Cows: Salmonella & Winter Dysentery
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A set of flashcards focused on key concepts related to infectious gastrointestinal diseases in cattle, particularly Salmonellosis and Winter Dysentery.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
What family does Salmonellosis belong to?
Family Enterobacteriaceae
How many serotypes of Salmonella are there?
There are 2200 serotypes based on O and H antigen groups.

What are the common serotypes of Salmonella that cause disease in cattle?
Salmonella Dublin, Salmonella Cerro, Salmonella Newport, Salmonella Montevideo, Salmonella Kentucky, Salmonella Typhimurium.
What is the transmission route for Salmonellosis?
Fecal-oral transmission, direct and indirect contact, contaminated environment, airborne, animal to animal
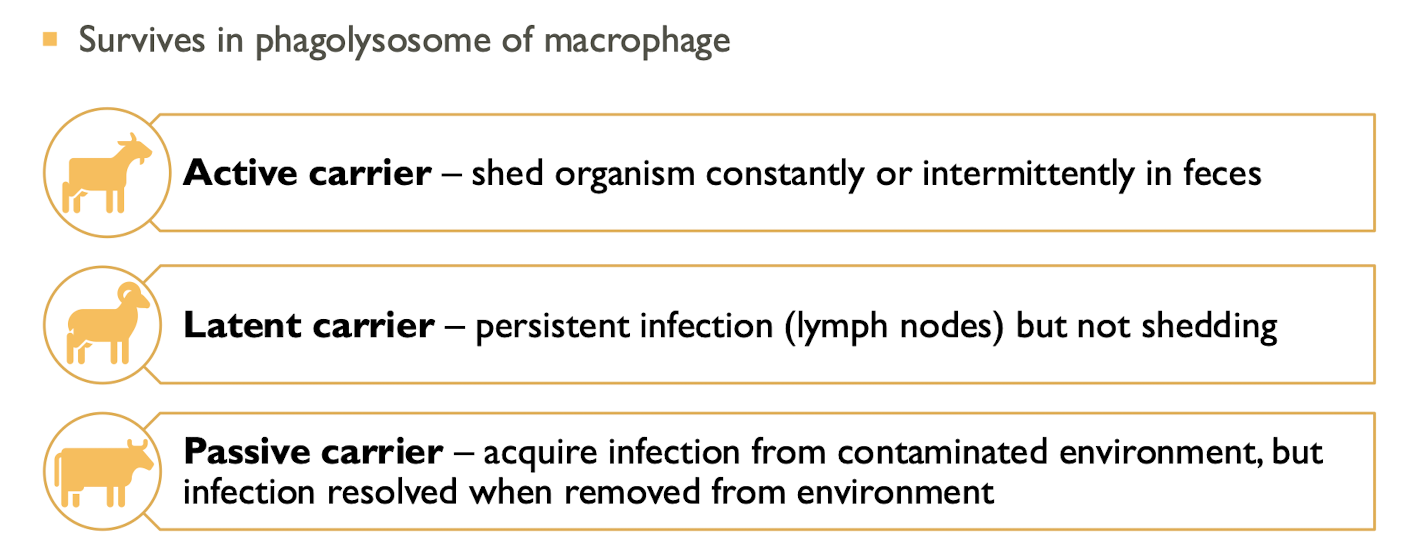
What are the types of carriers for Salmonella?
Active carrier, latent carrier, and passive carrier.
Pathogenesis of salmonellosis
Penetrates into ocular, nasal, oral, & intestinal membranes → S. dublin Invades through intestinal wall of ileum & cecum → infects mesenteric lymph nodes
factors affecting type of disease: immune status, age, stress, virulence
adhesion pilli, flagella, cytotoxins, enterotoxins, LPS, inflammatory response
Virulence plasmid causes macrophage dysfunction → systemic infection
General clinical signs of salmonella
Septicemia
Acute enteritis
Chronic enteritis
Terminal dry gangrene of the extremities
Abortion
What clinical signs are associated with septicemia in calves related to Salmonellosis?
Depression, toxemia, fever, dyspnea, weakness, nervous signs(incoordination, nystagmus), diarrhea.
What is a significant clinical sign of acute enteritis in older calves and adults with salmonellosis?
Acute protein losing enteropathy
Abortions
Polyarthritis (calves)
Diarrhea
Agalactia
Abdominal pain → rolling, kicking, crouching, groaning, flank watching
What are the clinical signs from Chronic enteritis with salmonellosis?
inappetence
reduced weight gain
unthrifitiness
What serovar causes abortion?
S. dublin
What laboratory findings are indicative of Salmonellosis?
CBC may show leukopenia, neutropenia, severe degenerative left shift
Biochem marked hyponatremia, mild hypokalemia (not eating anymore), hypoproteinemia (they are losing a lot)

How do we treat salmonellosis?
antimicrobials → only for septicemia
fluids
electrolytes
NSAIDs → only if animal is in pain because it delays mucosal healing
What types of vaccines are available for controlling Salmonella in cattle?
Killed and modified live vaccines.

What is the main cause of Winter Dysentery in cattle?
Bovine coronavirus → Tropism for intestinal & respiratory tract, common in northern climates
Morbidity: 30-59%
Mortality <1 %
How is Winter Dysentery transmitted among cattle?
Fecal-oral route from infected or asymptomatic carriers → highly contagious
Pathogenesis of winter dysentery
Virus has tropism for GI and respiratory tract → Mild small intestinal enteritis → Respiratory disease & pneumonia → Destroys epithelial cells of colon crypts → Mechanism of voluminous watery diarrhea not clear → Inflammatory medicators may lead to hyper-secretion in the small intestine & large colon
What are clinical signs of Winter Dysentery?
3-7 days incubation → Explosive diarrhea 4-7 days, fever, decreased milk production, dehydration
young animals have mild signs
nasolacrimal discharge and cough before GI signs
What diagnostic methods are used for identifying Winter Dysentery?
Electron microscopy, ELISA test, paired serology testing (8 weeks apart)
What are the necropsy lesions associated with fatal cases of Winter Dysentery?
Severe hemorrhage, hyperemia of colonic and cecal mucosa, frank blood in the lumen of large intestine, microscopically widespread necrosis with degeneration of large bowel epithelium
What treatments are generally recommended for Winter Dysentery?
Supportive therapy, fluids, and electrolytes
DDx for winter dysentery
BVDV - Mucosal disease
Coccidiosis
Salmonellosis
Johne’s disease
Dietary
Copper deficiency
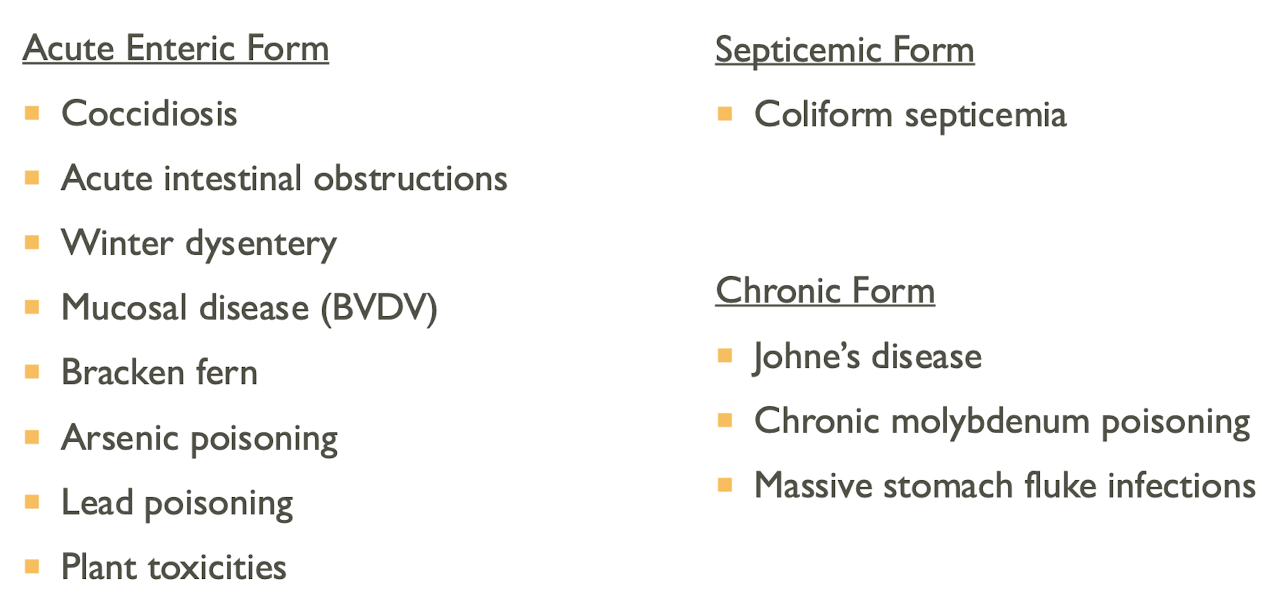
DDx for Salmonellosis
Acute enteric form
Septicemic form
Chronic form