Histo 10 | Cardiovasccular System
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
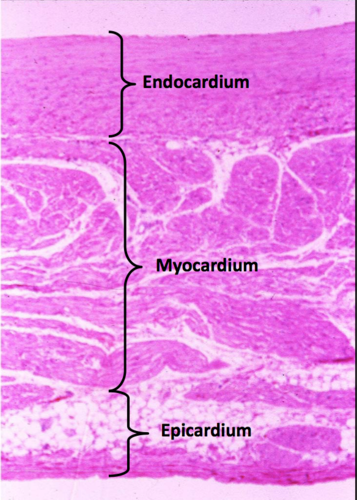
What are the three layers of the heart?
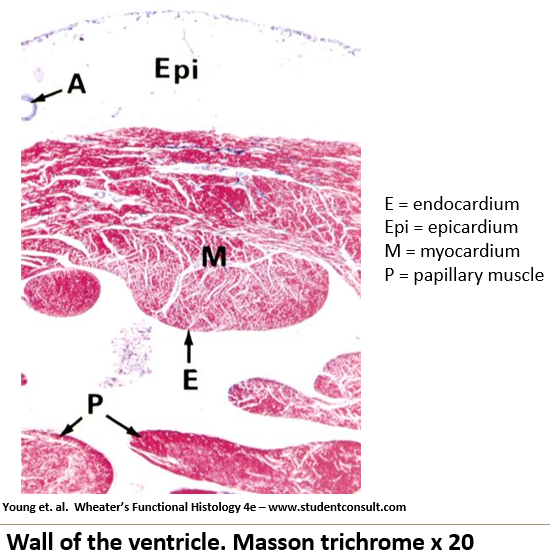
Endocardium: Inner layer
Myocardium: Middle layer
Epicardium: Outermost layer
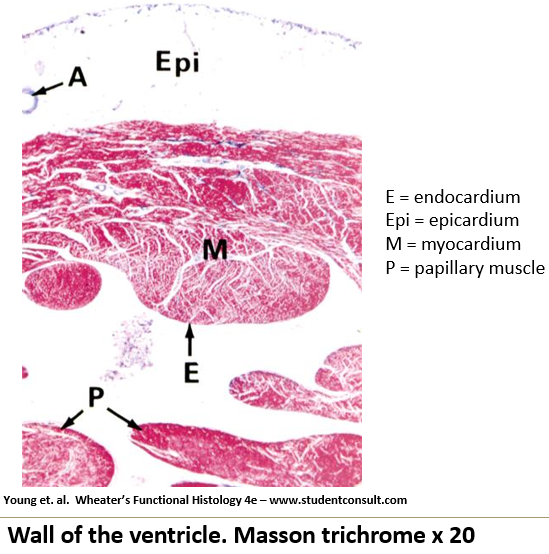
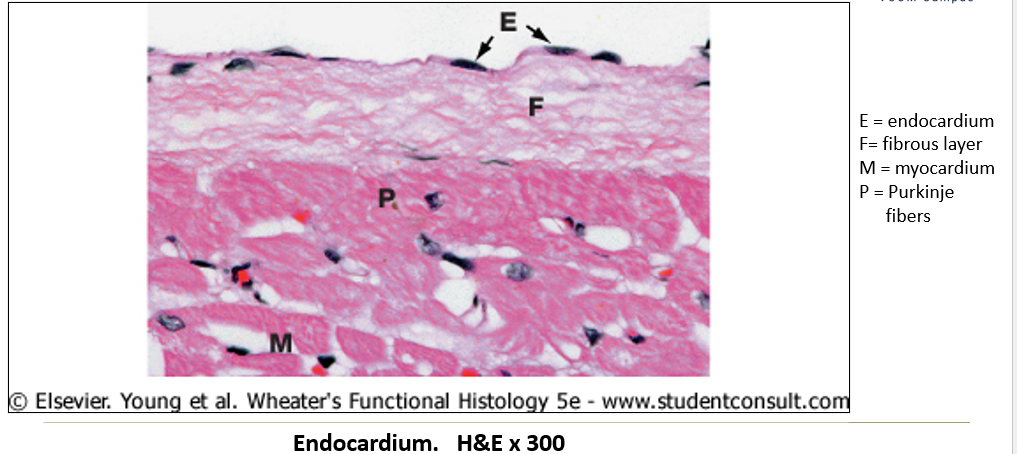
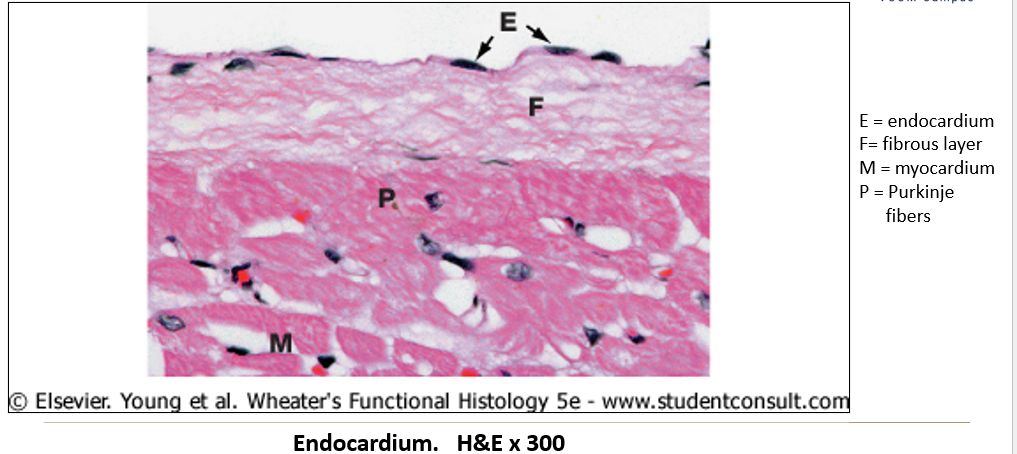
Appearance of endocardium on histological slide?
Inner layer made of simple squamous epithelium with fine connective tissue.
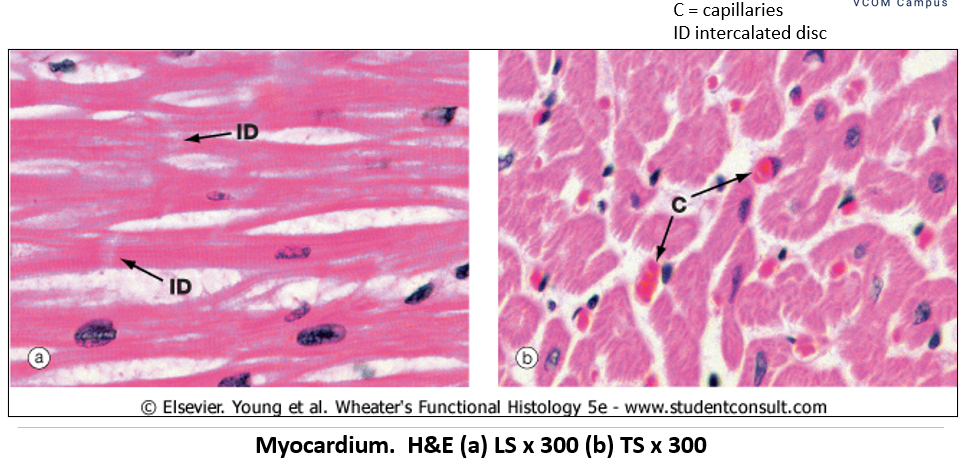
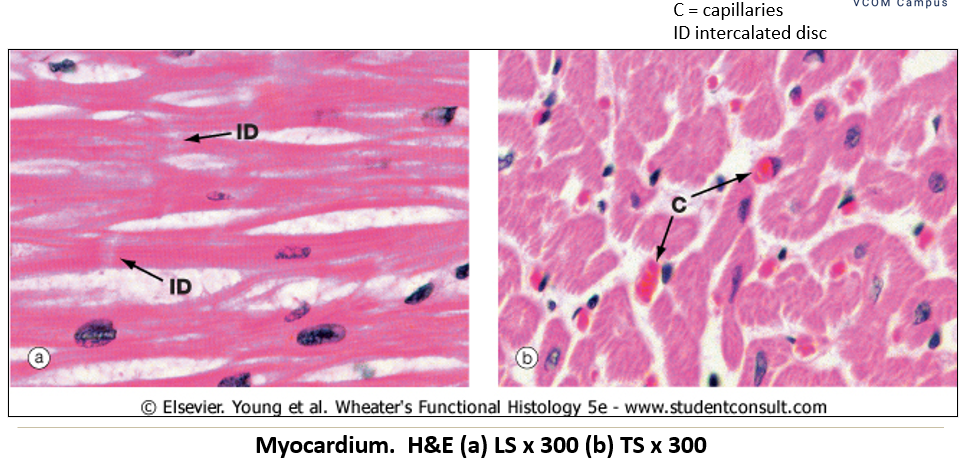
Appearance of myocardium on histological slide?
Middle layer, made of cardiac muscle, and the thickest layer. Contains intercalated discs; woven appearance
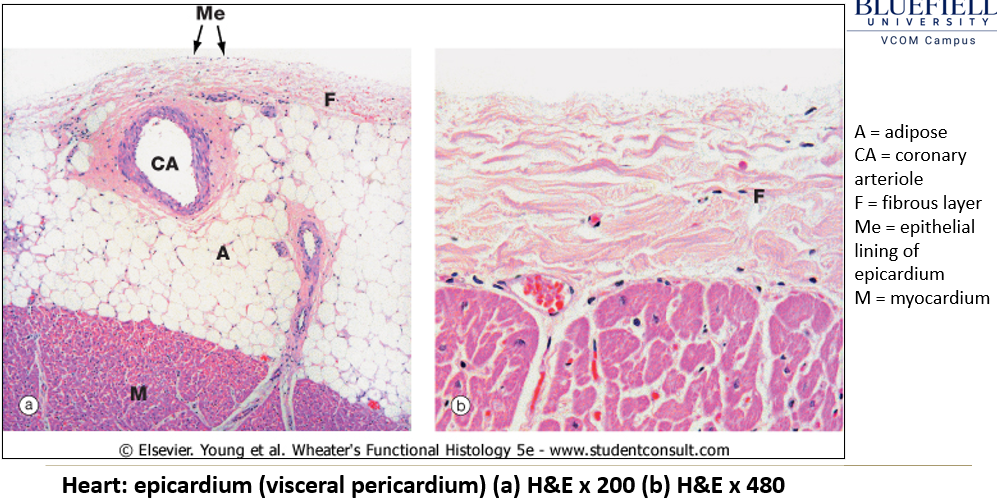
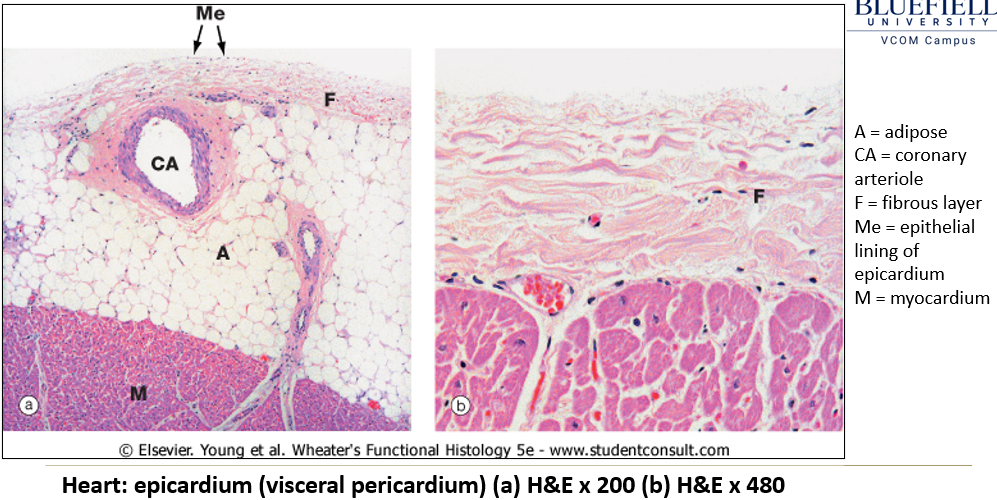
Appearance of epicardium on histological slide?
Outermost layer containing adipose tissue beneath a simple squamous epithelium.
How does myocardium thickness vary between different heart chambers?
Atria: Thinnest because they operate at low pressure.
Left ventricle: Thickest because it pumps against the highest pressure.
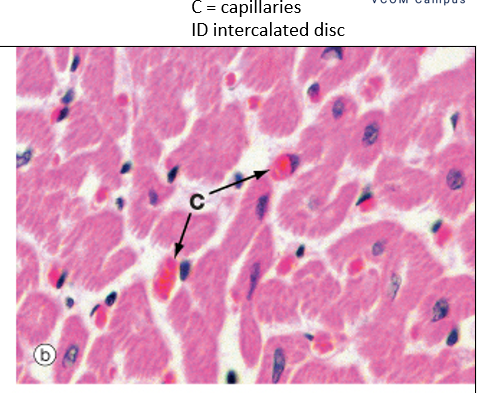
What is found between cardiac myocytes in the myocardium?
A rich capillary network to supply oxygen and nutrients.
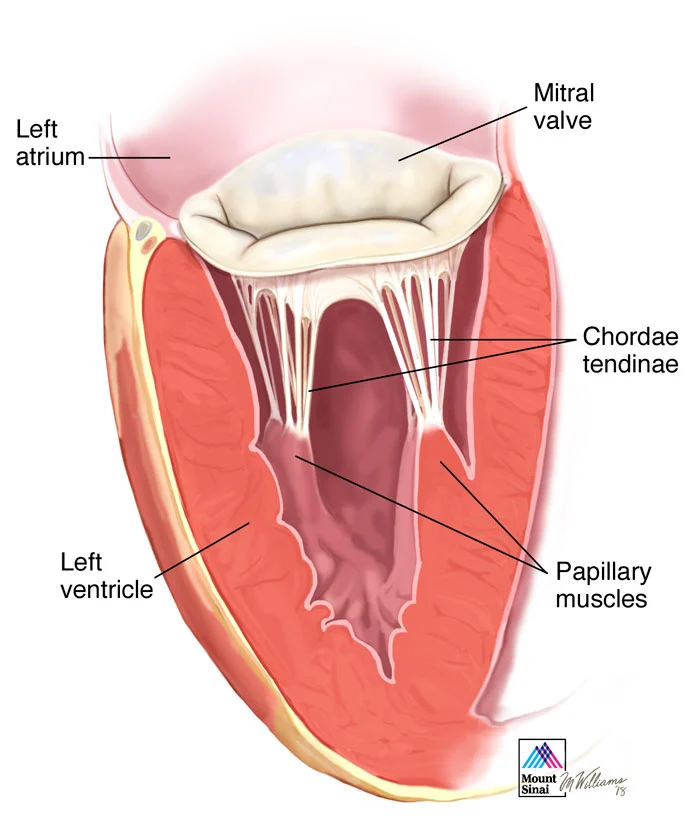
What are papillary muscles, and what do they do?
They hold tension on the chordae tendineae, preventing valve prolapse.
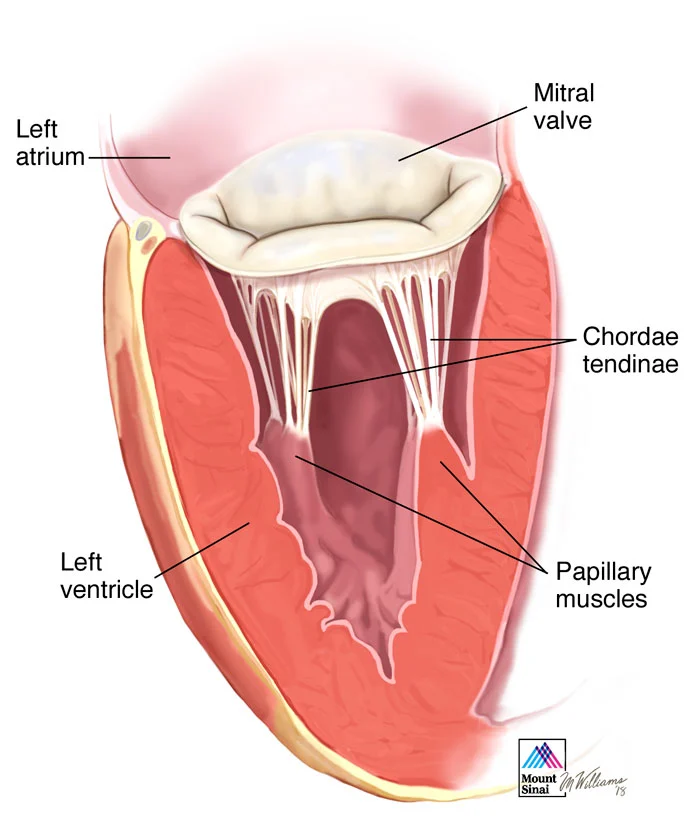
What are chordae tendineae, and what is their function?
Collagenous and elastic structures that prevent atrioventricular valve prolapse.
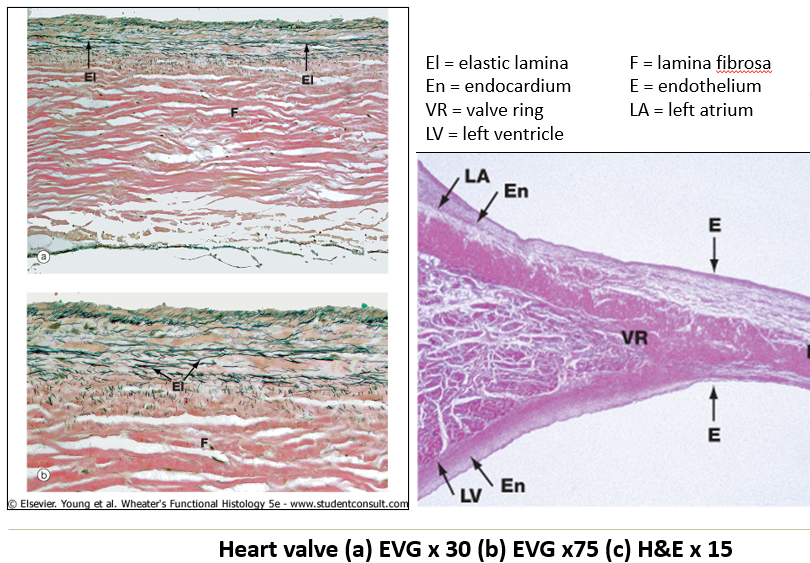
What is the histological structure of heart valves?
Lamina fibrosa – Central collagenous plate.
Elastic fibers – Prominent on the atrial surface.
Covered by endocardium on both sides.
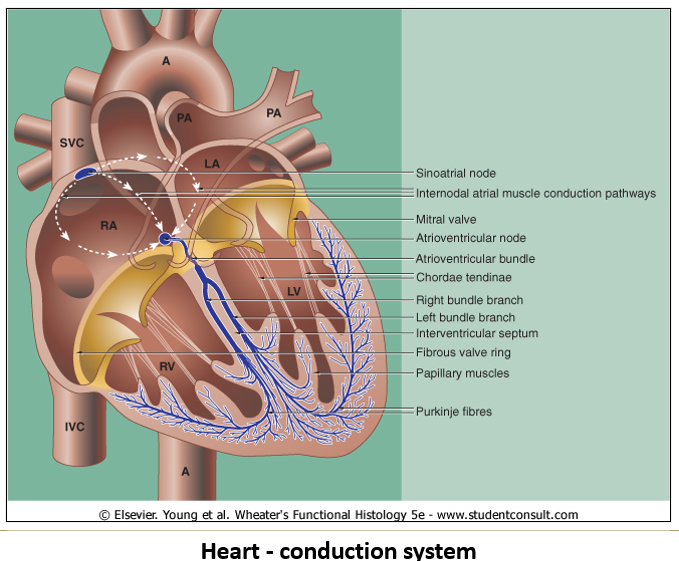
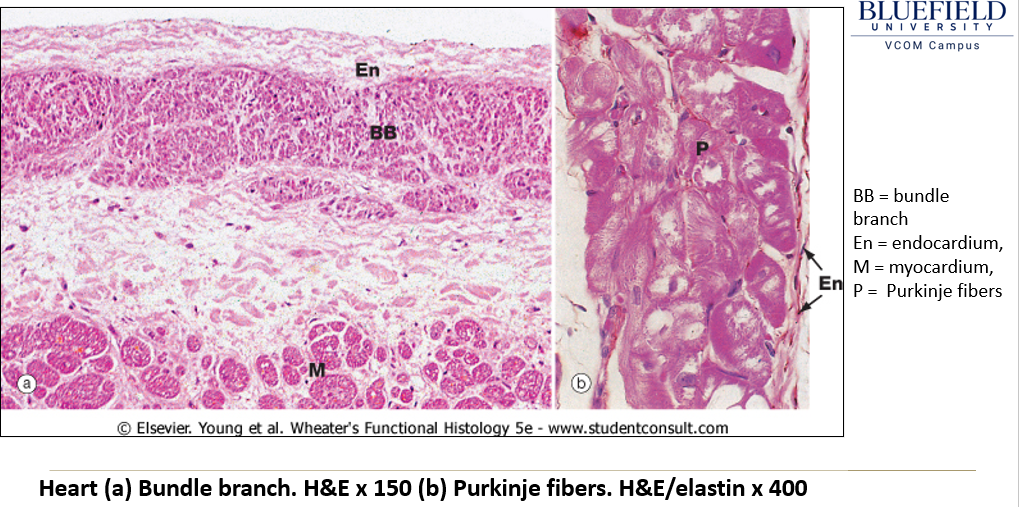
What components of the cardiac conduction system can be seen histologically?
Sinoatrial and Atrioventricular nodes: Small fibers without intercalated discs, embedded in collagenous connective tissue.
Purkinje cells: Large modified myocytes found just deep to the endocardium.
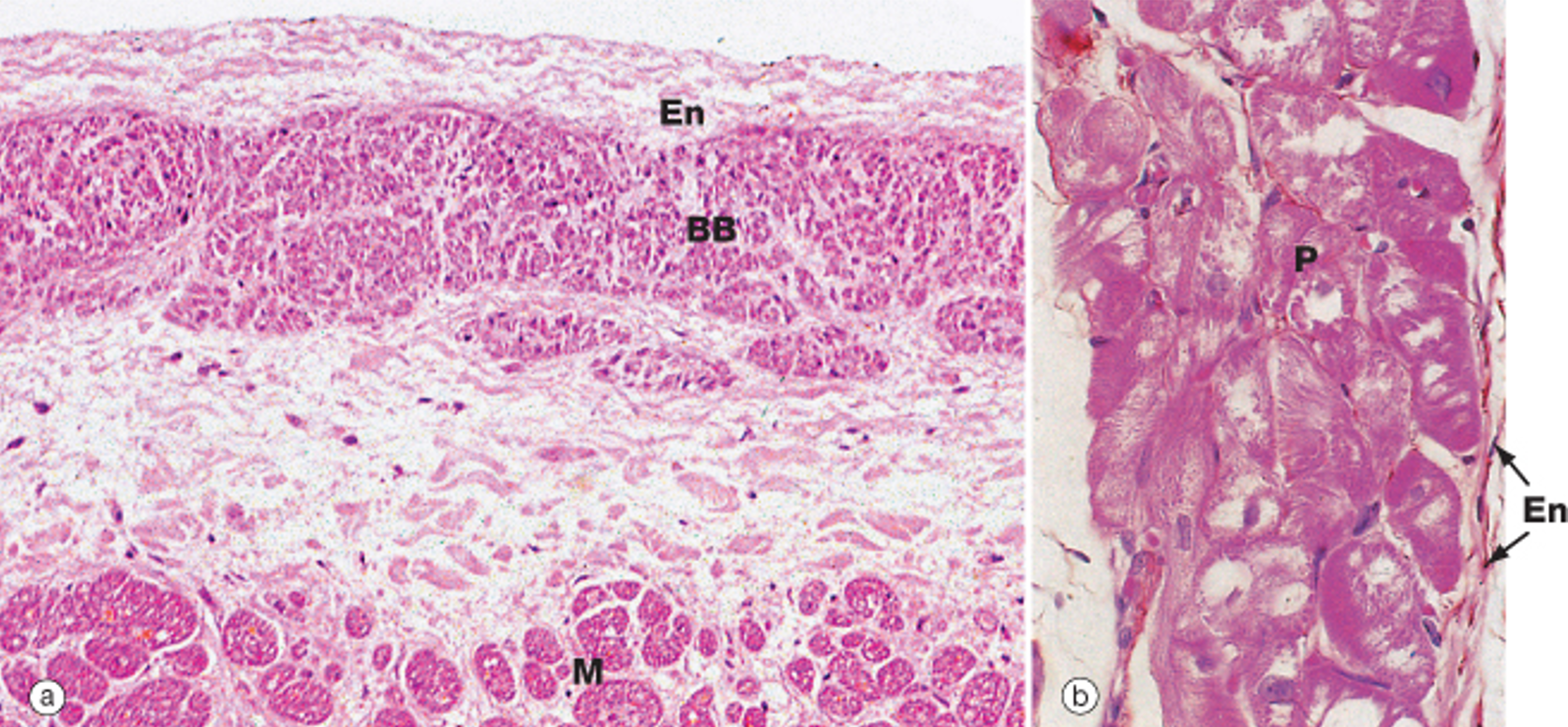
How do Purkinje cells appear histologically?
Larger than cardiac myocytes, often binucleated.
Fewer myofibrils than typical myocytes.
Large glycogen stores around the nucleus, creating a clear area (halo) in histological sections.
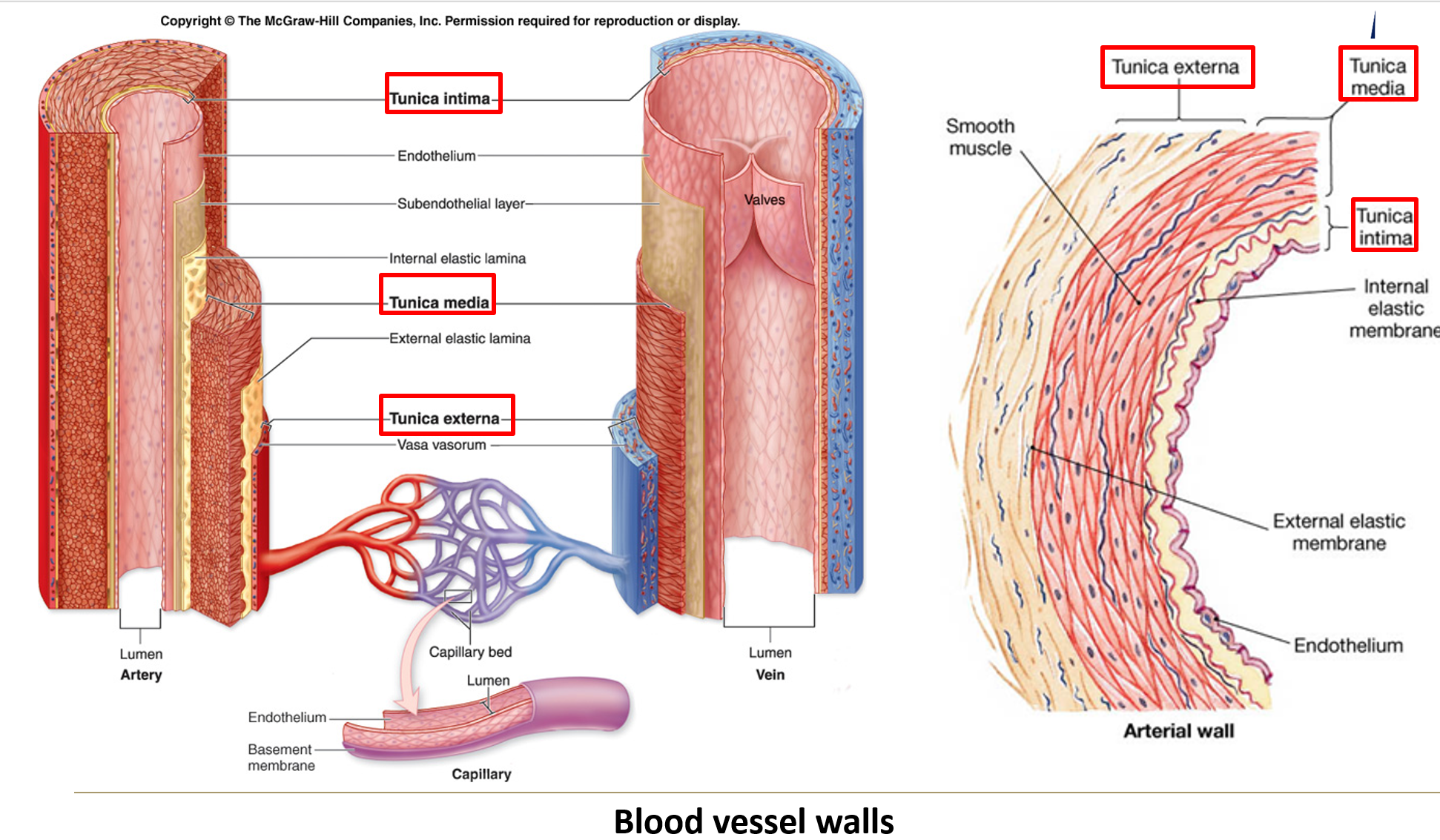
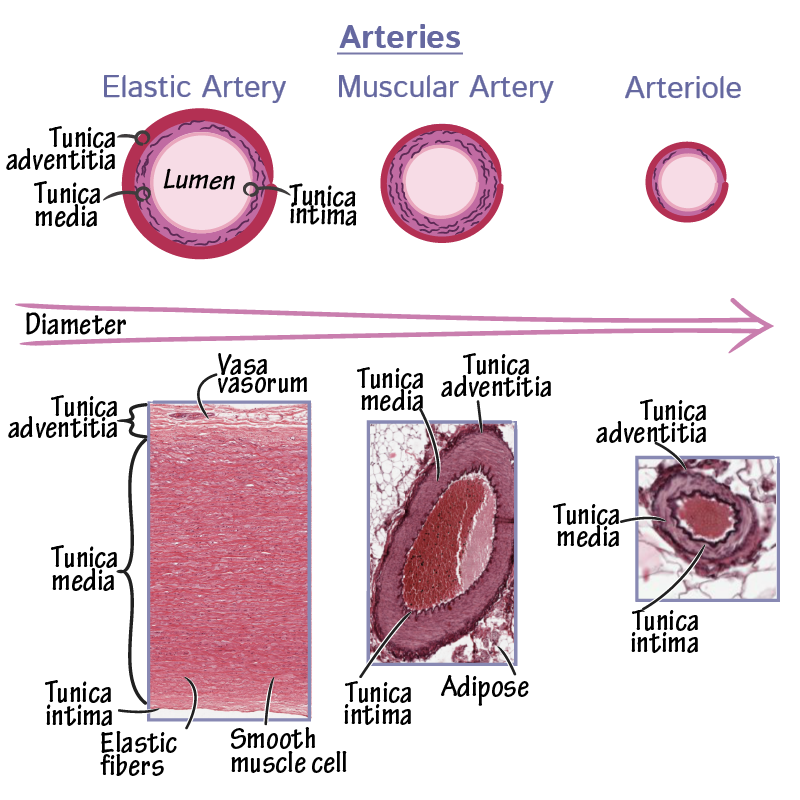
What are the three layers of blood vessels?
Tunica intima: Innermost layer, made of endothelial cells and connective tissue.
Tunica media: Middle layer, composed of circularly oriented smooth muscle cells.
Tunica adventitia: Outermost layer, made of connective tissue, merging with surrounding tissues.
What are the main types of arteries?
Elastic arteries, muscular arteries, and arterioles.
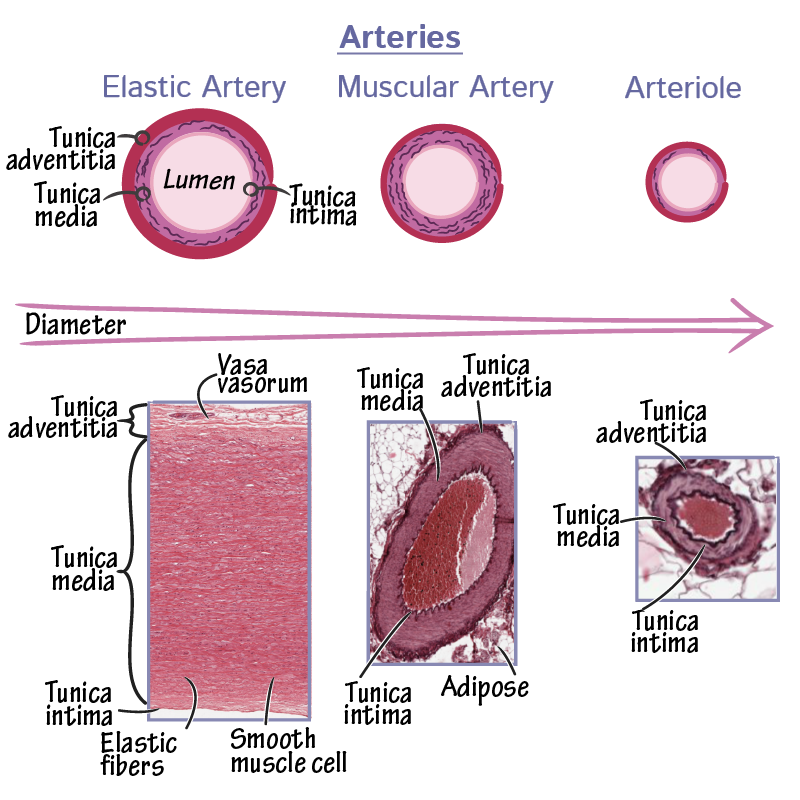
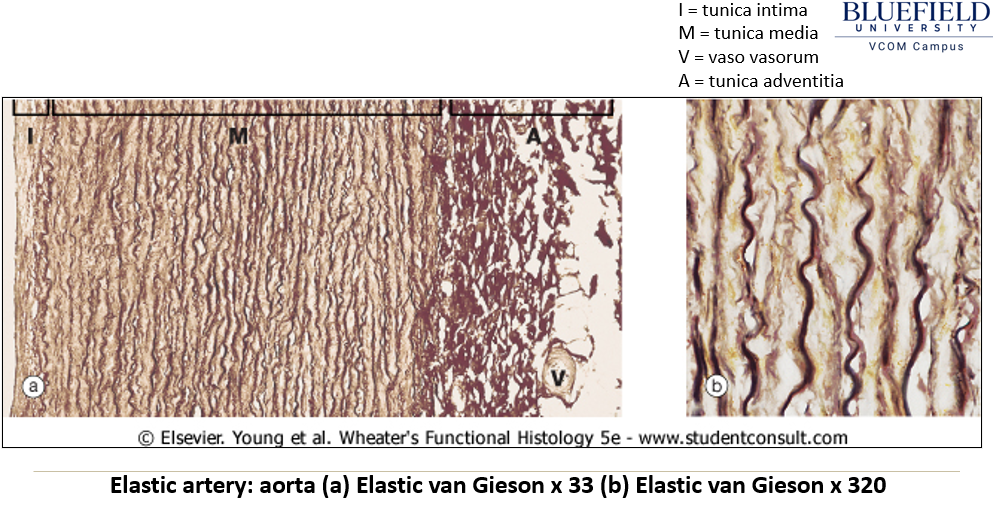
What are the features of elastic arteries?
Largest arteries near the heart.
Contain circumferential and fenestrated elastic fibers in the tunica media.
Have internal and external elastic laminae.
Stretch during systole and relax between beats to moderate blood pressure.
Vasa vasorum supplies blood to the tunica media.
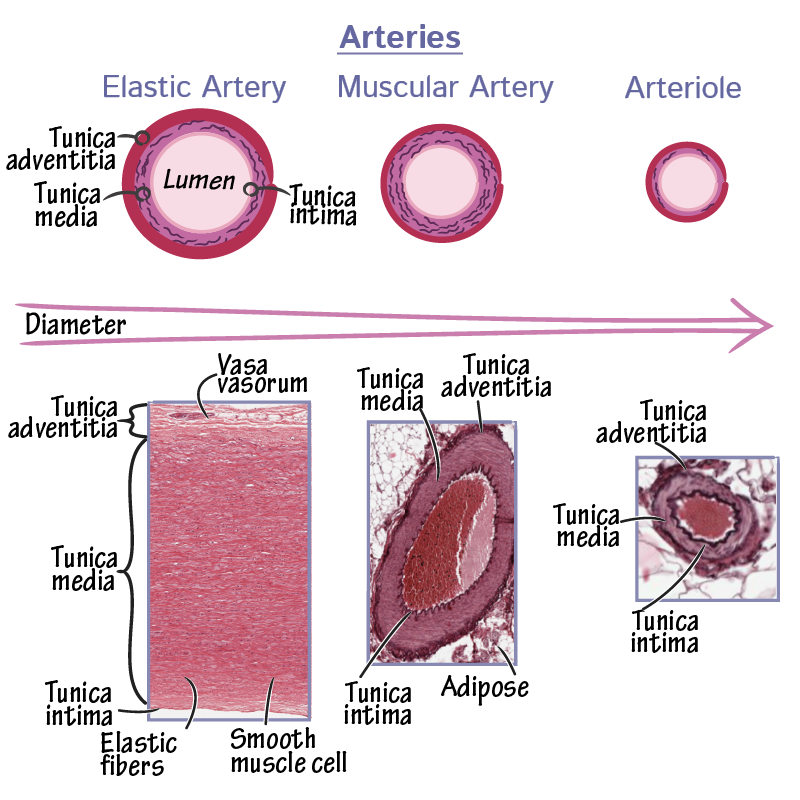
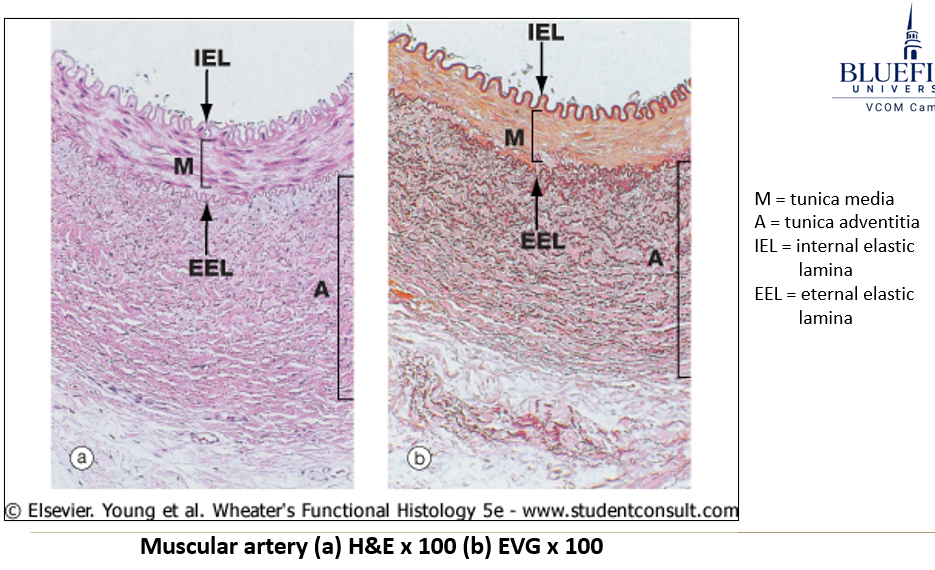
What are muscular arteries, and how do they function?
Distributing arteries that branch off elastic arteries to supply organs and extremities.
Smooth muscle in tunica media controls blood flow by constriction/dilation.
Distinct internal and external elastic laminae.
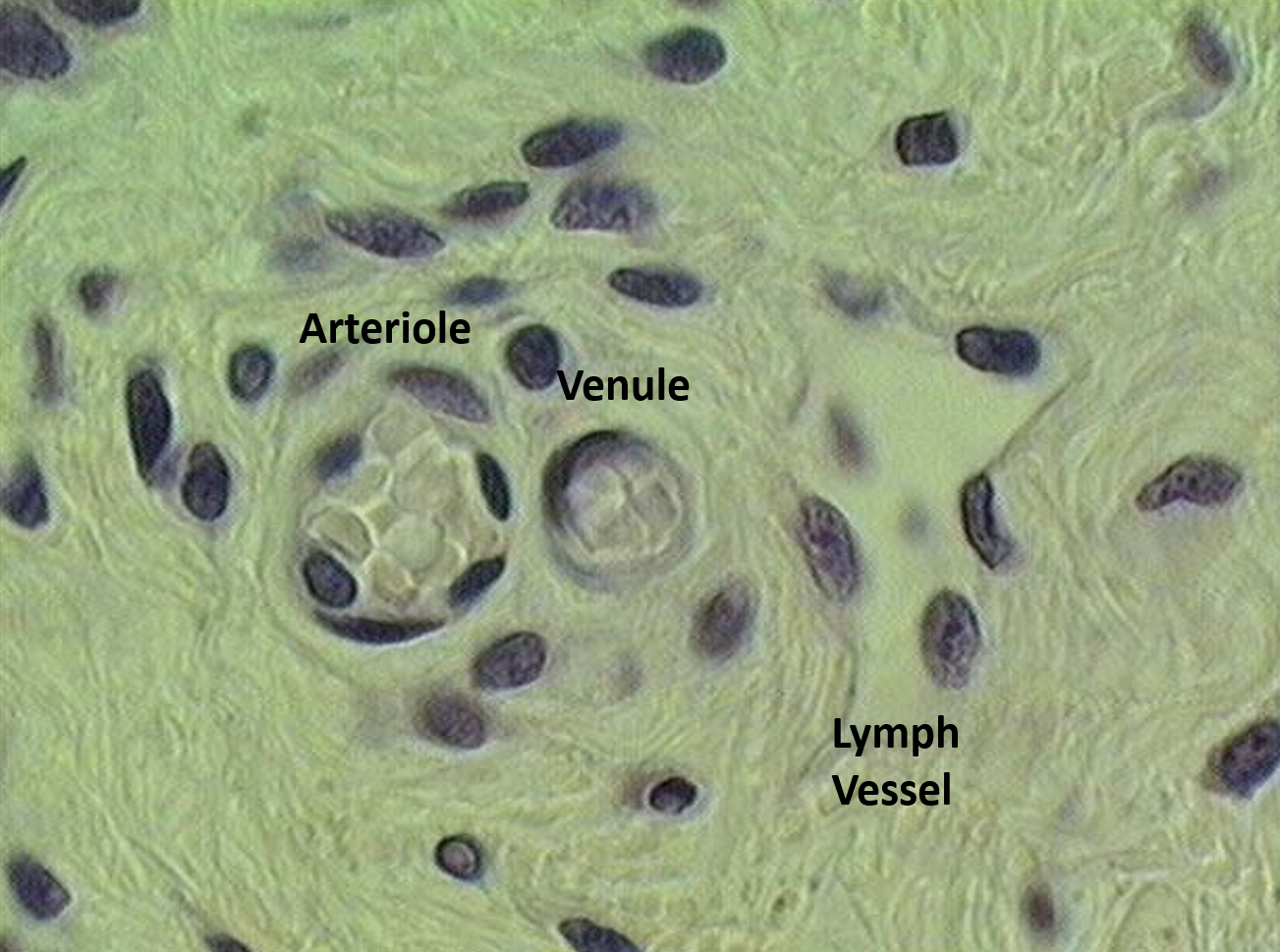
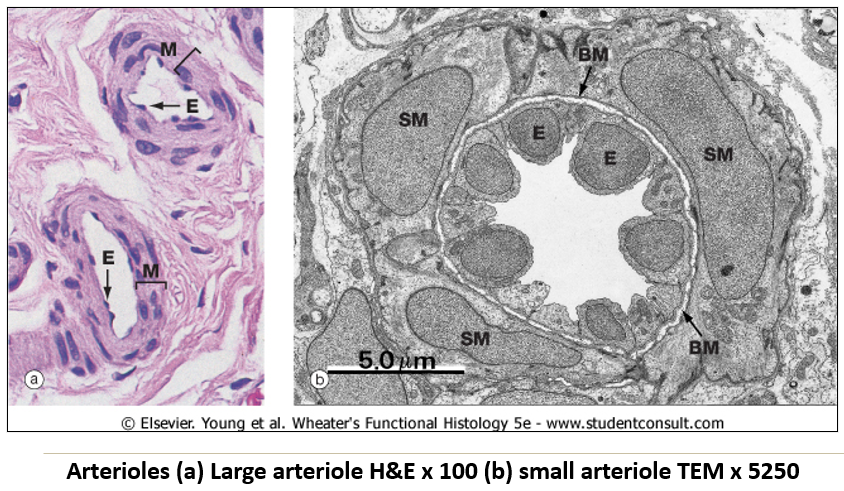
What are arterioles, and why are they important?
Smallest arteries before capillaries, with a continuous smooth muscle layer.
Most important for blood flow and pressure control.
What are metarterioles, and what is their role?
Small pre-capillary vessels with only occasional smooth muscle cells.
Control blood flow into capillary networks.
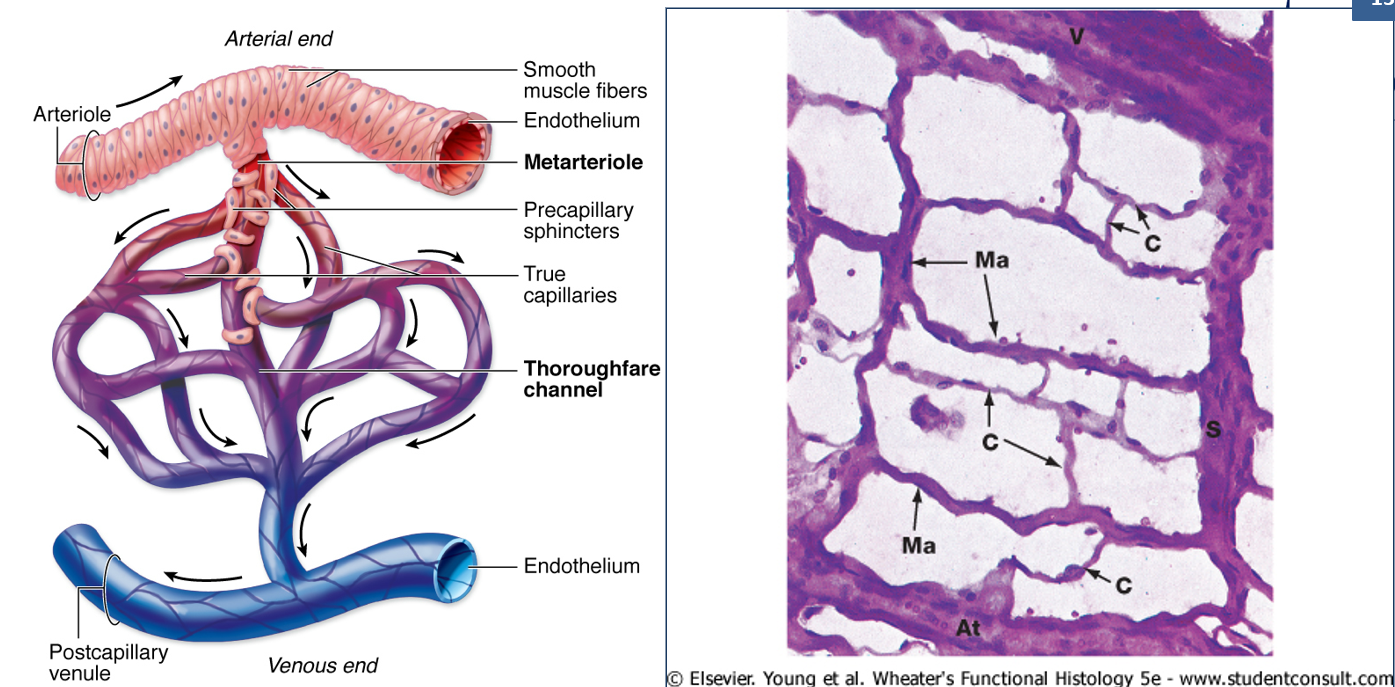
What are capillaries, and why are they important?
Smallest blood vessels, only one cell thick, and the site of gas and nutrient exchange.
What are pericytes, and where are they found?
Contractile cells that wrap around small vessels, supporting capillaries.
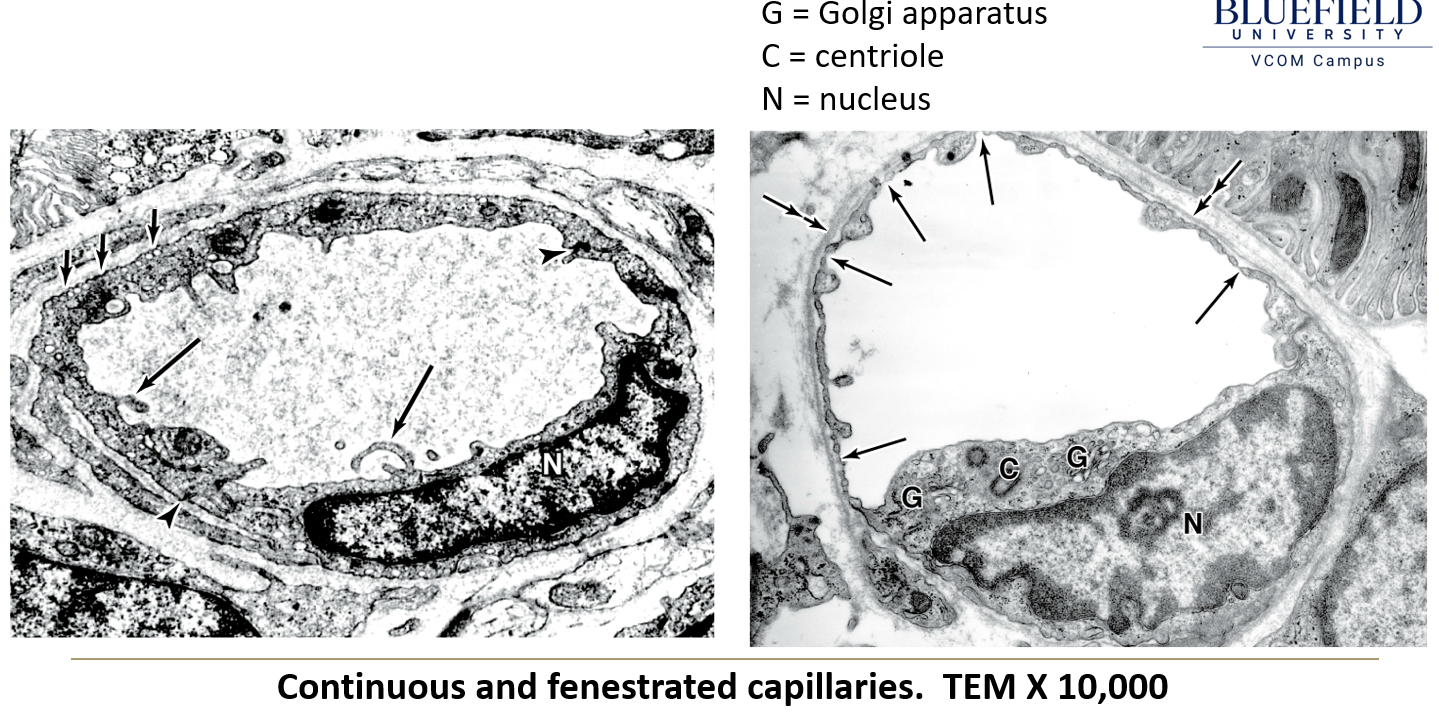
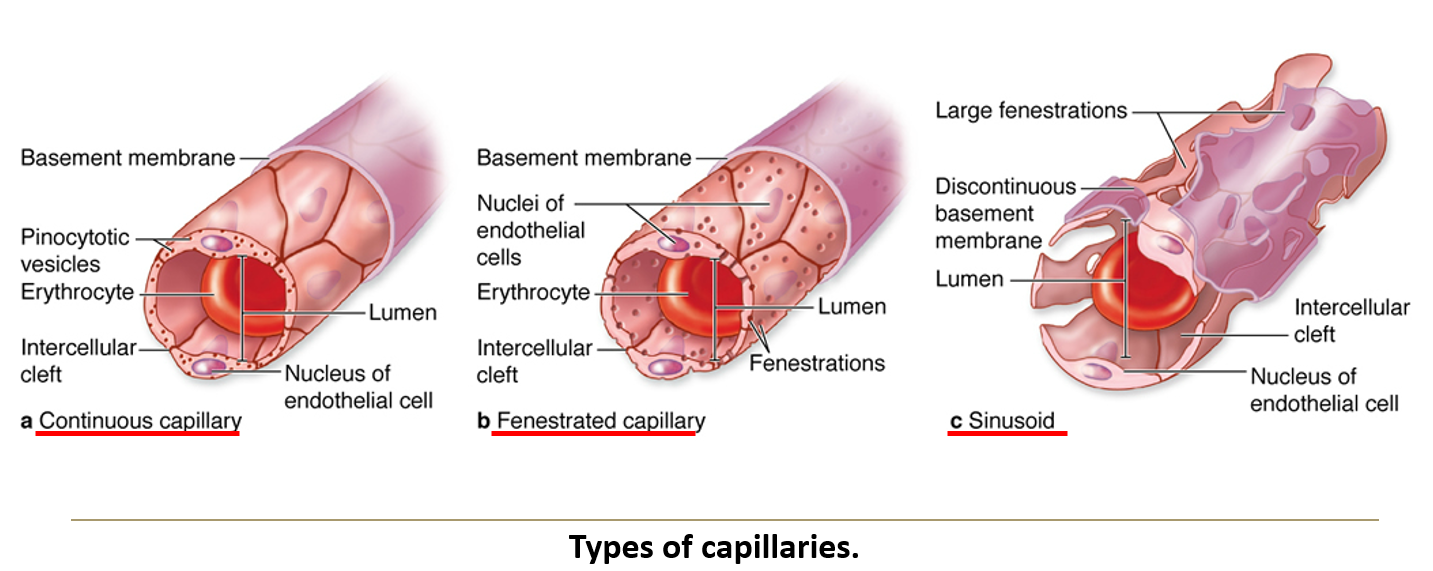
What are the three types of capillaries?
Continuous capillaries – No pores, forming a complete endothelial lining. Most common type.
Fenestrated capillaries – Have small pores, allowing increased permeability. Found in GI tract, endocrine glands, kidneys, and choroid plexus.
Sinusoids – Large, irregular channels with a fenestrated basal lamina. Found in liver, spleen, bone marrow, and some endocrine glands.
What are postcapillary venules, and what are their significance?
The points where capillaries connect to venules
Receive blood from capillaries.
Endothelium lacks junctions, making them the primary site of white blood cell migration.
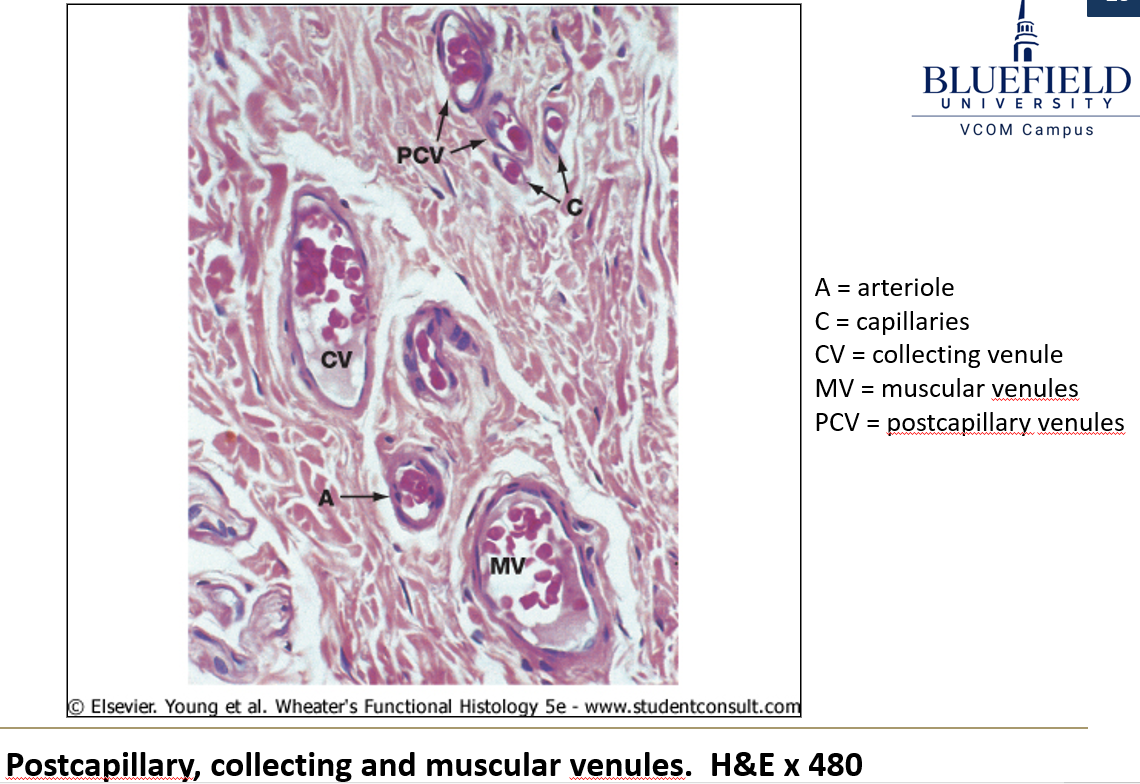
How do collecting venules and muscular venules differ?
Collecting venules – Larger than postcapillary venules, with more pericytes.
Muscular venules – Even larger, with smooth muscle fibers replacing pericytes.
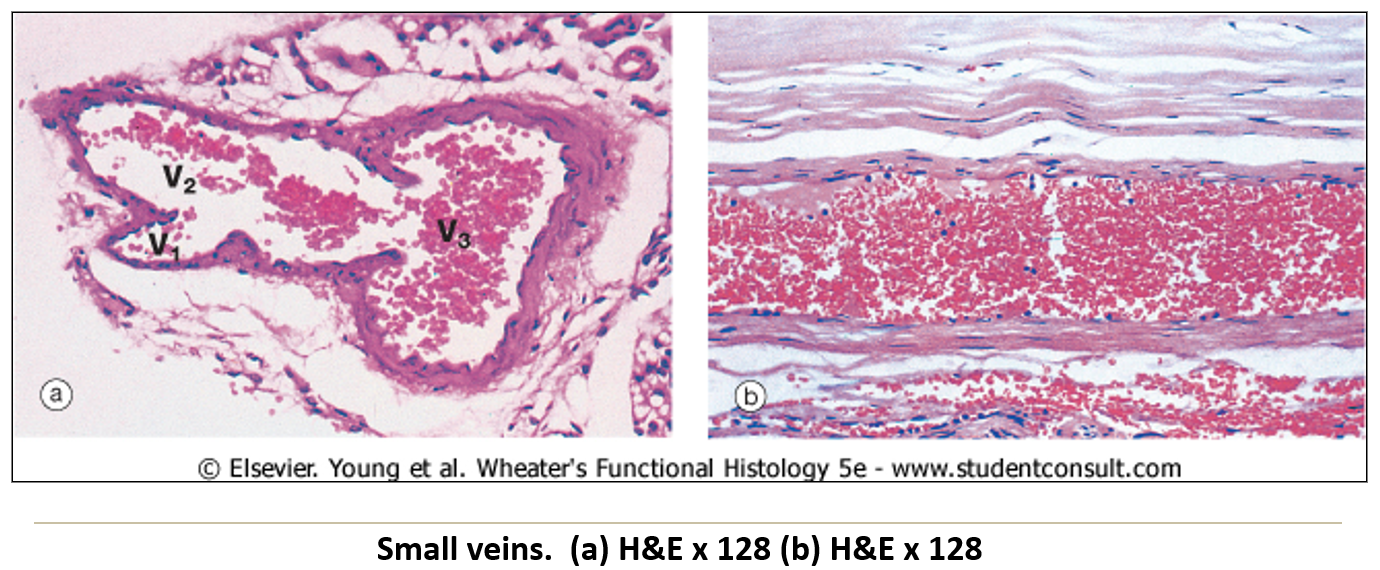
What are the main characteristics of veins?
Large lumens with thin walls.
Less distinct tunica layers than arteries.
Low-pressure system requiring valves in extremities to return blood to the heart.
What type of vessel system is the lymphatic system?
A blind-end system of vessels that runs parallel to capillaries and veins in the cardiovascular system.
What is the primary function of the lymphatic system?
It drains surplus fluid from tissues, immunologically screens it, and returns it to the blood.
What are the two types of lymphatic vessels?
Lymph capillaries and lymphatic veins.
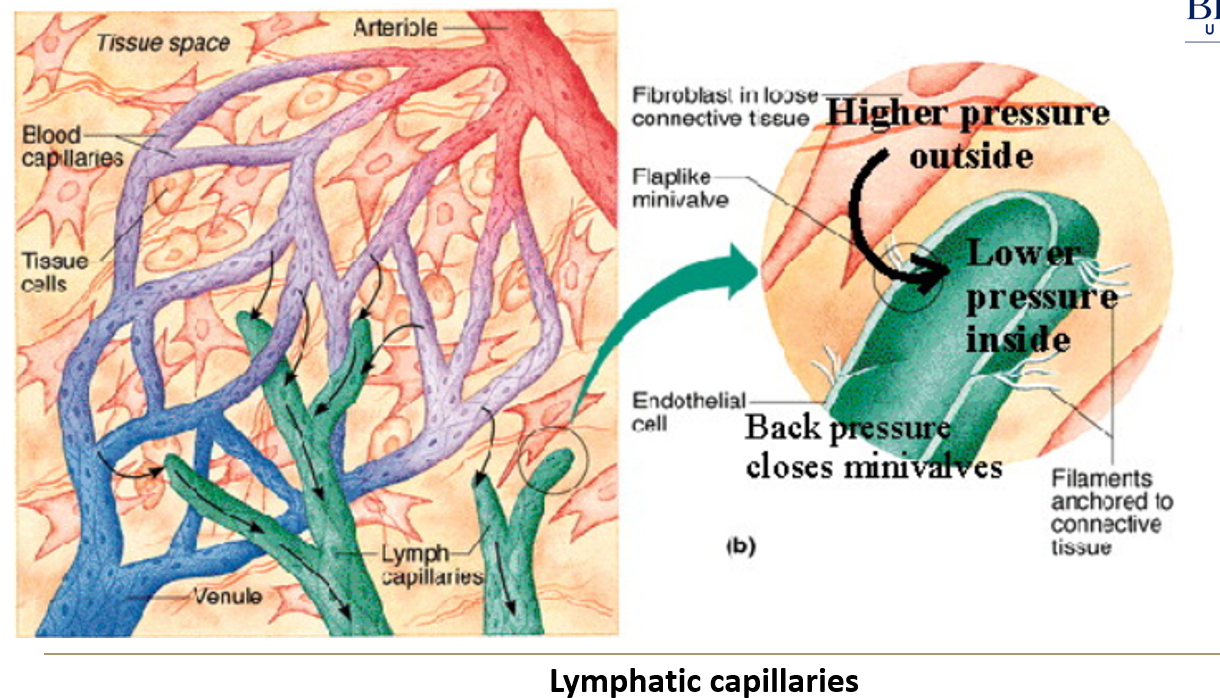
How does lymph move through the vessels if the heart does not pump it?
Incidental compression by skeletal muscles helps push lymph through the vessels.
Valves within the vessels prevent backflow, ensuring one-way movement.
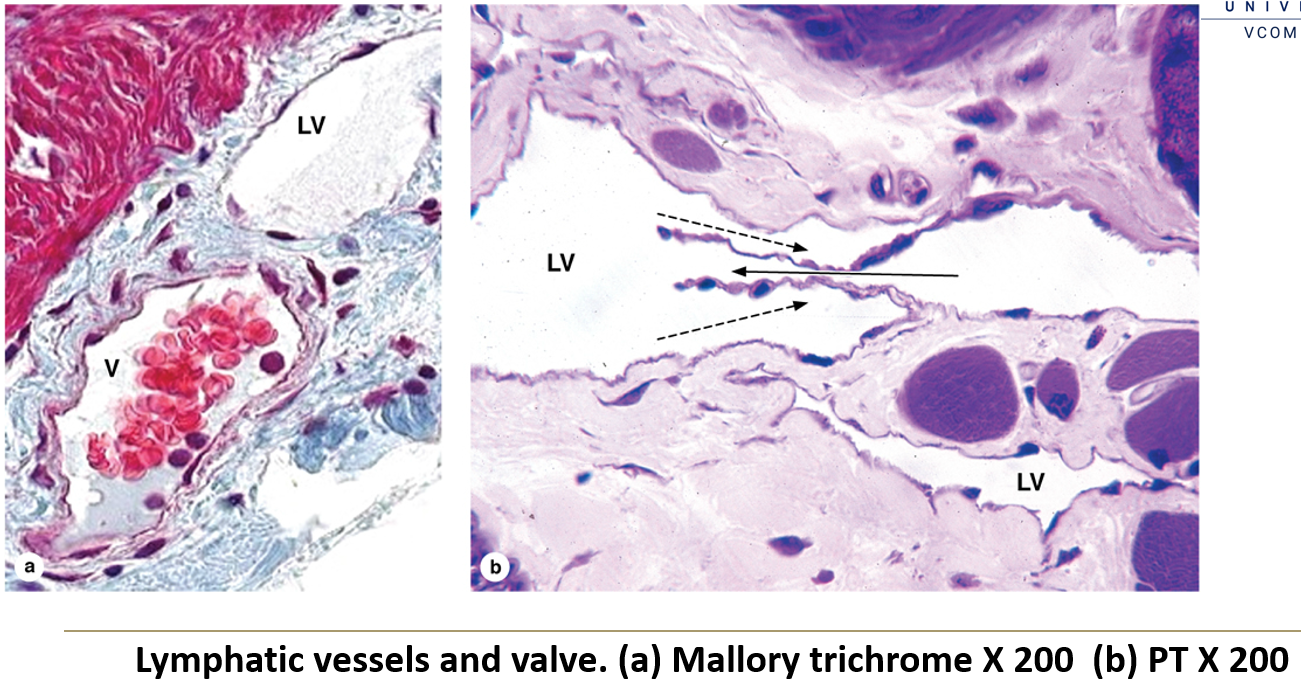
What is the structure of lymphatic vessels?
They have thin walls, allowing fluid exchange but requiring external pressure to move lymph.
Identify structure
Identify: tunica intima, tunica media, tunica adventitia (externa)
Aorta
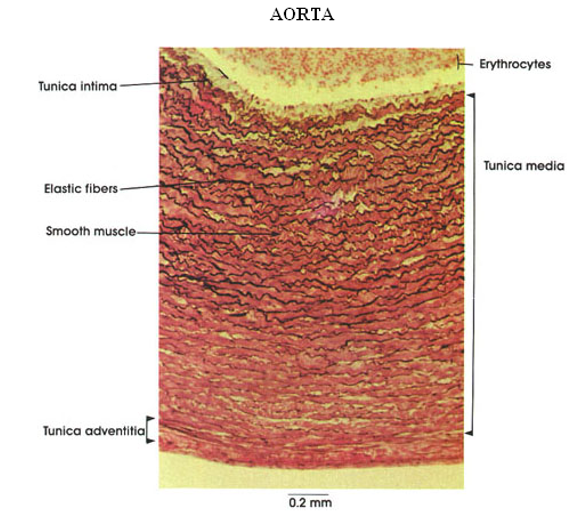
Identify the type of vessel and the three tunicas. What are the white wavy lines in the walls of this vessel?
Aorta
Wavy lines = elastic fibers
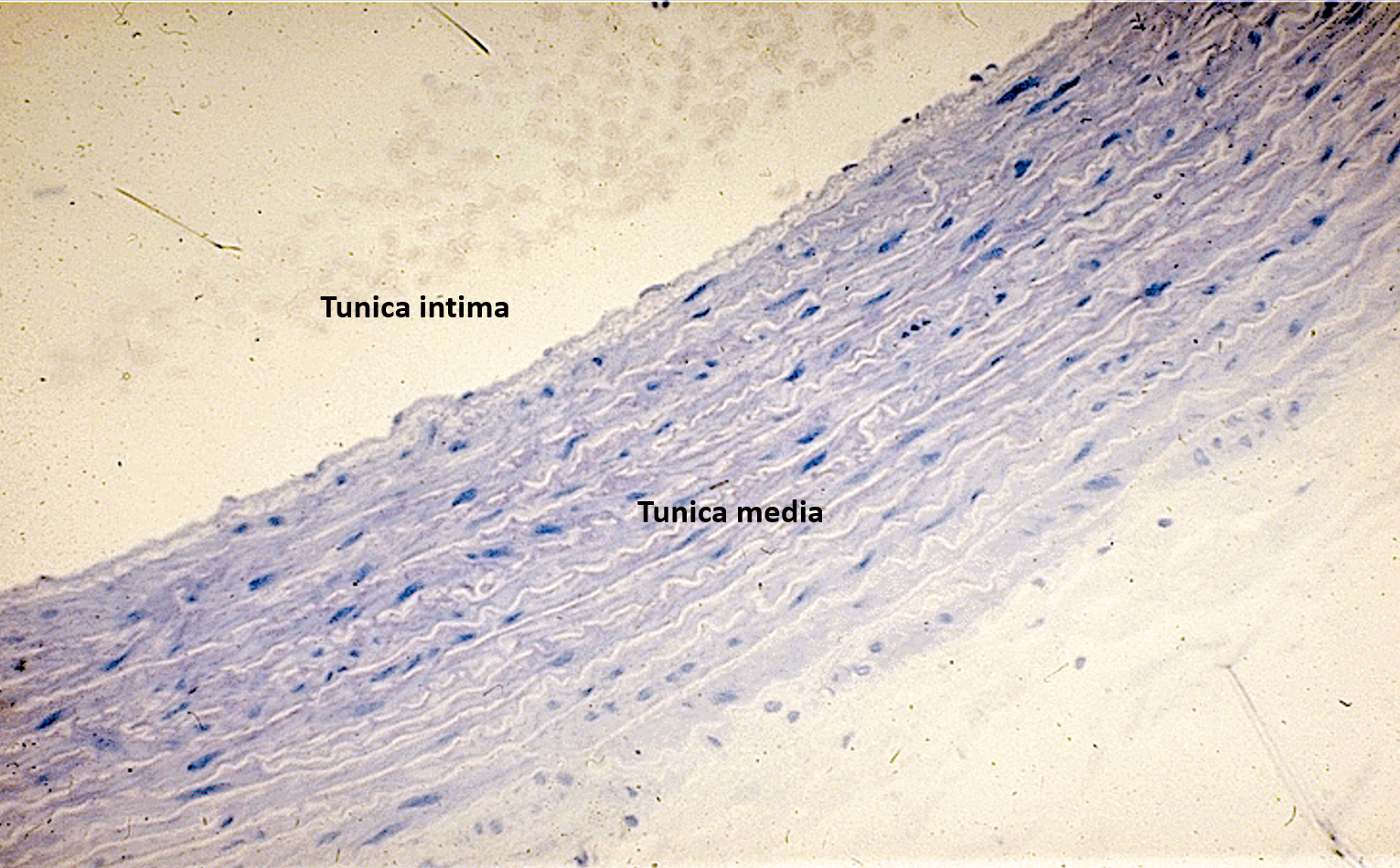
Identify the blood vessel type, the three tunicas and the internal and external elastic membranes.
The tunica intima is the thin innermost layer lining the lumen (central opening).
The tunica media is the thickest layer, made of smooth muscle and elastic fibers.
The tunica externa (adventitia) is the outermost layer, made of connective tissue.
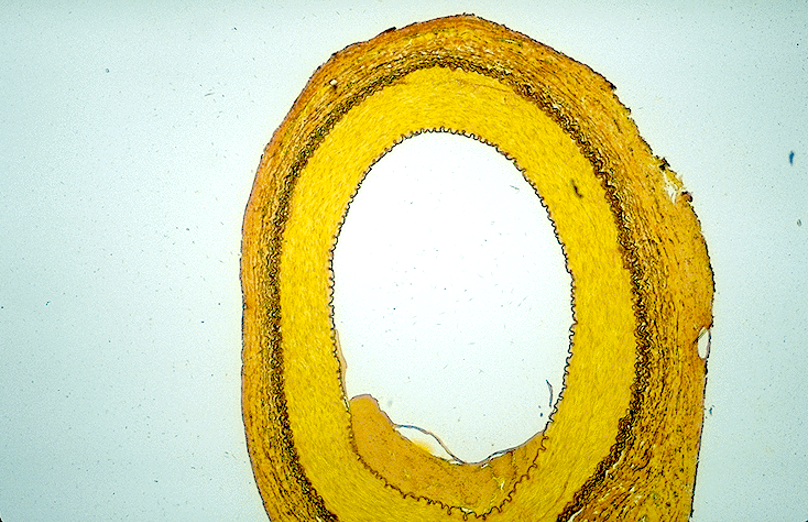
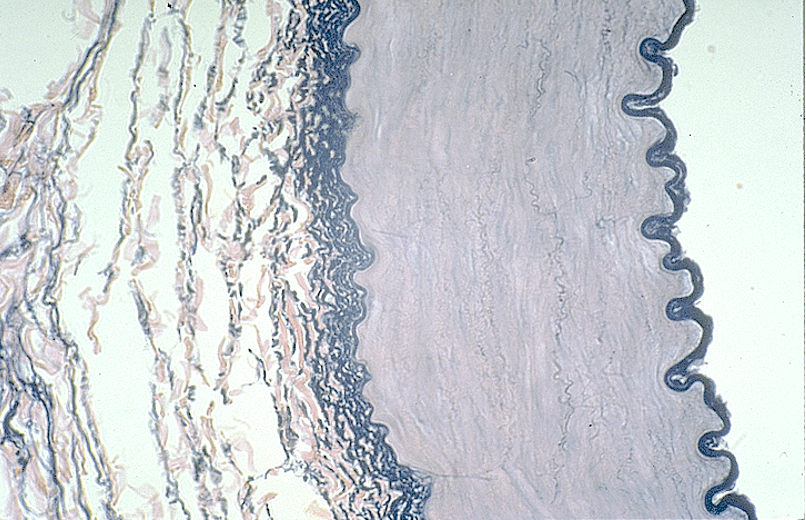

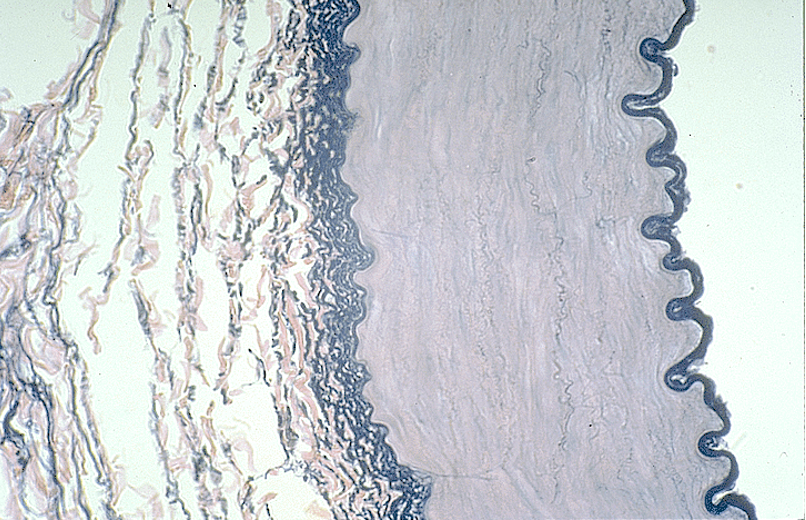
Identify the blood vessel type, the three tunicas and the internal and external elastic membranes.
Aorta
The tunica intima is the thin innermost layer lining the lumen (central opening).
The tunica media is the thickest layer, made of smooth muscle and elastic fibers.
The tunica externa (adventitia) is the outermost layer, made of connective tissue.
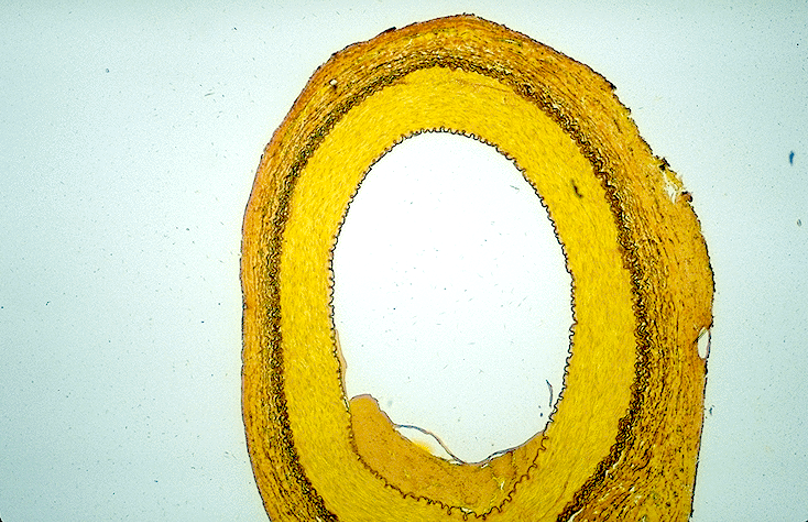

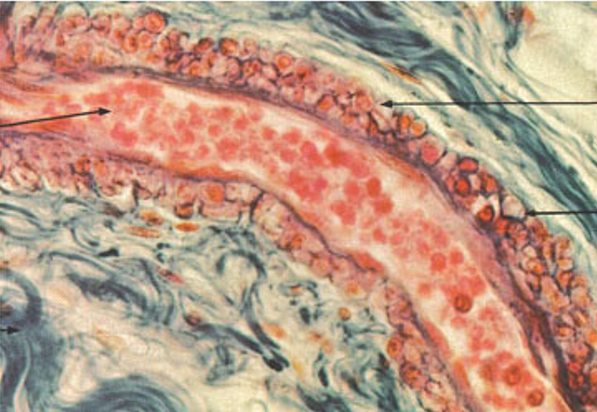
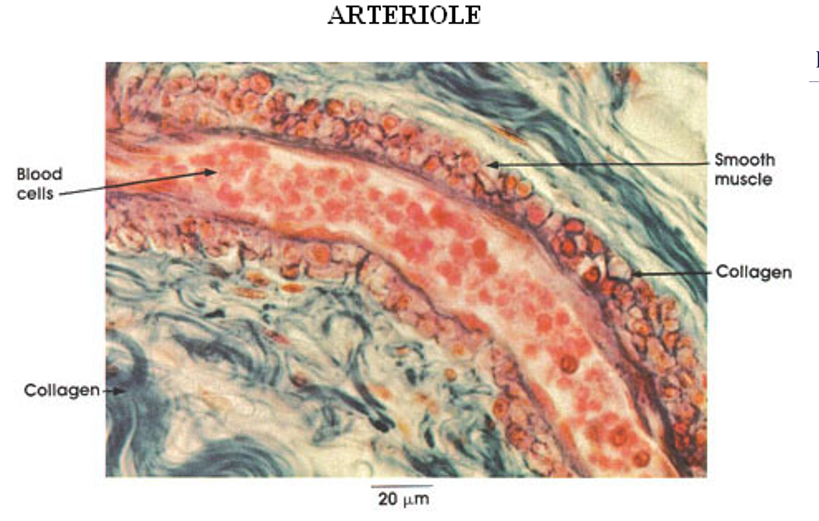
Identify the blood vessel type, the three tunicas and the internal and external elastic membranes.
Arteriole (3 cell layers thick—small)
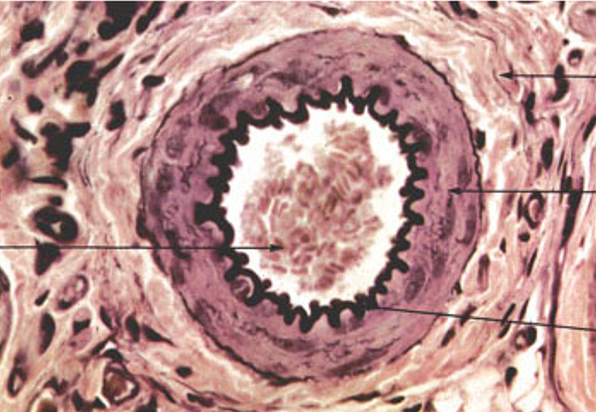
Identify the blood vessel type
Arteriole
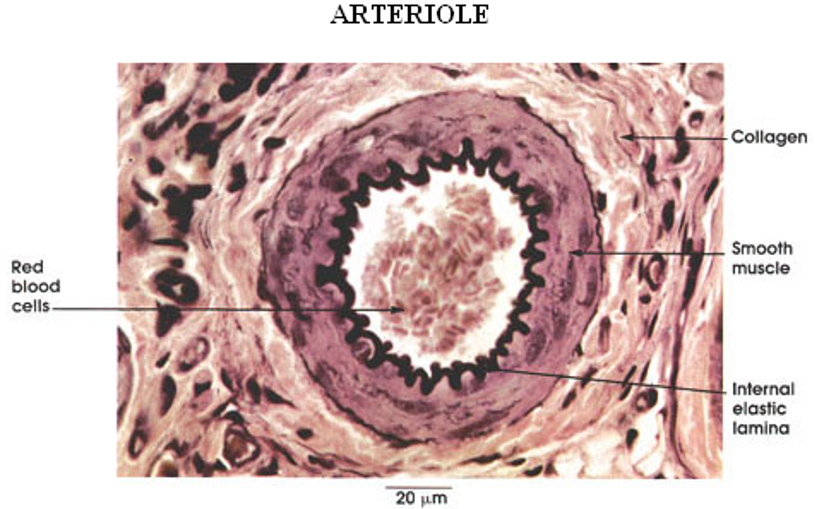
Identify the type of vessel.
Arteriole (1 cell layer thick)
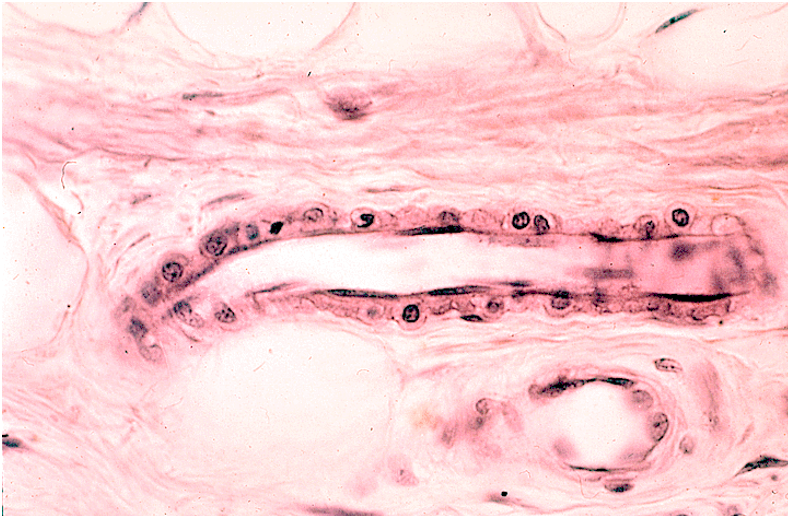
Identify the type of vessel.
Venule because:
Larger lumen than a capillary but still relatively small.
Thin wall with a single layer of endothelial cells and some surrounding connective tissue.
No thick tunica media (unlike arteries).
More nuclei than typically seen in a capillary, indicating a slightly larger vessel.
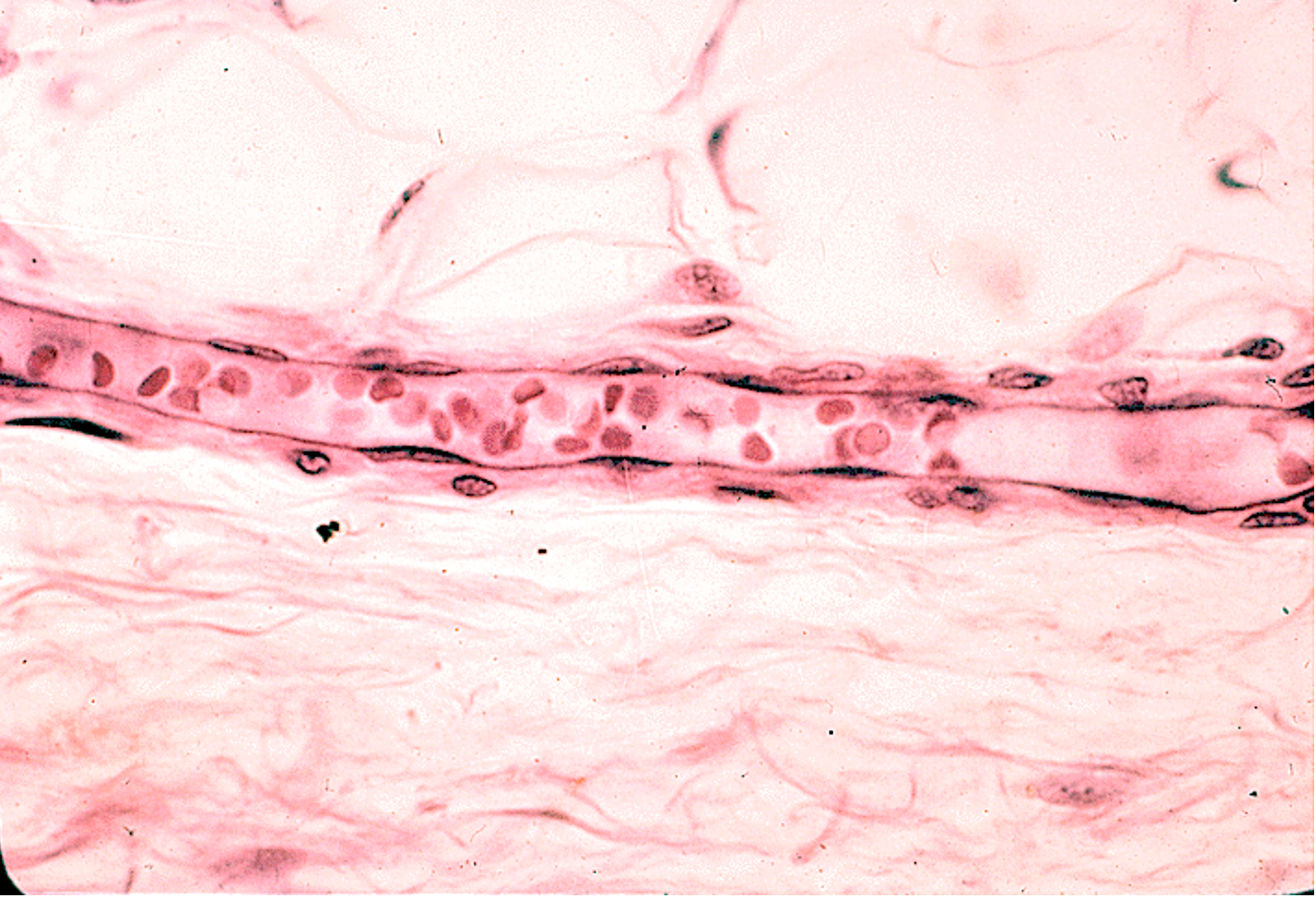
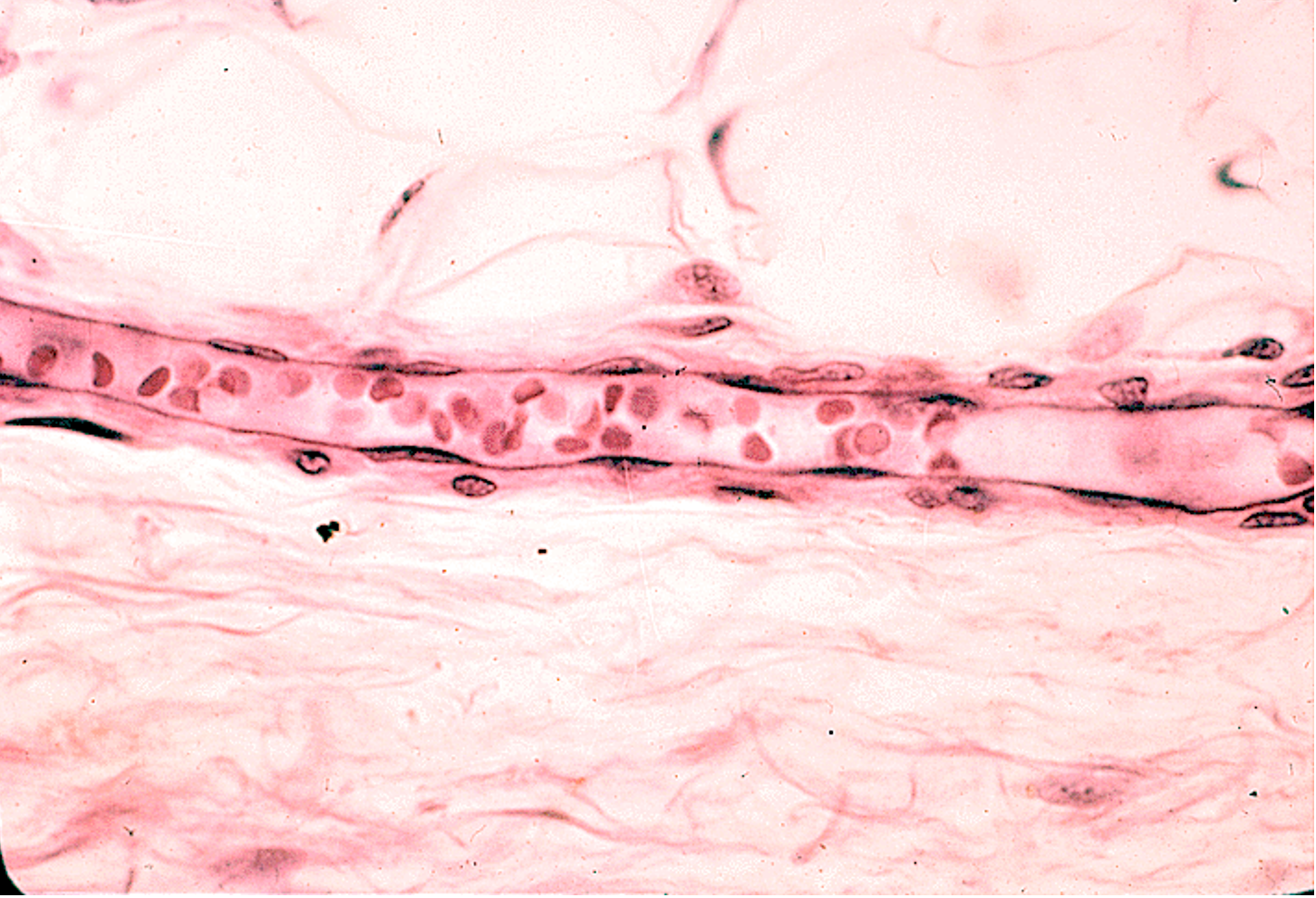
Identify the type of vessel running horizontally on this slide.
Capillary
No tunica media meaning no smooth muscle layer, unlike arteries and veins
Has pericytes which wrap around the endothelial cells
Thin endothelial wall allowing efficient exchange of gases, nutrients, and waste
Small lumen just wide enough for red blood cells to pass through single file
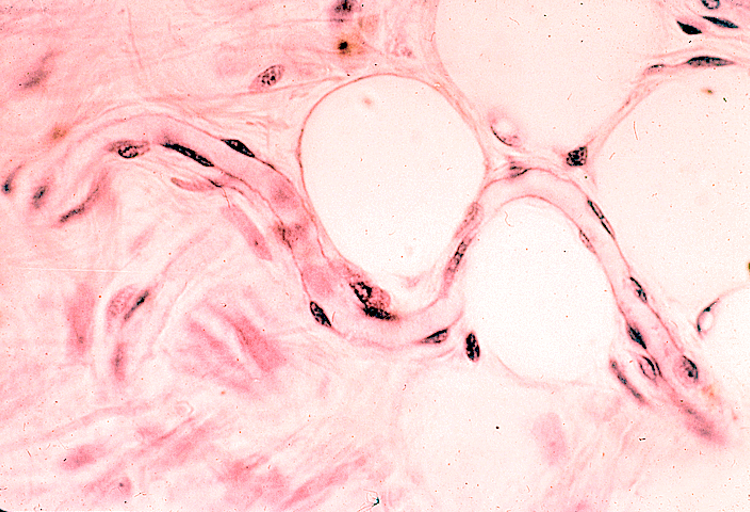
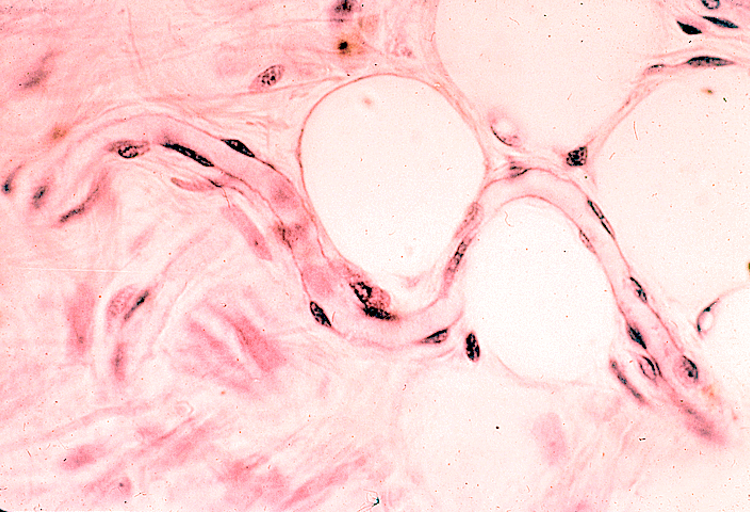
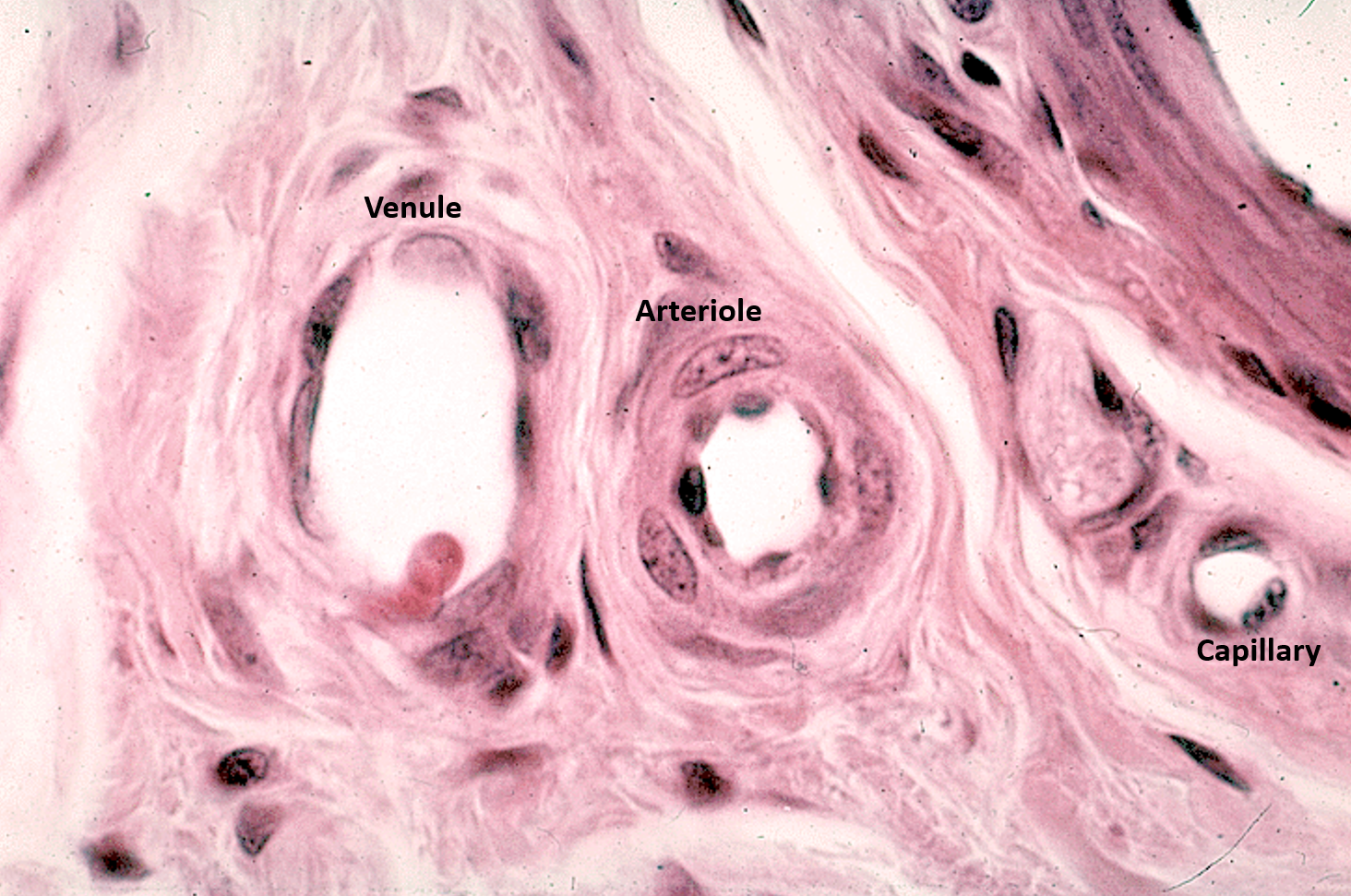
Identify the arteriole, venule and capillary.
Arteriole has one layer of smooth muscle surrounding it, giving it a small, circular lumen
Venules typically run adjacent to the arteriole, have a larger lumen, and lack a thick muscle layer
Capillary is the smallest vessel; has endothelial nuclei and thin walls without smooth muscle
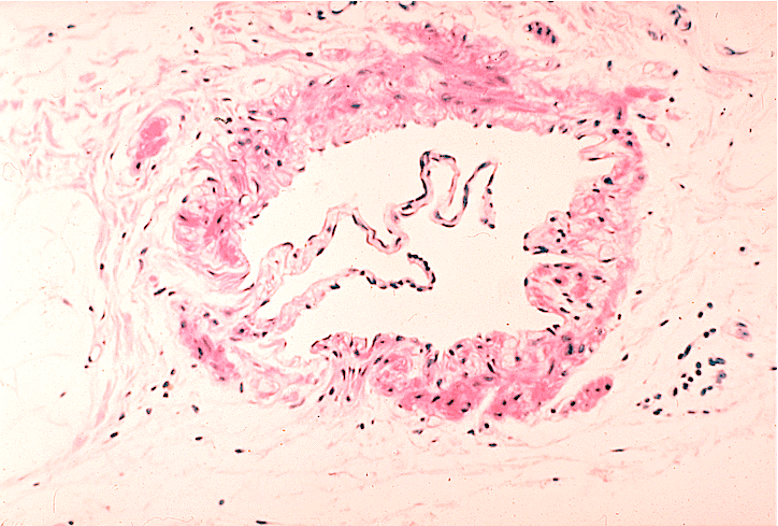
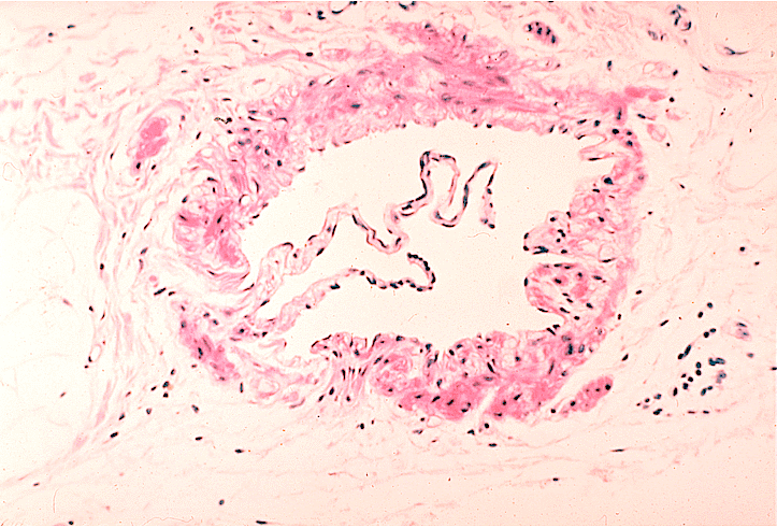
Identify the wavy structure in the lumen of this vessel.
Venule; Can’t be lymphatics as they wouldn’t have the red smooth muscle fibers surrounding.
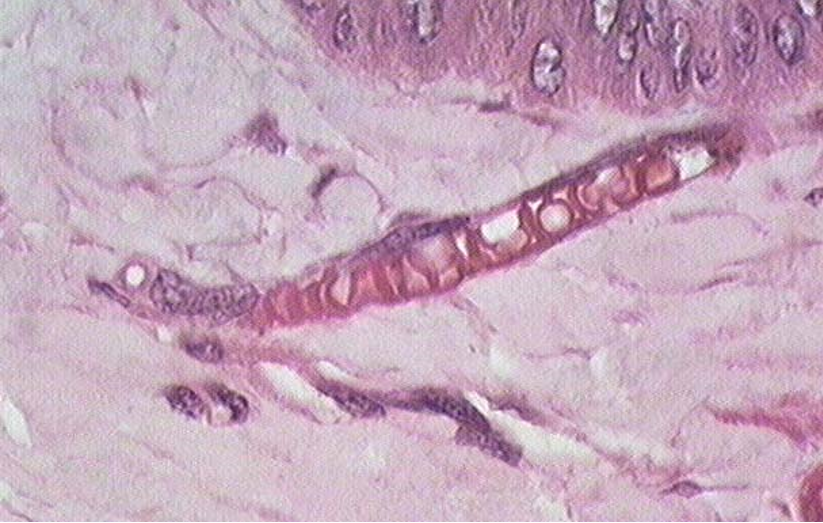
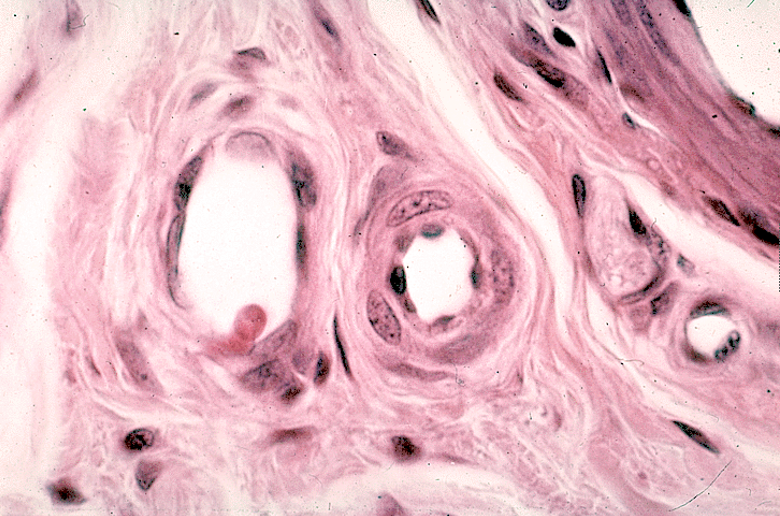
Identify the structure
capillary
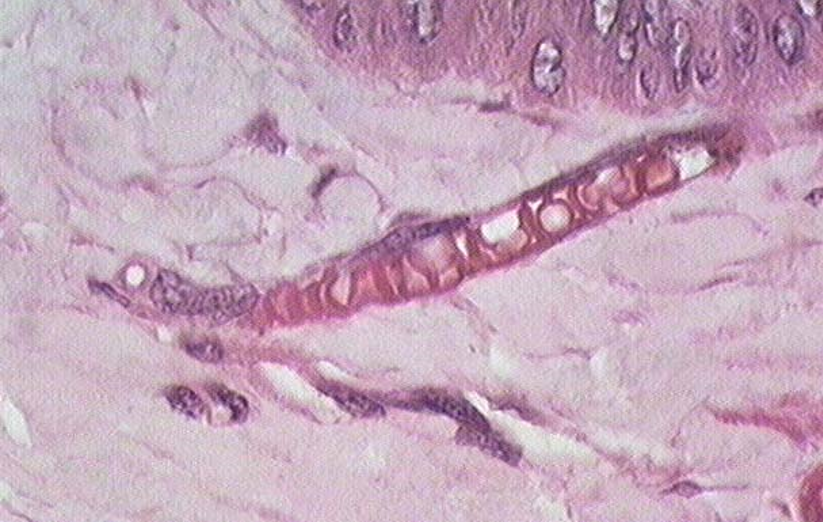
Identify the structure
Capillary
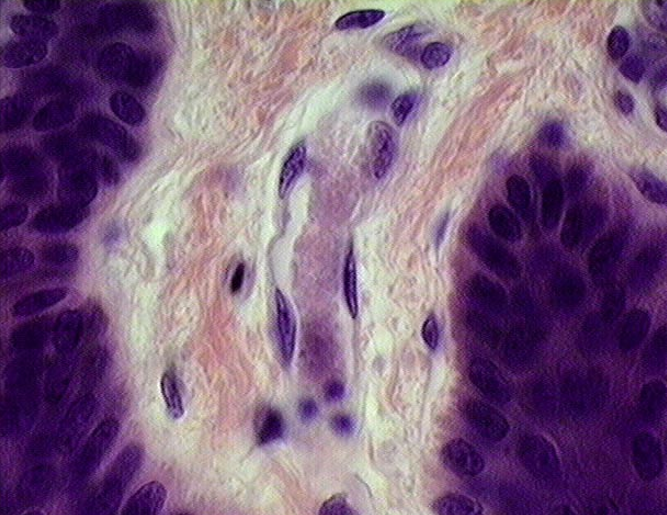
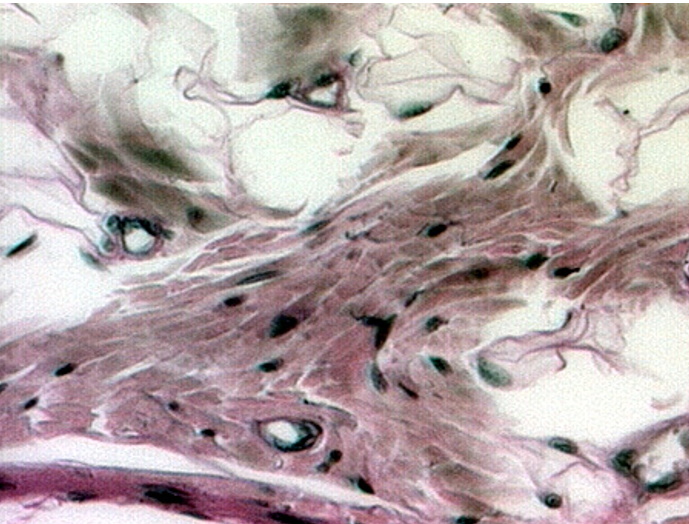
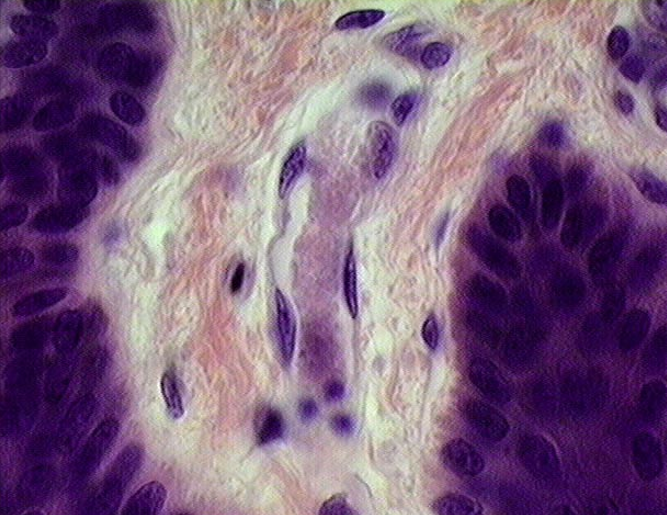
Identify four capillaries in this slide.
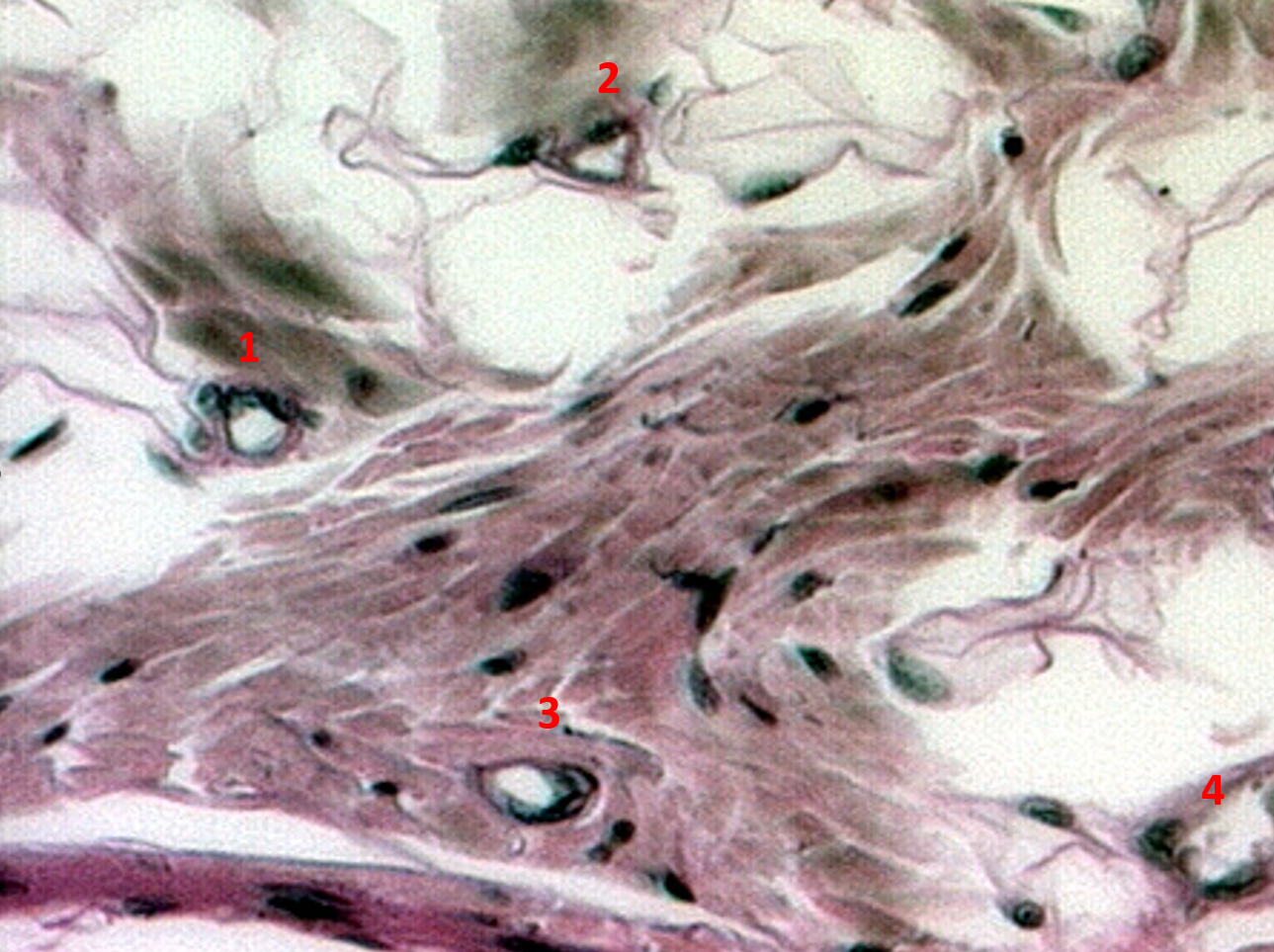
Identify the structure
Capillaries
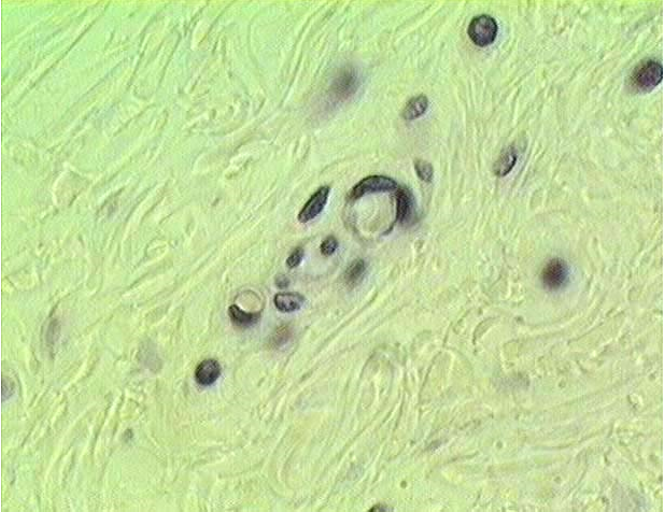
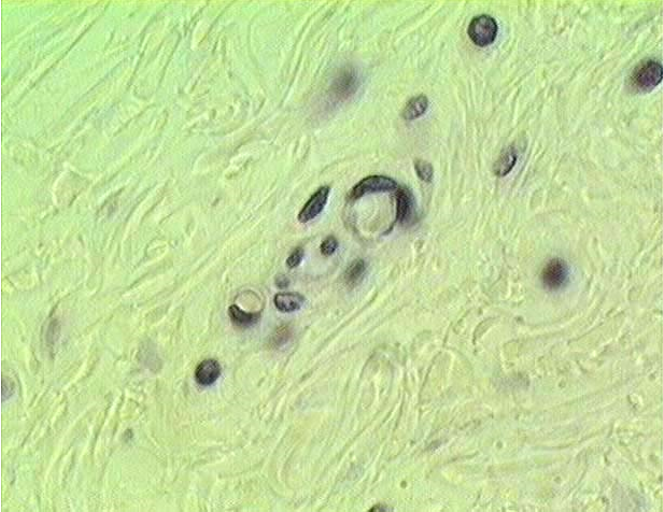
Identify the structure
4 capillaries
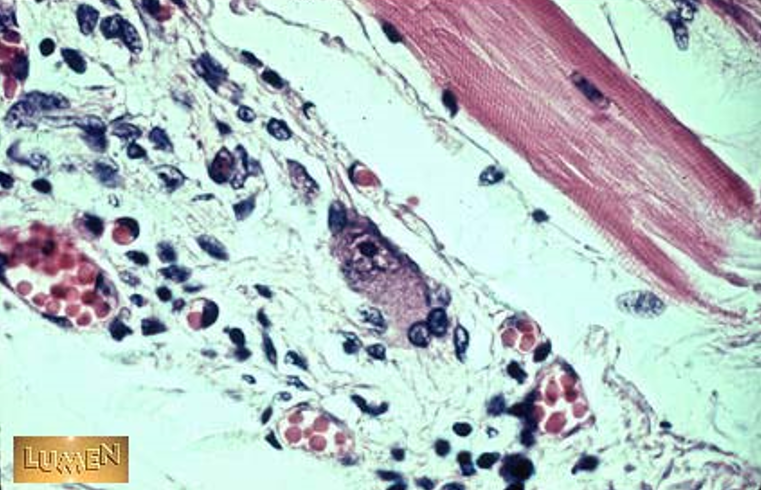
Identify the structure
Capillary
No tunica media observed must be capillary
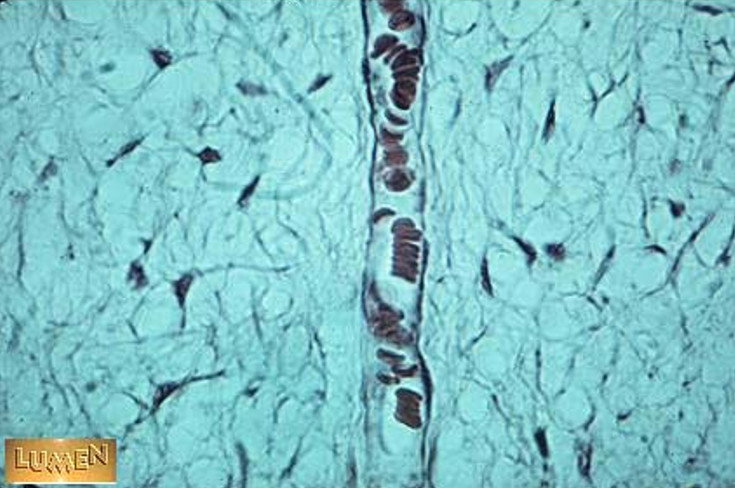
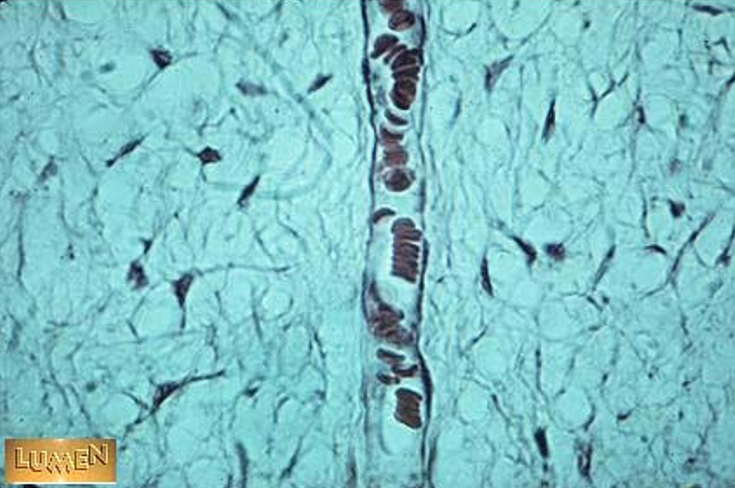
Identify the structure
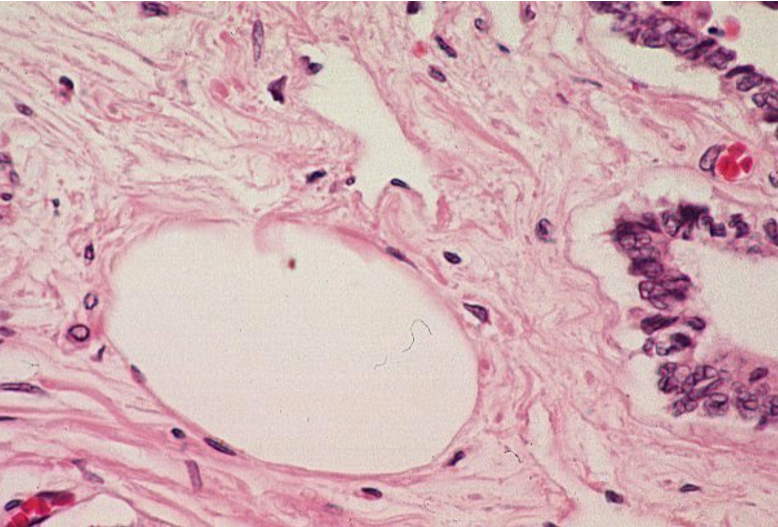
Lymphatic vessel. The lymphatic vessel in this slide is dilated, making it much easier to recognize.
endothelial cell nuclei surrounding lumen
lumen is too large to be a capillary
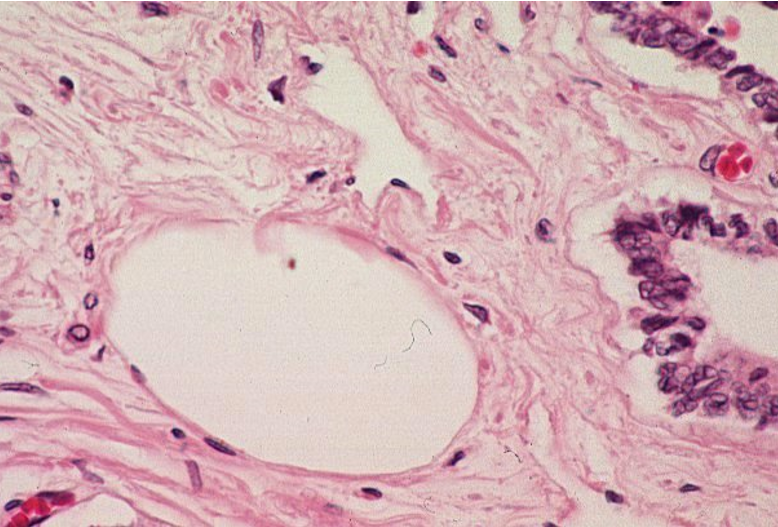
Identify the structure
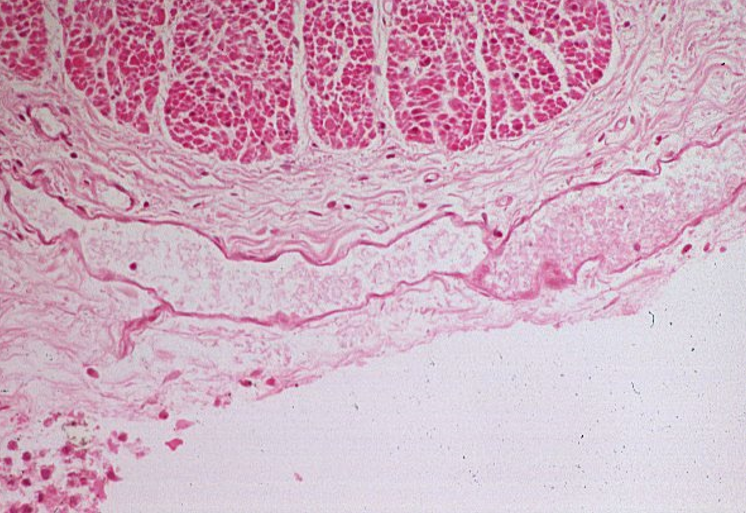
Lymphatic vessel.
Thin, irregular walls with a lack of well-defined tunics, unlike arteries and veins, which have structured layers.
No red blood cells in the lumen, as lymphatic vessels carry lymph, not blood.The lumen appears clear
Valves may be visible as thin folds of endothelium, preventing backflow of lymph.
Surrounding loose connective tissue, typical of lymphatic vessels, which often run parallel to veins.
Identify the structure
Collapse lymphatic vessel
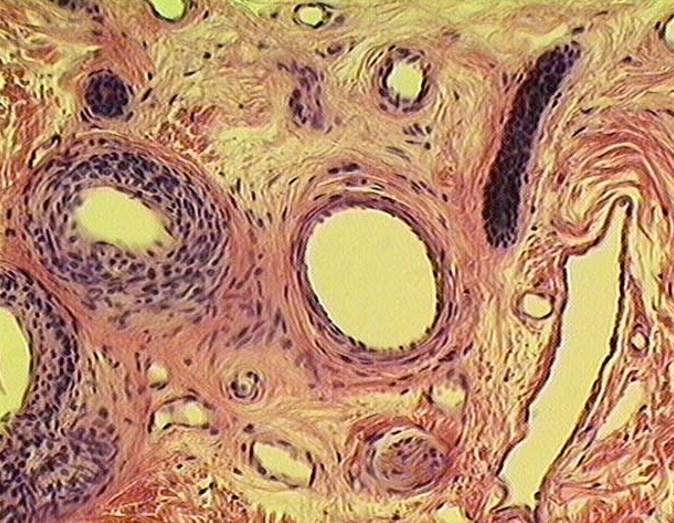
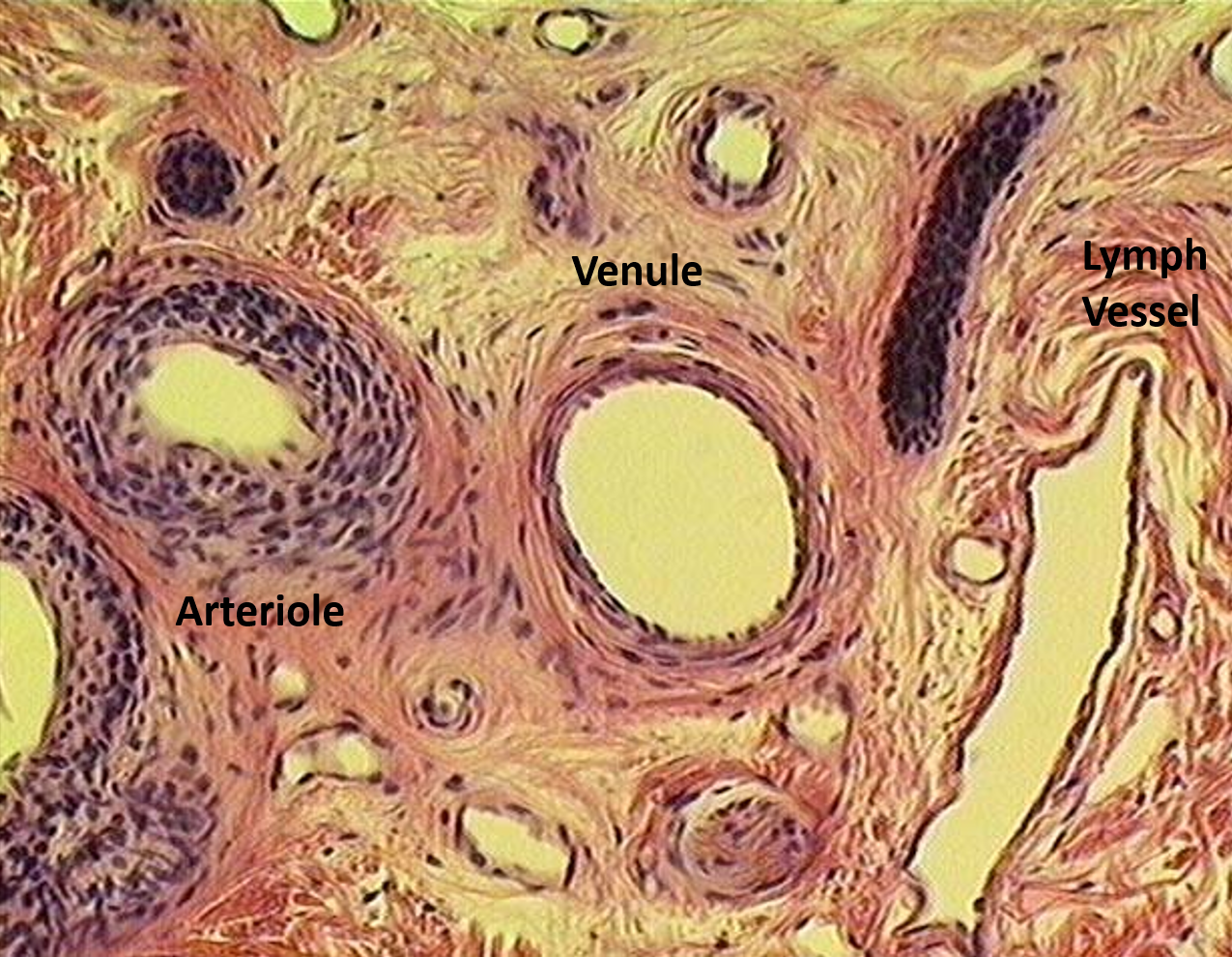
Identify the various vessels seen in the section.
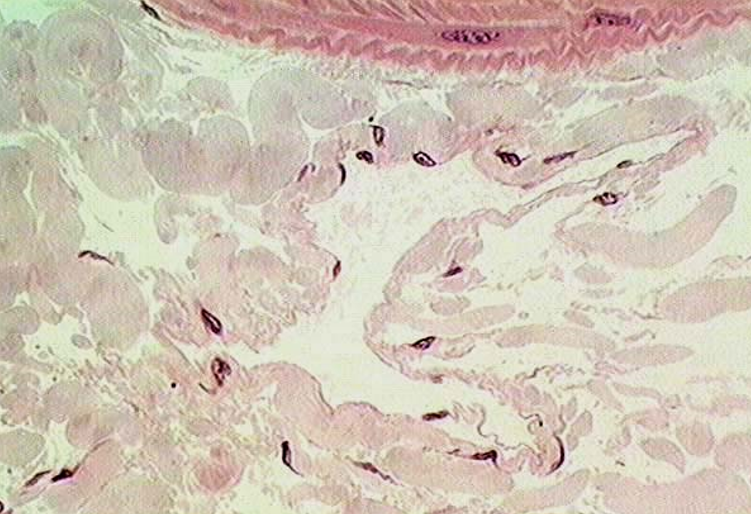
Identify the structure
Lymphatic vessel
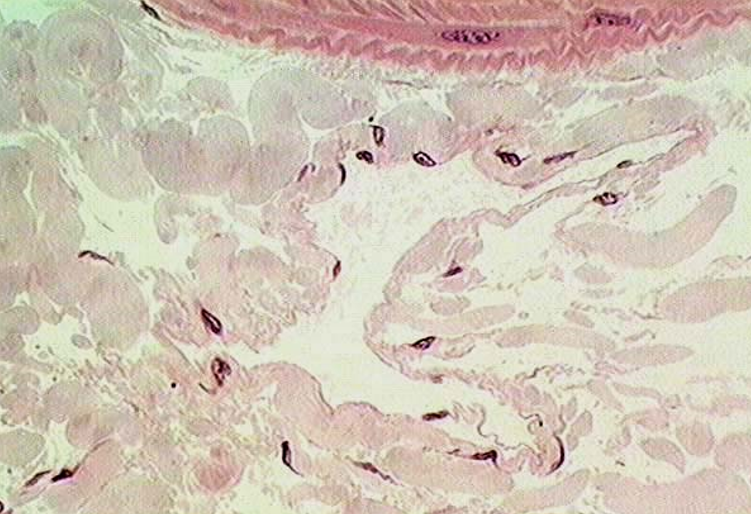
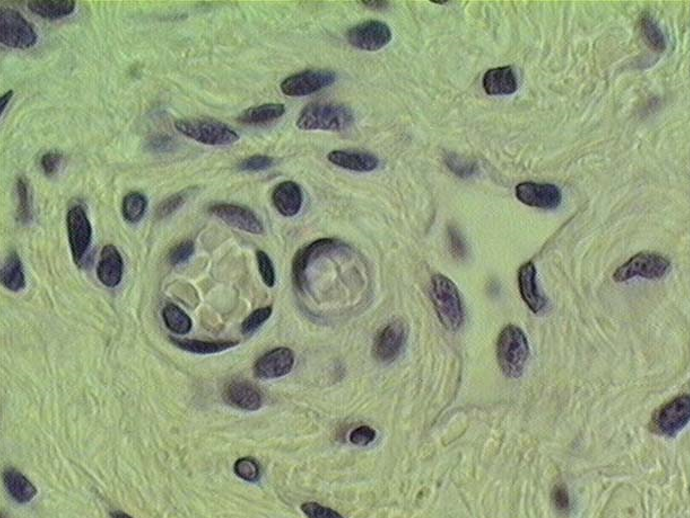
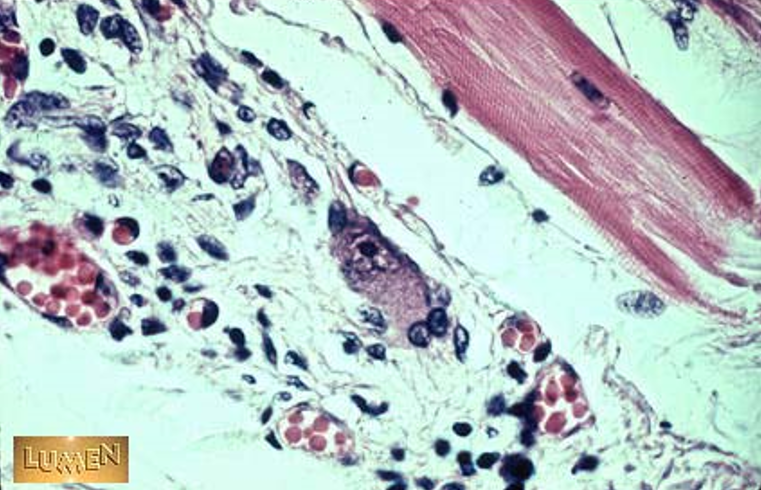
Identify the arteriole, capillary and lymphatic vessel in this slide.