Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
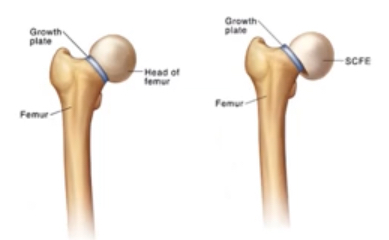
Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis
Adolescent Hip Condition : 10-16 (M>F)
Slippage of overlying epiphysis on the growth plate of the femur (femoral head slips off neck of femur) — hip joint heals abnormally
during periods of rapid growth (puberty)
Untreated = severe hip OA
SCFE - Presentation
Hip, Groin, Medial Thigh and or Knee Pain
Pain increases with activity
Acute (trauma) or Insidious onset of a limp (gradual onset — no history of injury
Decreased hip ROM : hip positioned ER with loss of IR
SCFE- Tests
X-ray
SCFE - Treatment
Surgery : Epiphysis (Head of Femur) is screwed into place — stops head of femur from slipping any further :
Stable Slips = PWB to Tolerance x 6 weeks post-op
Unstable Slips = FWB x 6 weeks post-op
WB determined : type of slip, severity of slip, type of surgery performed
Stable Slip
Stiffness/Pain — increases with activity or with rest
Antalgic Gait
Gait aid — crutches
PWB x 6 weeks post op
Unstable Slip
Likely due to trauma and more painful — cannot walk or WB with gait aid
restriction of blood flow to hip joint = death of head of femur
TTWB (FWB) x 6 weeks post op
SCFE PT Treatment
ROM Exercises
General Strengthening as tolerated — full return to sport and activity
SCFE
Most common adolescent hip condition — most often seen b/w age 10-16 years old
Caused by slippage of the overlying epiphysis on the growth plate of the femur
present with pain in the hip, groin, medial thigh, knee
Pain increases with activity
Often associated with a decreased ROM in the hip