oral suspensions 2
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
What is zeta potential?
• Zeta potential provides a measure of the magnitude of the electrostatic attraction between particles at the slipping plane,
between the particle and its associated double layer and the the solvent.
Electrical Double Layer - Formation
In aqueous solution, water undergoes self-ionization:
H₂O ⇄ H⁺ (cations) + OH⁻ (anions)Solid/drug particle surface appears negatively charged in liquid
System must maintain overall neutral charge
Cations form a layer around the negatively charged solid particle
This layer is called the "electrical double layer"
Plays a fundamental role in the electrostatic stabilization of colloids
Zeta Potential - Flocculation
what happens if zeta potnetial falls very low
If zeta potential is reduced below a certain value, attractive forces (van der Waals) overcome repulsion
Particles come together to form floccules
Zeta Potential - Repulsion
If a suspension has a large negative or positive zeta potential, particles successfully repel each other
This prevents aggregation and maintains stability
Effect of excipients on the electrical double layer
Excipients can affect suspension properties
Ionic salts (e.g., NaCl) increase mobile charges
Effect of Excipients - Low Concentration
At low concentrations, affect the diffuse layer
Easier to neutralize particle charge
Thins the diffuse layer
Effect of Excipients - High Concentration
At higher concentrations, ionic salts affect the fixed layer
Charge on the particle surface decreases
Surfactants - Critical Micelle Concentration (CMC)
(CMC) is the concentration of surfactants above which micelles form
surfactants - Micelle Formation
above cmc micless have a
Above CMC, micelles have a hydrophobic core
Hydrophobic drugs can dissolve in the hydrophobic core of the micelles
Surfactants - Below CMC
surfavtants at cocnetration below cmc enchance
Below CMC, surfactants cover the particle surface
Help reduce interfacial tension between particle and liquid medium
Surfactants at concentrations below CMC enhance suspension stability
An idea suspesnion
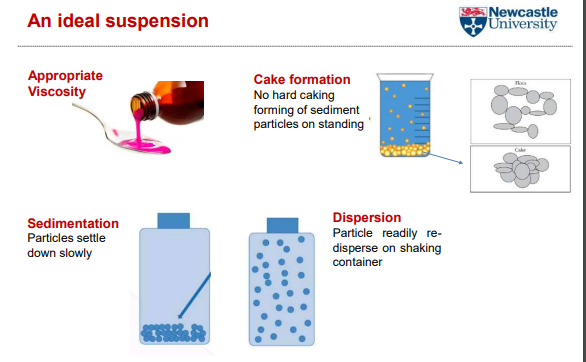
what are Excipients to improve palatability
• Flavours, sweeteners and colourings
– Common sweeteners are ionisable
what do preservatives do?
• Prevent microbial growth.
what is a buffer and what do they do?
will it affect fluocataion?
• A mixture of a weak acid/base and salts.
• To maintain the pH of the aqueous system
• Ionic in nature, so will affect flocculation behaviour.
Suspending Agents - Function
• Suspending agents (viscosity modifiers) reduce particle sedimentation.
What are Flocculating agents
• Decrease zeta potential of the suspended charged particle = cause aggregation (flock formation) of the particles.
• The final excipient added to the formulation.
What do • Chemical stabilisers do?
– Improve chemical stability of the drug
e.g antioxidants
and chealtors
what do Wetting agents do?
– Reduce interfacial tension between particle and liquid medium.
– Improve homogeneity of drug particle distribution.