osmoregulation
1/17
Earn XP
Description and Tags
bio aqa gcse
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
what is osmoregulation?
regulation of the blood water concentration
why is osmoregulation important?
so cells don’t gain/lose too much water by osmosis and burst/shrivel up
what 4 processes affect blood water/blood ion concentration?
drinking and eating, sweating, urinating and exhaling
what is the effect of drinking and eating?
gains water
what is the effect of sweating?
water, ion (e.g. salt) and urea loss
what is the effect of urinating?
lose water, ions and urea
what is the effect of exhaling?
lose water vapour
what is urea?
byproduct (waste) of deamination in the liver
why is urea excreted?
it is toxic (less than ammonia but still toxic)
what is deamination?
when amino acids are broken down in the liver
what is excretion?
removal of waste products of metabolism
what is the role of the kidneys?
filtering the blood
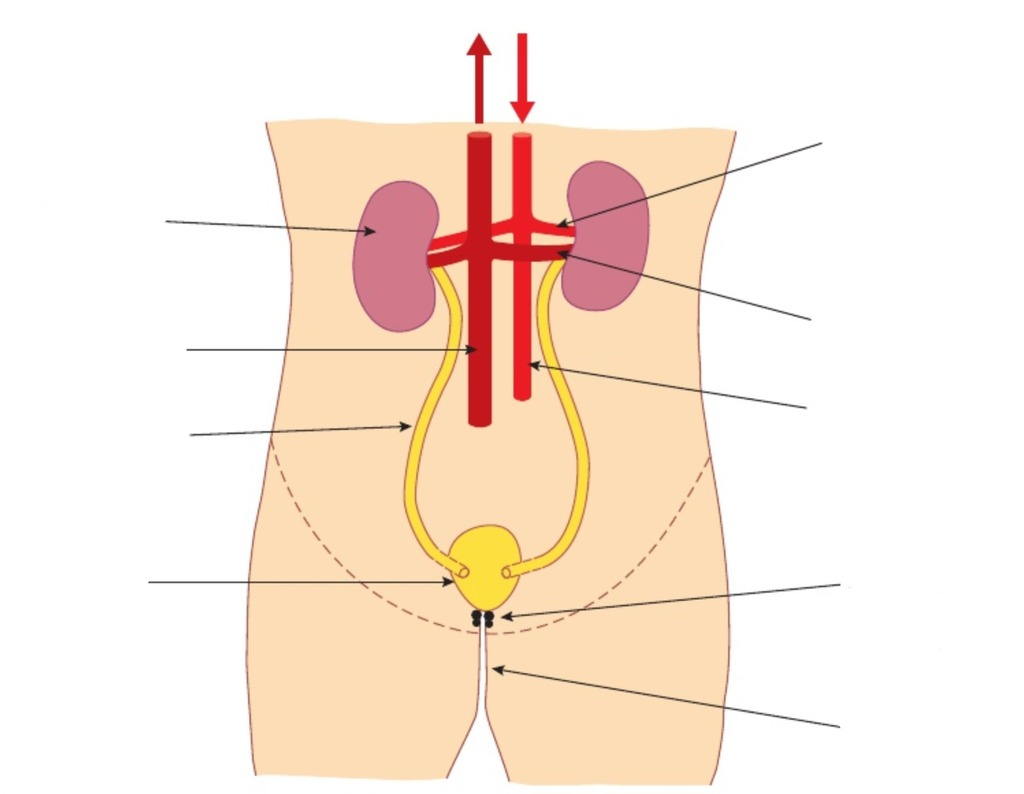
label the diagram (using letter markers a-k, top right clockwise to top left)
a) blood from heart, b) renal artery, c) renal vein, d) aorta, e) sphincter muscles, f) urethra, g) bladder, h) ureter, i) vena cava, j) right kidney, k) blood to heart
what is a kidney tubule?
a long, curvy tube found in the kidney that is the functional unit; there are millions in each kidney
how does the kidney filter the blood?
the blood is subjected to high pressure and small molecules are forced out through the walls of the capillary and into the filtrate in the kidney tubule (filtration), only cells and large molcules (e.g. protein molecules) stay in the blood, molecules needed by the body are selectively reabsorbed back into the blood, rest is excreted in the urine
what happens when the blood water concentration is too high?
pituitary gland releases less ADH, kidney tubules reabsorb less water, more urine of a lower concentration produced
what happens when the blood water concentration is too low?
pituitary gland releases more ADH, kidney tubules reabsorb more water, less water of a higher concentration produced
how does kidney dialysis work?
blood temporarily removed from patient’s body, filtered through dialysis machine, blood passes over dialysis fluid which has no urea, urea and waste products diffuse from high concentration in blood to low concentration in dialysis fluid, blood returned to patient’s body