KIN 3304 Exam #3
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/180
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 5:29 AM on 11/12/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
181 Terms
1
New cards
The hip joint is a _____ joint
ball and socket
2
New cards
The tibiofemoral joint is a _____ joint
modified hinge
3
New cards
The _____ forms the ‘ball’ and the _____ forms the ‘socket’ of the hip joint.
femoral head, acetabulum
4
New cards
During standing, the weight of the body is transferred from the spinal column to the _____ (hip) to the _____ (upper leg) to the _____ (lower leg).
pelvis, femur, tibia
5
New cards
The three boney segments that form the pelvic skeleton are _____, _____ and _____
Ilium, ischium, pubis
6
New cards
The longest muscle in the body is the _____; the longest bone in the body is the _____
Sartorius, femur
7
New cards
The iliotibial (IT) band consists of the combined tendons from the _____ and the _____
Tensor fasciae latae, gluteus maximus
8
New cards
The group of muscles known as the iliopsoas consists of the _____ and the _____
Iliacus, psoas major/minor
9
New cards
The gastrocnemius, soleus, and plantaris muscles all insert at the _____ of the foot.
Posterior surface of calcaneus with achilles tendon
10
New cards
The _____ and _____ share the Achilles as a tendon of insertion.
Gastrocnemius, soleus
11
New cards
The muscle of the quadriceps group that crosses both the hip and knee joint is the ______
Rectus femoris
12
New cards
Muscles that cross the posterior aspect of the knee are usually involved in _____ at the knee.
Flexion
13
New cards
Supination of the foot is a combination of ______, _____, and forefoot ______
Ankle plantar flexion, subtalar inversion, forefoot adduction
Basically, plantar flexion, inversion, and adduction
Basically, plantar flexion, inversion, and adduction
14
New cards
The _____ is the prominent bony landmark on the distal end of the tibia.
Medial malleolus
15
New cards
There is more movement in the _____ and _____ regions of the spinal column than in the _____ region.
Cervical, lumbar, thoracic
16
New cards
The _____ muscles are different in that they attach from bone to an aponeurosis.
Abdominal
17
New cards
The fundamental movements of the hip joint are
Flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, internal rotation, external rotation, diagonal abduction (out and away from body), diagonal adduction (in and towards body), horizontal abduction, horizontal adduction
18
New cards
List the anterior hip muscles and the primary action of this group + action
Iliopsoas
Pectineus
Rectus femoris
Sartorius
Action: hip flexion
Pectineus
Rectus femoris
Sartorius
Action: hip flexion
19
New cards
List the posterior hip muscles and the primary action of this group + action
Gluteus maximus
Bicep femoris*
Semitendinosus*
Semimembranosus*
External rotators
*These indicate the muscles that make up your hamstring, more action at knee than the hip
Action: Hip extension
Bicep femoris*
Semitendinosus*
Semimembranosus*
External rotators
*These indicate the muscles that make up your hamstring, more action at knee than the hip
Action: Hip extension
20
New cards
List the deep posterior muscles of the hip and the primary action of this group + action
Deep lateral rotators (Quadratus femoris, piriformis, gemellus superior and inferior, internal, and external obturator)
Action: external rotation
Action: external rotation
21
New cards
List the lateral muscles of the hip and the primary action of the group + action
Gluteus Medius
Gluteus minimus
External rotators
Tensor fasciate latae
Action: Hip abduction
Gluteus minimus
External rotators
Tensor fasciate latae
Action: Hip abduction
22
New cards
List the medial muscles of the hip and the primary action of the group + action
Adductor brevis
Adductor longus
Adductor magnus
Gracilis
Action: hip adduction
Adductor longus
Adductor magnus
Gracilis
Action: hip adduction
23
New cards
List the muscles of the hamstrings. What is the primary action of this group at the hip and knee joints?
Biceps femoris
Semitendinosus
Semimembranosus
Action at hip: Hip extension
Action at knee: Knee flexion
Semitendinosus
Semimembranosus
Action at hip: Hip extension
Action at knee: Knee flexion
24
New cards
List the anterior knee muscles and the primary action of this group + action
Rectus femoris
Vastus intermedius
Vastus lateralis
Vastus medialis
Sartorius
Gracilis
Action: knee extension
Vastus intermedius
Vastus lateralis
Vastus medialis
Sartorius
Gracilis
Action: knee extension
25
New cards
List the posterior knee muscles and the primary action of this group + action
Bicep femoris
Semimembranosus
Semitendinosus
Popliteus
Gastrocnemius
Plantaris
Action: Knee flexion
Semimembranosus
Semitendinosus
Popliteus
Gastrocnemius
Plantaris
Action: Knee flexion
26
New cards
List the muscles of the anterior compartment of the lower leg and the primary action of this group + action
Tibialis anterior (dorsiflexion, inversion)
Peroneus tertius (dorsiflexion, eversion)
Extensor digitorum longus (extends the toe, dorsiflexion)
Extensor hallucis longus (extends the big toe, dorsiflexion
Action: dorsiflexion
Peroneus tertius (dorsiflexion, eversion)
Extensor digitorum longus (extends the toe, dorsiflexion)
Extensor hallucis longus (extends the big toe, dorsiflexion
Action: dorsiflexion
27
New cards
List the muscles of the lateral compartment of the lower leg and the primary action of the group + action
Peroneus longus
Peroneus brevis
Action: Eversion
Peroneus brevis
Action: Eversion
28
New cards
List the muscles of the superficial posterior compartment of the lower leg and the primary action of the group + action
Gastrocnemius
Soleus
Plantaris
Action at knee: flexion
Action at ankle: plantar flexion
Soleus
Plantaris
Action at knee: flexion
Action at ankle: plantar flexion
29
New cards
List the muscles of the deep posterior compartment of the lower leg and the primary action of the group + action
Popliteus
Flexor digitorum longus
Flexor hallucis longus
Tibialis posterior
Action at ankle: plantar flexion
Action at foot: inversion, flexes toe
Flexor digitorum longus
Flexor hallucis longus
Tibialis posterior
Action at ankle: plantar flexion
Action at foot: inversion, flexes toe
30
New cards
List the anterior muscles of the thorax and the primary action of the group
Rectus abdominis (lumbar flexion and posterior pelvic rotation)
External oblique abdominal (lumbar flexion, lumbar lateral flexion, posterior pelvic rotation)
Internal oblique abdominal (lumbar flexion, posterior pelvic rotation, lumbar lateral flexion)
Transverse abdominis (forced expiration)
Psoas major and minor (lumbar flexion, lumbar lateral flexion, anterior pelvic rotation)
Basically, lumbar flexion
External oblique abdominal (lumbar flexion, lumbar lateral flexion, posterior pelvic rotation)
Internal oblique abdominal (lumbar flexion, posterior pelvic rotation, lumbar lateral flexion)
Transverse abdominis (forced expiration)
Psoas major and minor (lumbar flexion, lumbar lateral flexion, anterior pelvic rotation)
Basically, lumbar flexion
31
New cards
List the posterior muscles of the thorax and the primary action of the group.
Erector spinae group : Iliocostalis, longissimus, spinalis ( extension, lateral flexion, and ipsilateral rotation of the spine and head, anterior pelvic rotation, contralateral pelvic rotation)
Quadratus lumborum (lateral flexion, extension of lumbar spine, anterior pelvic rotation, contralateral pelvic rotation)
Sternocleidomastoid (extension of head, cervical flexion, rotation and lateral flexion of cervical spine)
Splenius (extension of head, rotation and lateral flexion of cervical spine)
Basically, lateral flexion
Quadratus lumborum (lateral flexion, extension of lumbar spine, anterior pelvic rotation, contralateral pelvic rotation)
Sternocleidomastoid (extension of head, cervical flexion, rotation and lateral flexion of cervical spine)
Splenius (extension of head, rotation and lateral flexion of cervical spine)
Basically, lateral flexion
32
New cards
List the muscles of the quadriceps group. What is the primary action of this group at the hip and knee joints?
Rectus femoris
Vastus intermedius
Vastus lateralis
Vastus medialis
Action: Hip flexion and Knee extension
Vastus intermedius
Vastus lateralis
Vastus medialis
Action: Hip flexion and Knee extension
33
New cards
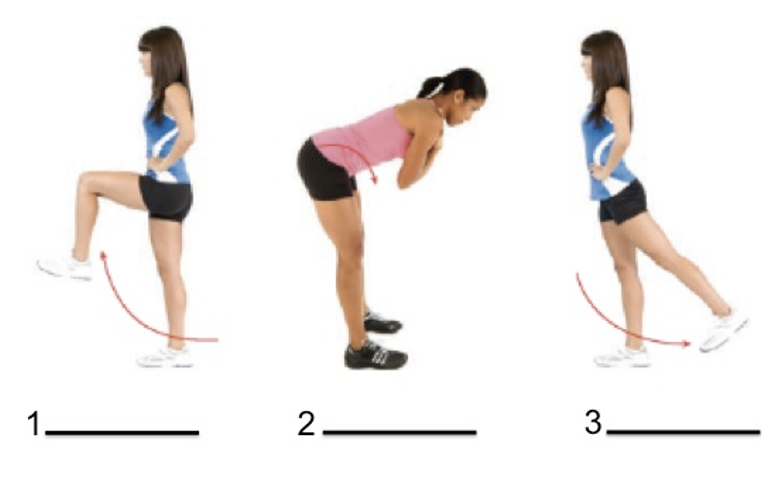
Label the first movement
Hip flexion
Knee flexion
Knee flexion
34
New cards
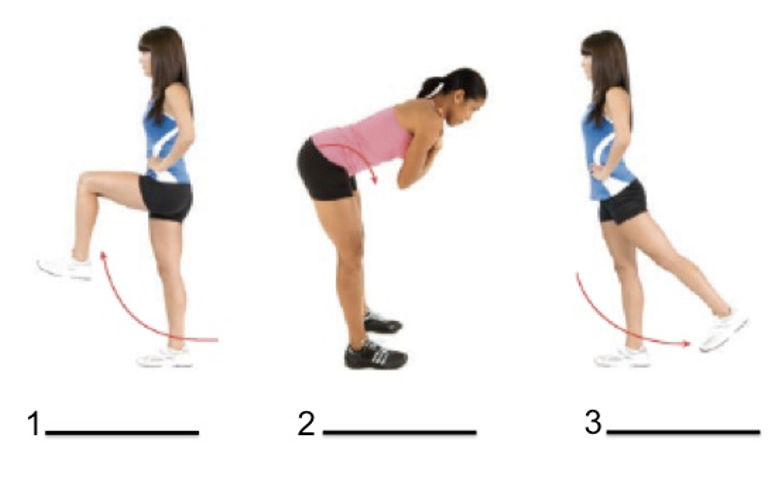
Label the second movement
Anterior pelvic tilt
Lumbar flexion
Lumbar flexion
35
New cards
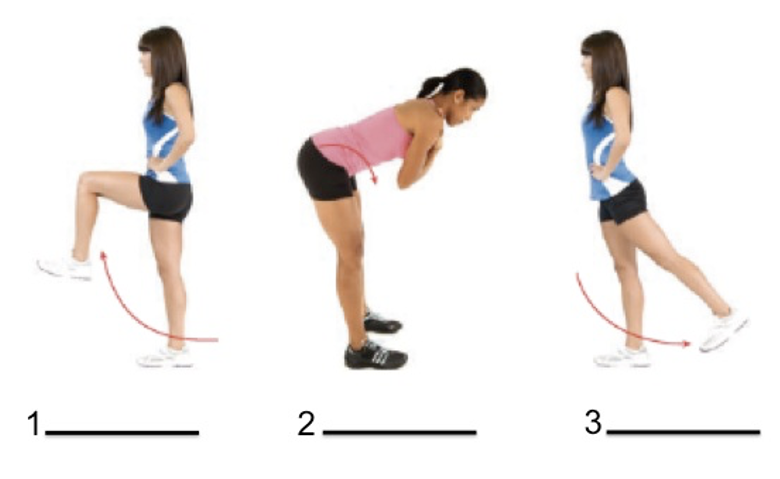
Label the third movement
Hip extension
Knee extension
Knee extension
36
New cards
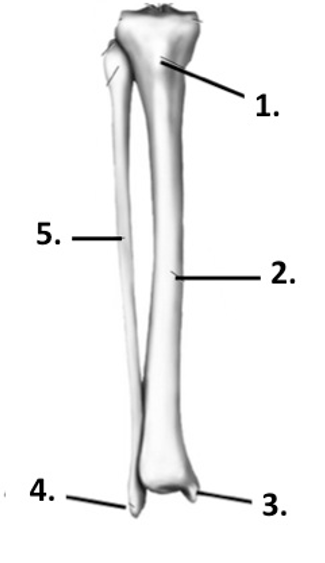
Label the structure at 1 (tibia + fibula)
Tibial tuberosity
37
New cards
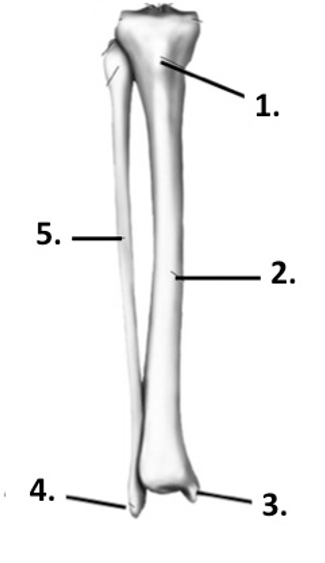
Label the structure at 2 (tibia + fibula)
Tibia
38
New cards
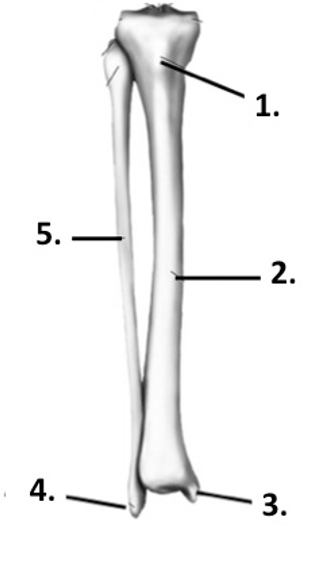
Label the structure at 3 (tibia + fibula)
Medial malleolus
39
New cards
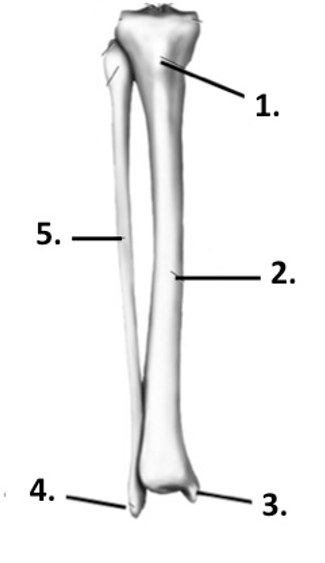
Label the structure at 4 (tibia + fibula)
Lateral malleolus
40
New cards
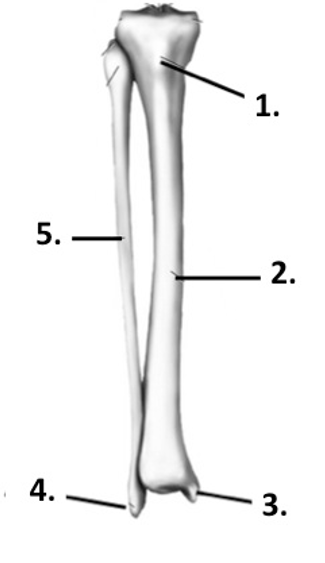
Label the structure at 5 (tibia + fibula)
Fibula
41
New cards
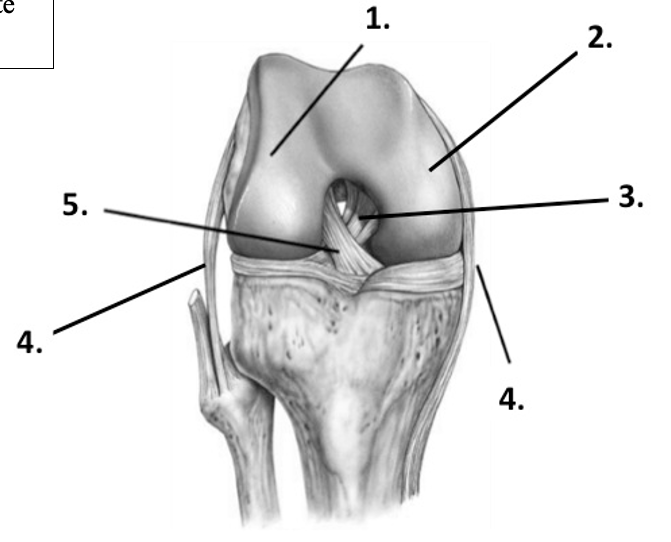
Label the structure at 1 (knee)
Lateral condyle of femur
42
New cards
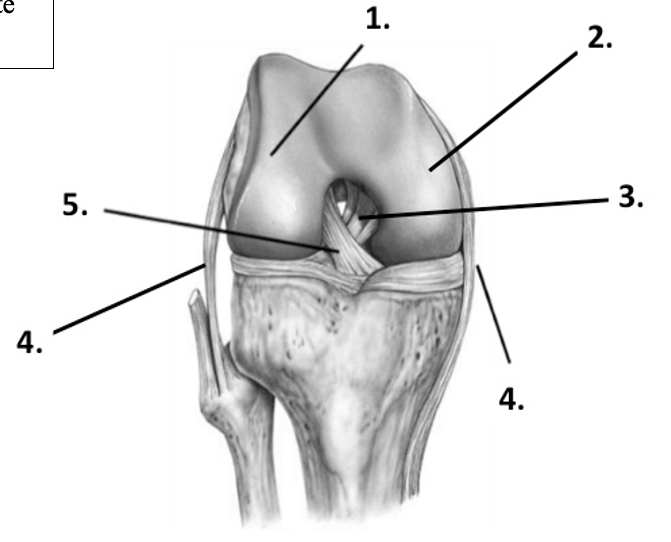
Label the structure at 2 (knee)
Medial condyle of femur
43
New cards
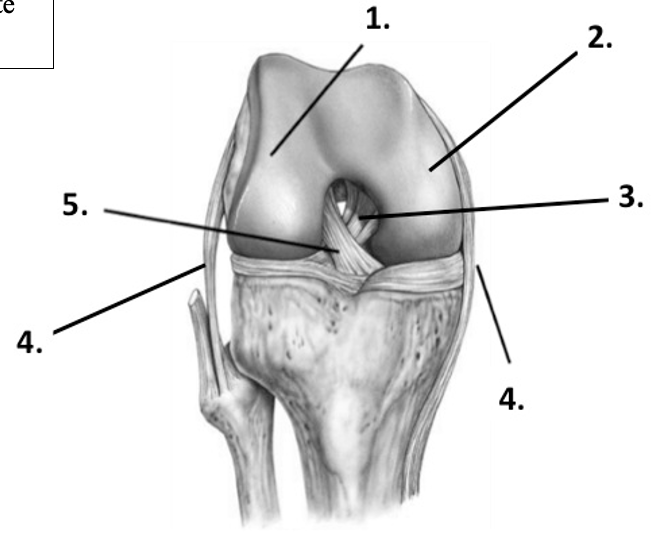
Label the structure at 3 (knee)
Posterior cruciate ligament
44
New cards
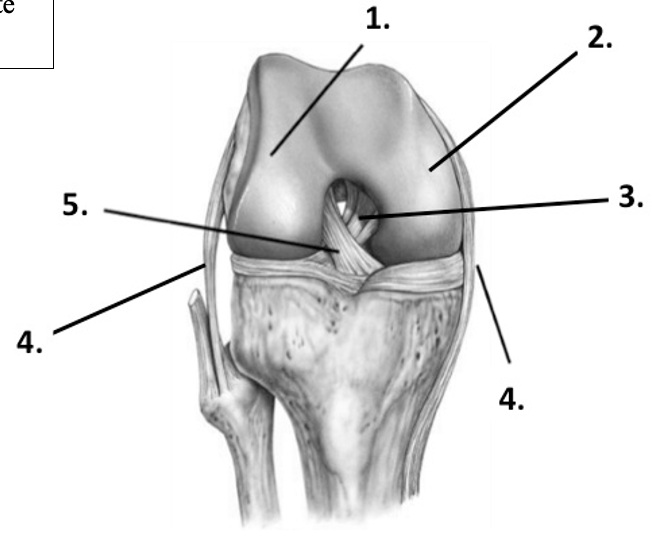
Label the structure at 4 (knee, lateral)
Fibular (lateral) collateral ligament
45
New cards
Label the structure at 4 (knee, medial)
Tibial (medial) collateral ligament
46
New cards
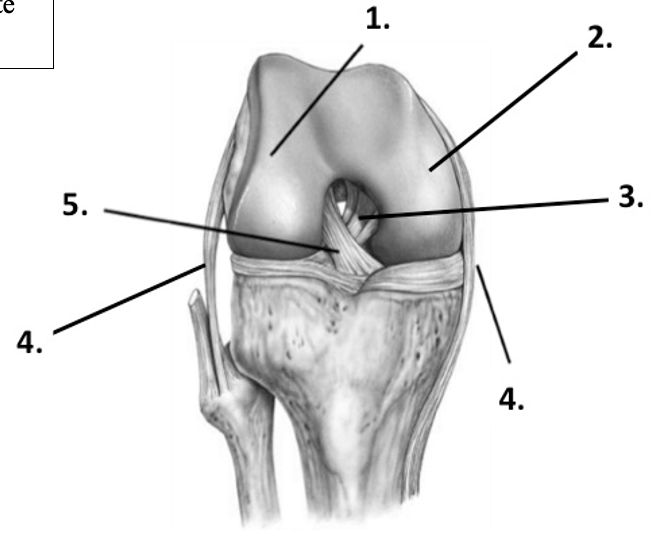
Label the structure at 5 (knee)
Anterior cruciate ligament
47
New cards
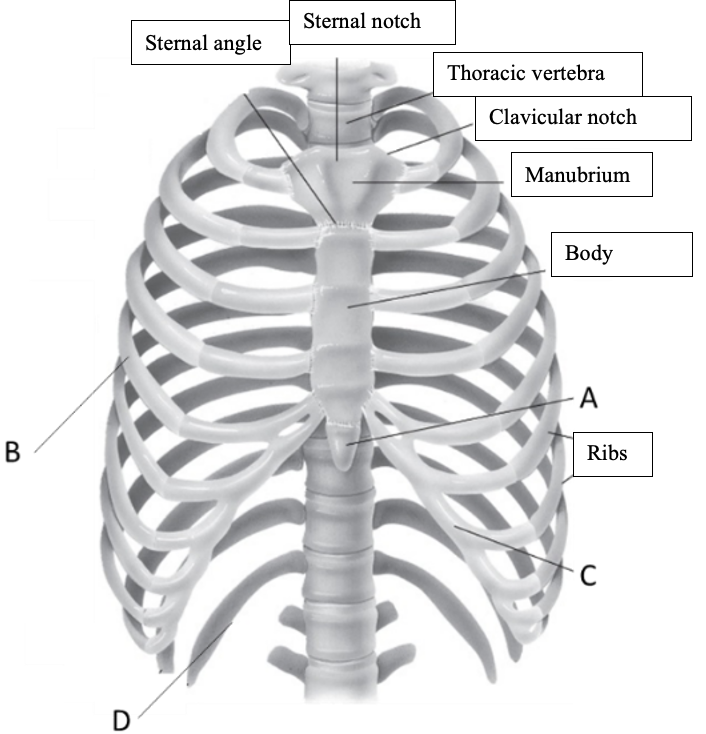
Label the structure at A
Xiphoid process
48
New cards
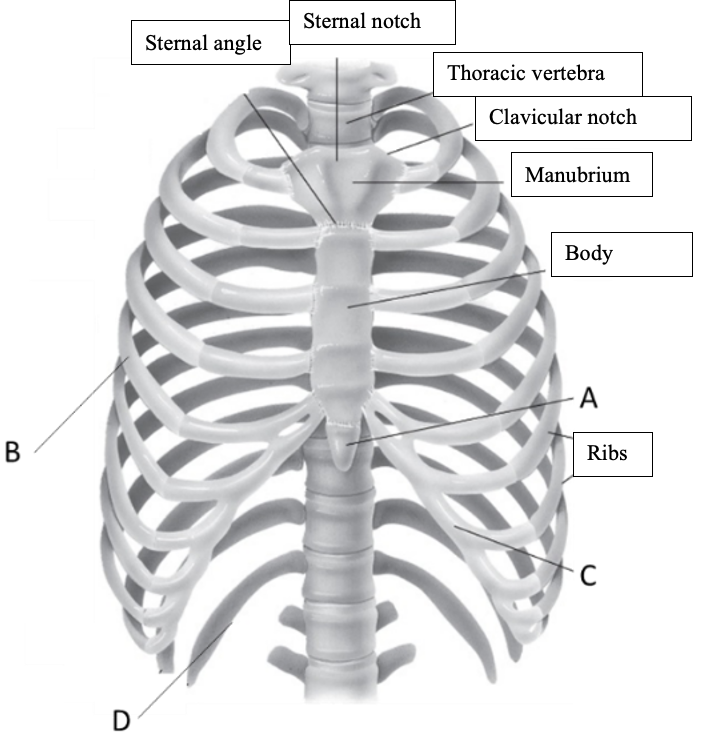
Label the structure at B
True ribs (vertebrosternal ribs)
49
New cards
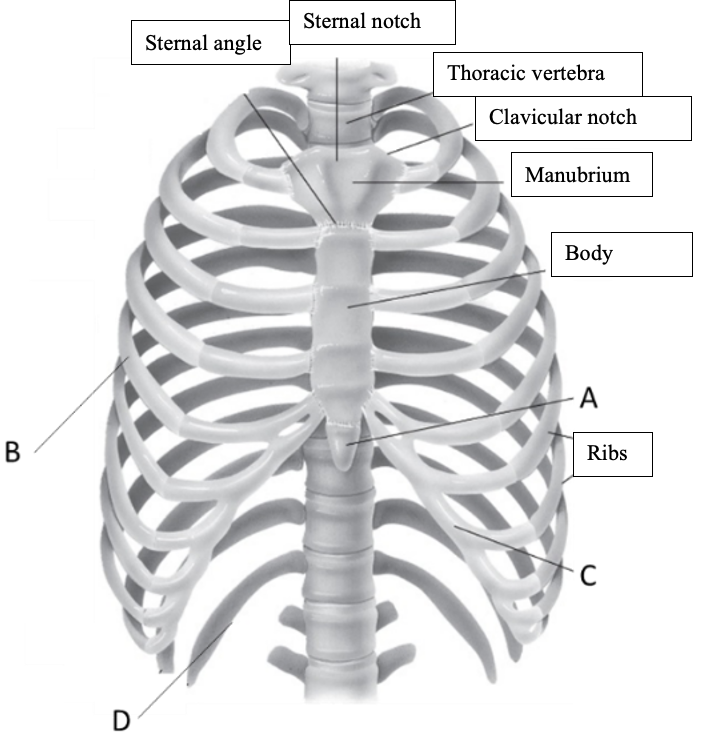
Label the structure at C
Costal cartilage
50
New cards
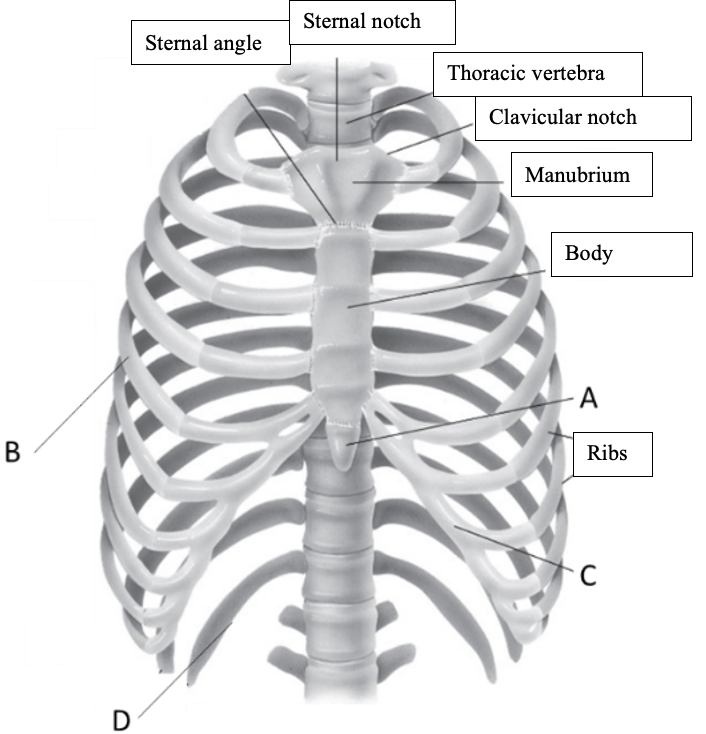
Label the structure at D
Floating ribs (vertebral ribs)
51
New cards
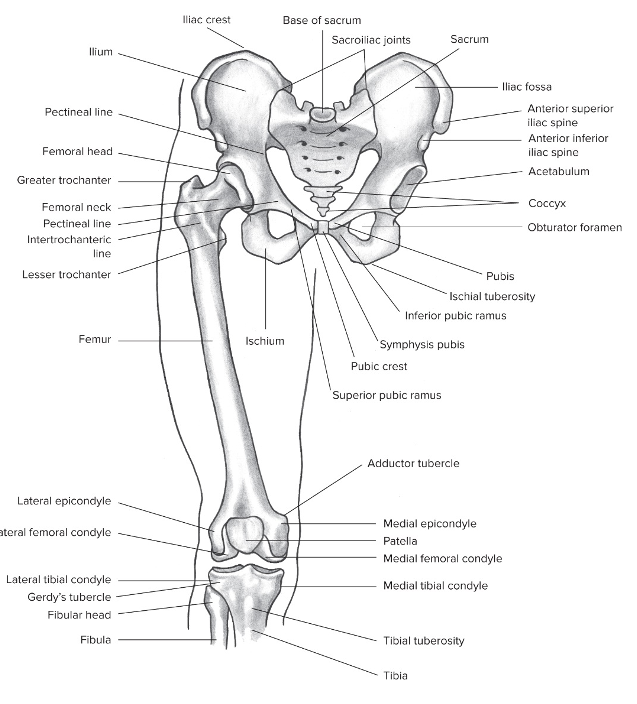
Overview of the hip joint
Relatively stable due to bony architecture, strong ligaments, and large muscles
Functions in both weight bearing and locomotion (walking running jumping)
Wide range-of-motion
Functions in both weight bearing and locomotion (walking running jumping)
Wide range-of-motion
52
New cards
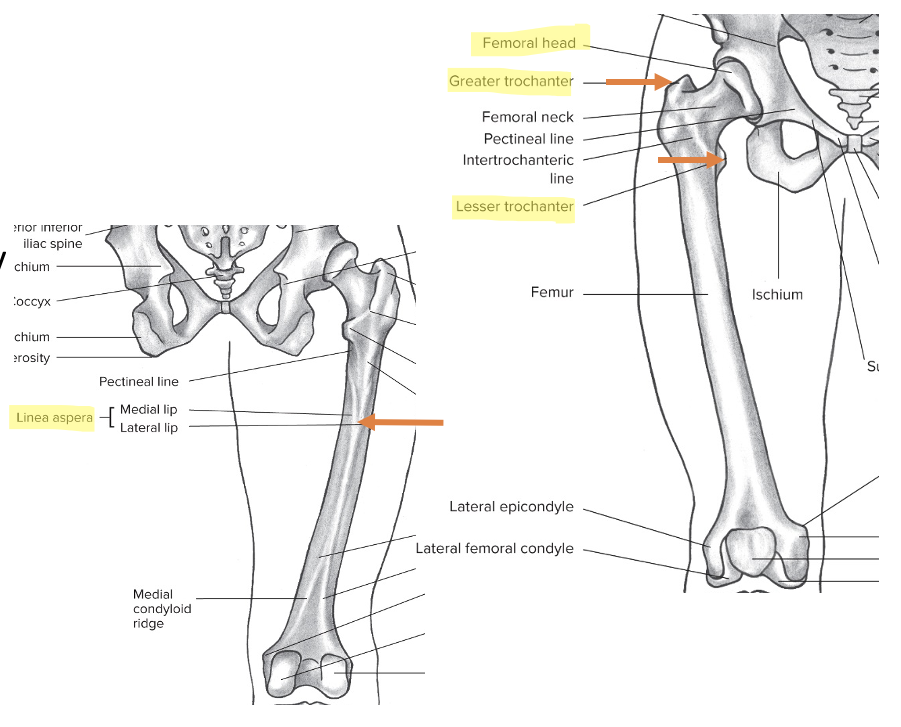
Overview of the femur + bony landmarks
The longest bone in the body
Bony landmarks:
Head
Great trochanter
Lesser trochanter
Linea aspera
Posterior shaft
Bony landmarks:
Head
Great trochanter
Lesser trochanter
Linea aspera
Posterior shaft
53
New cards
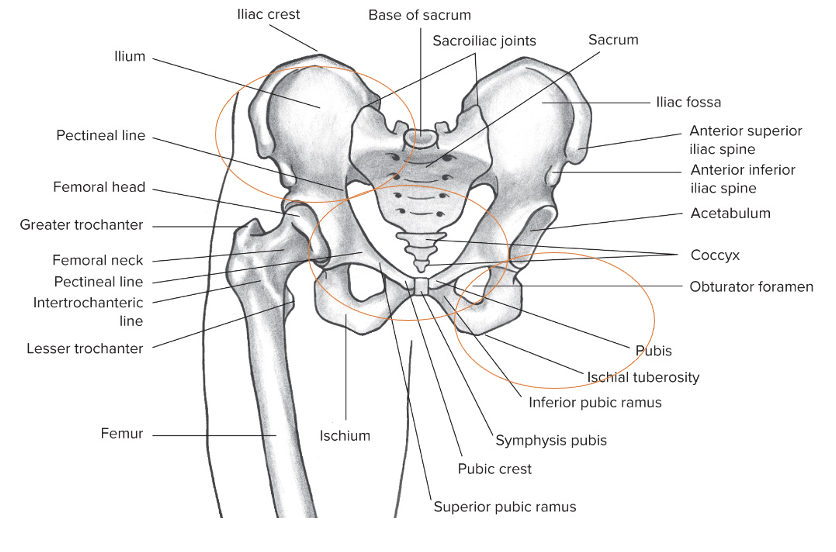
What bones make up the pelvic girdle?
Ilium: superior
Ischium: posterior
Pubis: anterior
They make up the three rings and all move together, never independently
Ischium: posterior
Pubis: anterior
They make up the three rings and all move together, never independently
54
New cards
Fun fact about the pelvic girdle
As a kid, the ilium, ischium, and pubis are three separate part but then it fuses together through puberty
55
New cards
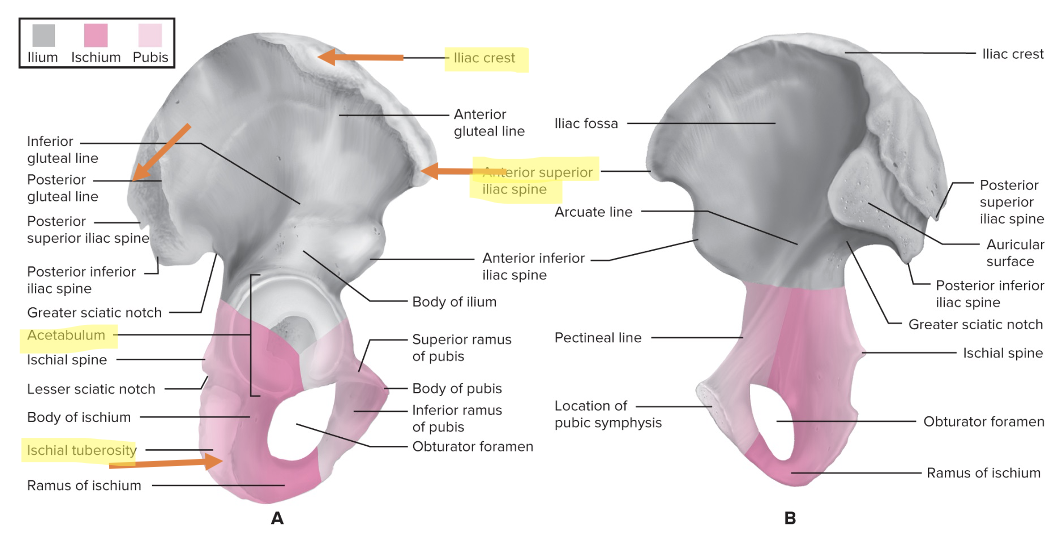
What are the bony landmarks on the pelvic girdle?
Iliac crest
Iliac spine
Ischial tuberosity: you can feel it while sitting down
Acetabulum
Iliac spine
Ischial tuberosity: you can feel it while sitting down
Acetabulum
56
New cards
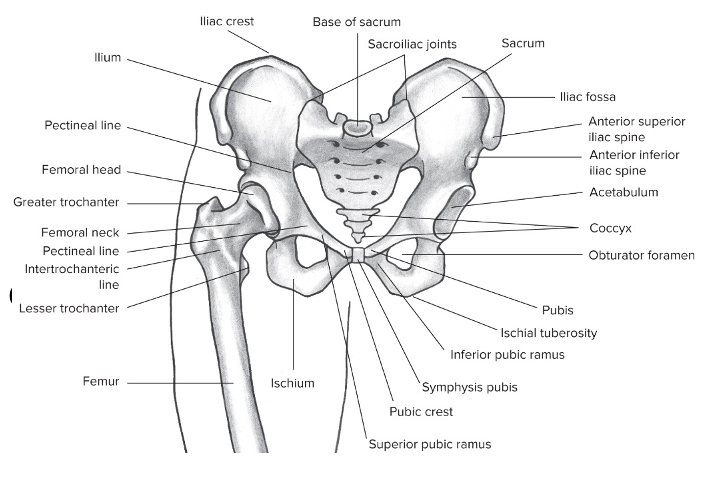
What type of joint is the pelvic girdle and what is its purpose?
Ampiarthrodial joint that consists of right and left pelvic bones
Function:
Minimal oscillating movement during hip flexion
Shock absorption
Function:
Minimal oscillating movement during hip flexion
Shock absorption
57
New cards
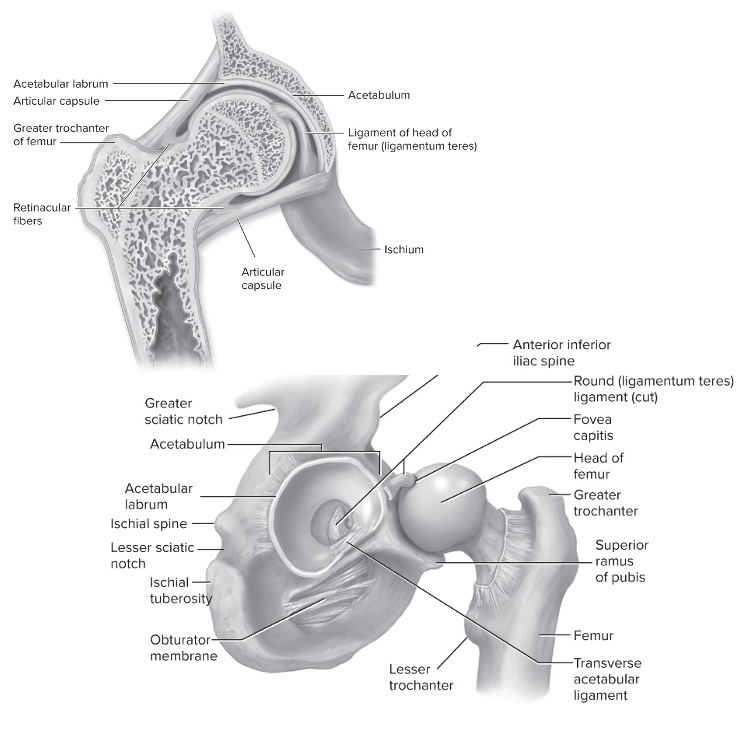
What type of joint is the hip?
Ball and socket joint
Head of femur (ball) with acetabulum (socket) of pelvic girdle
Head of femur (ball) with acetabulum (socket) of pelvic girdle
58
New cards
What are the movements of the hip joint?
Extension
Abduction
Adduction
Internal rotation
External rotation
Diagonal abduction (out and away from body)
Diagonal adduction (in and towards body)
Horizontal abduction
Horizontal adduction
Abduction
Adduction
Internal rotation
External rotation
Diagonal abduction (out and away from body)
Diagonal adduction (in and towards body)
Horizontal abduction
Horizontal adduction
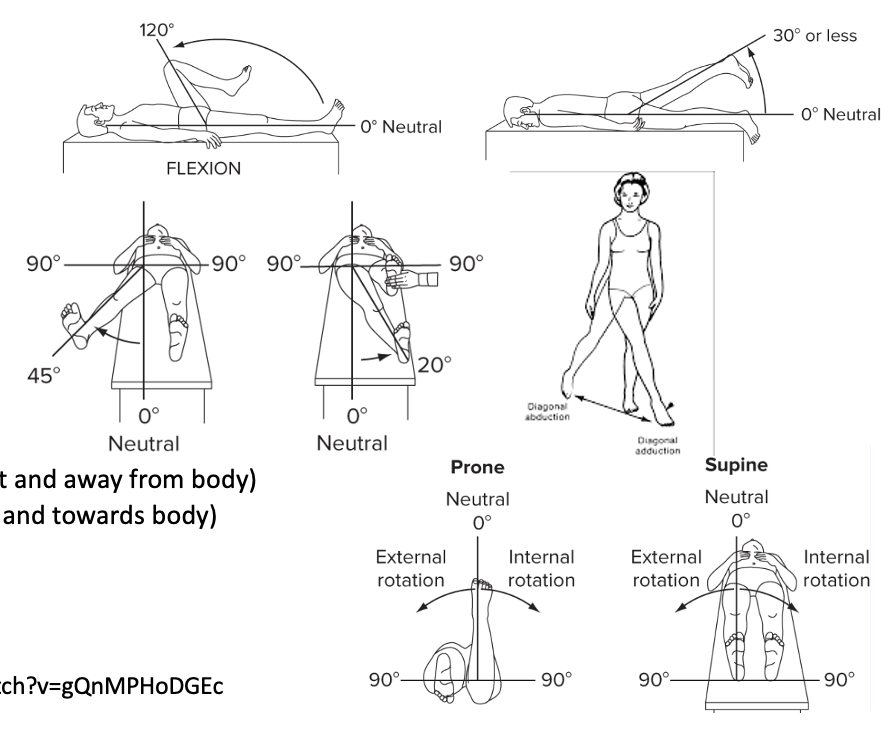
59
New cards
Movements of the pelvic girdle
6 rotational movements in three planes
Results from motion at either hip and/or lumbar spine:
Anterior and posterior pelvic rotation
Left and right lateral pelvic rotation
Left and right transverse pelvic rotation
Consider each movement from perspective of person’s pelvic that is actually moving
Results from motion at either hip and/or lumbar spine:
Anterior and posterior pelvic rotation
Left and right lateral pelvic rotation
Left and right transverse pelvic rotation
Consider each movement from perspective of person’s pelvic that is actually moving
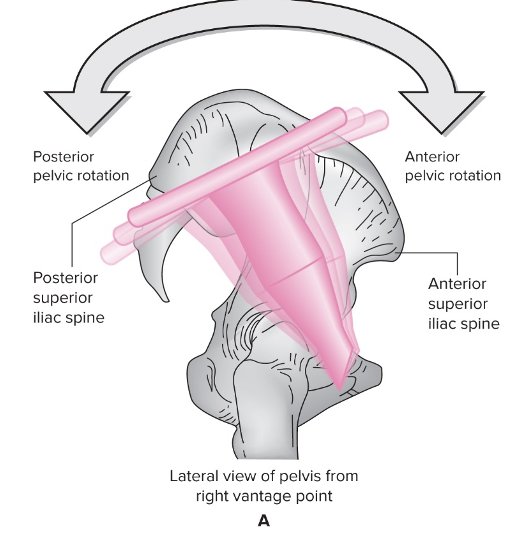
60
New cards
Anterior pelvic rotation (anterior tilt)
Iliac crest tilts forward in sagittal plane
61
New cards
Posterior pelvic rotation (posterior tilt)
Iliac crest tilts backwards in sagittal plane
62
New cards
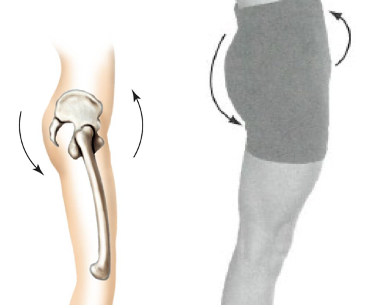
Left lateral pelvic rotation (left lateral tilt)
Frontal plane: left pelvis move inferiorly relative to right pelvis
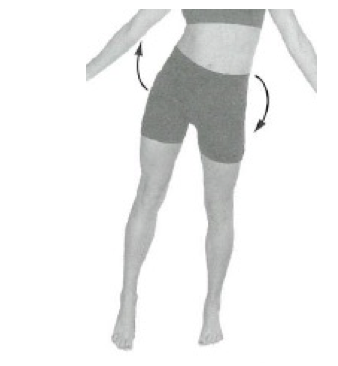
63
New cards
Right lateral pelvic rotation (right lateral tilt)
Frontal plane: right pelvis moves inferiorly relative to left pelvis
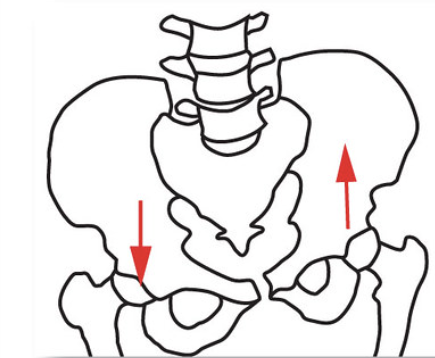
64
New cards
Left transverse pelvic rotation
In horizontal plane, rotation of pelvis to the body’s left
Right iliac crest moves anteriorly relative to left iliac crest
Right iliac crest moves anteriorly relative to left iliac crest
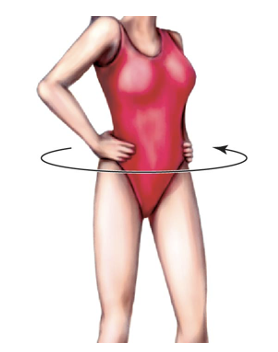
65
New cards
Right transverse pelvic rotation
In horizontal plane, rotation of pelvis to the body’s right
Left iliac crest moves anteriorly relative to right iliac crest
Left iliac crest moves anteriorly relative to right iliac crest
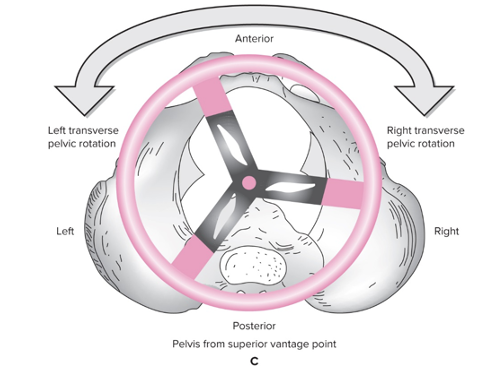
66
New cards
Body part that moves the most will be the _____ stabilized
Least
67
New cards
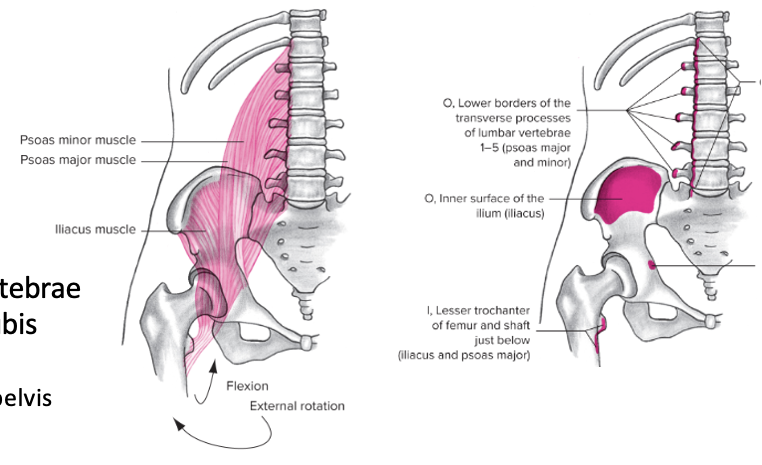
Iliopsoas (true groin)
Anterior, contains the Iliacus, psoas major and minor
Origin: Ilium and lumbar vertebrae
Insertion: Lesser trochanter and pubis
Action at pelvis: anterior pelvic rotation, transverse pelvis rotation
Action at hip: Flexion and external rotation
Origin: Ilium and lumbar vertebrae
Insertion: Lesser trochanter and pubis
Action at pelvis: anterior pelvic rotation, transverse pelvis rotation
Action at hip: Flexion and external rotation
68
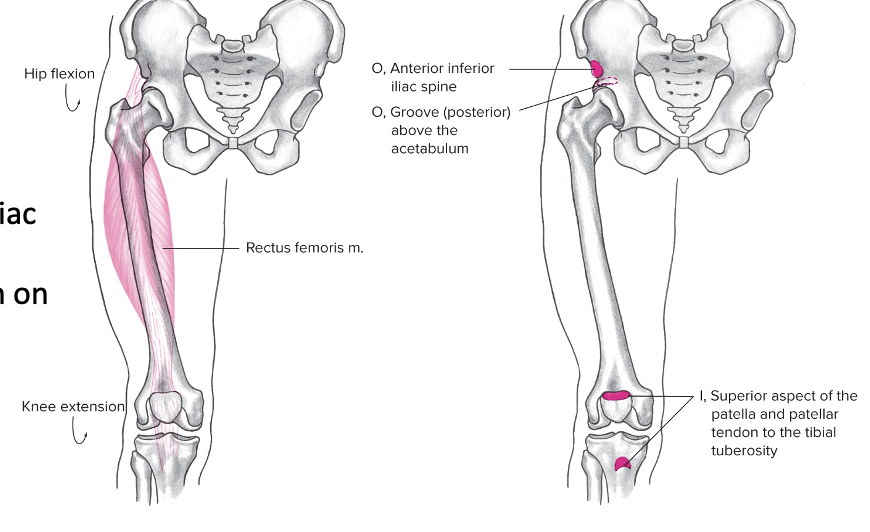
New cards
Rectus femoris
Anterior, part of the quadriceps
Origin: Anterior inferior iliac spine, groove (posterior) above the acetabulum (inferior aspect of pelvic)
Insertion: Superior aspect of patella/patellar tendon on the tibial tuberosity
Action at pelvis: Anterior pelvic rotation
Action at hip: Flexion
Action at knee: Extension
Origin: Anterior inferior iliac spine, groove (posterior) above the acetabulum (inferior aspect of pelvic)
Insertion: Superior aspect of patella/patellar tendon on the tibial tuberosity
Action at pelvis: Anterior pelvic rotation
Action at hip: Flexion
Action at knee: Extension
69
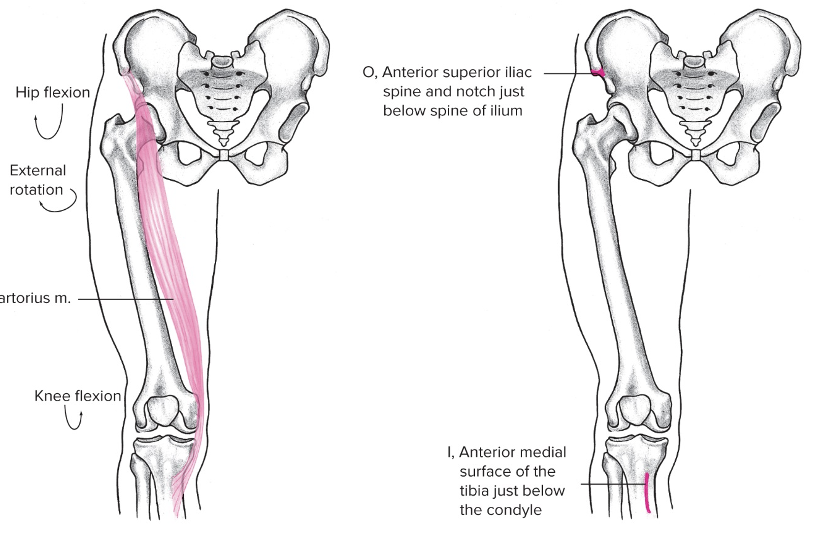
New cards
Sartorius
Anterior, longest muscle in the body
Origin: Anterior superior iliac spine/ notch just below spine of ilium
Insertion: Below knee (biarticular, anterior medial surface of the tibia below the condyle)
Action at pelvis: Anterior pelvic rotation
Action at hip: Flexion, abduction
Action at knee: flexion
Origin: Anterior superior iliac spine/ notch just below spine of ilium
Insertion: Below knee (biarticular, anterior medial surface of the tibia below the condyle)
Action at pelvis: Anterior pelvic rotation
Action at hip: Flexion, abduction
Action at knee: flexion
70
New cards
Is the rectus femoris and Sartorius great at doing motions at both joints at the same time?
Wont be great at doing motion at both joints at the same time
Due to optimal muscle length
Example: Rectus femoris in hip flexion -> not as effective at knee extension at the same time due to beginning at a slighlt shorter and contracted position
Due to optimal muscle length
Example: Rectus femoris in hip flexion -> not as effective at knee extension at the same time due to beginning at a slighlt shorter and contracted position
71
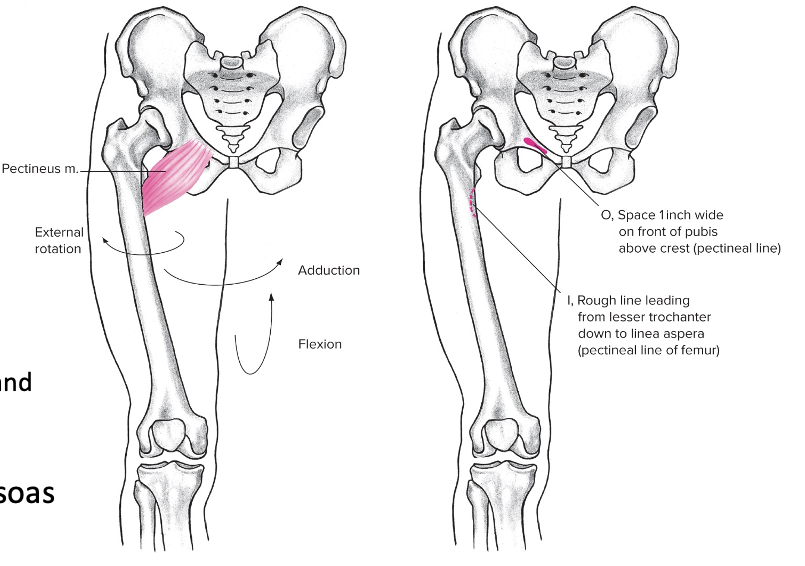
New cards
Pectineus (common groin)
Anterior
Origin: Pubis region
Insertion: Upper portion of femur
Action at pelvis: Forward tilt
Action at hip: Flexion, strong adductor and external rotator
Origin: Pubis region
Insertion: Upper portion of femur
Action at pelvis: Forward tilt
Action at hip: Flexion, strong adductor and external rotator
72
New cards
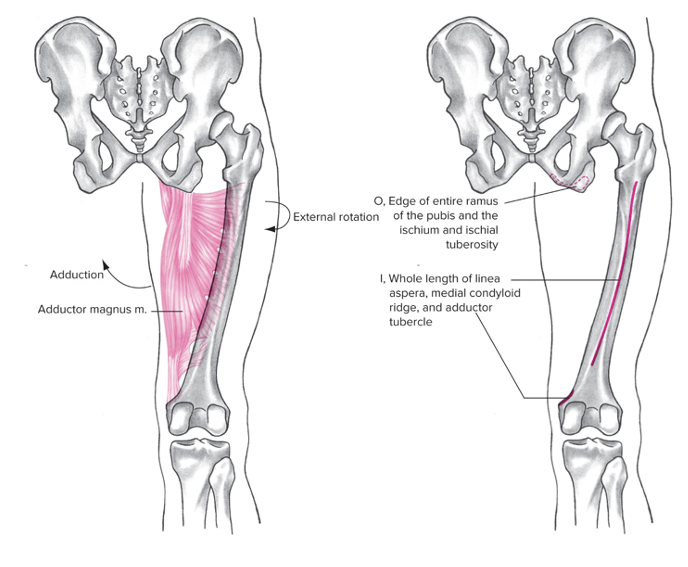
Adductor magnus (common groin)
Medial
Origin: pubis
Insertion: linea Aspera
Action at hip: Adduction (main role, thigh), extension, external rotation
Origin: pubis
Insertion: linea Aspera
Action at hip: Adduction (main role, thigh), extension, external rotation
73
New cards
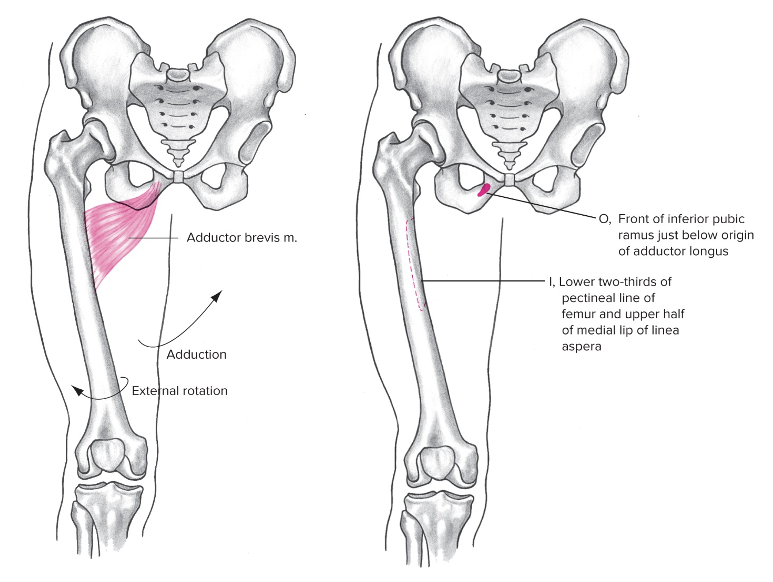
Adductor brevis
Medial
Origin: pubis
Insertion: upper shaft of medial anterior femur
Action at the hip: Adduction (thigh), external rotation
Origin: pubis
Insertion: upper shaft of medial anterior femur
Action at the hip: Adduction (thigh), external rotation
74
New cards
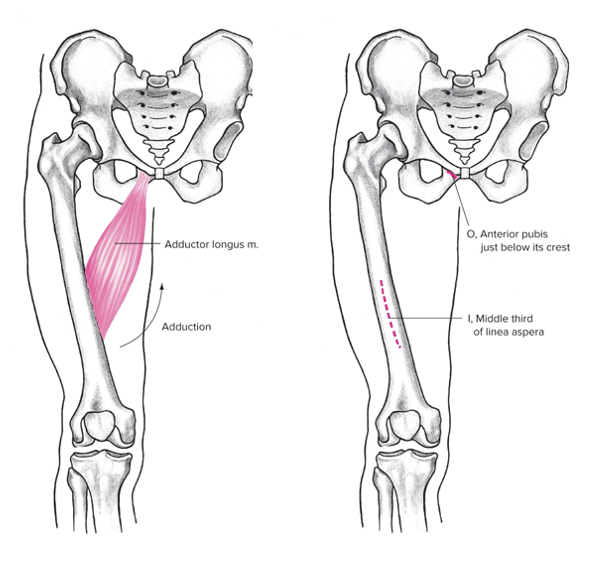
Adductor longus
Medial
Origin: Pubis
Insertion: Middle of linea aspera
Action at hip: Adduction (thigh), flexion
Origin: Pubis
Insertion: Middle of linea aspera
Action at hip: Adduction (thigh), flexion
75
New cards
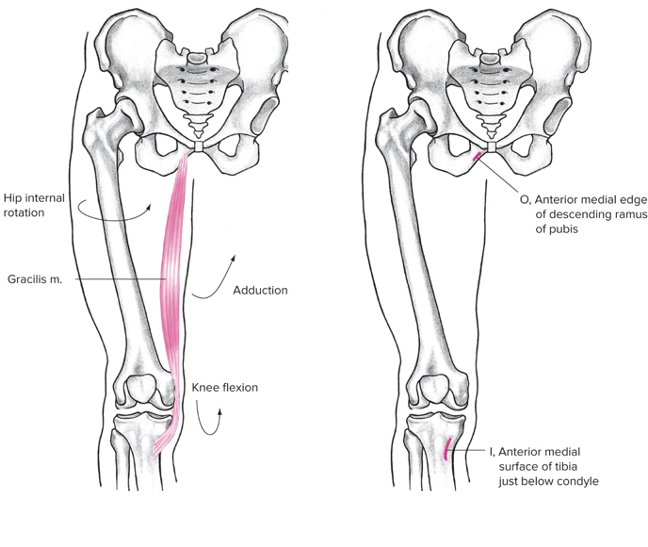
Gracilis (common groin)
Most medial
Origin: Pubis/ anterior medial edge of descending ramus of pubis
Insertion: Tibia (biarticular, anterior medial surface of tibia just below condyle)
Action at hip: Internal rotation
Action at knee: flexion, adduction
Origin: Pubis/ anterior medial edge of descending ramus of pubis
Insertion: Tibia (biarticular, anterior medial surface of tibia just below condyle)
Action at hip: Internal rotation
Action at knee: flexion, adduction
76
New cards
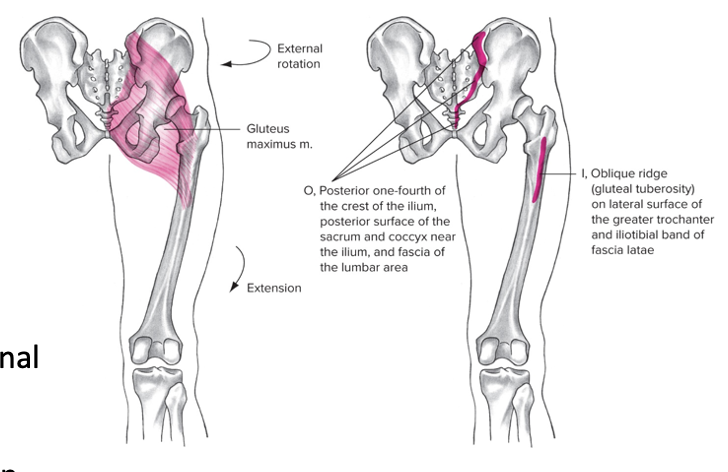
Gluteus maximus
Posterior
Origin: iliac crest, sacrum, coccyx
Insertion: posterior femur
Action at hip: Extension, adduction, external rotation, abduction of flexed hip
Action at pelvis: backward tilt
Origin: iliac crest, sacrum, coccyx
Insertion: posterior femur
Action at hip: Extension, adduction, external rotation, abduction of flexed hip
Action at pelvis: backward tilt
77
New cards
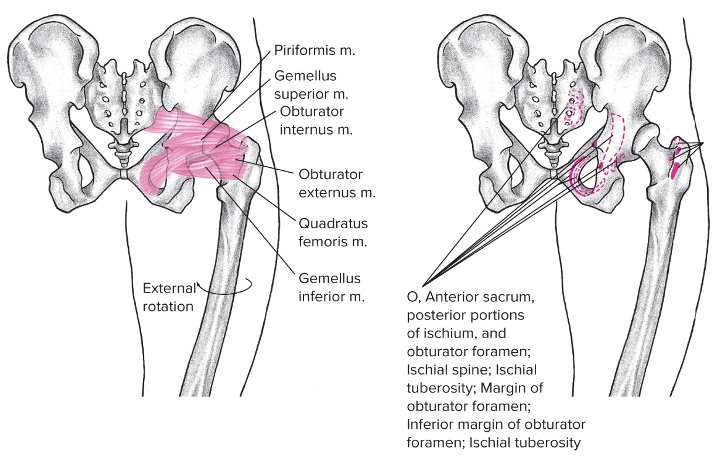
Deep lateral rotators
Posterior, lateral
Consists of quadratus femoris, piriformis, gemellus superior and inferior, internal and external obturator
Origin: pelvis
Insertion: greater trochanter
Action at hip: external rotation, also keeps the ball (head of femur) in the socket (acetebellum)
Consists of quadratus femoris, piriformis, gemellus superior and inferior, internal and external obturator
Origin: pelvis
Insertion: greater trochanter
Action at hip: external rotation, also keeps the ball (head of femur) in the socket (acetebellum)
78
New cards
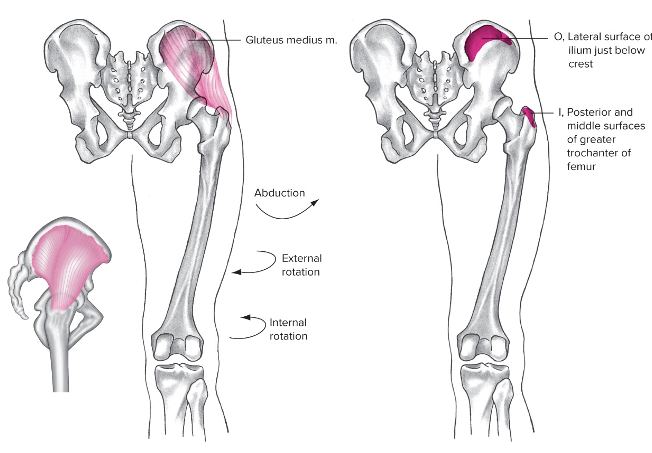
Gluteus medius
Lateral
Origin: Lateral surface of ilium below crest
Insertion: greater trochanter
Action at hip: abduction, flexion, extension, internal and external rotation
Action at pelvis: anterior and posterior pelvic rotation, lateral tilt
Various action depend on which aspect of muscles fibers are contracted
Origin: Lateral surface of ilium below crest
Insertion: greater trochanter
Action at hip: abduction, flexion, extension, internal and external rotation
Action at pelvis: anterior and posterior pelvic rotation, lateral tilt
Various action depend on which aspect of muscles fibers are contracted
79
New cards
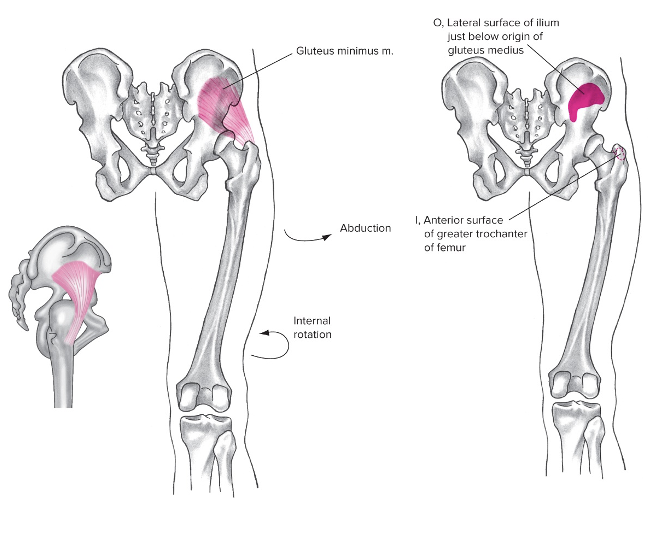
Gluteus minimus
Lateral
Origin: lateral ilium, below gluteus medius
Insertion: Greater trochanter
Action at hip: abduction, flexion, internal rotation
Action at pelvis: anterior pelvic rotation, lateral tilt
Used in walking, maintains proper hip abduction while running
Origin: lateral ilium, below gluteus medius
Insertion: Greater trochanter
Action at hip: abduction, flexion, internal rotation
Action at pelvis: anterior pelvic rotation, lateral tilt
Used in walking, maintains proper hip abduction while running
80
New cards
Tensor fasciate latae (TFL)
Lateral + a bit anterior
Origin: Anterior iliac crest
Insertion: below knee- along with IT band
Action at hip: abduction, flexion, internal rotation
Action at pelvis: anterior rotation, lateral tilt
Prevents external rotation of hip when hip is flexed by other muscles, helps direct the leg forward to ensure proper foot placement while walking/running
Origin: Anterior iliac crest
Insertion: below knee- along with IT band
Action at hip: abduction, flexion, internal rotation
Action at pelvis: anterior rotation, lateral tilt
Prevents external rotation of hip when hip is flexed by other muscles, helps direct the leg forward to ensure proper foot placement while walking/running
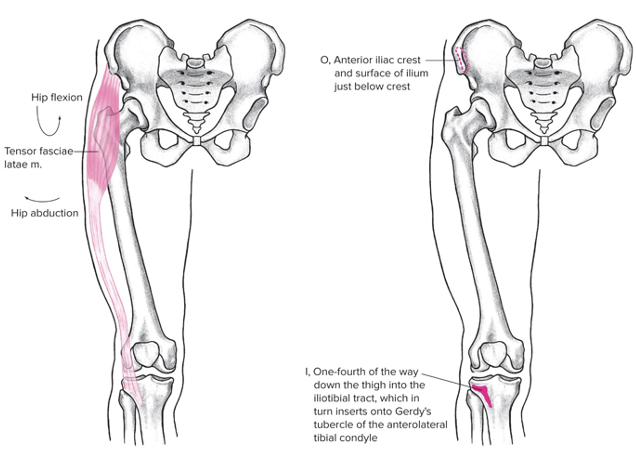
81
New cards
True groin function + muscles contained in it
Hip flexion
Psoas major and minor, iliacus
Strained by hyperextension
Psoas major and minor, iliacus
Strained by hyperextension
82
New cards
Common groin function + muscles contained in it
Hip adduction
Adductor brevis, longus, magus, pectineus, and gracilis
Strained by overstretching, more common
Adductor brevis, longus, magus, pectineus, and gracilis
Strained by overstretching, more common
83
New cards
Iliotibial band (IT band)
Thick band of connective tissue
Insertion of tensor fasciae latae and gluteus maximus
Passes across greater trochanter of the femur as the hip joint flexes and extends
Trochanerica burs finish latera
Insertion of tensor fasciae latae and gluteus maximus
Passes across greater trochanter of the femur as the hip joint flexes and extends
Trochanerica burs finish latera
84
New cards
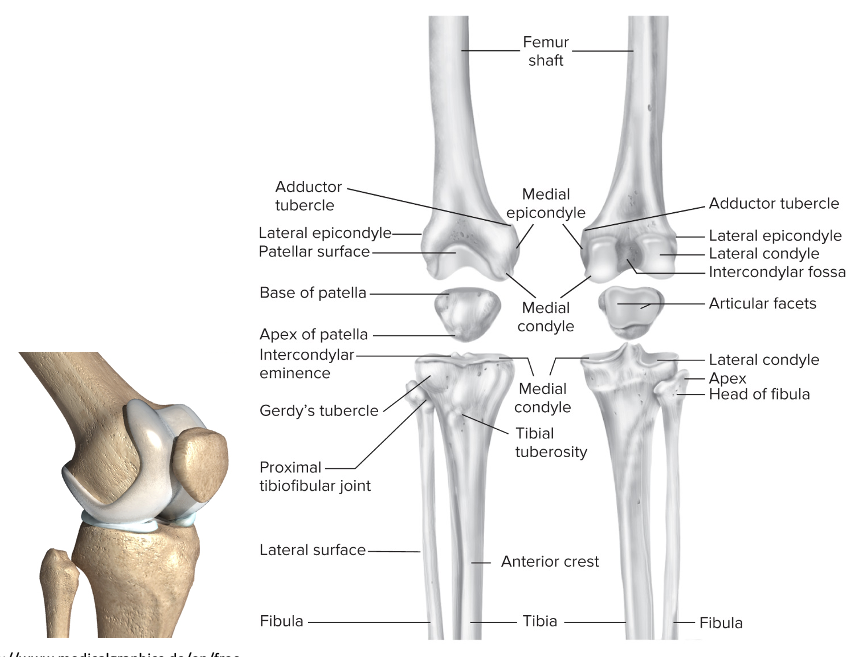
Overview of the knee
Large, complex joint:
Both weight bearing and involved in locomotion
This combination places stress on the joint
Stability:
In extension: vertical alignment and the fit of the joint surfaces
In flexion: capsule and ligament, muscles
Both weight bearing and involved in locomotion
This combination places stress on the joint
Stability:
In extension: vertical alignment and the fit of the joint surfaces
In flexion: capsule and ligament, muscles
85
New cards
Bones apart of the knee
Femur
Patella: sesamoid
Tibia: weight-bearing
Fibula: non-weight bearing
Patella: sesamoid
Tibia: weight-bearing
Fibula: non-weight bearing
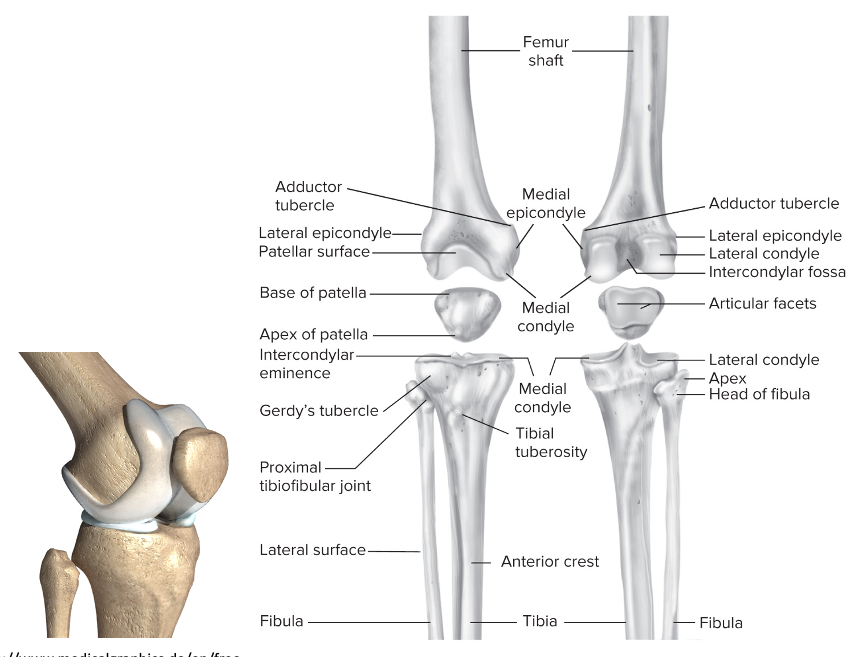
86
New cards
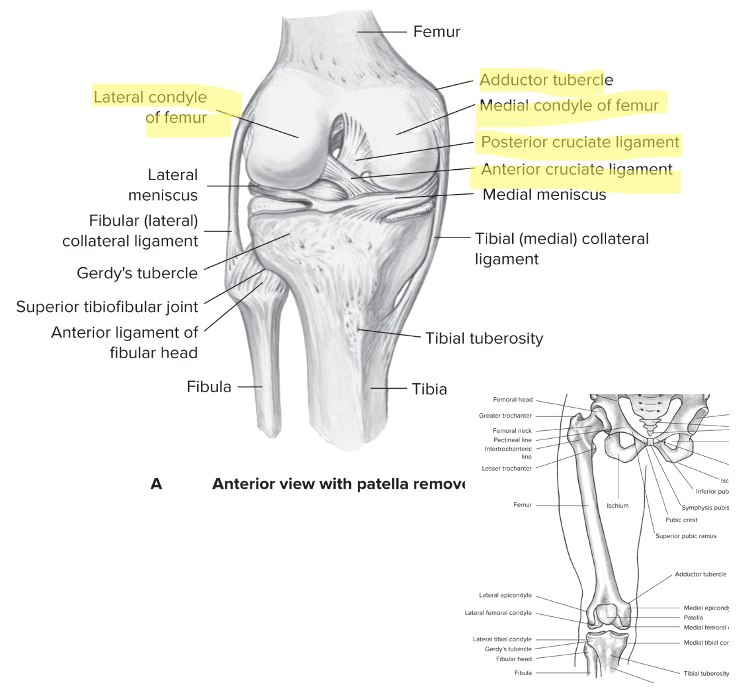
Distal femoral landmarks
Lateral and medial femoral condyles
Articulation
Medial condyle: more distal, larger
Articulation
Medial condyle: more distal, larger
87
New cards
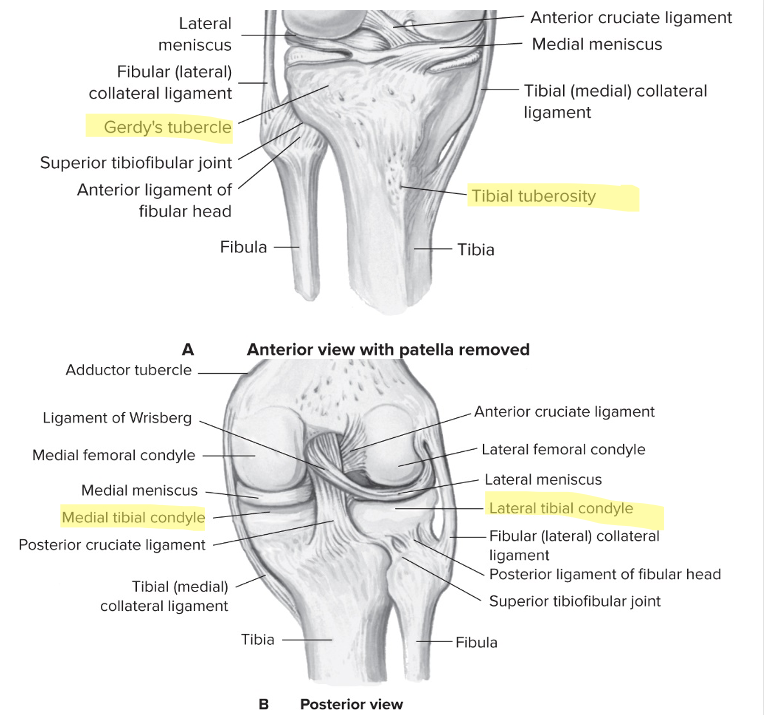
Tibial landmarks
Lateral and media tibial condyles
Articulation with femur
Articulation with femur
88
New cards
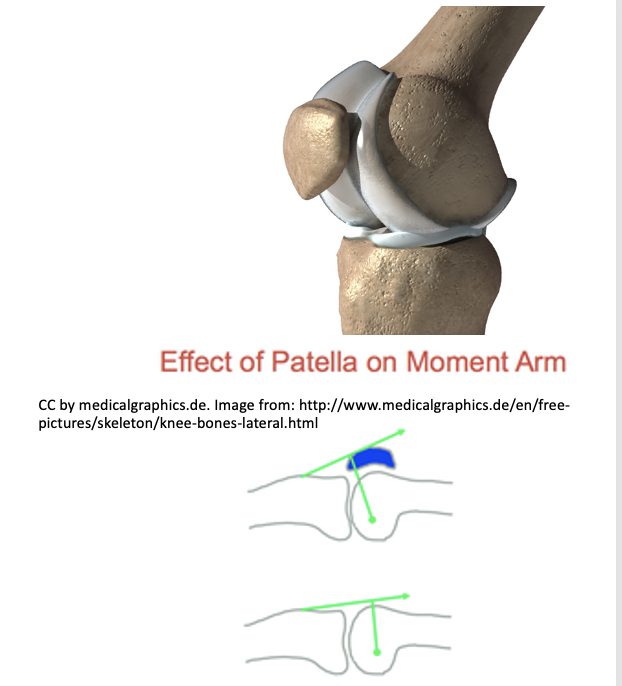
Patellofemoral articulation: type of joint + function
Posterior base of patella fits between lateral and medial condyles on anterior surface of femur
Plane joint
Function:
Improves the mechanical advantage of quadriceps group
Increases angle of pull
Plane joint
Function:
Improves the mechanical advantage of quadriceps group
Increases angle of pull
89
New cards
What motion does the patellofemoral joint provide?
Gliding motion
90
New cards
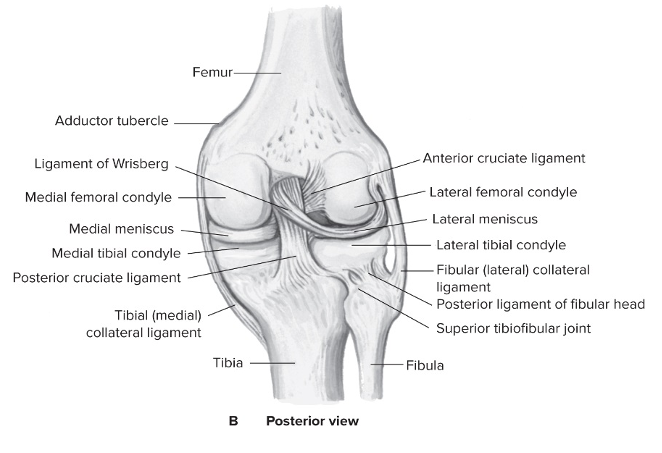
Tibiofemoral articulation (knee joint): type of joint + function
Femoral condyles with tibia condyles
Modified hinge joint (condyloid?):
Flexion and extension
Internal and external rotation during flexion
Static stability from ligaments, dynamic stability from hamstrings and quadriceps muscle groups
Modified hinge joint (condyloid?):
Flexion and extension
Internal and external rotation during flexion
Static stability from ligaments, dynamic stability from hamstrings and quadriceps muscle groups
91
New cards
Collateral ligaments: function
Provides side-to-side stability
Prevents abduction and adduction
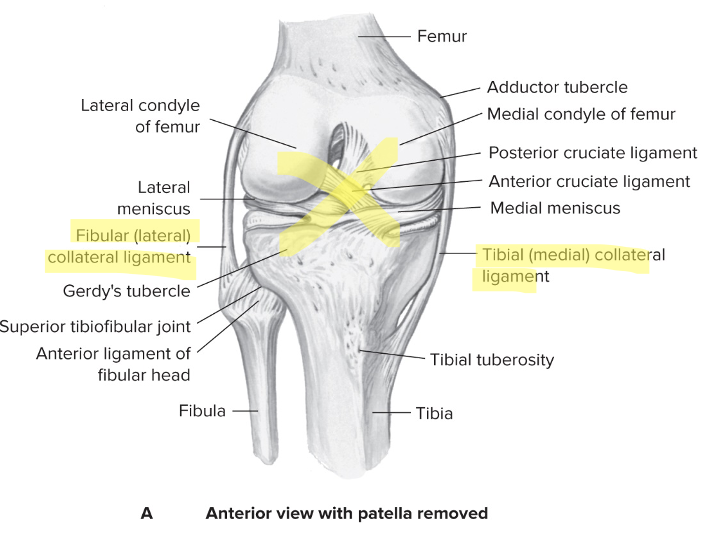
Prevents abduction and adduction
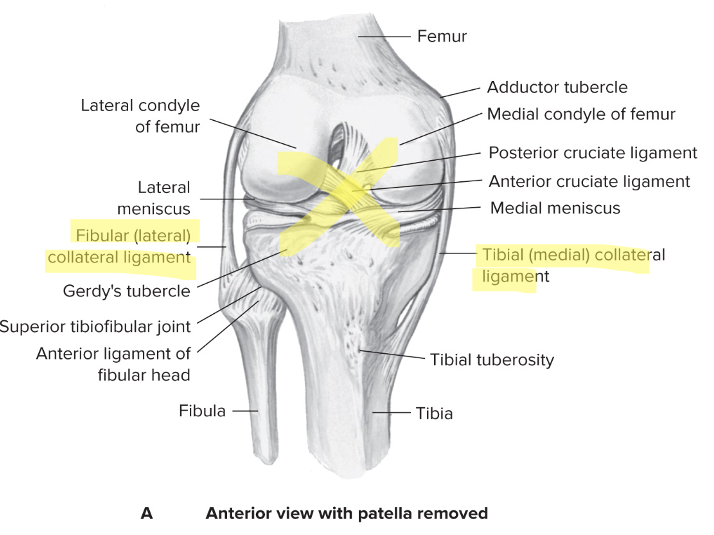
92
New cards
Cruciate ligaments
Provide front-to-back stability
Prevents anterior/posterior displacement
Prevents anterior/posterior displacement
93
New cards
Menisci
Fibrocartilaginous
Proximal end of tibia on condylar surfaces:
Lateral meniscus
Medial meniscus
Function:
Cushion
Enhances stability
Deepen receptacle for femoral condyle
Proximal end of tibia on condylar surfaces:
Lateral meniscus
Medial meniscus
Function:
Cushion
Enhances stability
Deepen receptacle for femoral condyle
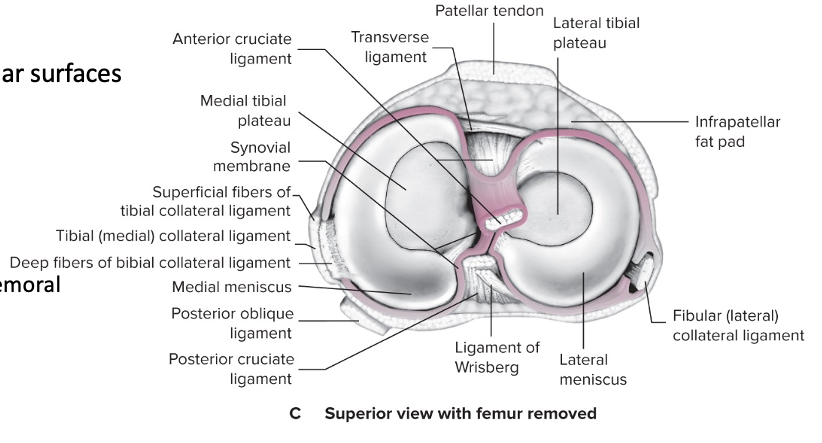
94
New cards
Tibiofemoral joint movement
Sagittal plane:
Extension and flexion
Transverse plane:
With knee flexed 30 degree or more
Extension and flexion
Transverse plane:
With knee flexed 30 degree or more
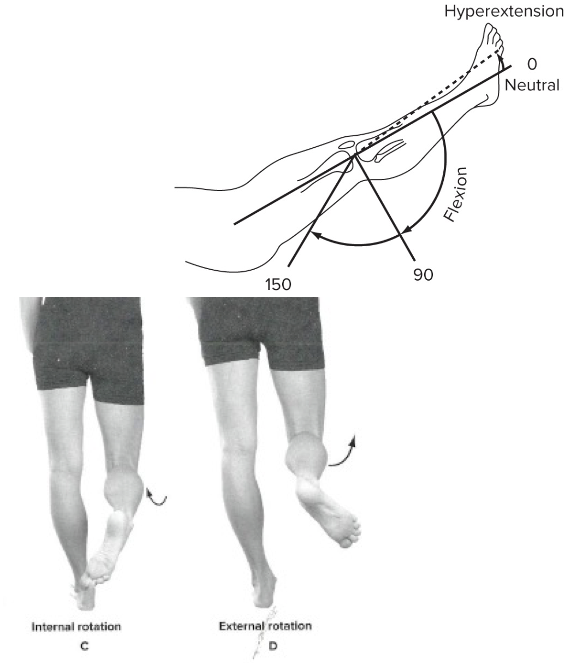
95
New cards
Why is the menisci important?
Femur rolls and glides over both menisci during extension-flexion
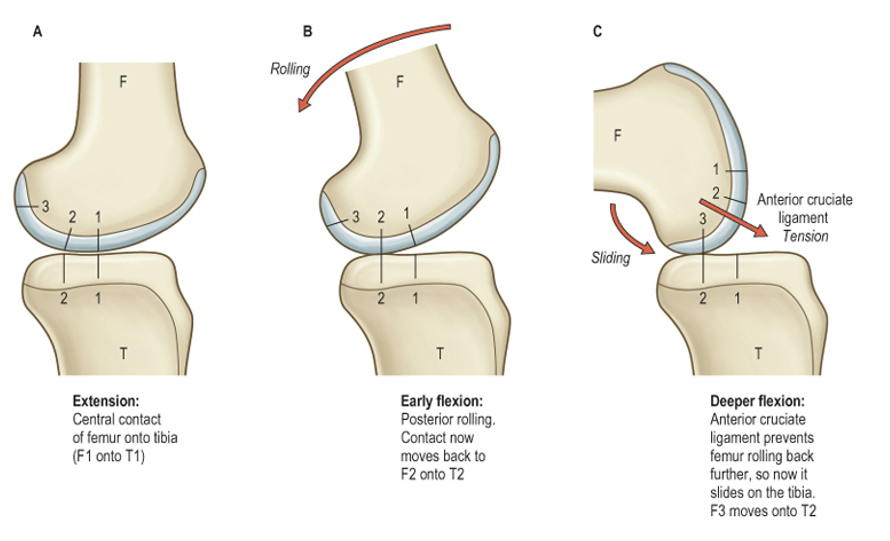
96
New cards
Obligatory terminal rotation (screw home movement)
Tibia externally rotates during knee extension on fixed femur
The tibiofemoral joint “locks” into place in full extension
The tibiofemoral joint “locks” into place in full extension
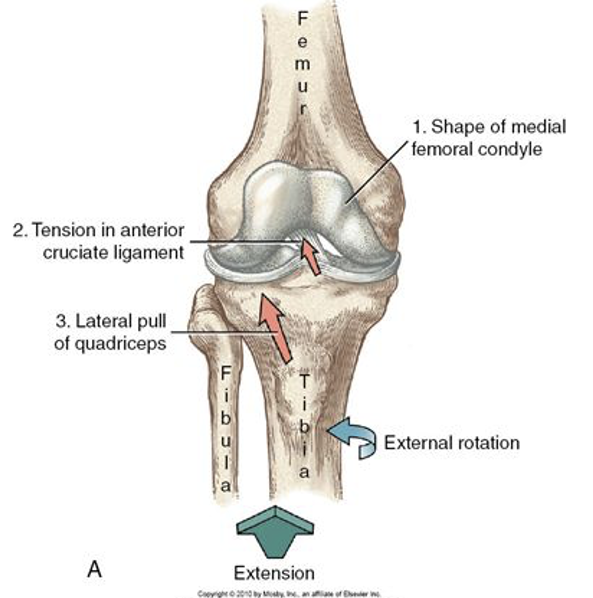
97
New cards
Q angle
Central line of pull of quadriceps runs from the anterior superior iliac spine to the center of patella
Line of pull of patella tendon runs from center of patella to center of tibial tuberosity
Angle formed by the intersection of these two lines at the patella is the Q angle
Line of pull of patella tendon runs from center of patella to center of tibial tuberosity
Angle formed by the intersection of these two lines at the patella is the Q angle
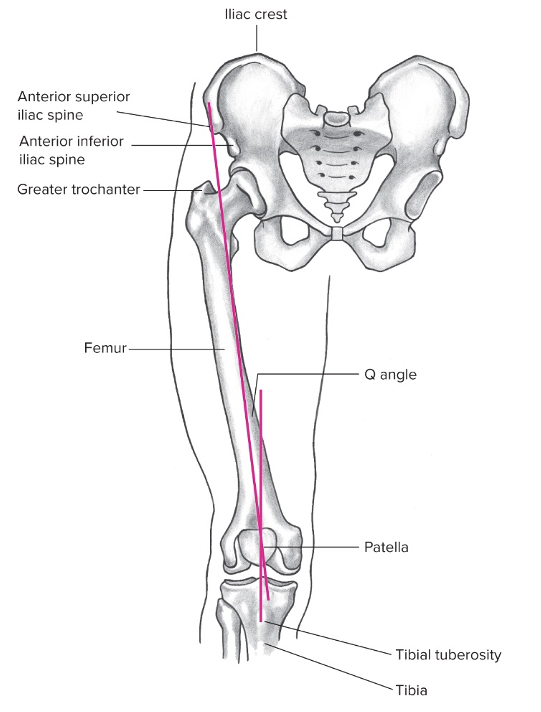
98
New cards
Biarticular muscles
Muscles that have actions at two different joints
Action at hip and knee:
Semimembranosus, semitendinosus, bicep femoris, rectus femoris, Sartorius, and gracillis
Action at knee and ankle:
Gastrocnemius
Plantaris
Action at hip and knee:
Semimembranosus, semitendinosus, bicep femoris, rectus femoris, Sartorius, and gracillis
Action at knee and ankle:
Gastrocnemius
Plantaris
99
New cards
Vastus lateralis
Origin: Proximal end of femur
Insertion: Patella
Action: Knee extension
Insertion: Patella
Action: Knee extension
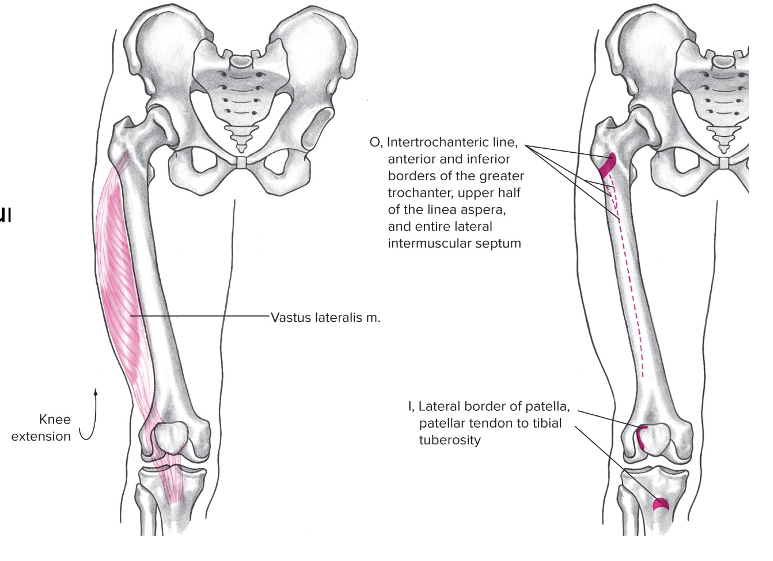
100
New cards
Vastus medialis
Origin: proximal end of femur
Insertion: patella
Action: knee extension, important to stability
Insertion: patella
Action: knee extension, important to stability