Physics 3 - Quality Assurance Module 1
1/223
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
224 Terms
Patient misdiagnosis
What may result if the images we see on ultrasound are not real/accurate
D=Cxt/2
What is the range equation
1540(constant)
What is C in the range equation
Looking for gradual detonation, minimize down time of machine, minimize repeat ultrasounds
What are the main 3 goals of quality assurance
Check for deterioration over time we often don't notice when scanning everyday (mmt off, etc)
What does quality assurance check for
A program that ensures proper and consistent operation of the imaging systems
What is quality assurance (QA)
Proper equipment operation, detection of gradual degradation of performance, minimizes machine down time, minimizes repeat examinations (misdiagnosis), sonographer and patient safety, cost efficiency, maintains standards
What 7 things does quality assurance ensure
At the end of the day, US is a business and it is important it is not loosing money by deteriorating machines
Why is U/S being cost efficient important
Physician, sonographer, service (biomedical/manufacturer)
What are the 3 main people responsible for quality factor
Director
What can the physician be referred to as in terms of QA
Assess images for overall quality
What is the responsibility of the radiologist/physician
They are looking at transferred image from computer so there is a possibility any QA problems may be caused from the transfer over and not the US machine
What is the problem with the radiologist assessing the quality of images
Front line people (we are the people who may experience a problem first hand)
What can the sonographers be referred to as in terms of QA
Routine testing/record keeping and perform routine maintenance such as cleaning filters, visual inspections
What else may the sonographer do besides assessing the images
Cleaning surfaces, cleaning recording devices (more for older machines), cleaning fan filters, assessing cables & transducer integrity, film/image recording quality (PAC system)
What are some routine preventative maintenance a sonographer may do
Sometimes what you see on the machine isn't the same on the PAC system (problem with transferring)
Why is it important to film/image recording quality (PAC system)
Manufacturer and biomedical personnel
What are the 2 types of service personnel
Routine preventative maintenance and repair equipment as needed
What will the manufacturer provided
Acceptance testing when machine arrives on site to ensure patient and employees after
What is the responsibility of the biomedical personnel
Testing that the machine will work with the outlets/other machines that are already in clinic or hospital
Explain more in depth what a biomedical personnel may do
Acceptance testing
What is the sophisticated testing done before systems are placed into operation
Image performance and power out put
What are measured with acceptance testing
System is checked to see if it will work with ancillary equipment in the department
What is the main goals of acceptance testing
Measuring image performance and assessing for changes over time
Routine quality assurance testing is mainly about:
Tissue equivalent phantom
What is used to test for QA
Record keeping
What is a key component of a good QA program besides just testing the machines
Resolution, sensitivity, accuracy, etc, changes over time
What can a tissue equivalent phantom assess
Daily, weekly, or monthly
When is routine maintenance done by the sonographer
2 to 3 times per year
How often do manufacturers perform PM per year (while machine is under warranty or a service contract)
Yearly
How often is routine performance testing typically done
AIUM
What is the institute that recommends the frequency of routine performance testing
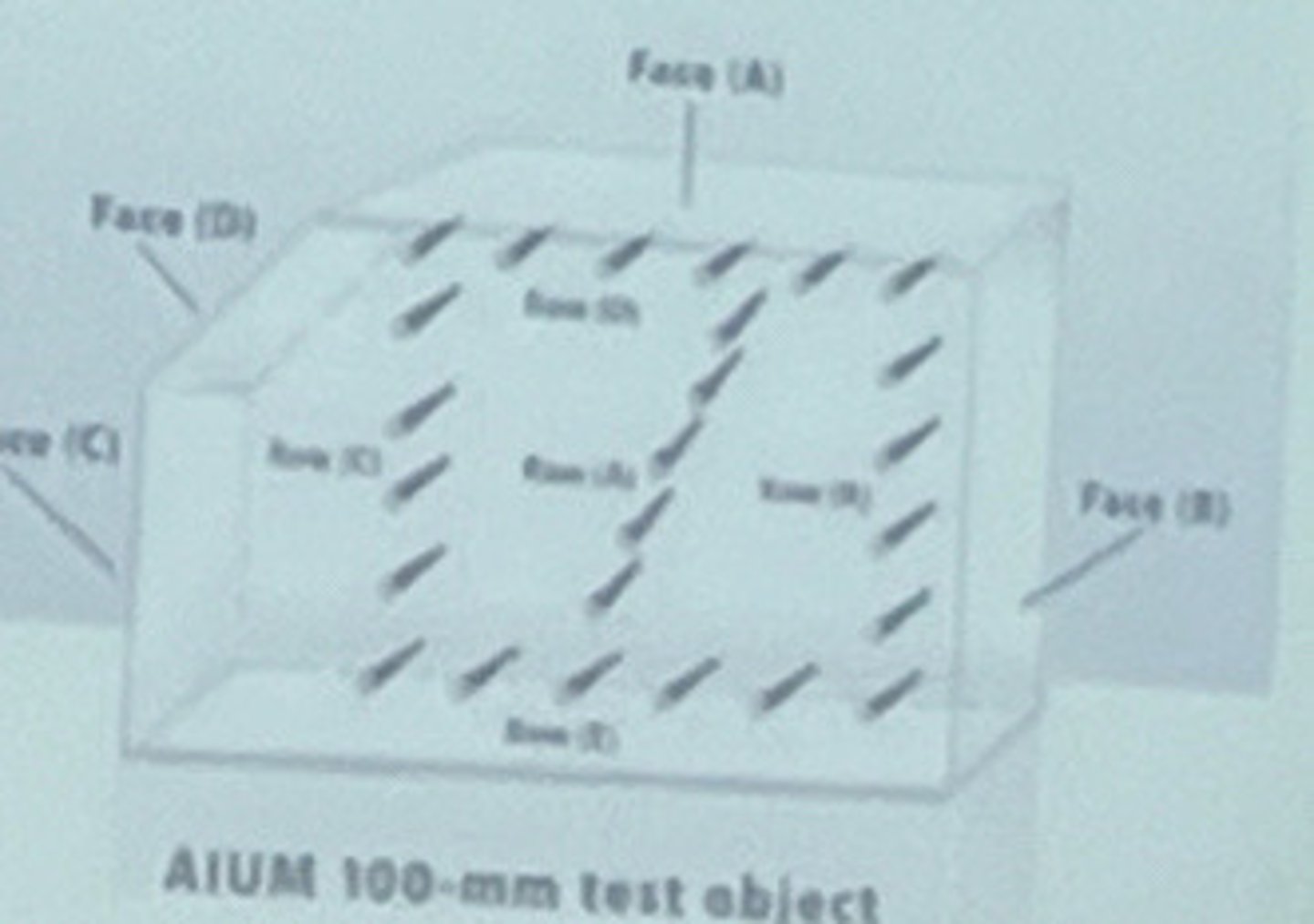
Older testing device
What is the AIUM 100
0.75mm steel rods arranged in groups filled with water, 9% alcohol and and algaecide
What is the AIUM 100 contain
Water, 9% alcohol and an algaecide
What if the mixture in the AIUM 100 consist of
0.75mm
How big are the steal rods in the AIUM 100
Inexpensive
What is the advantage of the AIUM 100
No gray scale and no attenuation (can't test for attenuation)
What is the disadvantage of AIUM 100
AIUM 100
What is this an image of
Absorption, reflection, refraction, scatter, wave-front divergence
What are the 5 different types of attenuation
Ability to differentiate between two perpendicular points
What is lateral resolution
Lateral resolution
What resolution is tested with face B and C
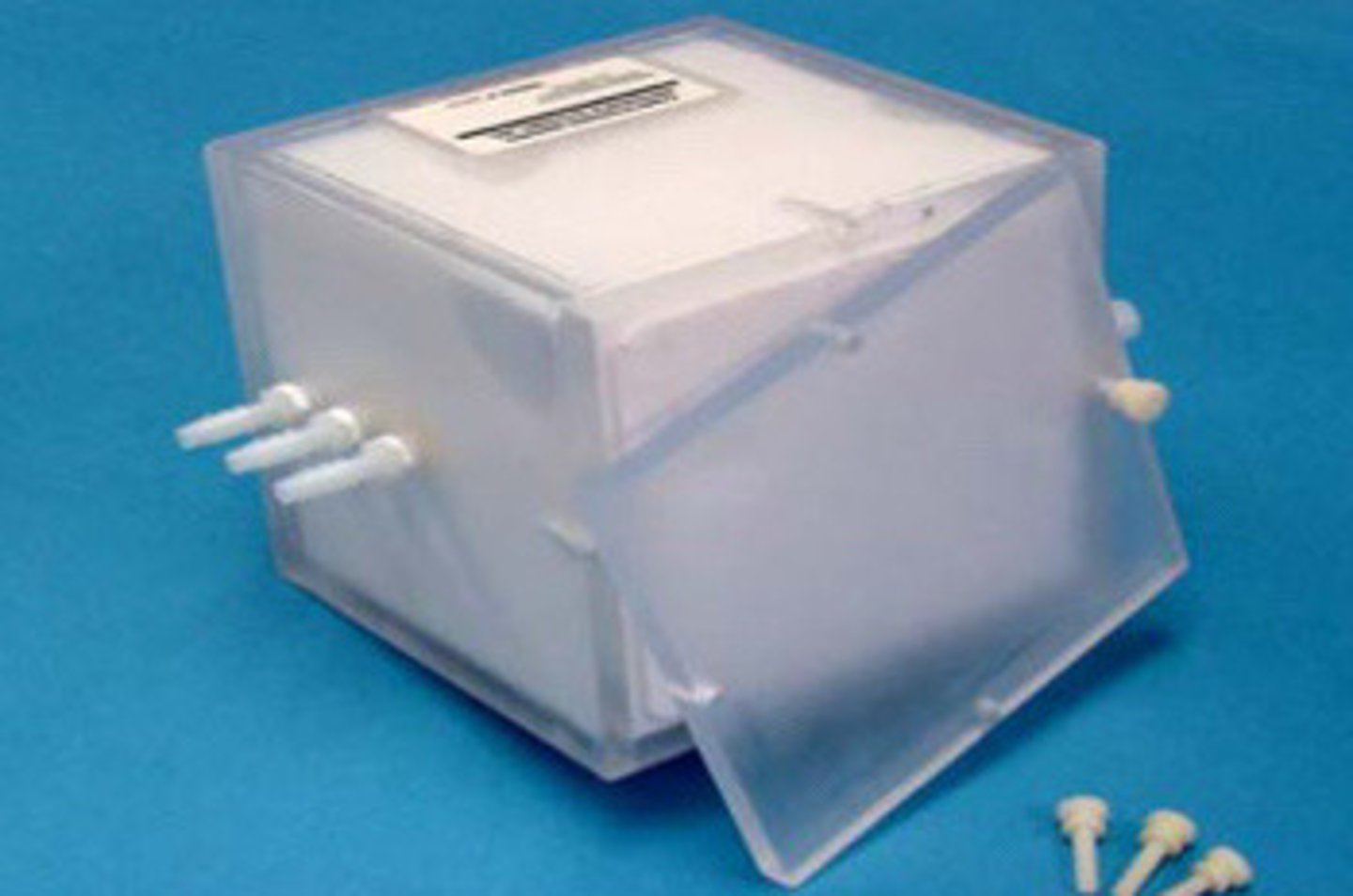
One or more materials that stimulate a dog os tissue in its interaction with ultrasound
What does a tissue equivalent phantom contain
Gel mixture with a graphite powder
What does the plastic case contain in the tissue phantom
Rod groups and solid and cystic "lesions"
What else do tissue phantoms
Grayscale, attenuation (TGC), and speed of sound
What else do the tissue phantoms allow to test
More expensive
What is the disadvantage of tissue phantoms
Dead zone, axial/lateral resolution, elevational resolution, depth calibration accuracy, length calibration accuracy, TGC characteristics, uniformity, system sensitivity, dynamic range, contrast resolution, lesion detection
What are the 11 things that the tissue phantoms can test
Tissue equivalent phantom
What does this image show

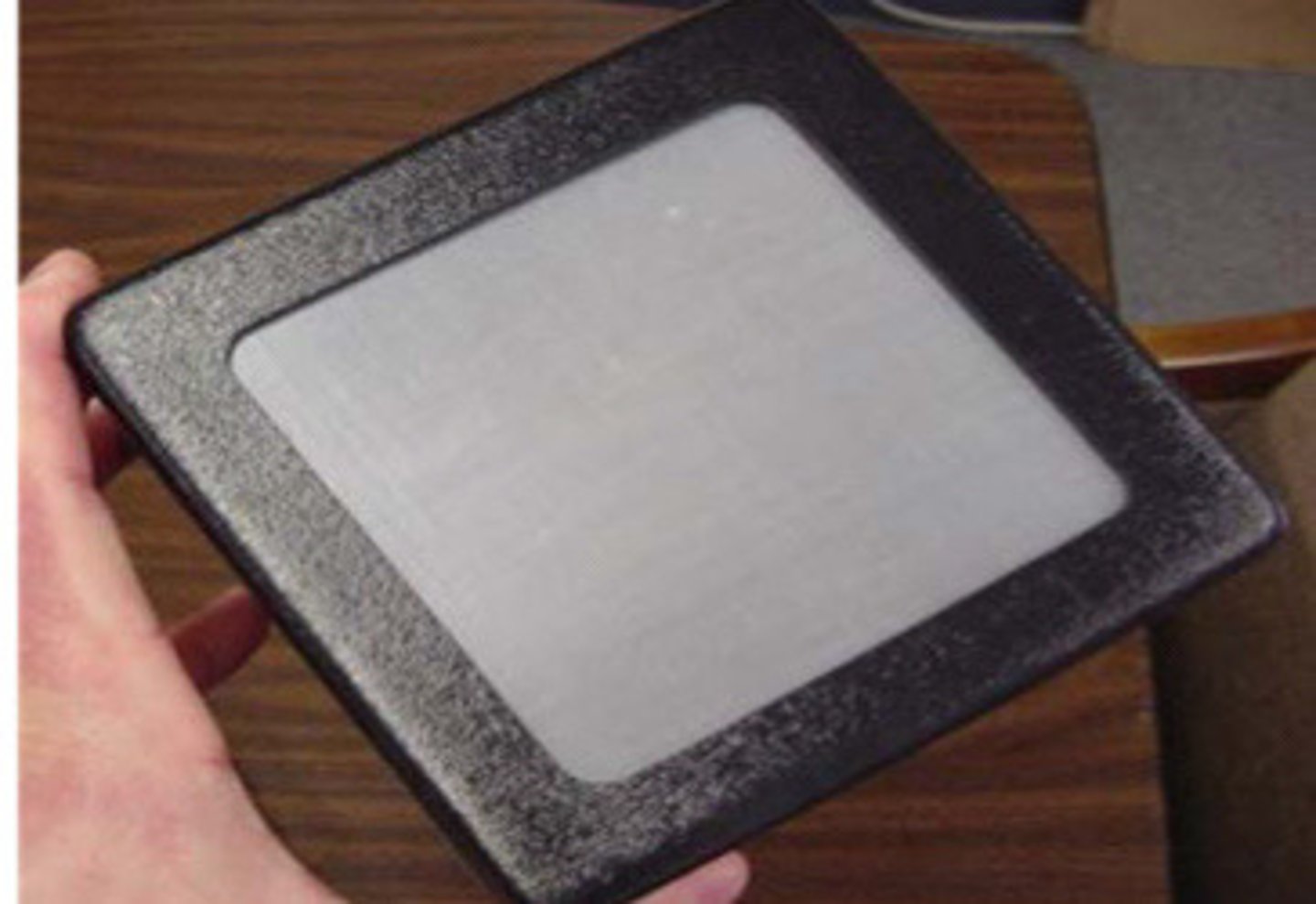
Tissue equivalent phantom
What does this image show

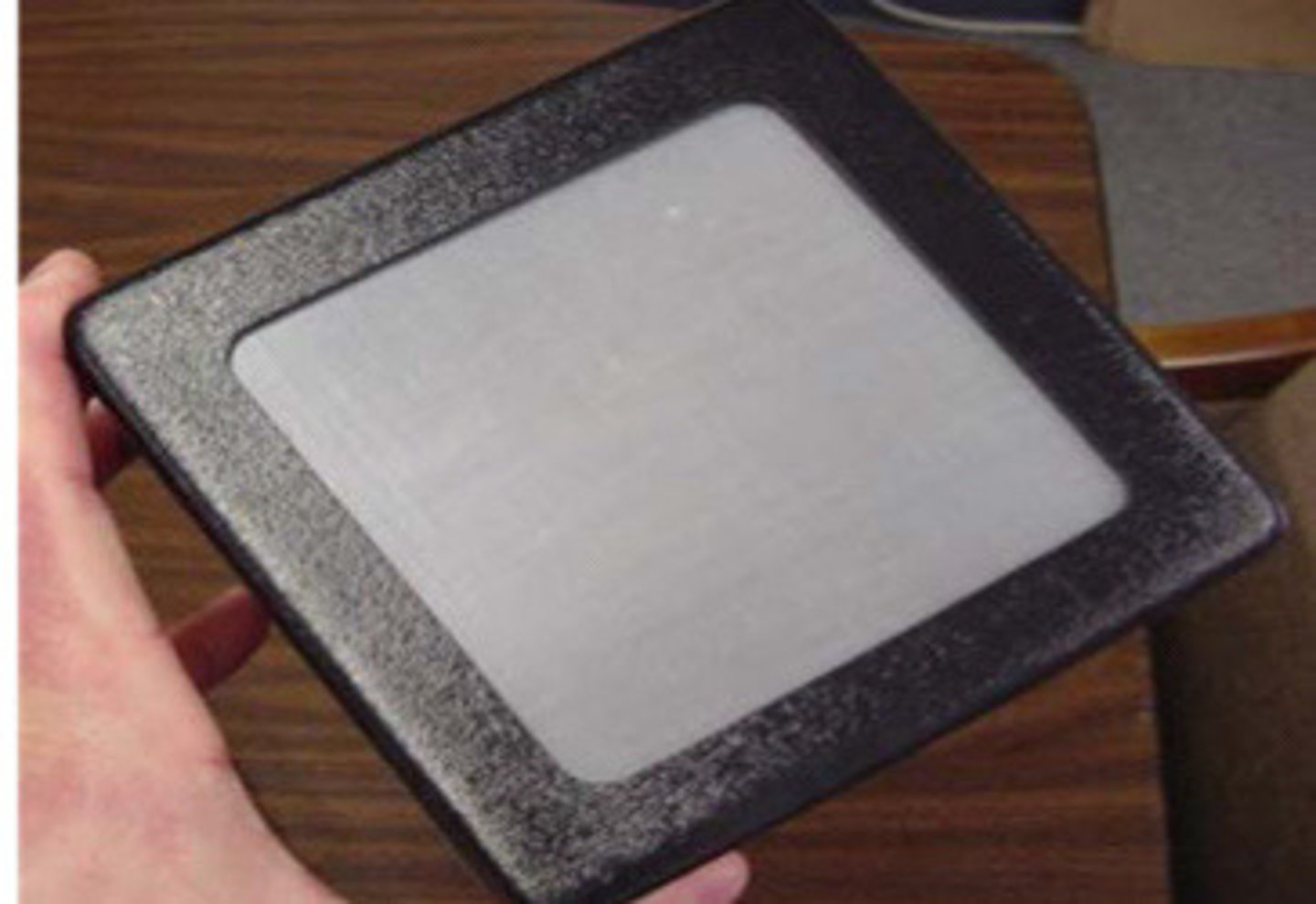
Tissue equivalent phantom
What does this image show

Saran or polyurethane
What are the films made of in tissue phantoms
Rigid and made of ABS, PVC, or acrylic
Describe the containers of tissue equivalent phantoms
Attenuation coefficient, speed of sound, backscatter coefficient/relative contrast, elasticity, thermal properties
What 5 characteristics must a good phantom have to be similar to soft tissue
5dB per cm
What is the attenuation coefficient
Temperature has an impact on the speed of the sound
Why must tissue phantoms have thermal properties
Dead zone mmt, detailed resolution, distance accuracy, image uniformity, depth of penetration, cyst imaging capabilities
What can tissue equivalent phantoms test for
Must make sure all other settings (focus, depth, gain, etc) are the exact same as the previous year
What must you make sure to do when testing the machines each year
Area in the near field close to transducer
What is the dead zone
Main bag
What is another term
Old machines
In what machines is a large dead zone seem to be quite a problem
Imaging the dead zone pins and observing change over time
Describe the technique for assessing the dead zone
<15mm of change
What is an acceptable change of dead zone over time
Dead zone
What does this image demonstrate
1/2 the SPL
What is the equation for the axial resolution
Dead zone test
What does this image demonstrate

Dead zone is getting worse
What would it mean if the next year you test for dead zone you can no longer see the pin at 1mm

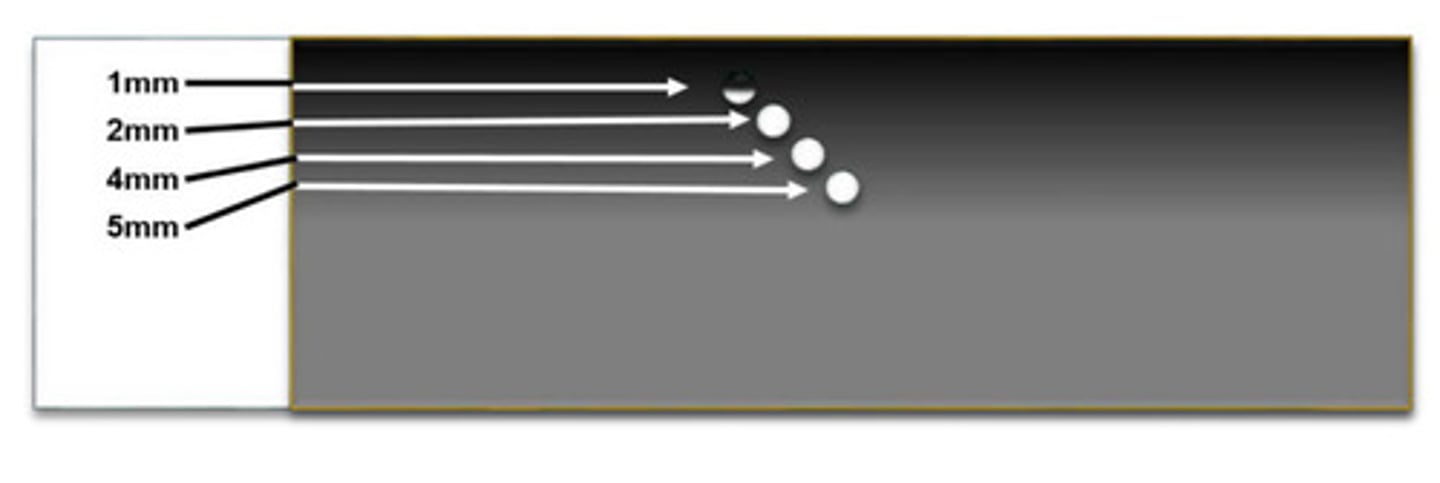
Axial resolution
What resolution does this image represent

SPL = wavelength x RD
What is the equation for SPL
RD = cycle x pulse
What is the equation for ring down (RD)
Test the systems ability to separate interfaces along the path of the beam
How can the phantoms test axial resolution
Increase damping material (electric or mechanical)
How can you decrease RD
Doppler
What application requires a longer pulse and therefore less damping
Measuring the smallest separate visible between the axial resolution pins at various depths
Describe the technique for testing axial resolution
Comet tail reverberation (would cover pins under it)
Why are the axial resolution pins offset
Systems ability to separate interfaces across the beam
What is lateral resolution
Axial resolution pins
What does this image represent

Focus (beam width), frequency, aperture
What are some things that can affect lateral resolution
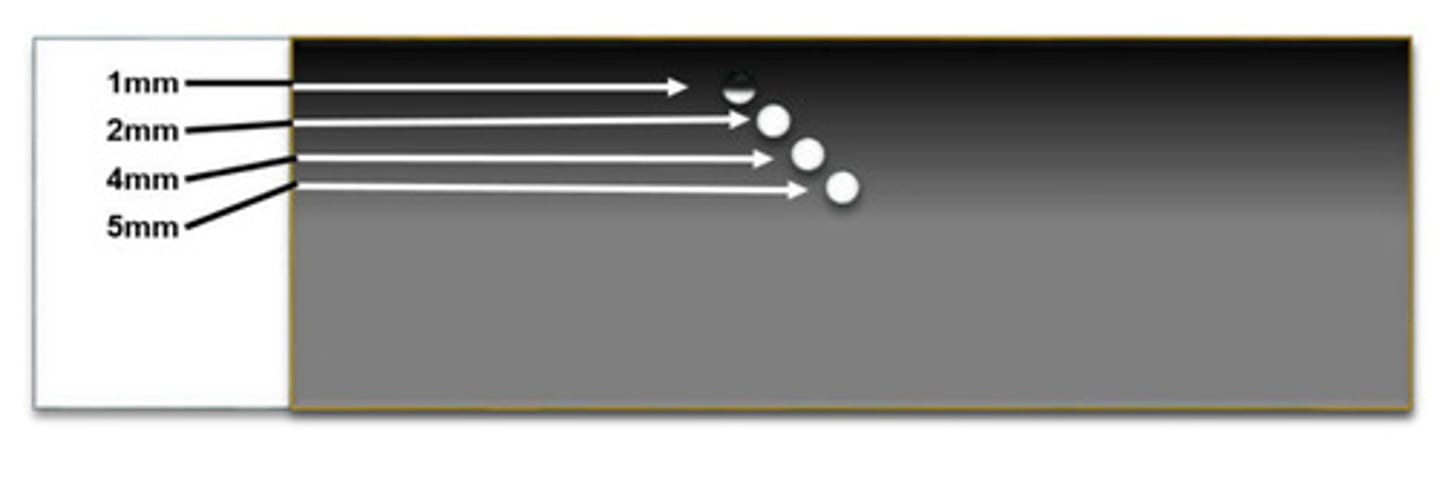
Lateral resolution
What does this image represent
Beam width
What is the main things that directly affects lateral resolution
Measuring the lateral resolutions that are dependant on the depth and focus, watch for changes over time
Describe the technique for testing lateral resolution
Width of the beam
How big will the object be if the beam is wider than an object
Lateral resolution
What resolution is this image testing
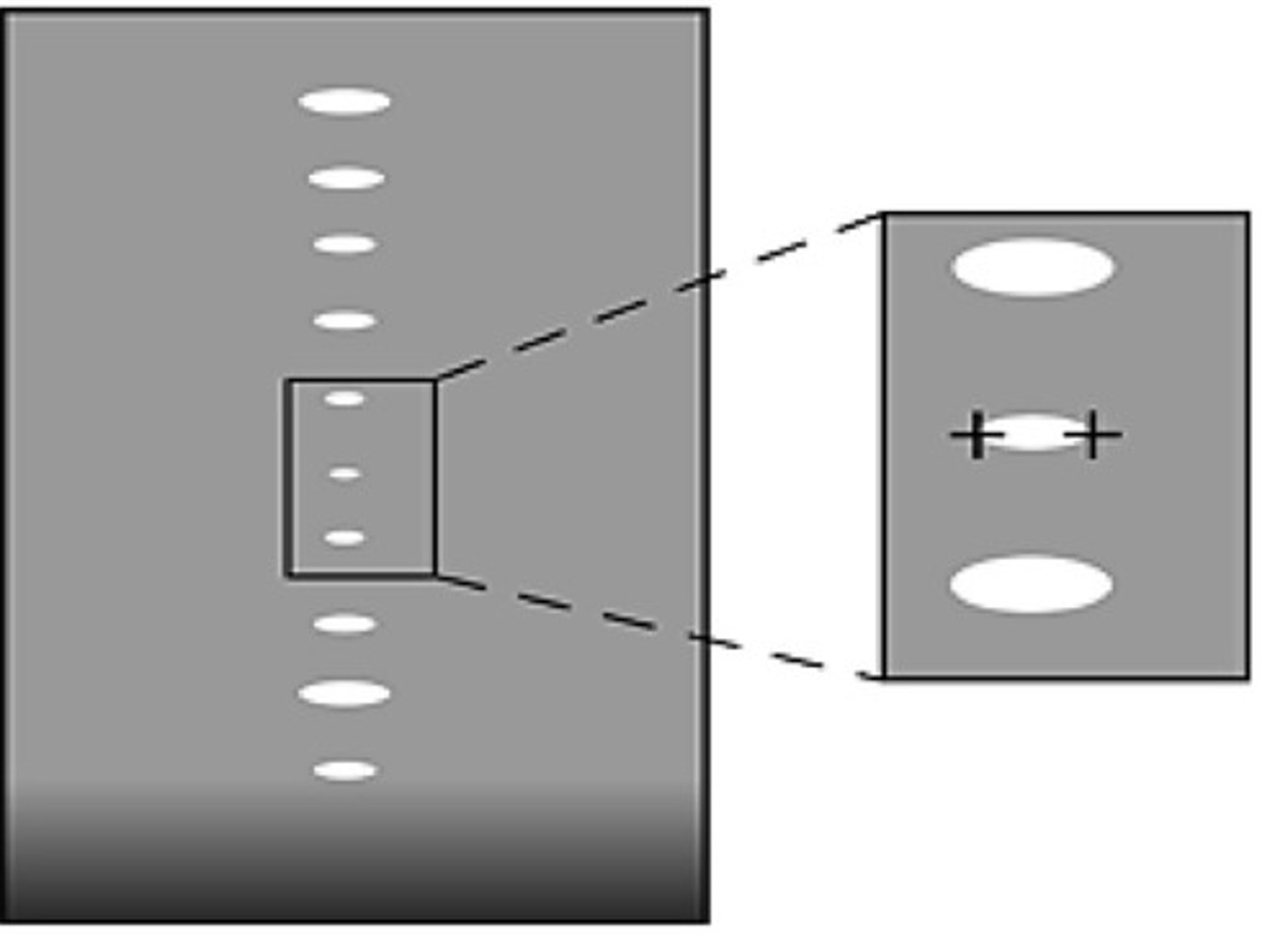
Pins in this image are all the same size but appear different due to different beam widths
Explain why the pins in these images are different size
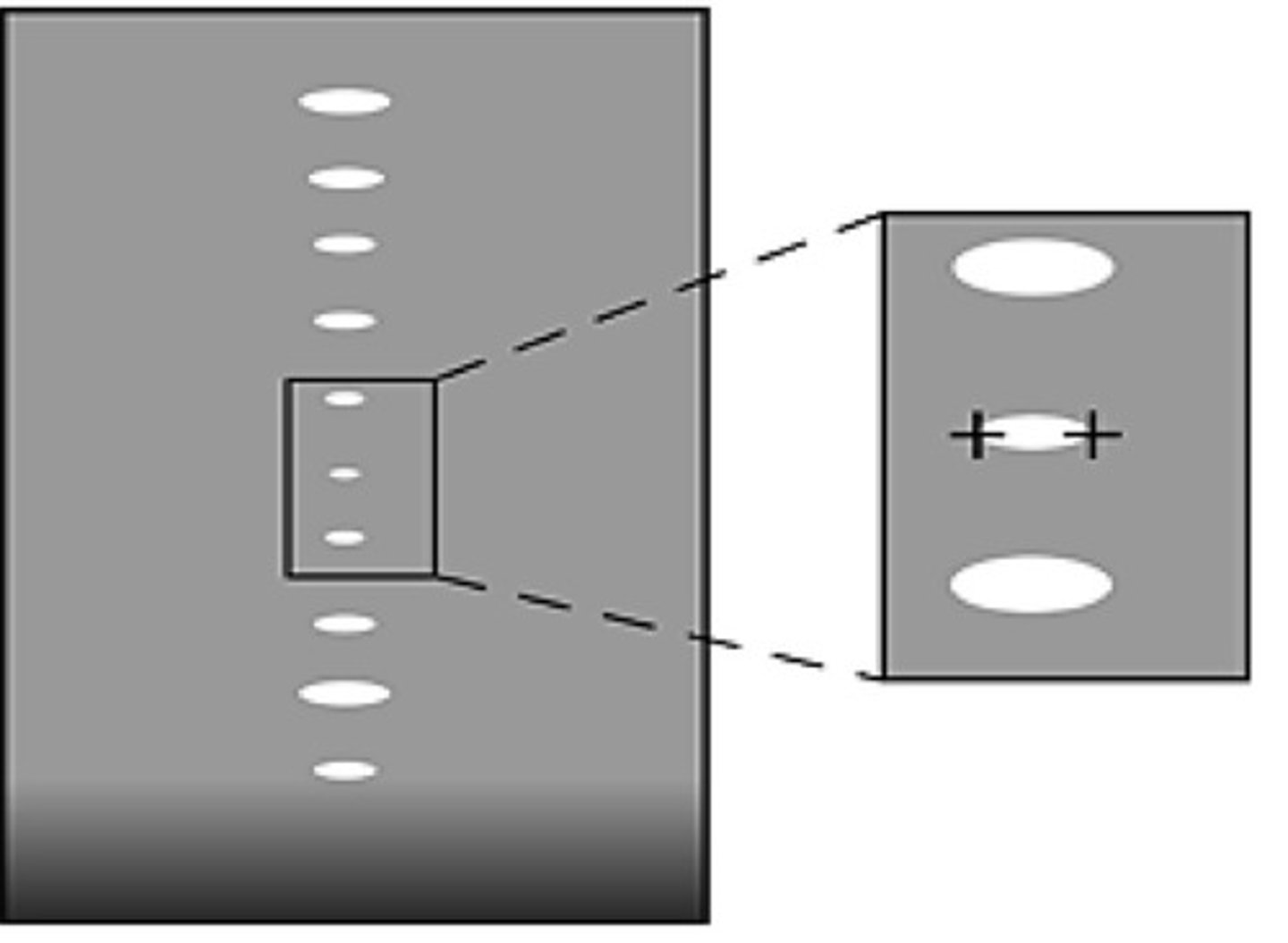
Point spreading
What is it called when an object shows up the size of the beam because it is smaller than the beam
Beam is swept across
Explain why point spreading occurs
Change focus to different depths to fully test lateral resolution at multiple depths
What else should you do when testing lateral resolution
Slice thickness
What is another term for elevational resolution
Z axis
What axis is being testing when assessing the elevational resolution
False
T/F: you can use the same tissue phantoms for elevational resolution that you use for axial/lateral resolution
Spherical void phantom or beam profile phantom
What is phantom is used to test elevational resolution
Expensive/ another phantom you have to pay for
What is a disadvantage of the spherical void phantom
Qualitative assessment using more common phantom (tissue equivalent)
How else can you assess for elevational resolution without the specific phantom
Using the cystic structures in the phantoms, if the focus is at the cysts and there are still echoes in them we can infer the elevation resolution is off because the lateral resolution is the best at the focus
Explain how we can use tissue phantoms to test elevational resolution
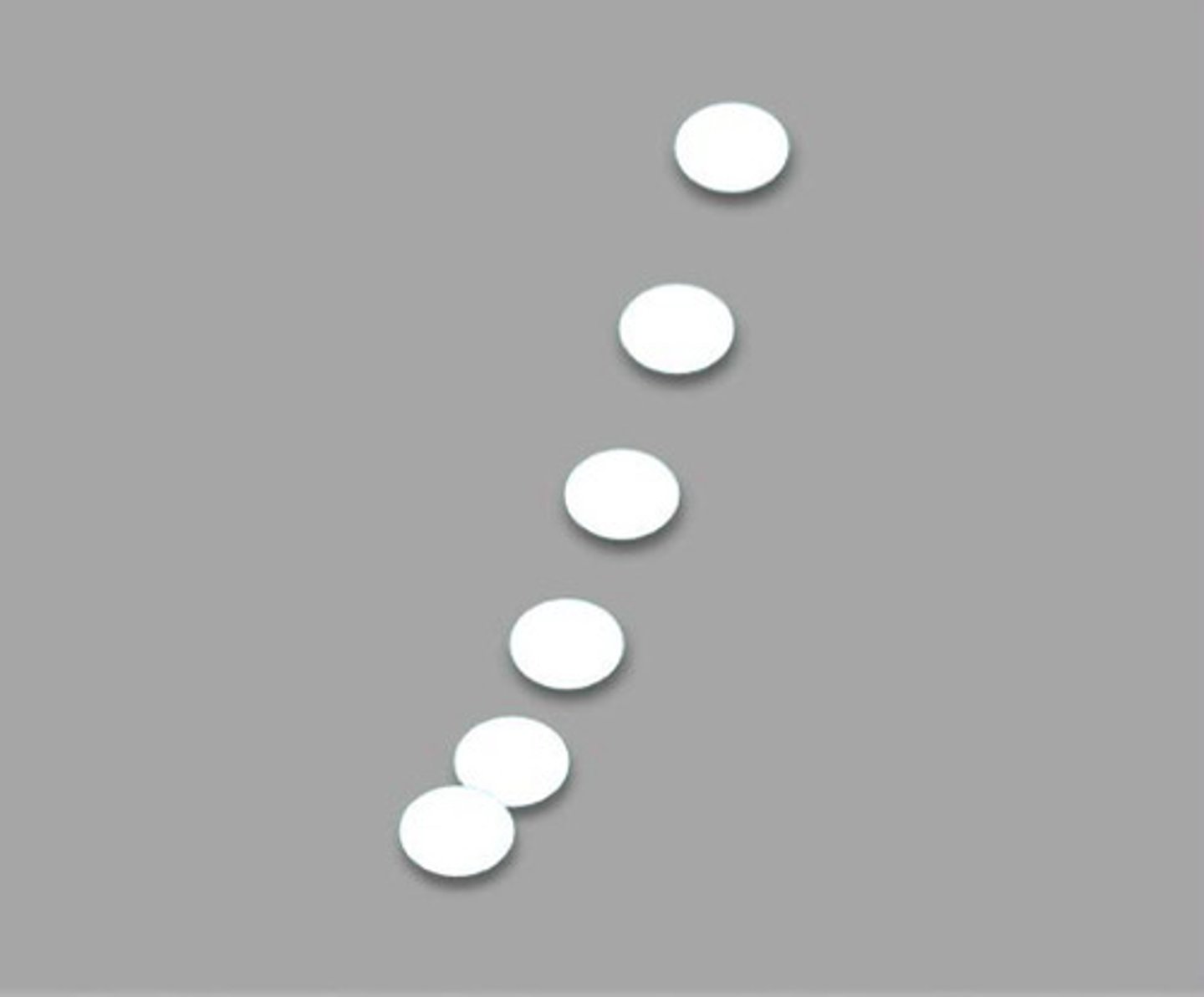
Elevational resolution
What resolution is this image testing
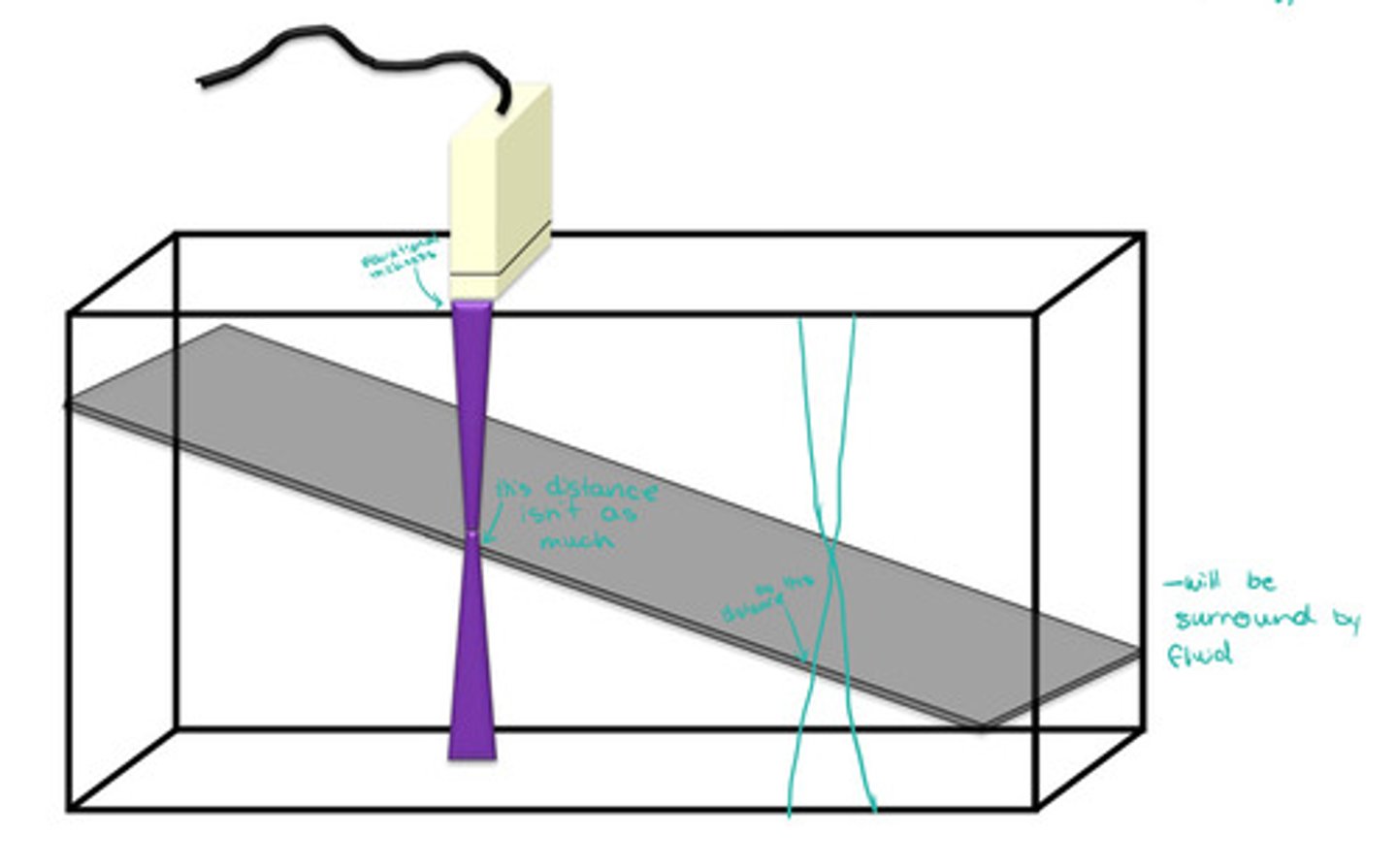
Move probe down ramp to test different depths of elevational resolution (it will be better at some spots because of natural beam shape)
Explain how to use the tool in the image for elevational resolution
Horizontal and vertical
What two types of distance accuracy do we test
Measuring pins at a know distance with callipers and comparing the numbers
Describe the technique of testing distance accuracy
Measure larger distance to detect smaller margins at error (a mmt of 1cm may be close but may be totally off at a mmt of 5cm)
What should you make sure to do when testing distance accuracy
True
T/F: TGC characteristic test is a user specific test
Observations of the individual performing the test
What are the result to a TGC characteristics test based on