed antigen.
4. MHC-II receptor binds to processed antigen = antigen-MHC-II complex.
5. Antigen-MHC-II complex moves to surface of B cell.
6. MHC-II complex displays processed antigen to Th2 cell.
7. TCR of Th2 binds to processed antigen.
8. CD4 receptor on Th2 binds to MHC-II receptor.
9. Th2 releases cytokines.
10. Cytokines activate B cell.
11. B cell proliferates and differentiates into either plasma cells or memory B cells.
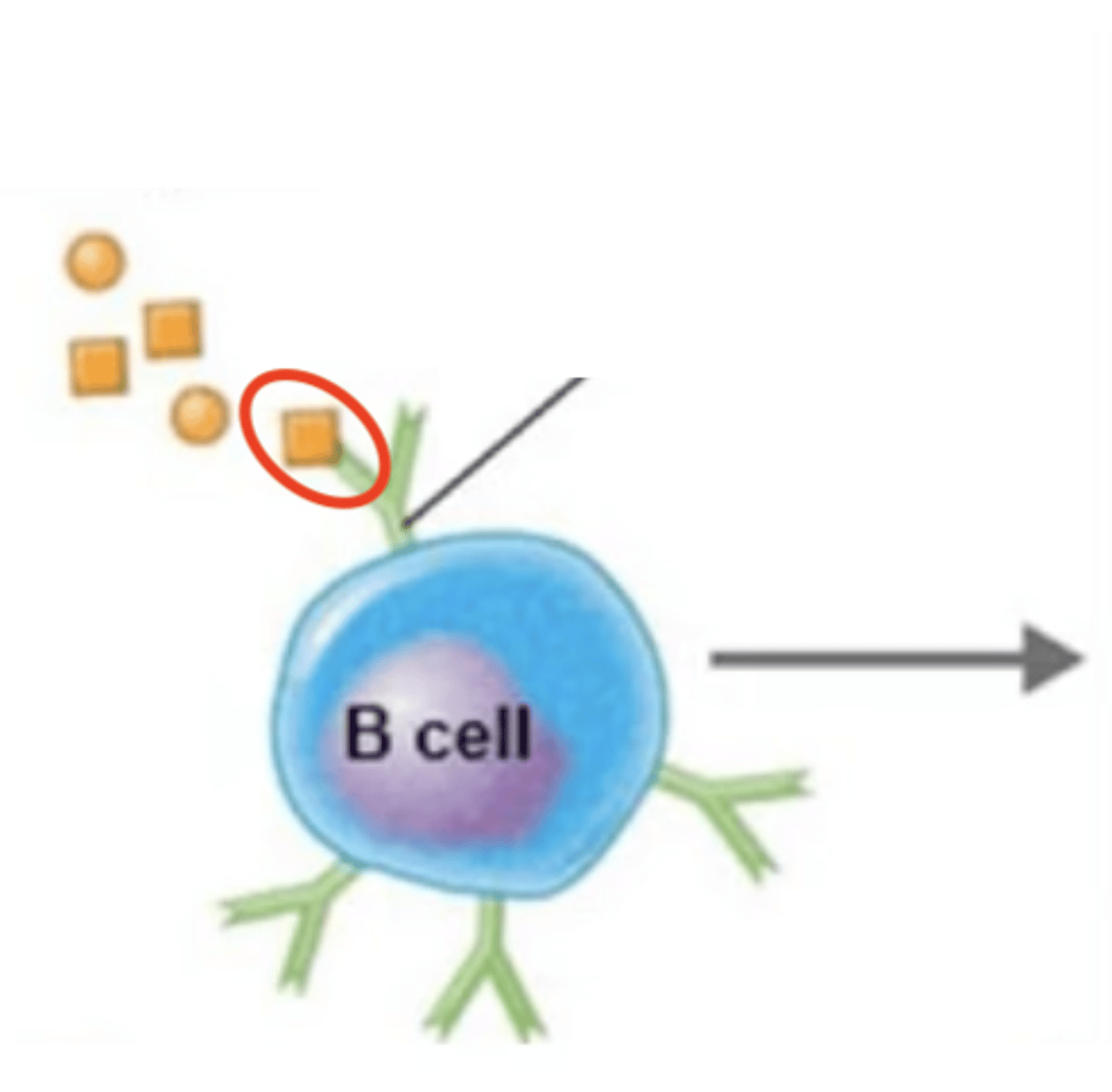
Extracellular antigen enters B cell via endocytosis.
B cell activation against T-dependent antigen
Fill in the blank:
1. BCR binds to extracellular antigen.
2.
3. Intracellular antigen is digested into antigen fragments = processed antigen.
4. MHC-II receptor binds to processed antigen = antigen-MHC-II complex.
5. Antigen-MHC-II complex moves to surface of B cell.
6. MHC-II complex displays processed antigen to Th2 cell.
7. TCR of Th2 binds to processed antigen.
8. CD4 receptor on Th2 binds to MHC-II receptor.
9. Th2 releases cytokines.
10. Cytokines activate B cell.
11. B cell proliferates and differentiates into either plasma cells or memory B cells.
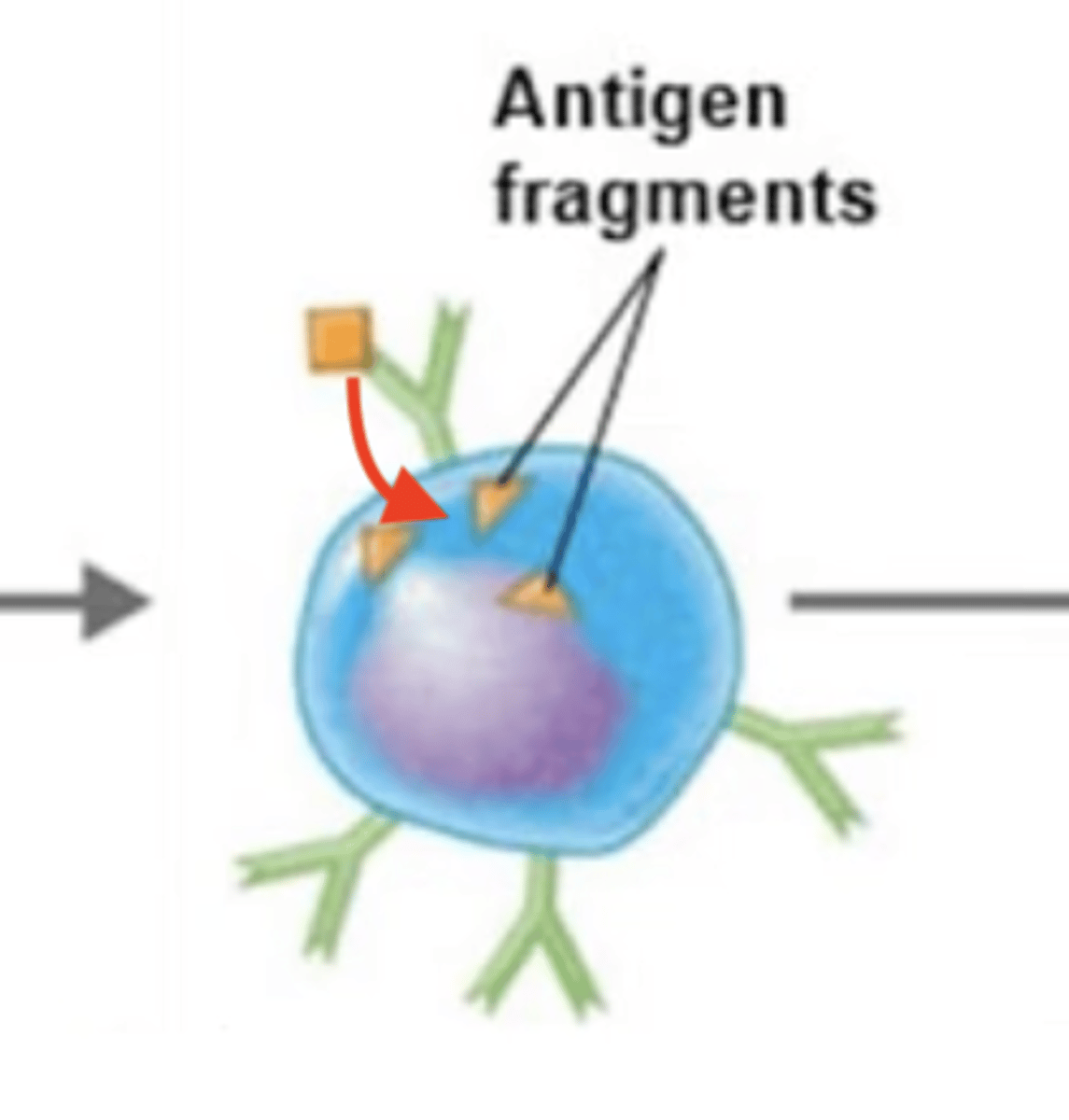
Intracellular antigen is digested into antigen fragments = processed antigen.
B cell activation against T-dependent antigen
Fill in the blank:
1. BCR binds to extracellular antigen.
2. Extracellular antigen enters B cell via endocytosis.
3.
4. MHC-II receptor binds to processed antigen = antigen-MHC-II complex.
5. Antigen-MHC-II complex moves to surface of B cell.
6. MHC-II complex displays processed antigen to Th2 cell.
7. TCR of Th2 binds to processed antigen.
8. CD4 receptor on Th2 binds to MHC-II receptor.
9. Th2 releases cytokines.
10. Cytokines activate B cell.
11. B cell proliferates and differentiates into either plasma cells or memory B cells.
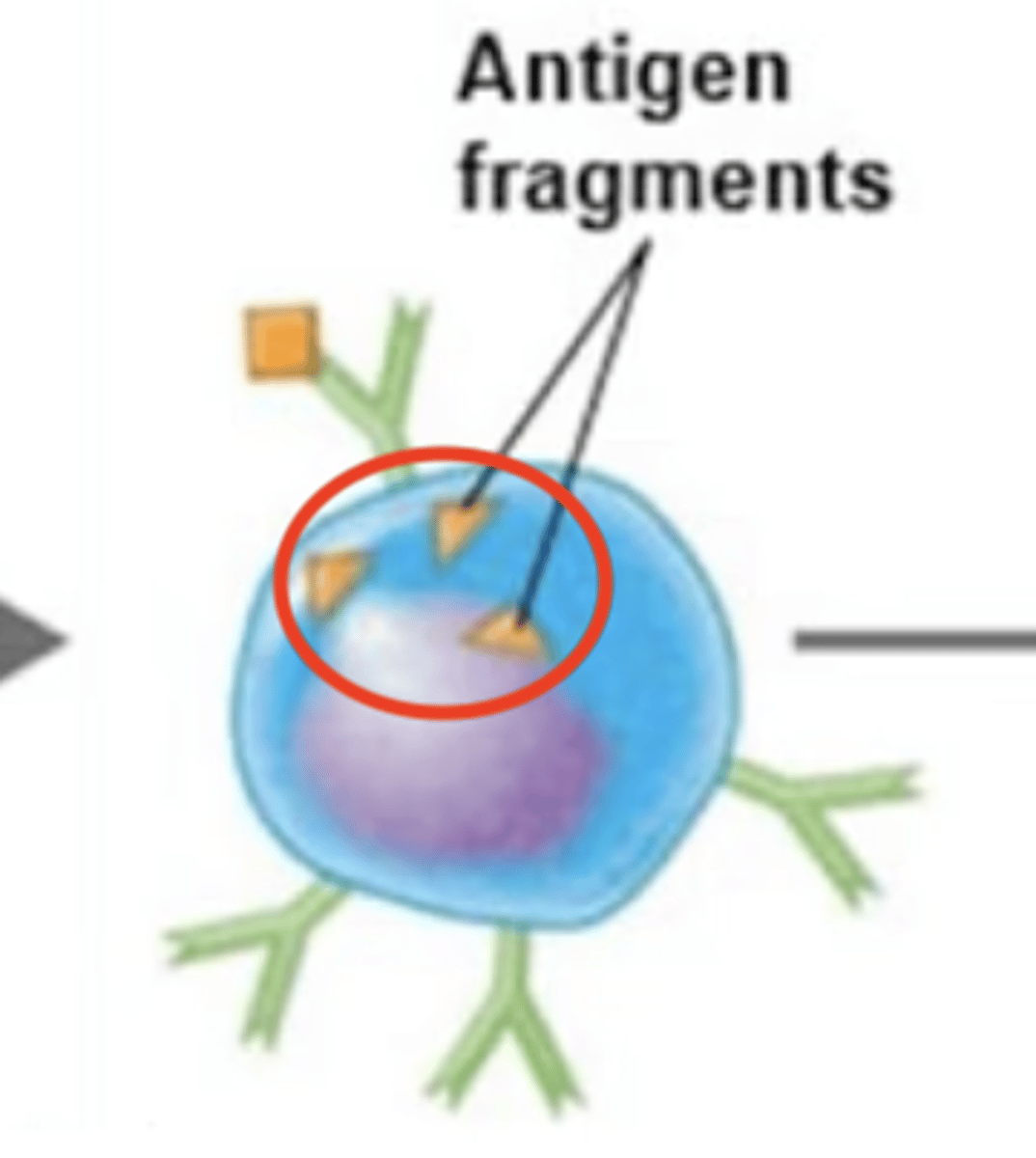
MHC-II receptor binds to processed antigen = antigen-MHC-II complex.
B cell activation against T-dependent antigen
Fill in the blank:
1. BCR binds to extracellular antigen.
2. Extracellular antigen enters B cell via endocytosis.
3. Intracellular antigen is digested into antigen fragments = processed antigen.
4.
5. Antigen-MHC-II complex moves to surface of B cell.
6. MHC-II complex displays processed antigen to Th2 cell.
7. TCR of Th2 binds to processed antigen.
8. CD4 receptor on Th2 binds to MHC-II receptor.
9. Th2 releases cytokines.
10. Cytokines activate B cell.
11. B cell proliferates and differentiates into either plasma cells or memory B cells.
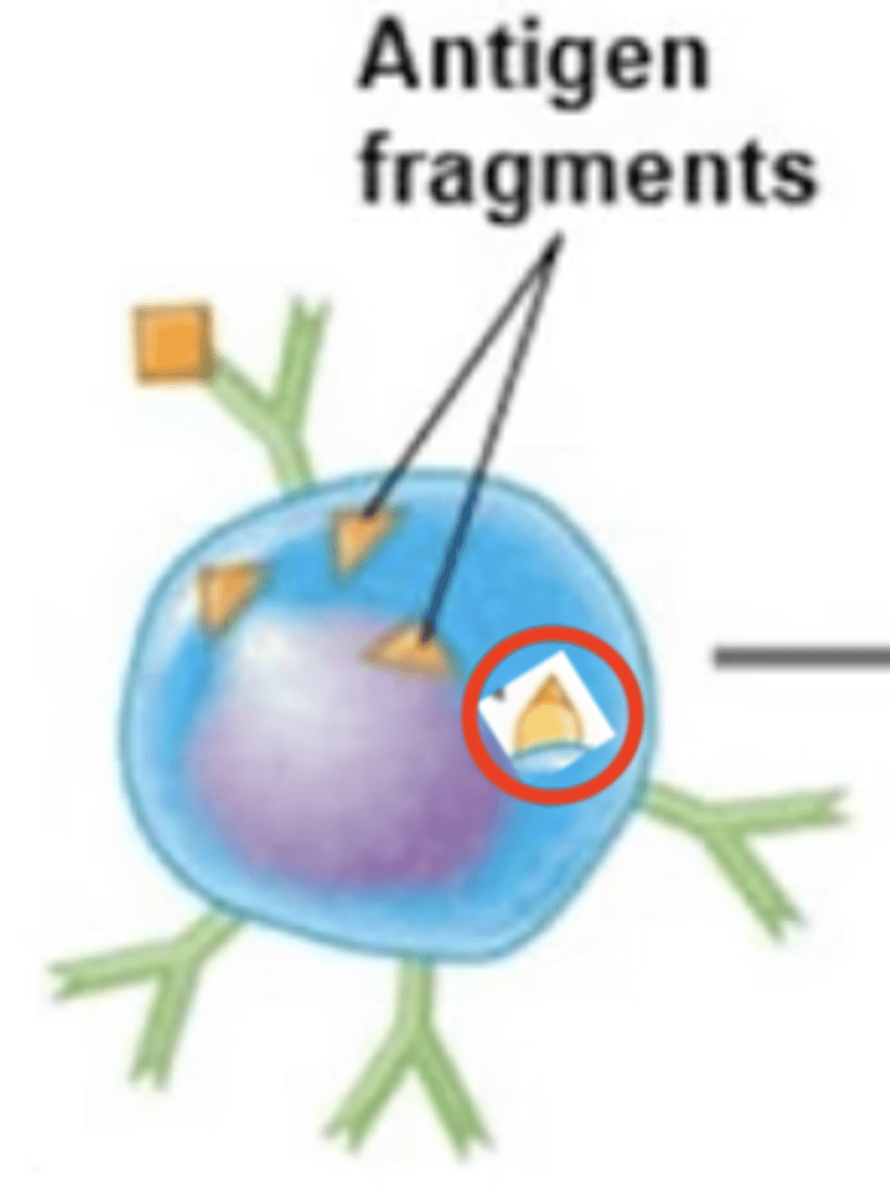
Antigen-MHC-II complex moves to surface of B cell.
B cell activation against T-dependent antigen
Fill in the blank:
1. BCR binds to extracellular antigen.
2. Extracellular antigen enters B cell via endocytosis.
3. Intracellular antigen is digested into antigen fragments = processed antigen.
4. MHC-II receptor binds to processed antigen = antigen-MHC-II complex.
5.
6. MHC-II complex displays processed antigen to Th2 cell.
7. TCR of Th2 binds to processed antigen.
8. CD4 receptor on Th2 binds to MHC-II receptor.
9. Th2 releases cytokines.
10. Cytokines activate B cell.
11. B cell proliferates and differentiates into either plasma cells or memory B cells.
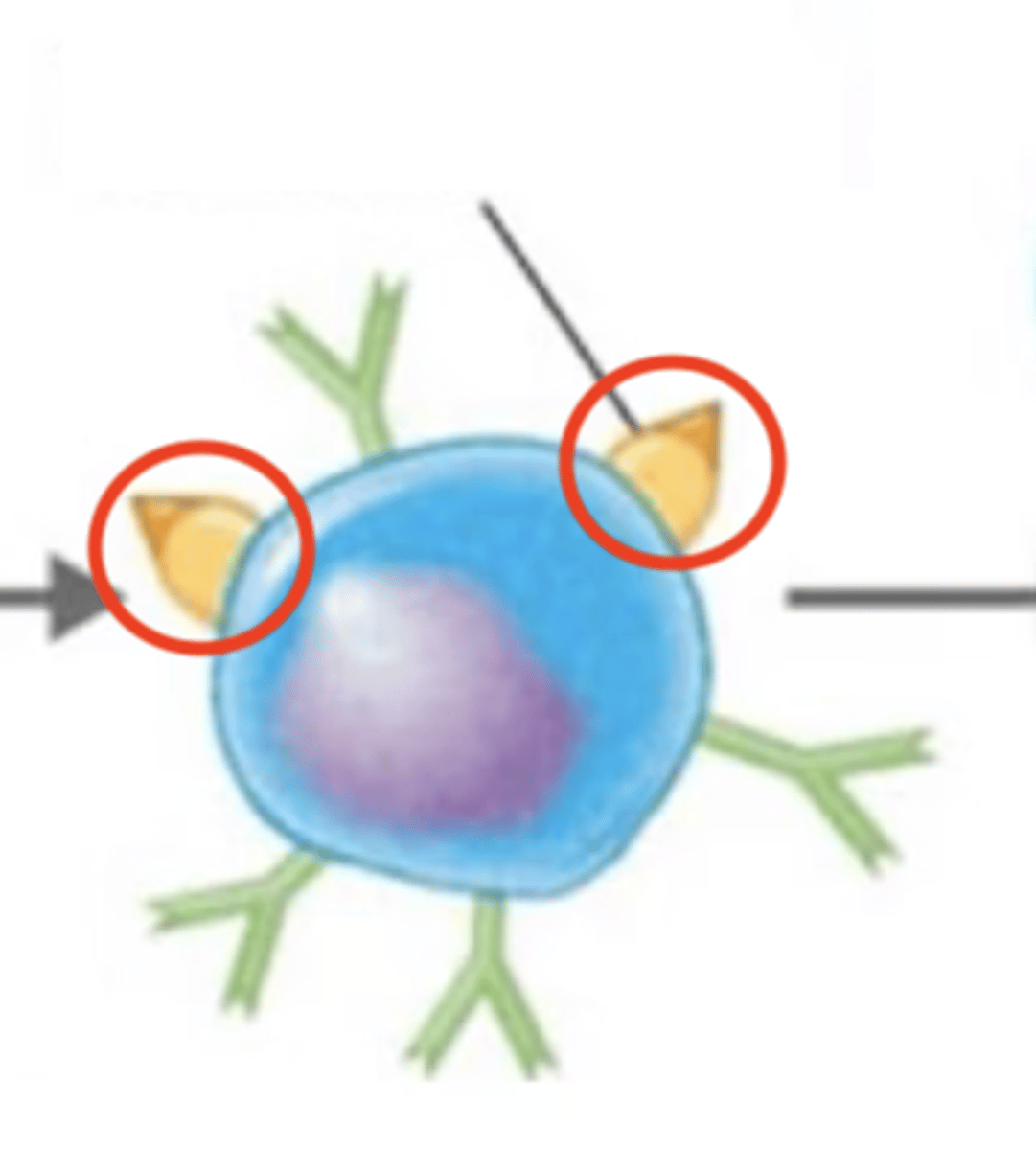
MHC-II complex displays processed antigen to Th2.
B cell activation against T-dependent antigen
Fill in the blank:
1. BCR binds to extracellular antigen.
2. Extracellular antigen enters B cell via endocytosis.
3. Intracellular antigen is digested into antigen fragments = processed antigen.
4. MHC-II receptor binds to processed antigen = antigen-MHC-II complex.
5. Antigen-MHC-II complex moves to surface of B cell.
6.
7. TCR of Th2 binds to processed antigen.
8. CD4 receptor on Th2 binds to MHC-II receptor.
9. Th2 releases cytokines.
10. Cytokines activate B cell.
11. B cell proliferates and differentiates into either plasma cells or memory B cells.
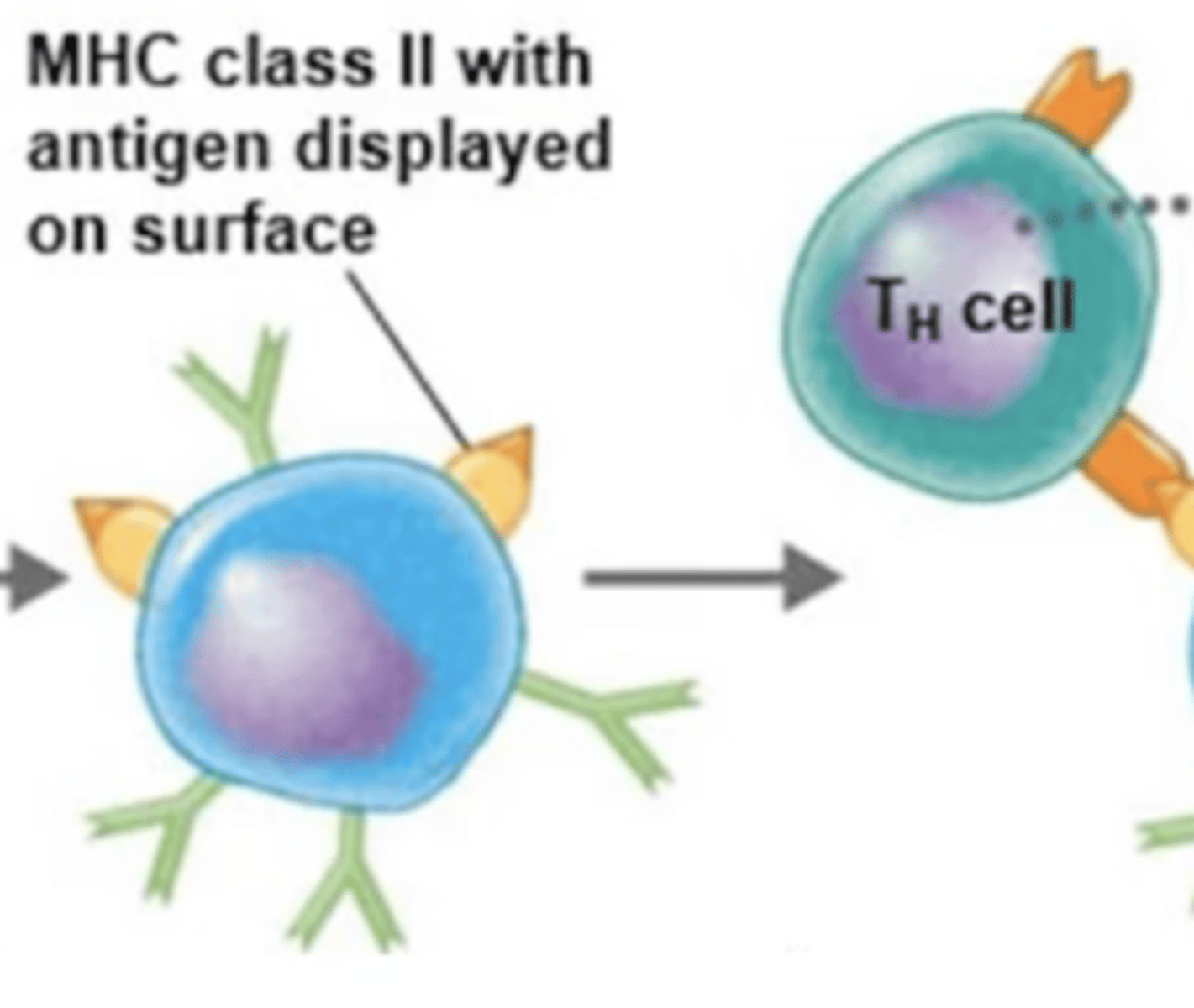
TCR of Th2 binds to processed antigen.
B cell activation against T-dependent antigen
Fill in the blank:
1. BCR binds to extracellular antigen.
2. Extracellular antigen enters B cell via endocytosis.
3. Intracellular antigen is digested into antigen fragments = processed antigen.
4. MHC-II receptor binds to processed antigen = antigen-MHC-II complex.
5. Antigen-MHC-II complex moves to surface of B cell.
6. MHC-II complex displays processed antigen to Th2 cell.
7.
8. CD4 receptor on Th2 binds to MHC-II receptor.
9. Th2 releases cytokines.
10. Cytokines activate B cell.
11. B cell proliferates and differentiates into either plasma cells or memory B cells.
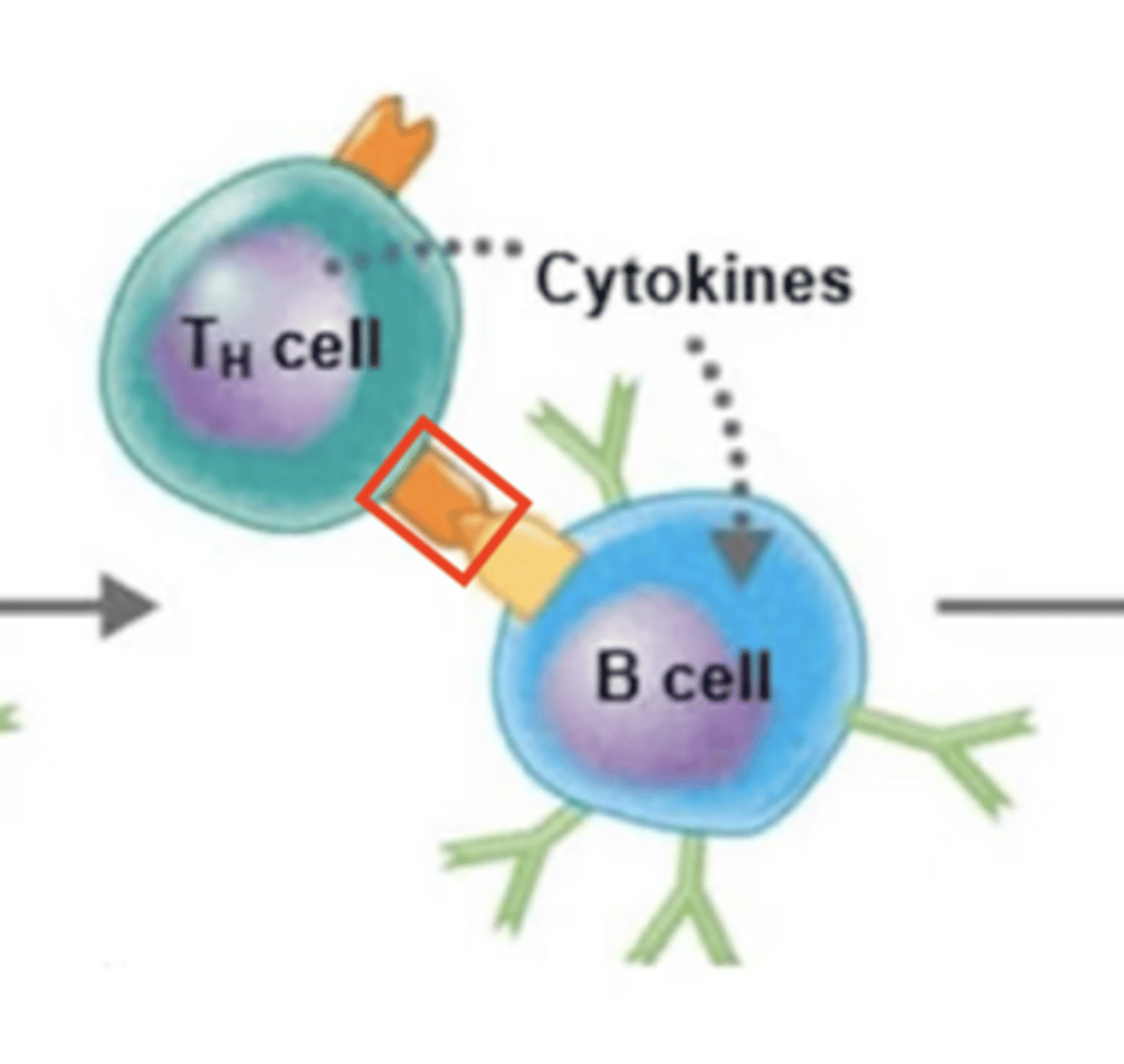
CD4 receptor on Th2 binds to MHC-II receptor.
B cell activation against T-dependent antigen
Fill in the blank:
1. BCR binds to extracellular antigen.
2. Extracellular antigen enters B cell via endocytosis.
3. Intracellular antigen is digested into antigen fragments = processed antigen.
4. MHC-II receptor binds to processed antigen = antigen-MHC-II complex.
5. Antigen-MHC-II complex moves to surface of B cell.
6. MHC-II complex displays processed antigen to Th2 cell.
7. TCR of Th2 binds to processed antigen.
8.
9. Th2 releases cytokines.
10. Cytokines activate B cell.
11. B cell proliferates and differentiates into either plasma cells or memory B cells.