SCB Lecture 9: Protein Synthesis
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
What is Protein Synthesis?
Process of making proteins from DNA via RNA
What does Protein Synthesis mean?
Production of Proteins
Where does Protein Synthesis occur?
Cytoplasm
What are Genes?
Portions of DNA that provide genetic information necessary to build a protein
What is Gene Expression?
Production of a protein from a specific gene, determines what proteins are made
Where is DNA located?
Nucleus
What are the 3 key differences between RNA and DNA?
RNA composed of one strand
RNA has sugar ribose that contains additional oxygen atom'
RNA contains Uracil instead of Thymine
What are the two major steps in Protein Synthesis?
Transcription and Translation
Where does Transcription occur?
Nucleus
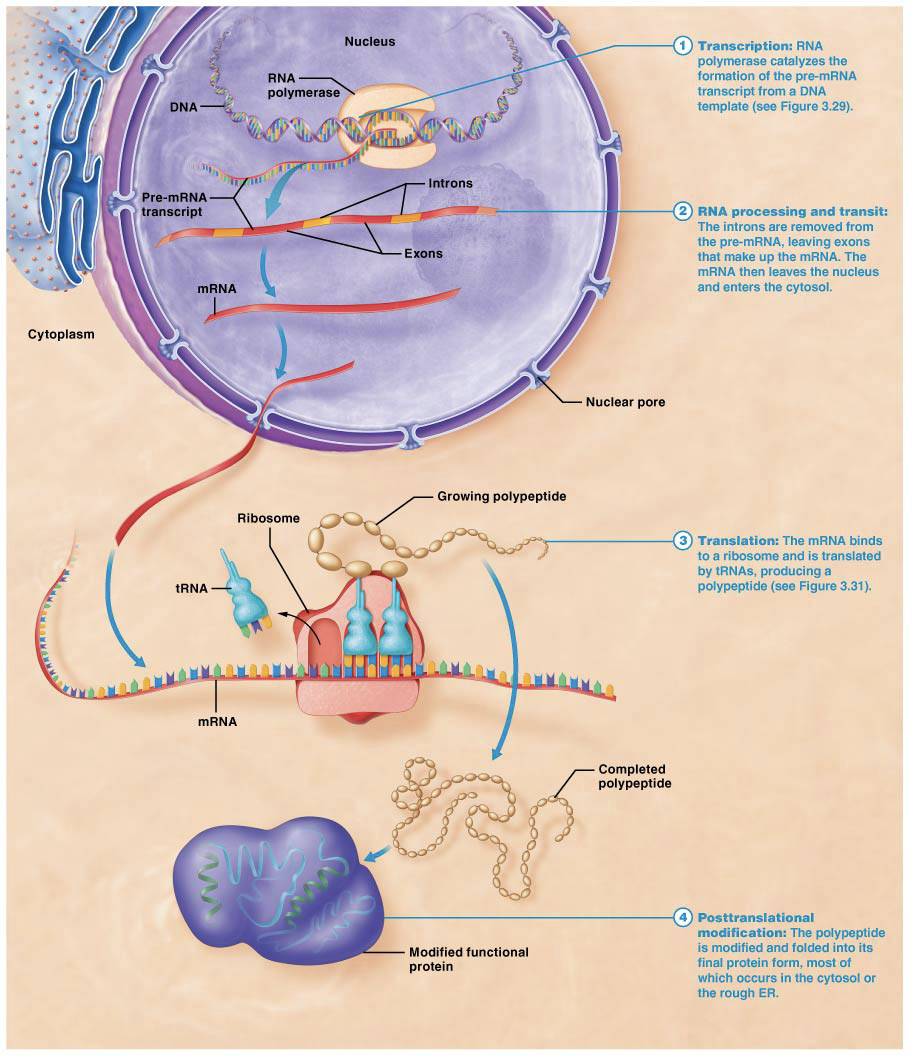
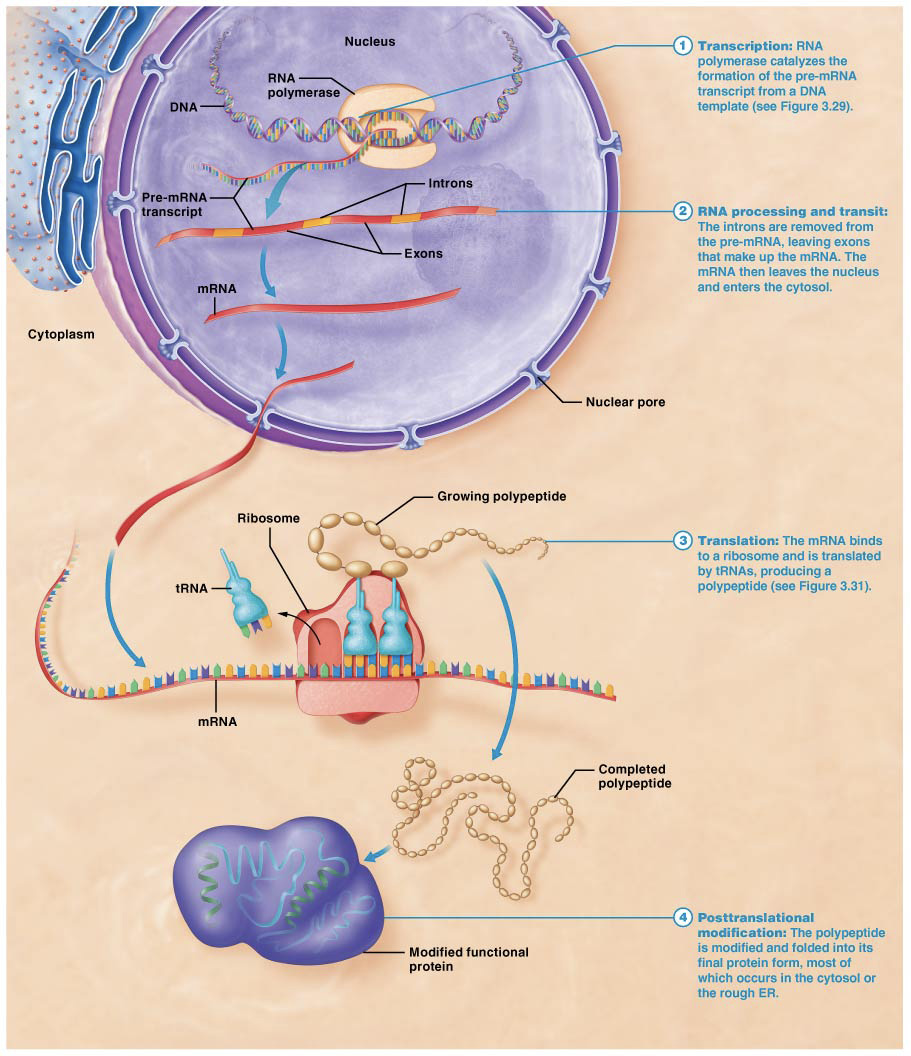
What happens in Transcription?
Gene is copied, creating a molecule of mRNA (messenger RNA).
Transcribes the DNA into a message.
What is the RNA copy during Transcription called?
mRNA, messenger RNA
What is mRNA?
Single stranded nucleic acid that carries a copy of the genetic code for a single gene out of the nucleus.
Are mRNA bound to the nucleus?
NO. Exits the nucleus through nuclear pores and enters the cytoplasm, then into a ribosome
What do Ribosomes do? What are they composed of?
Making of proteins, composed of rRNA and proteins
What is the first step in Transcription?
Transcription factors bind and activate promoter of a gene
What is the second step in Transcription?
Enzyme RNA Polymerase binds to the promoter (gene).
What is the third step in Transcription?
Using the template strand as a guide, RNA Polymerase uses the base pair rule to assemble free nucleotides, into a complementary strand of RNA (A,U,G,C, etc), creating mRNA strand.
After DNA is copied into mRNA, double helices go back together
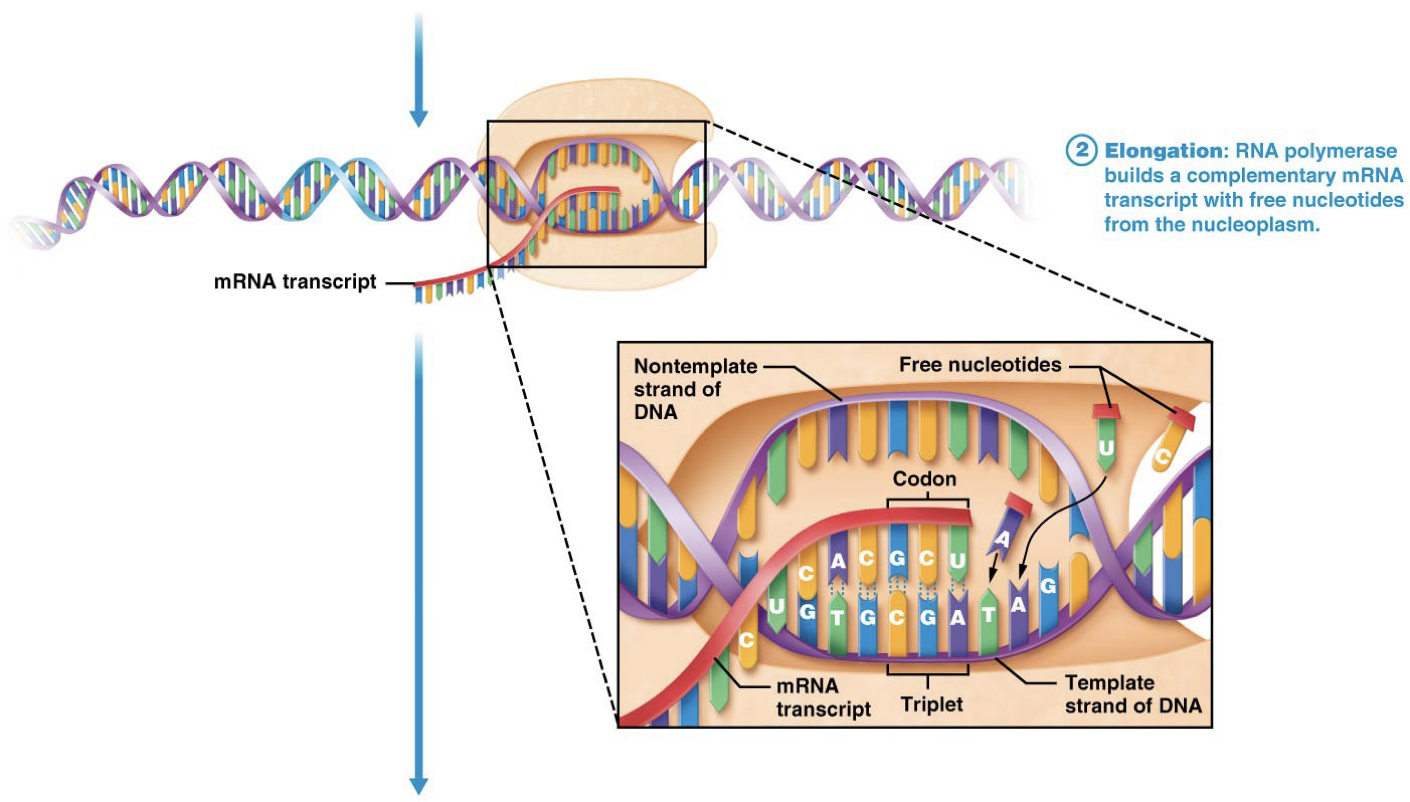
What is the fourth step in Transcription?
RNA reaches a stop codon that signals the end of the gene. The enzyme RNA Polymerase detaches.
What needs to happen before “pre-mRNA” leaves the nucleus?
RNA Processing; Splicing.
What does Splicing do?
Removes non-coding regions from pre-mRNA transcript.
What is the removed segment called of the pre-mRNA transcription?
Introns
What is the segment that stays during Splicing?
Exons, remaining exons are pasted together
What happens after RNA Processing?
mRNA can exit the nucleus through nuclear pores into the cytoplasm to find ribosomes.
What is Translation?
Second step of protein synthesis, mRNA is converted into amino acids,
Process of synthesizing a chain of amino acids (polypeptide)
Where does Translation occur?
Ribosomes
What 2 things are Translation assisted by?
Ribosomes and Transfer RNA (tRNA)
Do Ribosomes have membranes?
Ribosomes are non-membrane bounded organelles
What are 3 characteristics of Ribosomes
Consist of Large and Small subunits
Composed of Ribosomal Proteins and Ribosomal RNA (rRNA). These two things compose the structure of the ribosome
May exist free or attached to membranes (rough ER)
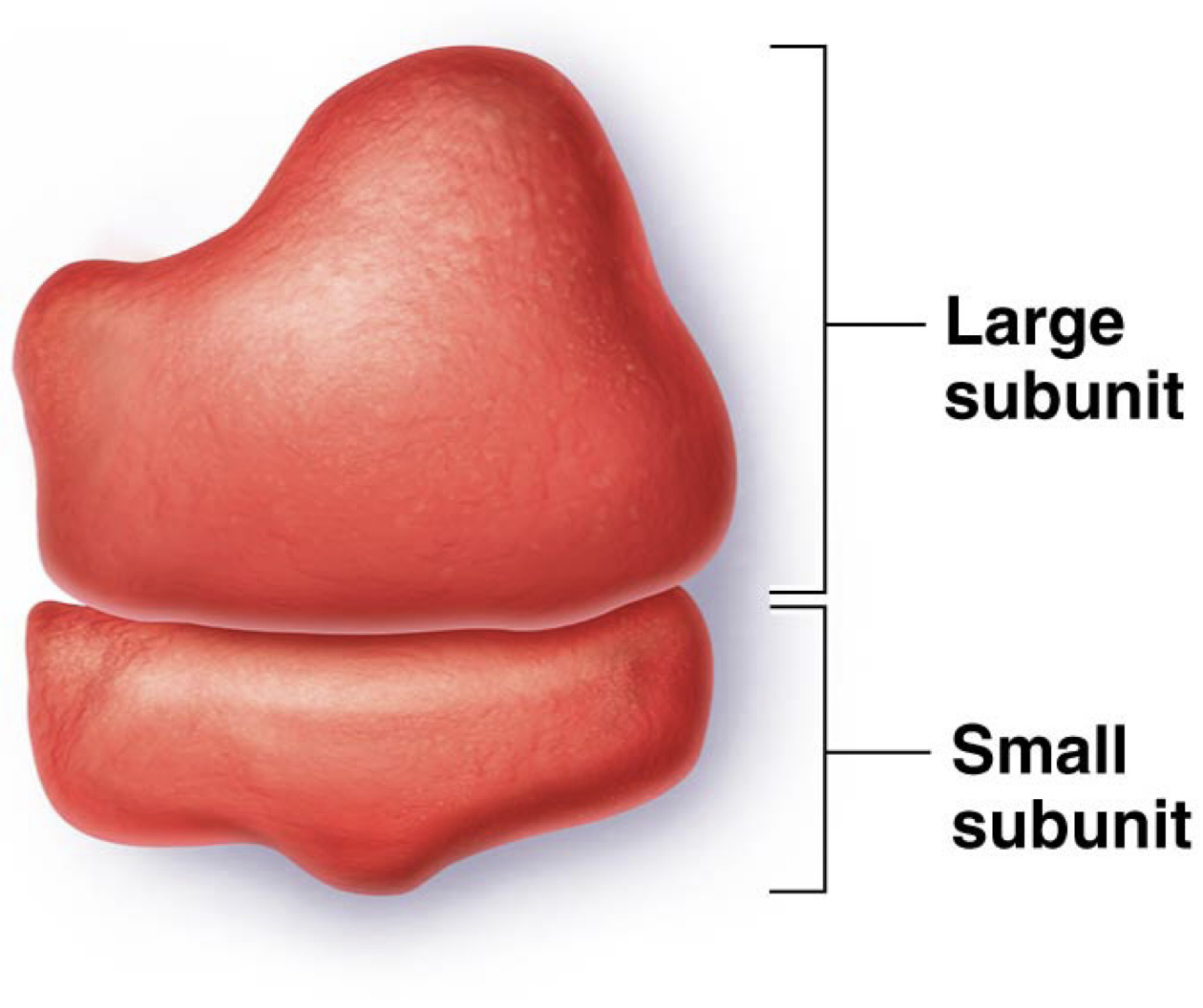
How many binding sites do Ribosomes have? What are the names?
A site (Aminoacyl)
P site (Peptidyl)
E site (exit)
What is the Aminoacyl (A) site? What does it do?
The Aminoacyl site binds to the incoming tRNA molecule
What is the Peptidyl (P) site? What does it do?
The Peptidyl site is where the Amino Acid is added to the growing protein
What is the Exit (E) site? What does it do?
The Exit site is where used tRNA departs
What is the function of tRNA? What is tRNA composed of/structure?
Picks up specific amino acids and transfers it to the growing polypeptide chain.
Composed of 1 amino acid, hydrogen bonds, RNA strand, and Anticodon
3 leaf clover formed by hydrogen bonds
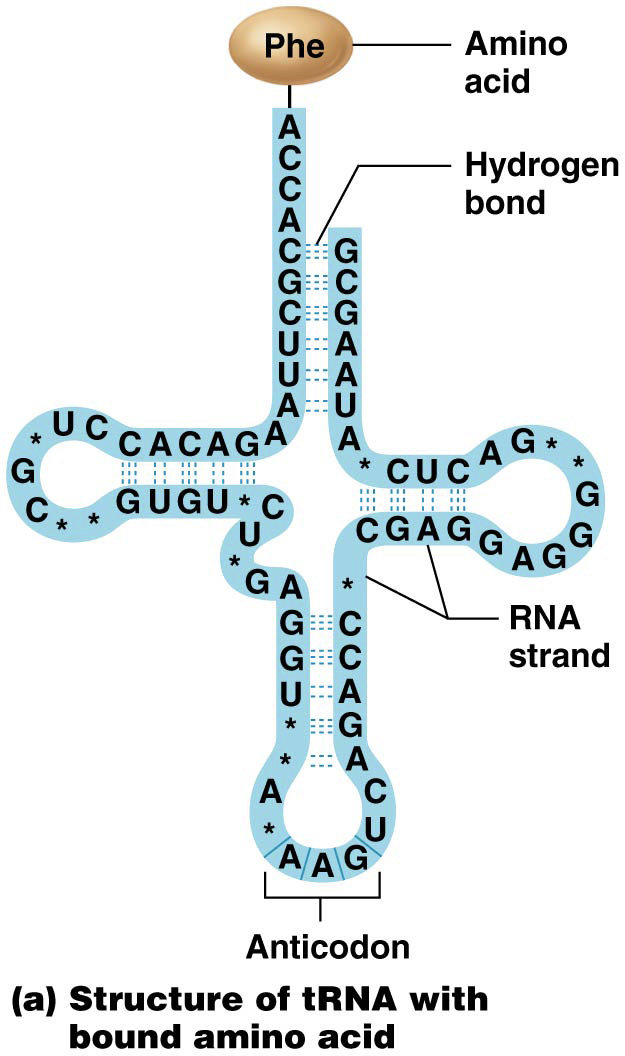
What do Anticodons contain?
3 Nucleotides complementary to a specific mRNA codon.
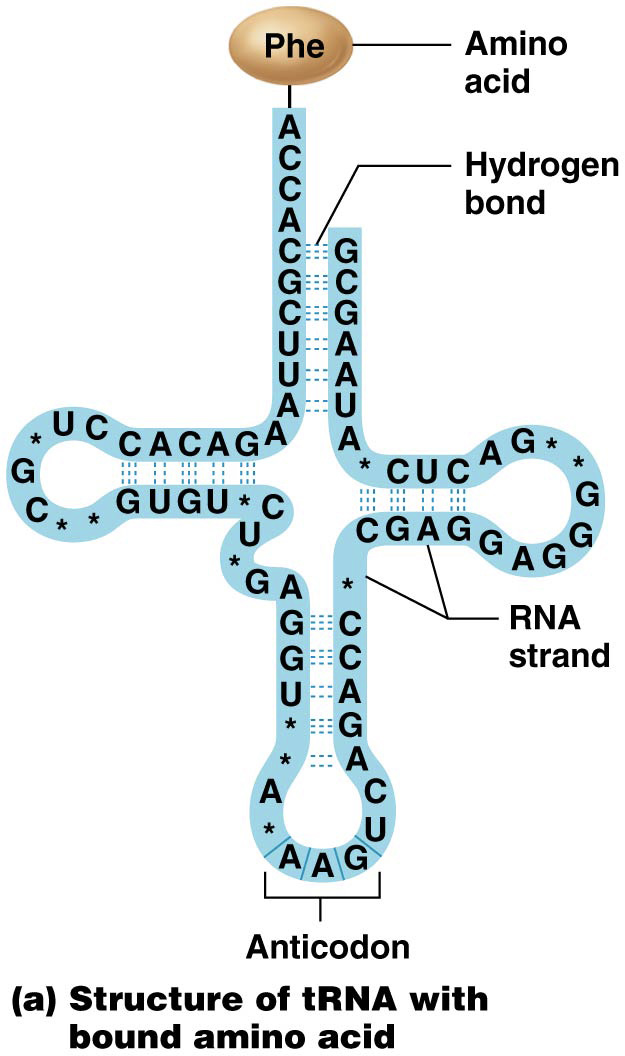
What is on the opposite side of Anticodons in tRNA?
Amino Acid
What do mRNA codons specify for?
Amino Acids
ex. UUC specifies for Phenylalanine
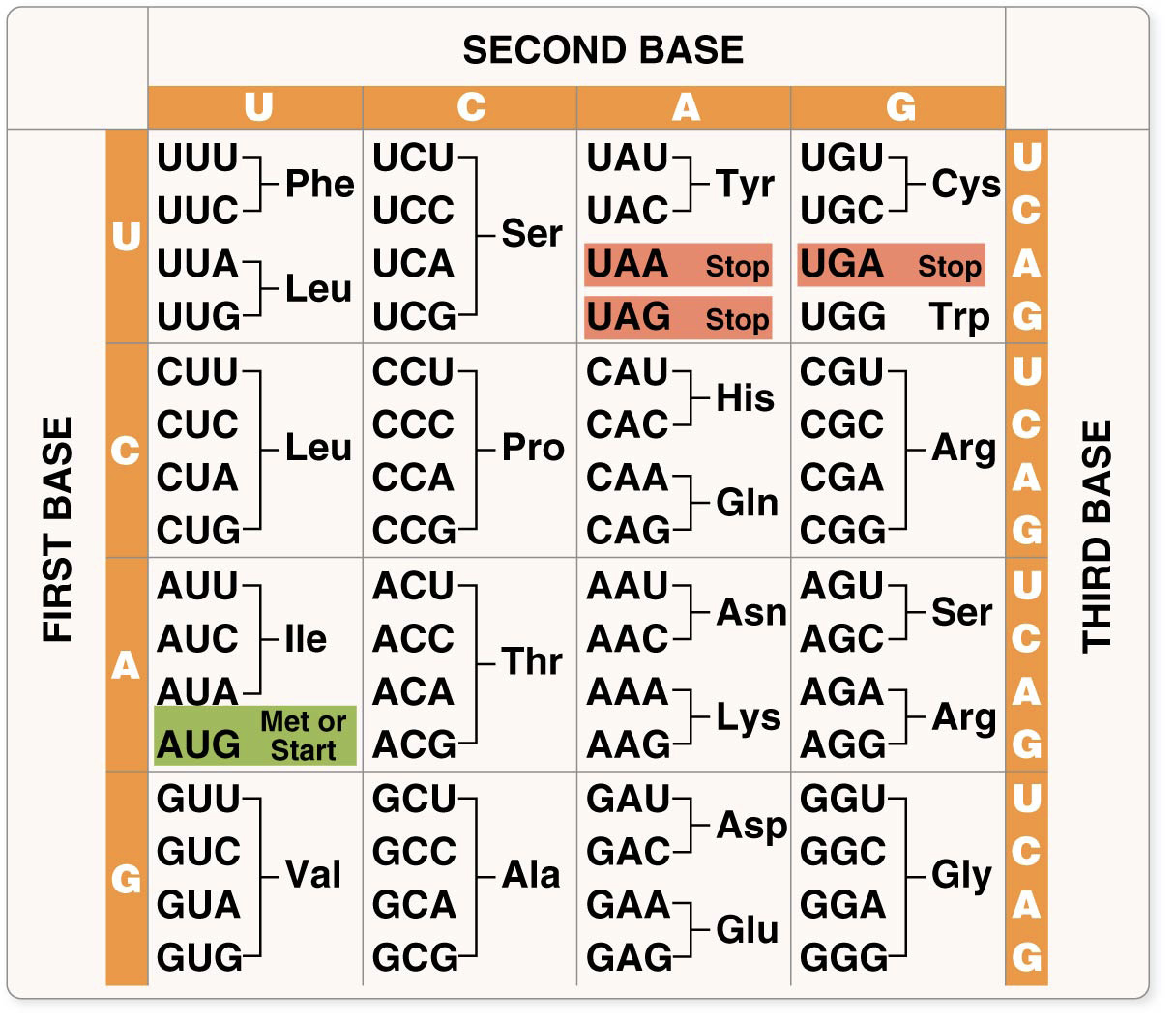
What does the mRNA codon bind to?
Anticodon on tRNA
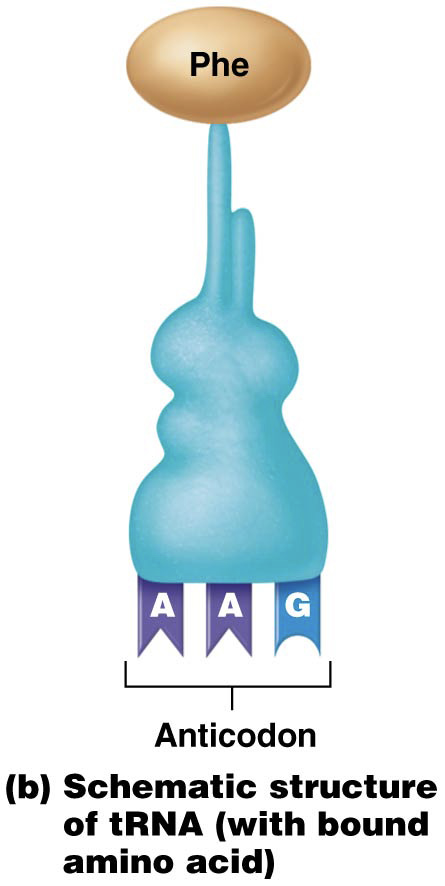

Does the Amino Acid on tRNA correspond to the anticodon or the mRNA codon?
mRNA Codon.
ex. mRN codon UUC specifies amino acid Phenylalanine.
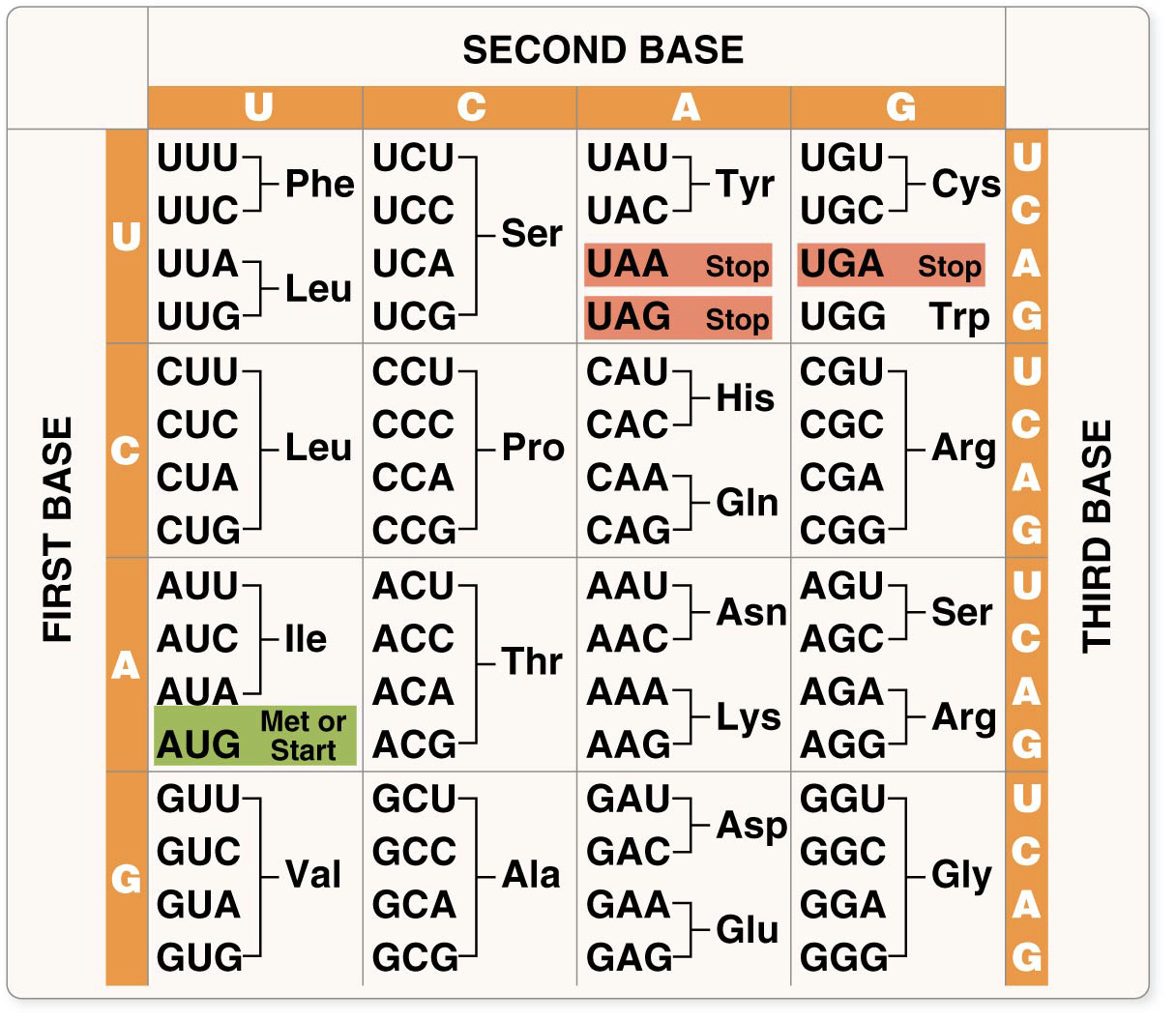
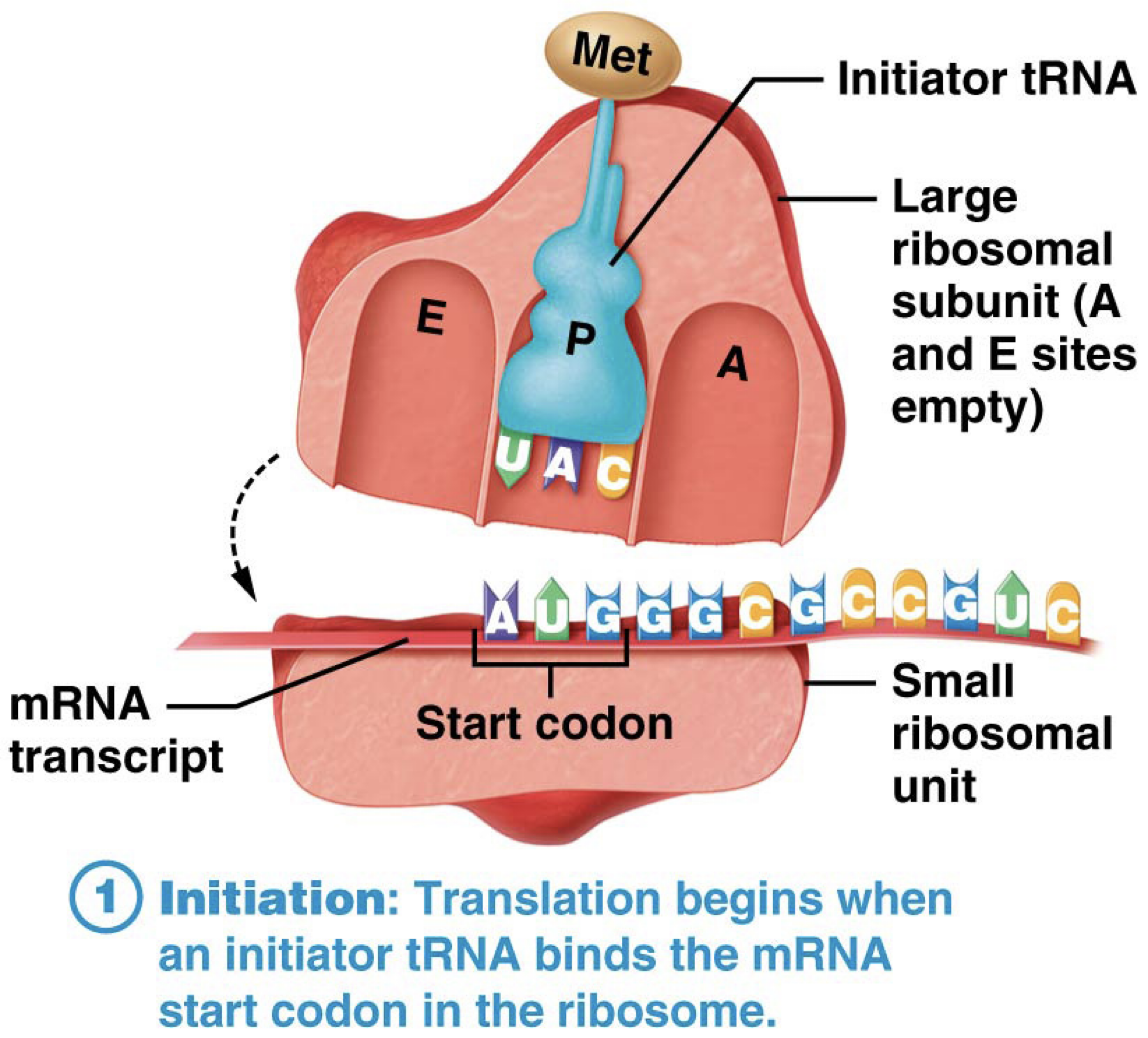
What is one Met/Start codon?
AUG
What are 3 stop codons?
UAA, UAG, UGA
What happens during Translation?
Ribosome holds mRNA transcript between 2 subunits (large and small) to allow interaction with tRNAs.
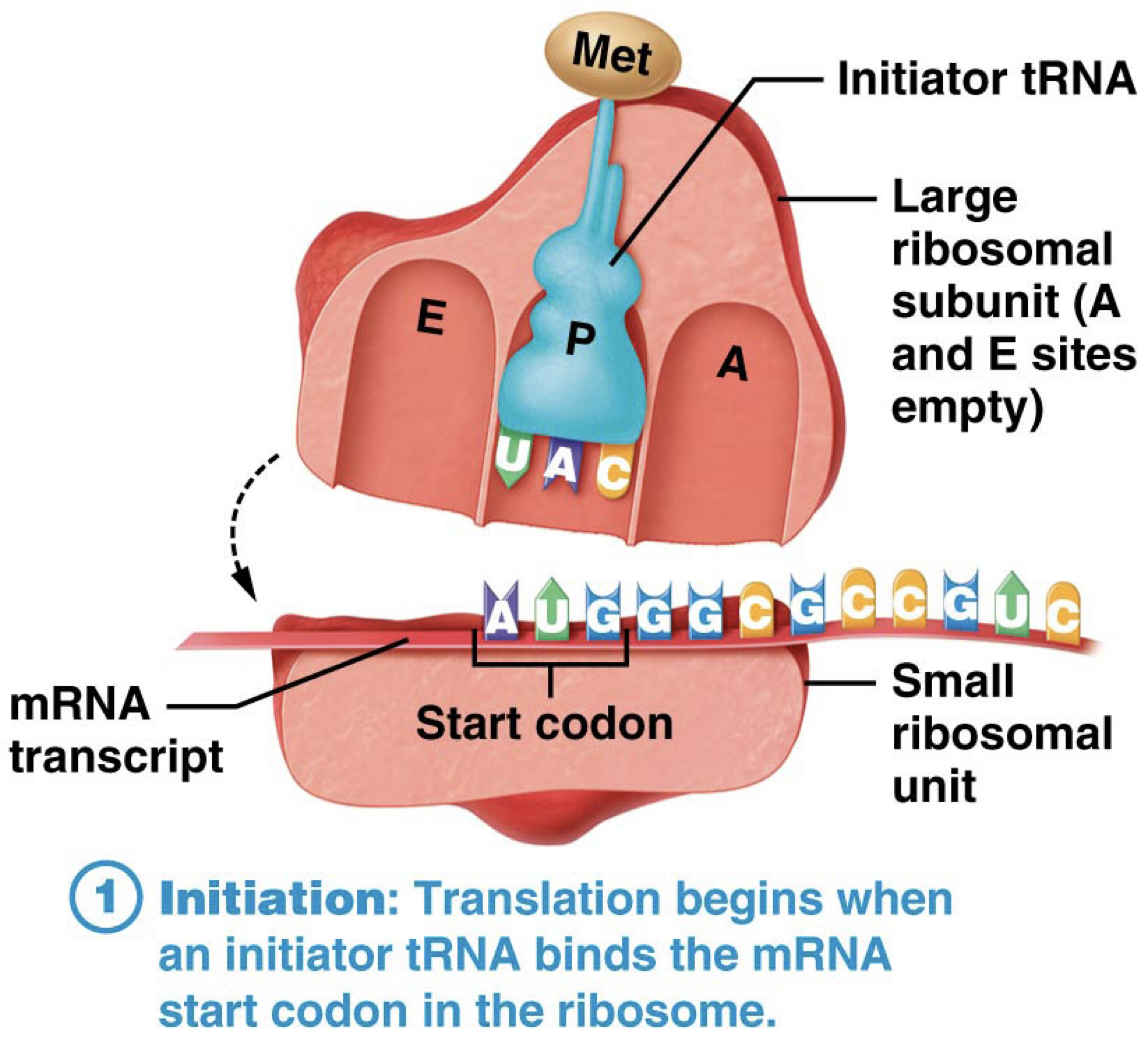
What is the first step in Translation?
Initiation. tRNA binds to mRNA start codon (AUG) in the Ribosome.
Brings Large Ribosomal Unit and Small Ribosomal Subunit together.
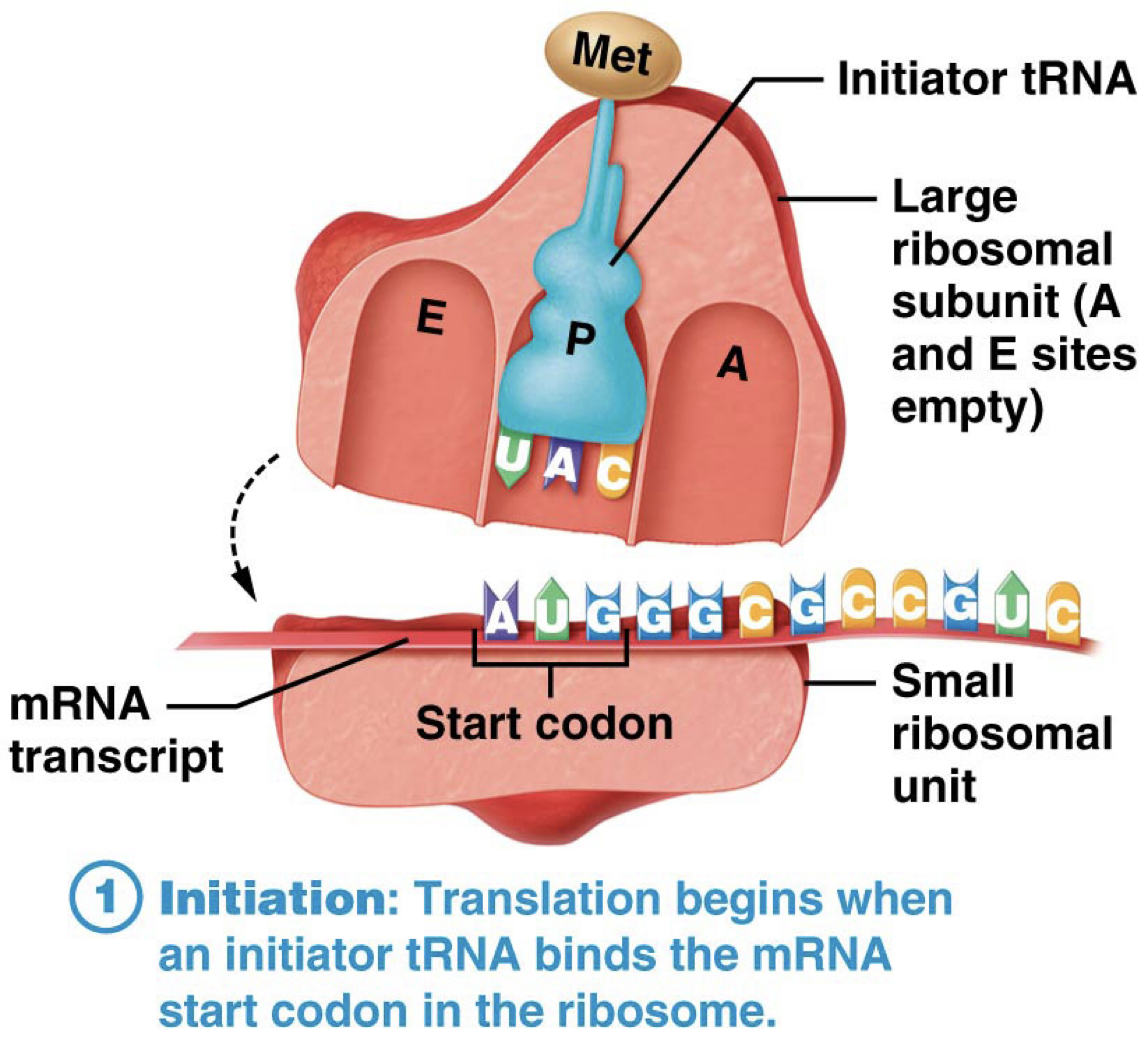
What Amino Acid does tRNA carry when the anticodon binds to the mRNA start codon?
Methionine
What is the Large subunit composed of?
tRNA in the P site, E site, A site
What is the second step in Translation?
Another tRNA binds to open site A, with an anticodon complementary to next mRNA codon.
First amino acid joins Second amino acid by peptide bonds.
What is the third step in Translation?
Empty tRNA shifts from P site into E (Exit) site and leaves. tRNA that was in A site moves into P site.
Repeats as ribosome moves to next codon on mRNA.
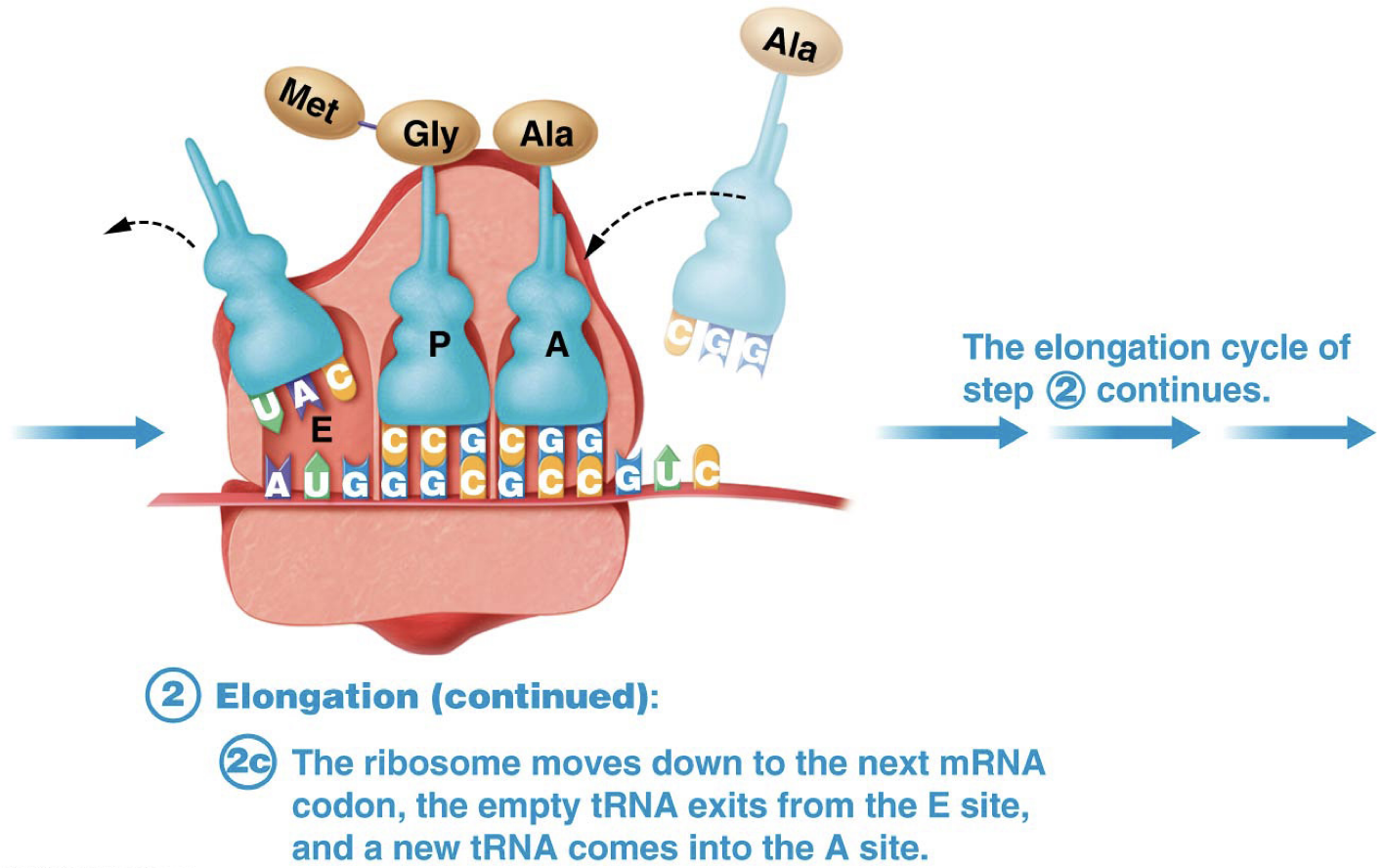
What is Elongation in Translation?
When the ribosome keeps moving down to the next mRNA codon. Empty tRNA exits from the E site, and new tRNA comes into the A site.
When does Translation stop?
When ribosome reaches a stop codon (UAG, UAA, or UGA) and polypeptide is released.
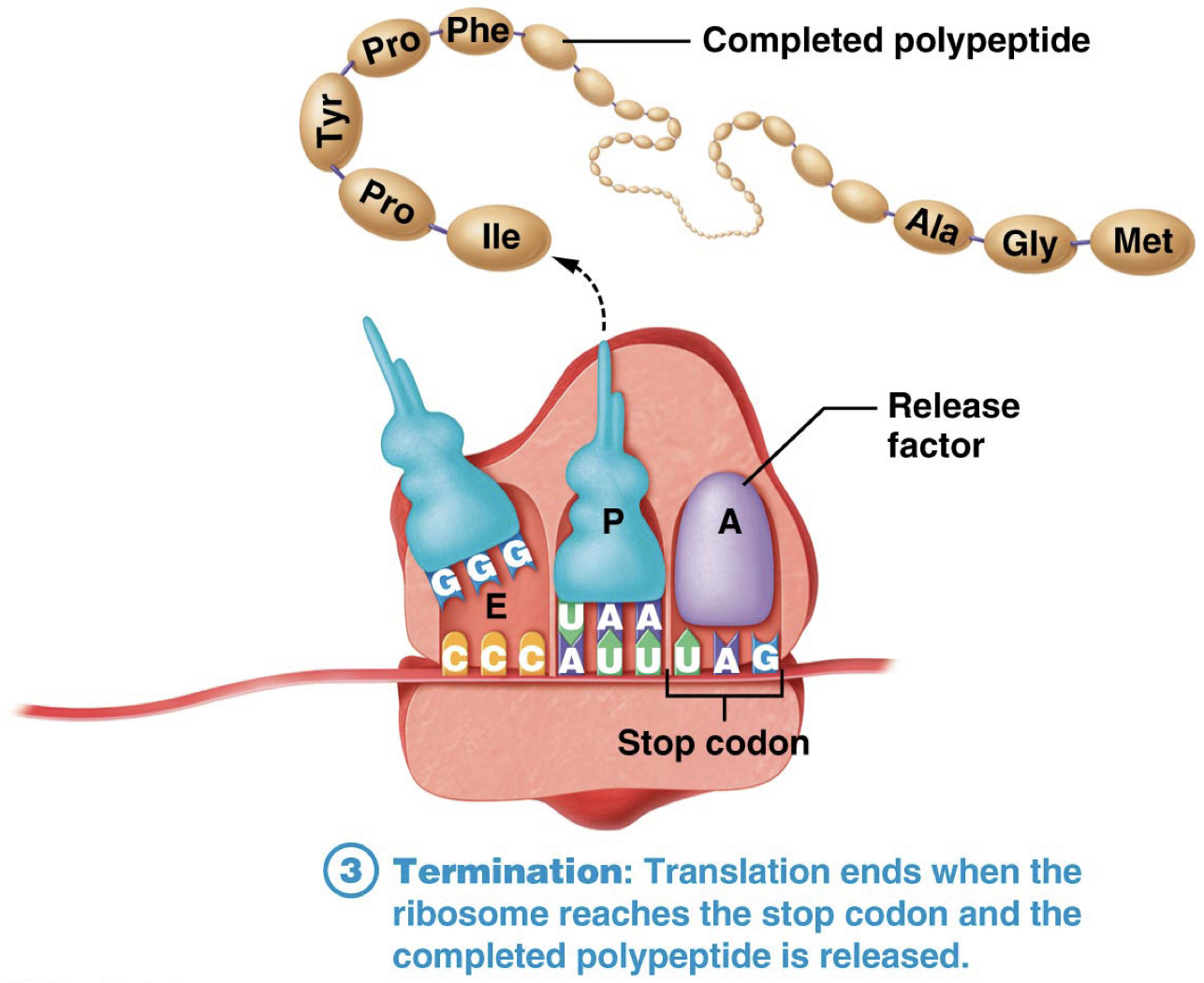
What is Termination?
When Translation ends
What is Post- Transitional Modification?
Folding of peptide into proper 3-dimensional shape. Occurs in the Cytosol or Rough ER.
Where are polypeptides destined for Cytosol synthesized?
Free Ribosomes
Where are polypeptides destined for secretion/ insertion into organelles/ membranes synthesized?
Synthesized on Bound Ribosomes, modified in Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum