5.2 Eating Disorders
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
29 Terms
List factors that can influence our food choices.
Memories
Stress
Culture
Mass Media
How does Mass Media influence food choices.
Media is comprised of television, billboards, magazines and the Internet. Media also advertises pictures of "acceptable" or "attractive" body types (often thin and/or toned), and yet these body types fail to align with the types of foods being advertised.
List the three types of eating patters.
Healthy Eating
Disordered Eating
Eating Disorder
Define the Healthy Eating pattern
Define the Disordered Eating pattern.
a short-term change in normal eating patterns related to a stressful event, illness, or desire to change physical appearance. Symptoms:
excessive food restriction, binging, purging, yo-yo dieting etc.
What are the three primary types of eating disorders?
anorexia nervosa
bulimia nervosa
binge-eating disorder
Define Nervosa?
refers to an attitude of disgust with one’s body. Typically begins in the teenage or early adult years
Define Anorexia Nervosa disorder.
Anorexia → “Denial of Appetite”
Extreme weight loss through starvation, a fear of becoming obese, and a distorted body image are all characteristics of anorexia.
Symptoms:
Nutrient Deficiences
Excessive Food Restriction
Distored body image.
hormonal changes, lower body temperature, a slow heart rate, decreased immune system,
What is the clinical diagnoises of anorexia nervosa
Body weight less than 85% of the normal weight relative to the person’s age, height, and gender and a BMI of less than or equal to 17 are clinical guidelines for a diagnosis.
What is the treatment spectrum for anorexia nervosa?
outpatient therapy involving the patient and a team of medical professionals, including a physician, dietitian, and a psychologist.
Achieve healthy weight, BMI >= 20
Cognitive behavior therapy, Family therapy and self-help groups
Involvement of other family members is also important to the outcome
Define Bulimia Nervosa disorder.
Bulimia =“Ox hunger”'
An eating disorder in which large quantities of food are consumed over a short time period, refered to as a binge. A great desire to get rid of the excess calories, usually through purging (vomiting) or the use of laxatives.
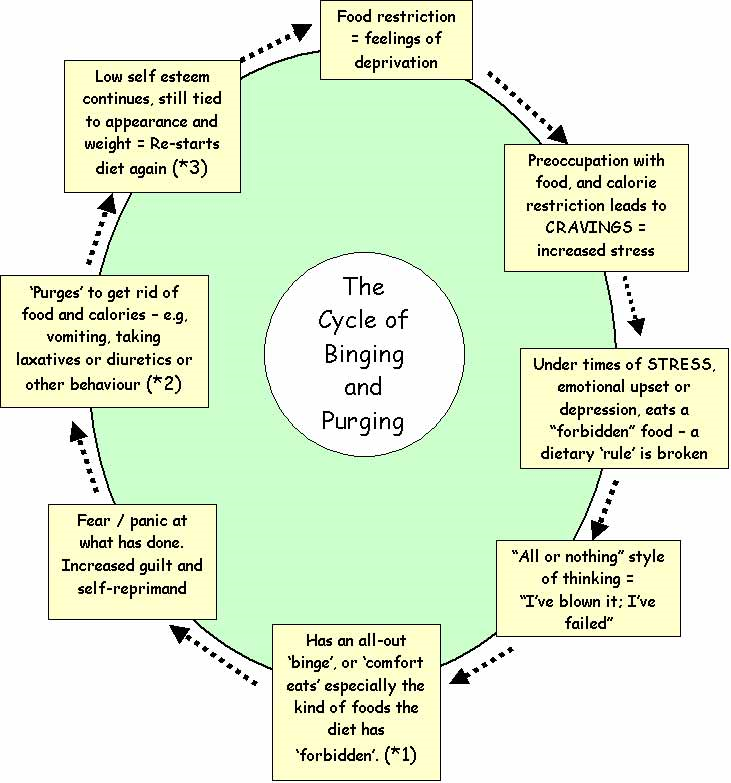
What is the clinical diagnoses for Bulimia Nervosa
Difficult to detect because binges and purges happen secretly.
Diagnostic criteria include:
Binge–purge cycle at least twice a week for 3 months
Loss of control during binges
Alternating between overeating and food restriction
How do bulimics differ from anorexics in terms of personality?
ulimics tend to be impulsive rasied w/ lax parenting;
anorexics tend to be controlled and perfectionistic.
What cycle do bulimics often get trapped in?
Binge → Shame & Guilt → Purge → Restrict → Repeat
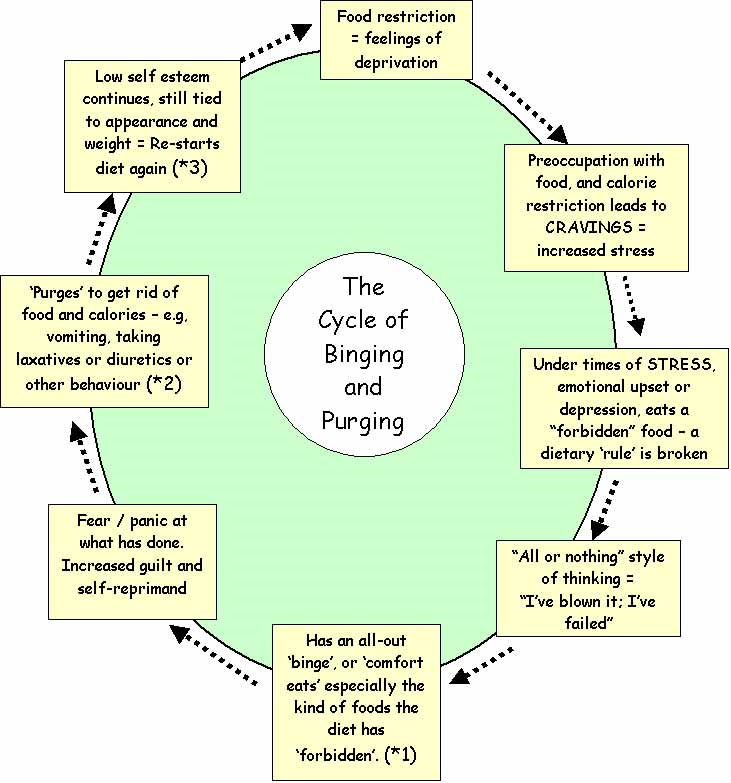
What are some symptoms of bulimia nervosa?
Demineralization of the teeth related to erosion from the stomach acids
burns on the knuckles related to the vomiting
swollen salivary glands
What is the treatment plan for bulimia nervosa?
The first goal is to address the binging and decrease the amount of food consumed in a sitting.
Allow healing of the esophagus and decrease damage to the teeth
Cognitive behavior theraphy to improve self esteem & learn to cope with stressful situations.
List triggers that start binge eating.
Stress
boredom
loneliness
depression.
List the Eating Disorders Not Otherwise Specified.
Binge-eating disorder
Night eating syndrome
Female athlete traid
Relative energy deficiency in sport (RED-S)
Define Binge Eating Disorder. What is the clinical diagnosis?
Characterized by binge eating episodes that are not accompanied by purging. Food is used as a coping mechanism.
Symptoms:
Lack of control
Rapid eating.
Obesity
Diagnosis: Compulsive overeating at least 2 times per week for >6 months.
How is binge-eating disorder treated?
Using behavior modification techniques, an individual with a binge-eating disorder must relearn hunger cues and normalized eating patterns.
Self-help groups and medication may also be part of the treatment plan.
Define intuitive eating.
Involves learning to listen to the internal cues on hunger and satiety, should be honored by adults and other care givers of young children and teens. AKA, eating and stopping when you feel full, regardless of how much food is left.
Define Night Eating Syndrome. What is the clinical diagnosis?
at least one-third of a person’s calories are consumed after the evening meal. The individual awakens at least once during the night and needs to eat prior to falling back to sleep. Symptoms:
Lack of hunger in the morning
Out-Of-Sync Circadian rhythm
What are some treatment options for Night Eating Syndrome?
A person suffering from night eating syndrome frequently suffers from depression, and the use of antidepressants has been found to beneficial in treating the disorder.
How does the Female Athlete Triad relate to eating disorders?
Involves disordered eating
lack of menstrual periods
osteoporosis related to inadequate calcium and vitamin D intake
The triad often affects females who are participating in appearance-based or endurance sports, such as gymnastics
What are treatment options for the Female Athlete Triad ED?
gradually increase caloric intake to achieve a normal weight and reduce the preoccupation with food.
training intensity should be decreased, and a normal menstrual cycle should be established
Define the Relative energy deficiency in sport (RED-S) diagnosis.
inclusive diagnosis that recognizes that male athletes may also experience ill effects from inadequate energy intake. The female athlete triad is a subset of RED-S.
What are some common warning signs of Anorexia?
distorted body image, which leads to low self-esteem, and abnormal eating habits. Wearing baggy clothes and weighing one’s self frequently
What are some common Physical signs of Anorexia?
Anemia
Weak muscles
Kidney Stones
Low BP,
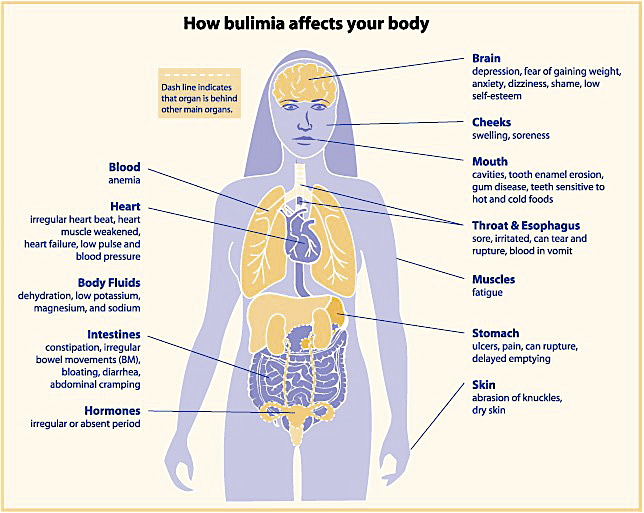
What are some common Physical signs of Bulimia?
Gum Disease, Cavities
Blood in vomit