AP Biology
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
Covalent Bonds
form cell's molecules
strong bonds
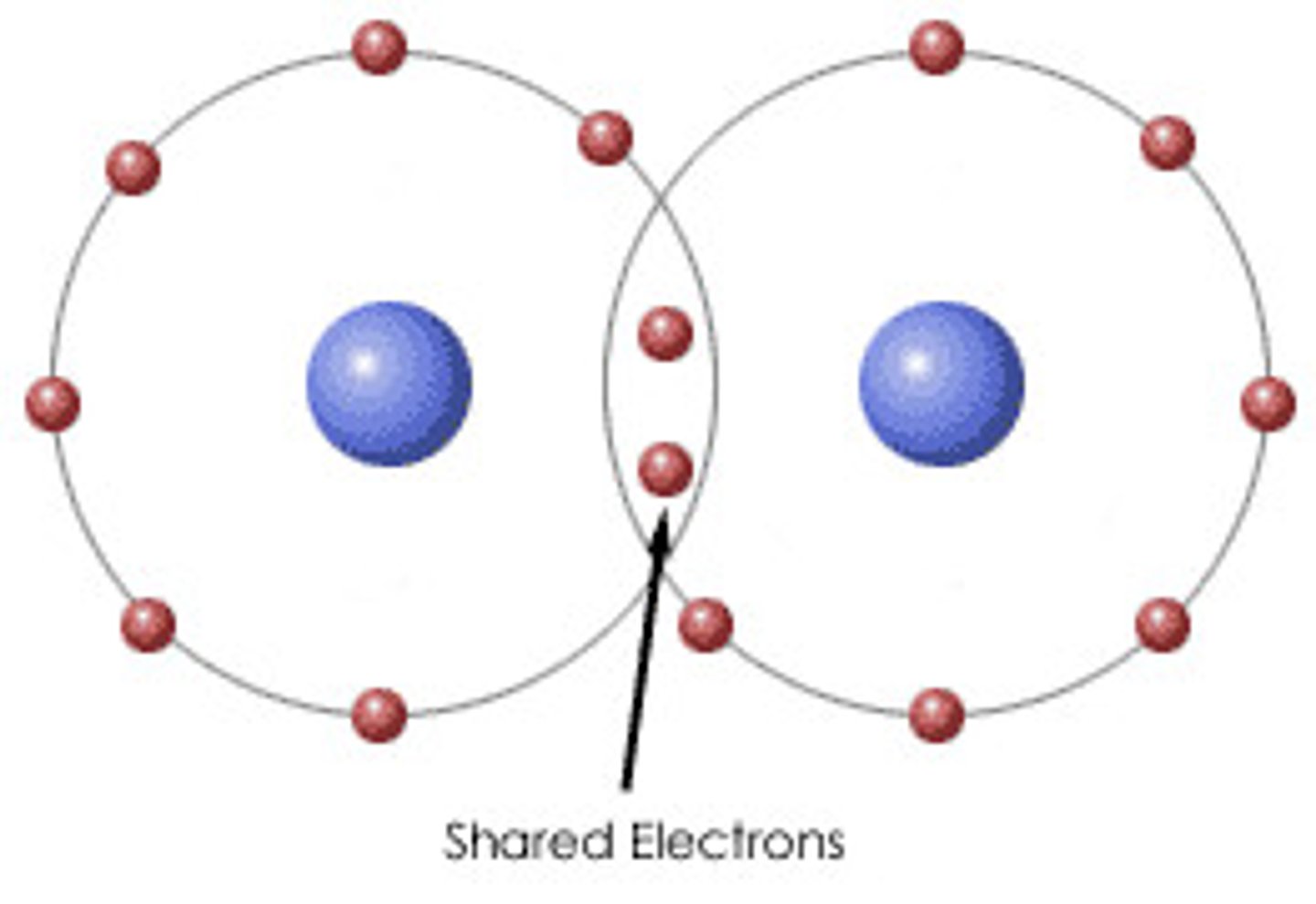
Ionic Bonds
quick reactions/responses
weaker bond (esp. in H2O)
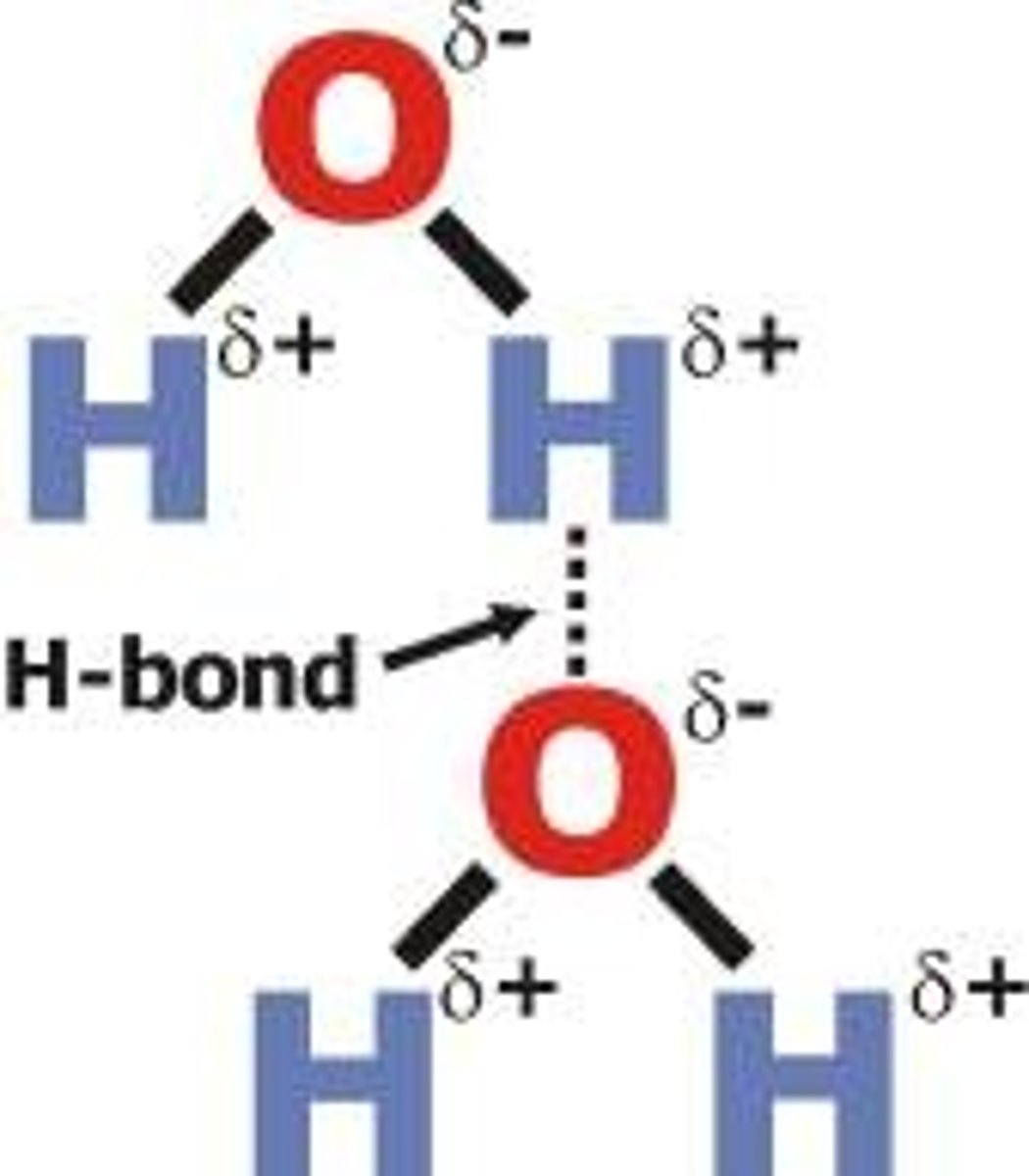
Hydrogen Bonds
H bonds to other electronegative atoms
weaker than ionic and covalent
pH
-log(H+) or -log(H3O)

Monomers/Polymers/Macromolecules
Macromolecules are made of 2 or more polymers
Polymers are made of monomers
amino acid --> peptide --> polypeptide --> protein
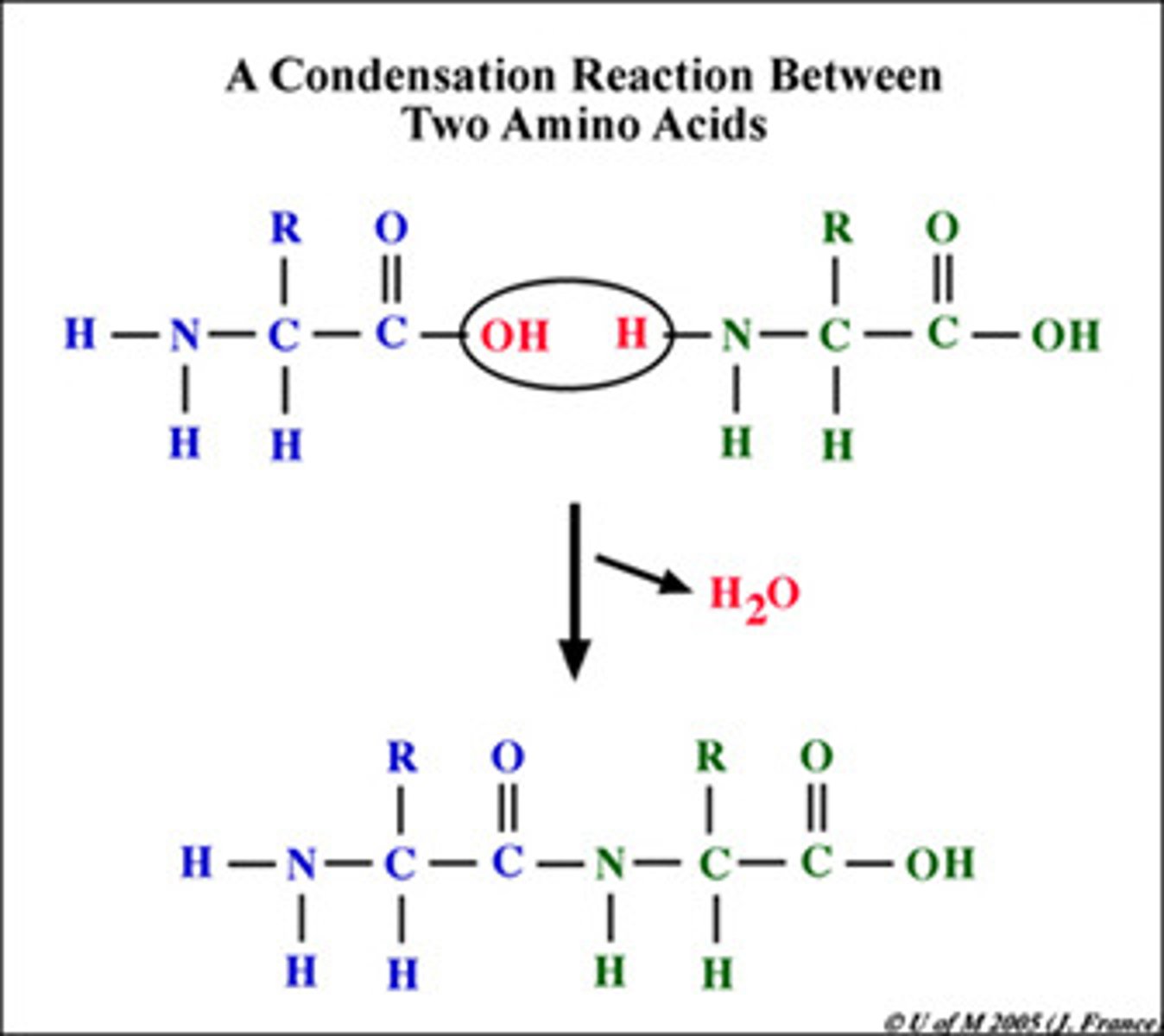
Building/breaking polymers
Build: dehydration synthesis (remove H2O)
Break: hydrolysis (add H2O)
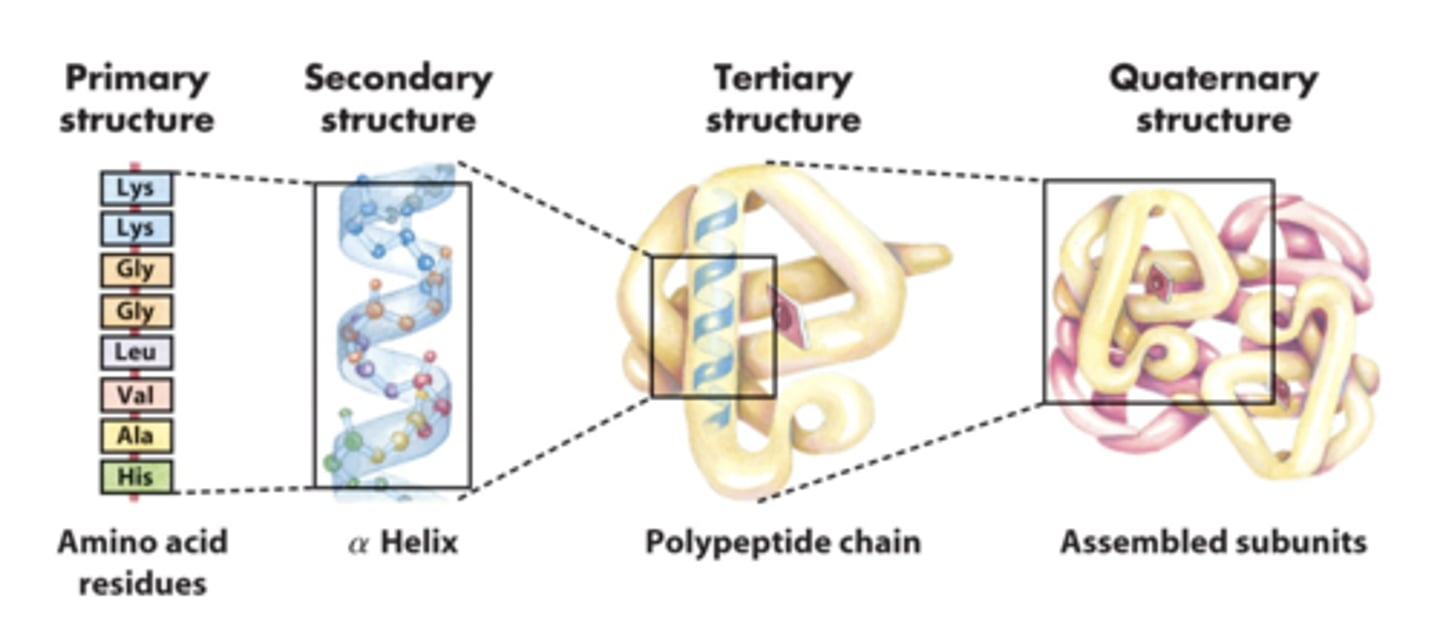
Orders of protein structure
Primary: amino acids in polypeptide chain
Secondary: local folded structures (α helix & β pleated sheet)
Tertiary: overall 3D shape
Quaternary: multiple chains
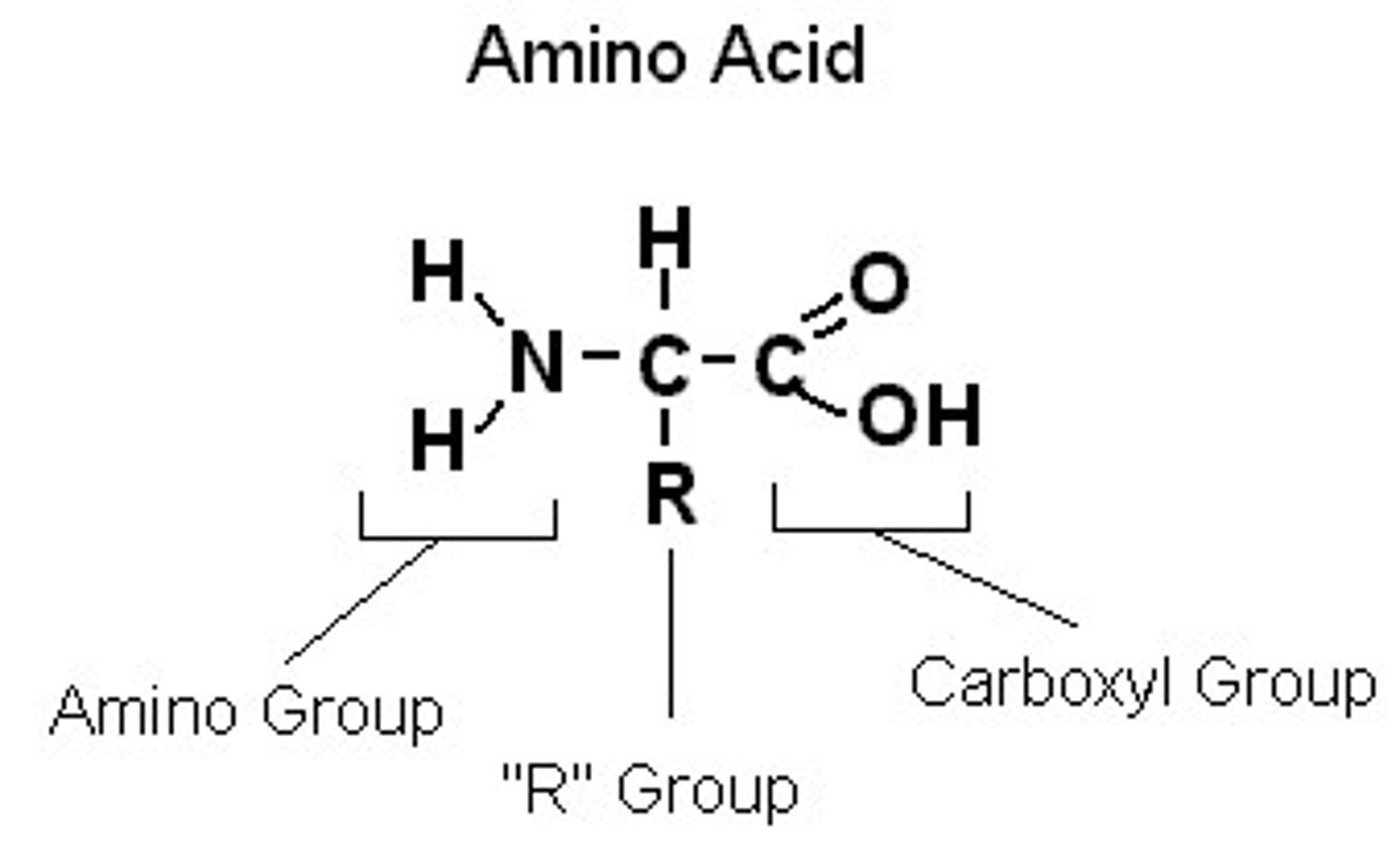
Amino Acid
Nonpolar side group (only C & H) = hydrophobic
Polar side group (O, N, S) = hydrophilic
Ionic = acidic (- charge) or basic (+ charge)
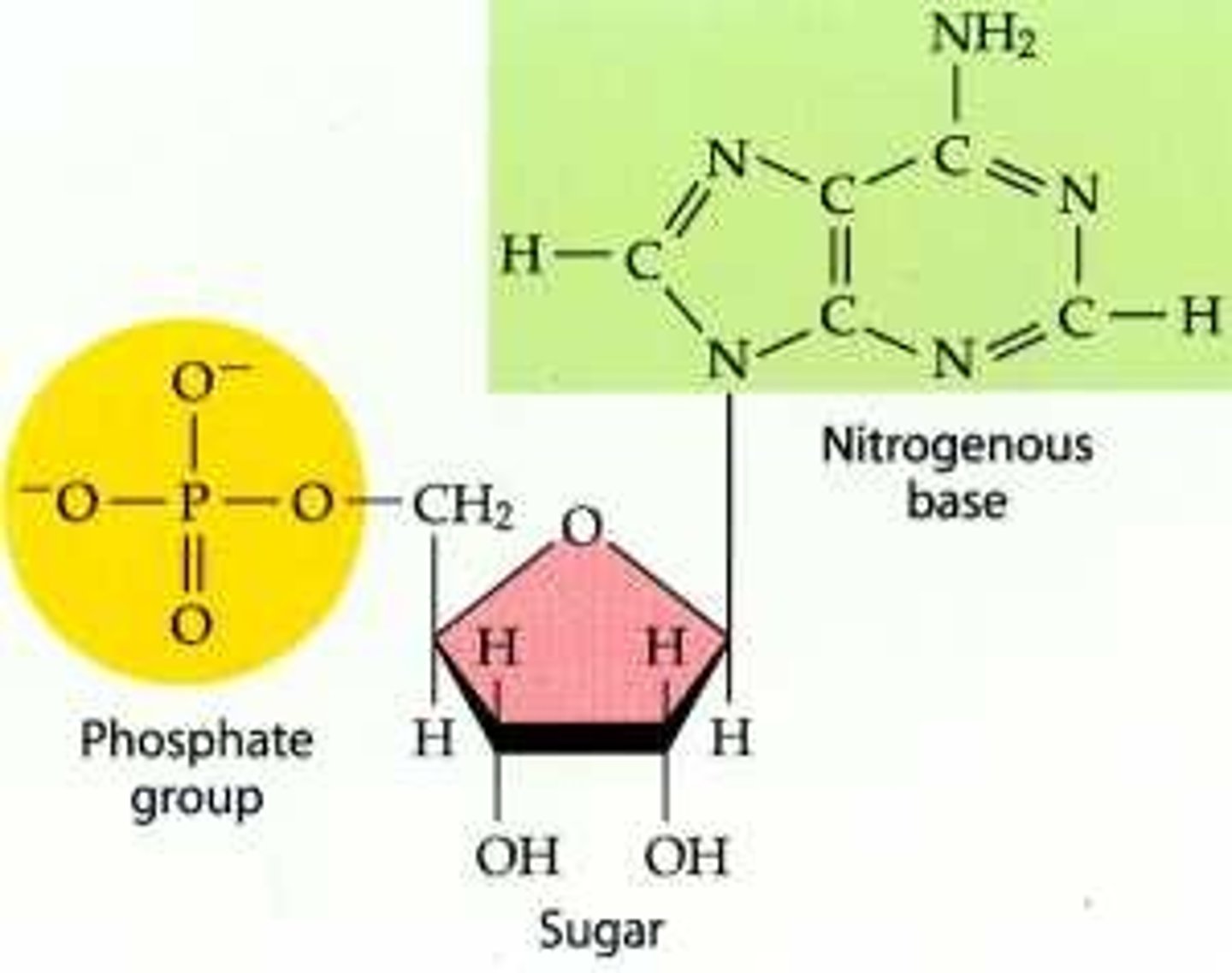
Nucleotide
Monomer of DNA & RNA (nucleic acids)
Deoxyribose (DNA) is missing an O in the sugar
Nucleoside (base + sugar) & phosphate group
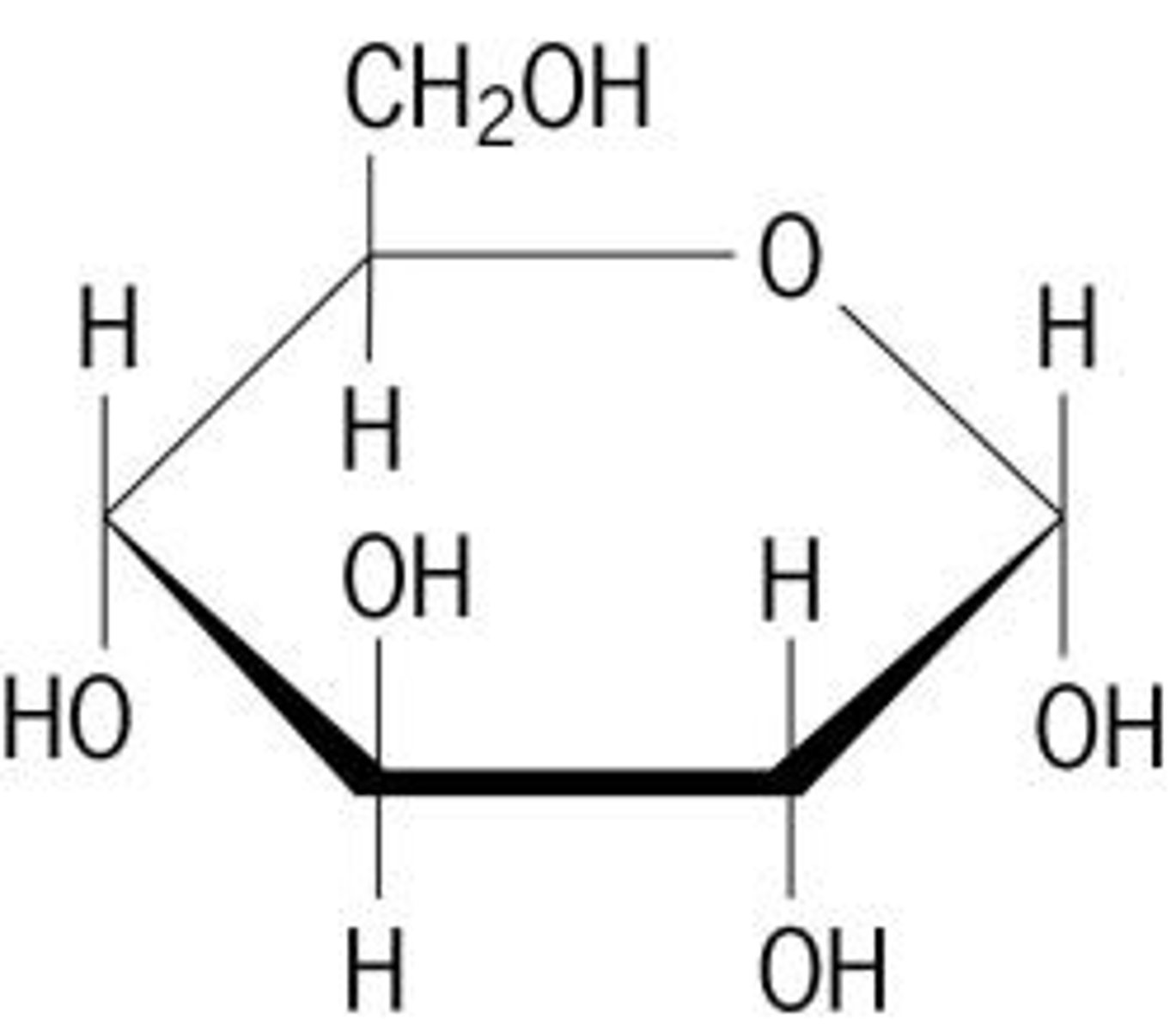
Carbohydrates
Sugars that contain only C, H, O
General Formula: Cₙ(H2O)ₙ
Name: (# of C) + (-ose), (# of rings) + (-saccharide)
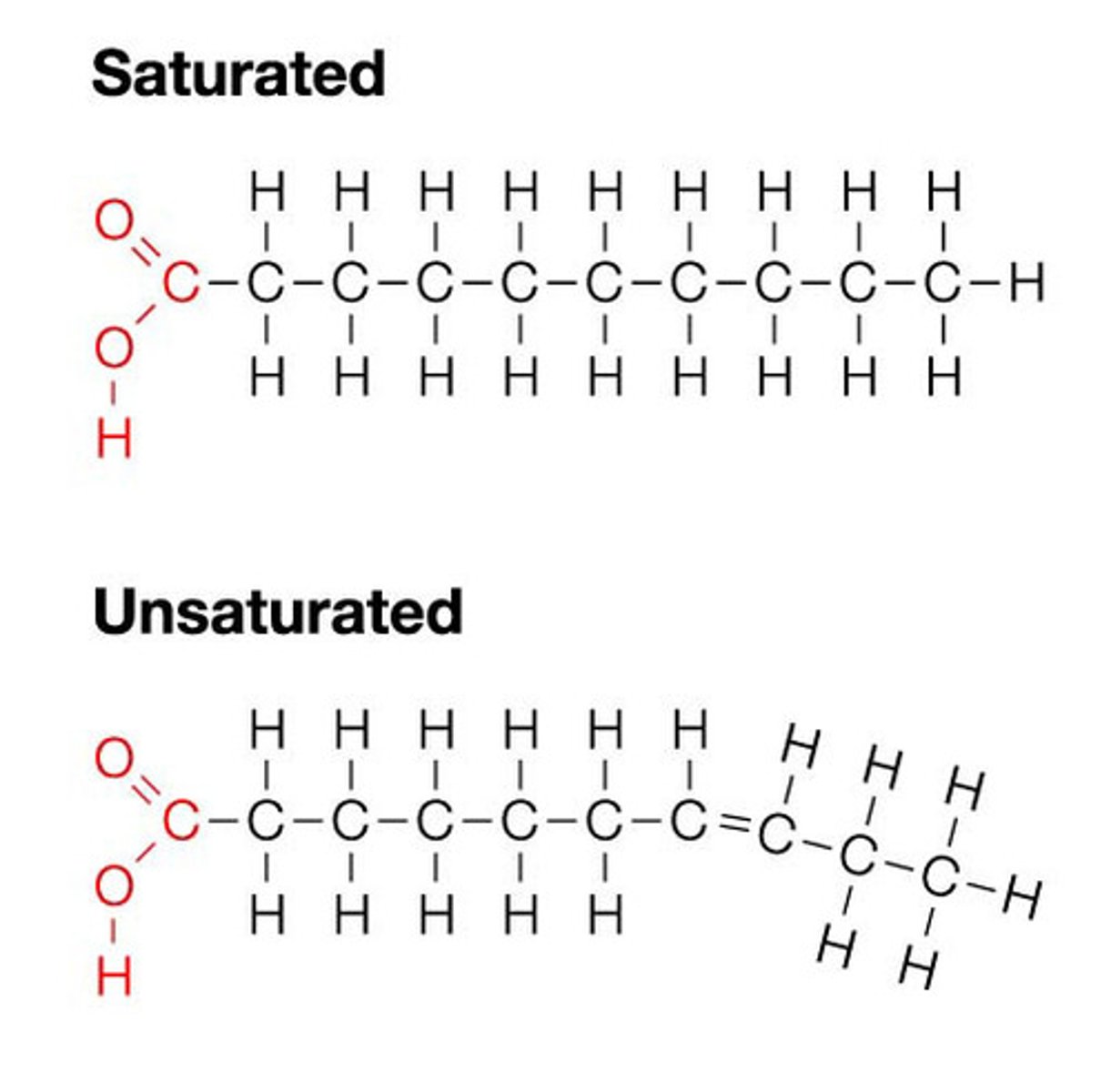
Lipids
Nonpolar
Steroids: multiple rings
Fatty Acids: hydrocarbon chains with a carboxyl (COOH) group, store energy
--Saturated: no double bonds
--Unsaturated: double bond(s)
Properties of Water
Adhesion: stick to another surface
Cohesion: stick to each other --> surface tension
High specific heat (lots of heat needed to raise temp)
Lower density when frozen
Evaporation of sweat cools body
Extracellular matrix and cell wall
Extracellular matrix: space outside cells
-Contain collagen for structural integrity
Cell wall is made of cellulose
Facilitated vs nonfacilitated diffusion vs active transport
Non: Only small, uncharged substances (water passes thru slowly)
Facilitated: Transport proteins let polar/ions pass
Active: Use ATP & carrier proteins, against concentration gradient
Path of Information in Neuron
Dendtrite --> axon --> synapse
Information Processing
sensory input --> integration --> motor output
Types of Neurons
Sensory: external stimuli/internal conditions
Interneurons: connect neurons, integration of sensory input
Motor: transmit signals to muscles
Nervous System Structure
Nerve: bundle of axons
CNS: brain, spinal cord
PNS: ganglia (nerve clusters)
Both have glia: support/protect neurons
Resting potential
Membrane potential of resting neuron (-70 mV)
More K+ and less Na+ & Cl- inside
NaK pump takes out 3 Na & takes in 2 K
Hyperpolarization
Stimulus --> voltage-gated K channels open --> K+ leaves --> cell more negative
Depolarization
Stimulus --> voltage-gated Na channels open --> Na+ enters --> cell less negative
Action Potential Process
Depolarization increases membrane potential past threshold (-55 mV) --> volted-gated Na channels open --> Na+ enters
Rising Phase: further depolarization --> more channels open (postive feedback loop, depolarizes neighboring region)
Falling Phase: Na channels become inactivated, K channels open --> cell becomes negative
Undershoot
Resting State: Na & K channels closed
Refractory Period
Na channels inactivated, stimulus won't trigger actional potential
Prokaryotic vs. eukaryotic cells
Eukaryotic cells have nucleus, membrane-bound organelles, & linear chromosomes
Plant vs. animal cell
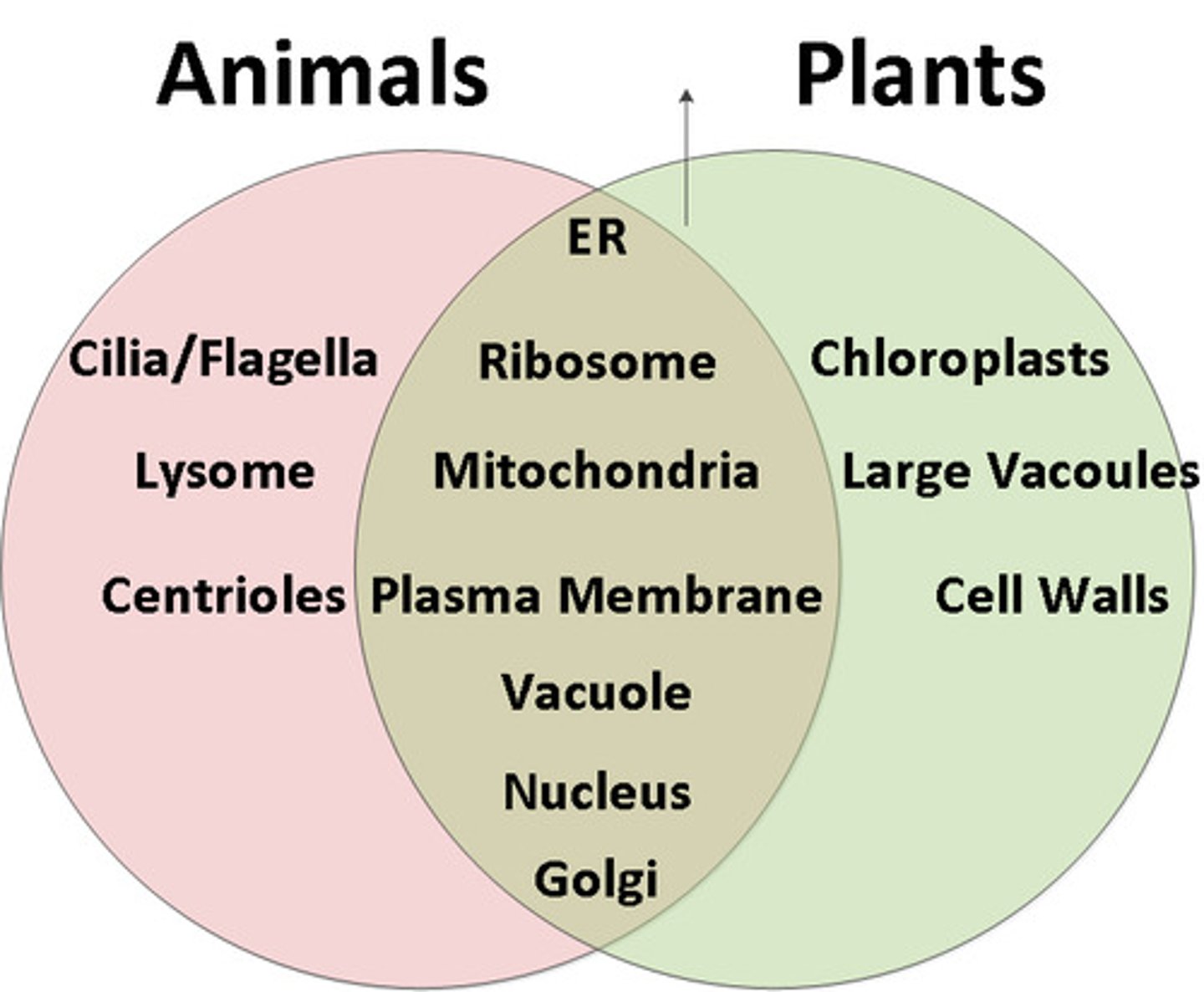
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Rough: has ribosomes (make proteins), package proteins into vesicles for transport
Smooth: synthesis of carbohydrates, lipids, and steroid hormones, stores calcium ions
Golgi apparatus
Protein/lipid sorting, tagging, packaging, and distribution
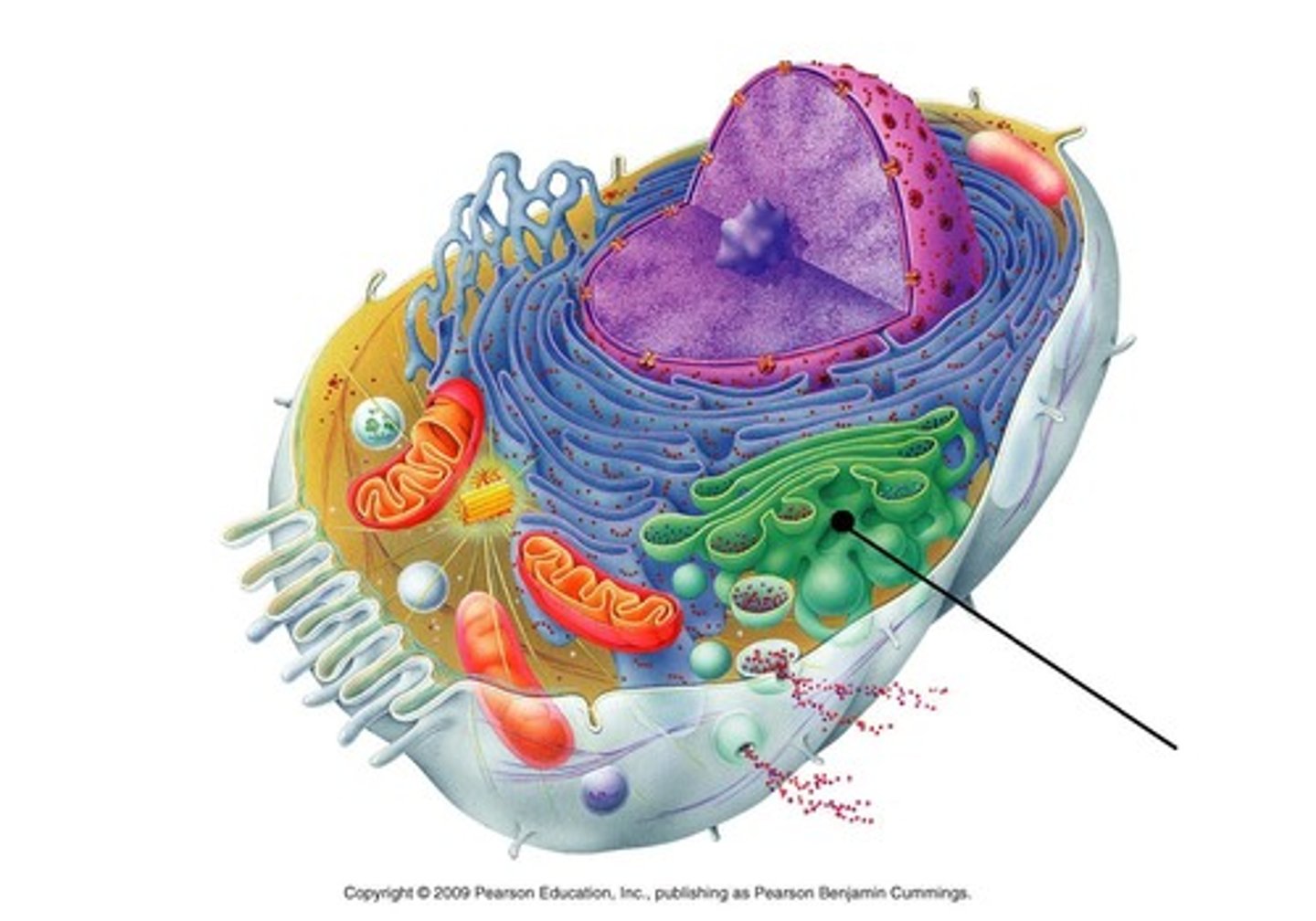
Lysosomes
Digestion, Recycling, Self-Destruction
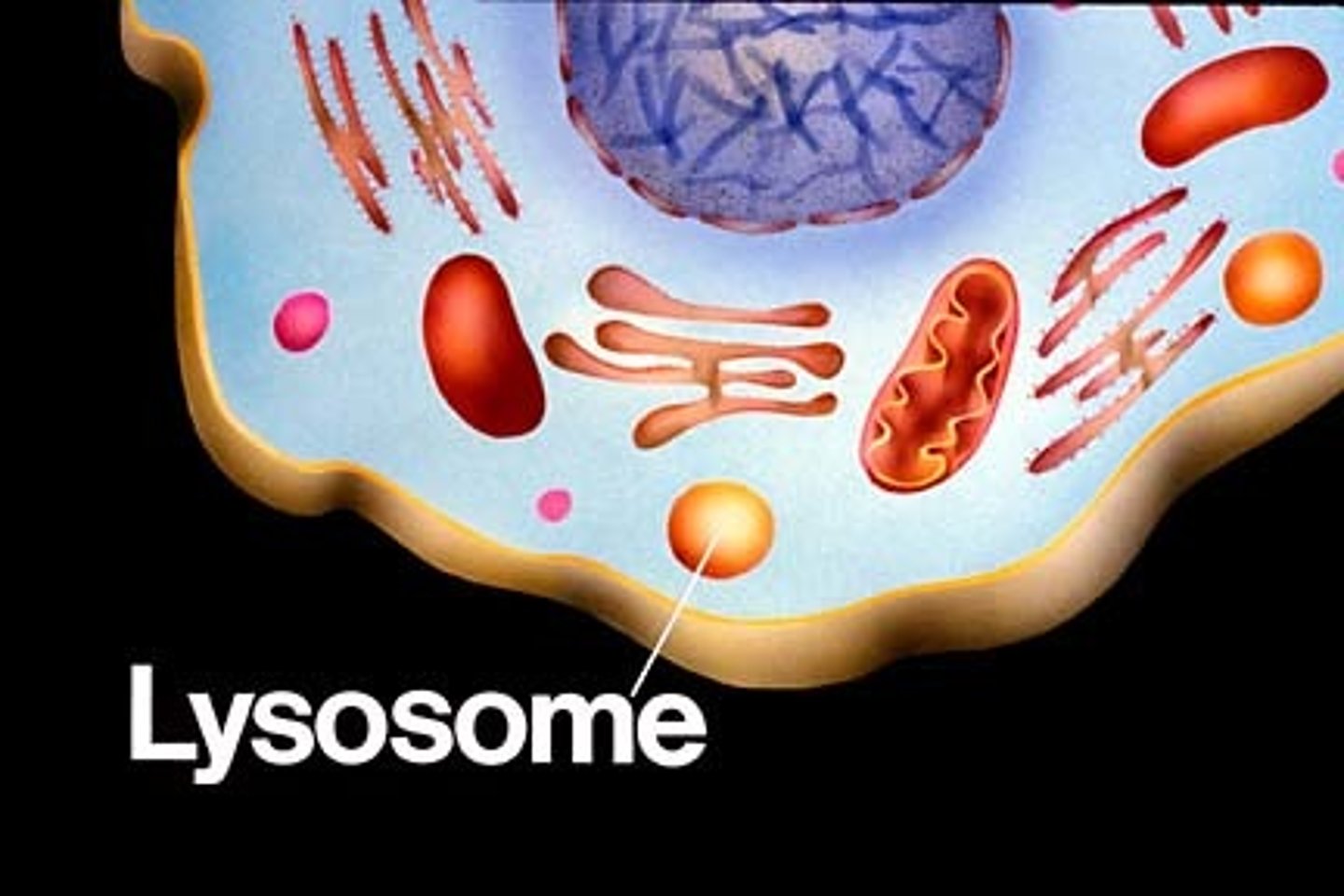
Vacuoles
central vacuole stores water and wastes
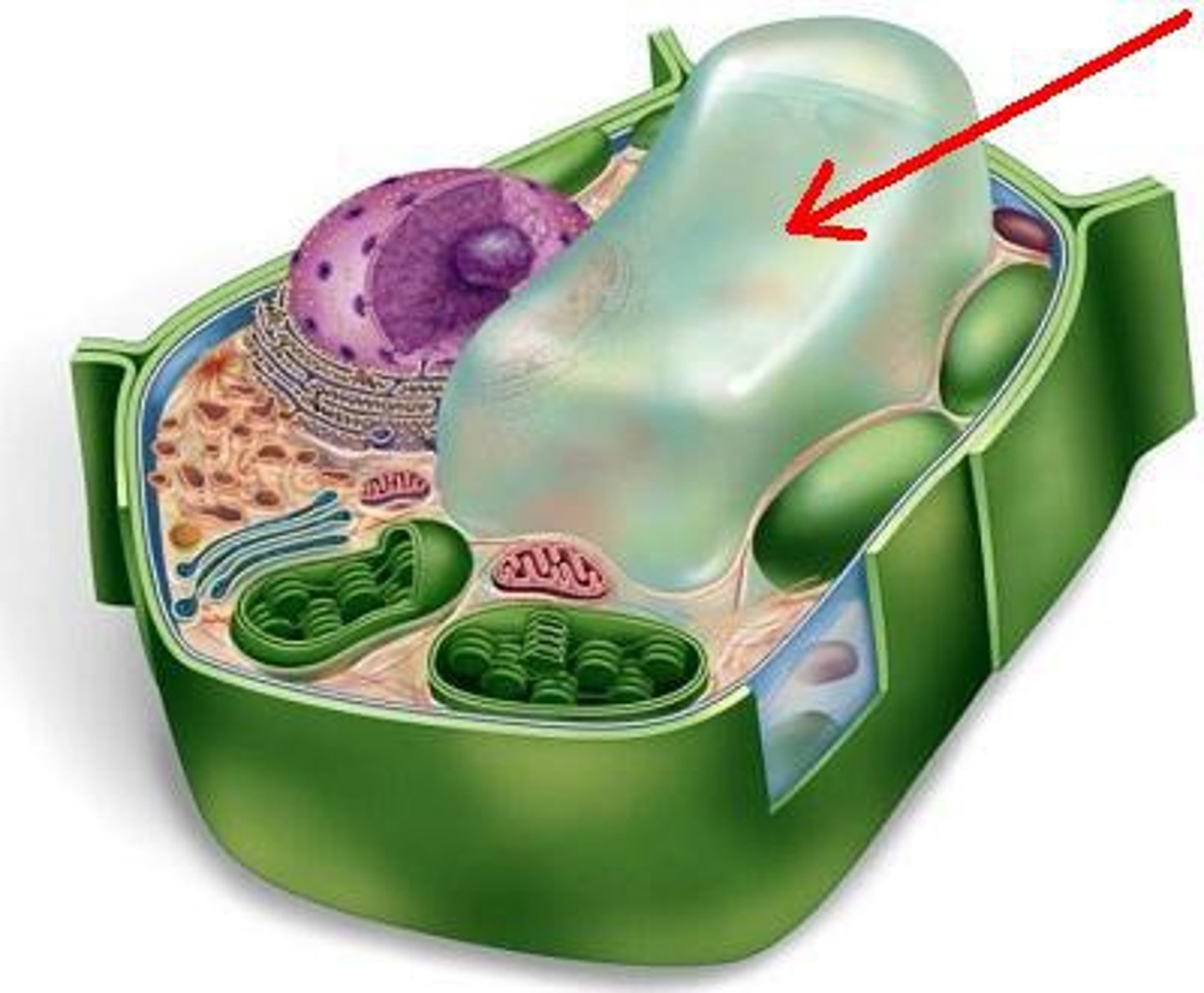
Endosymbiosis
Pre-eukaryotic cells absorbed prokaryotes
Evidence: Mitochondria & chloroplasts have DNA, membrane, & reproduce independently
Cell Membrane
Large SA:V better for chemical exchange
Amphipathic Phospholipid Bilayer: hydrophilic head, hydrophobic tail
Selective permeability: no ions or large polar molecules
Hypertonic (high solute), hypotonic (low solute), isotonic
Water Potential
the potential energy of a volume of water, expressed as a pressure
high --> low
Enzymes 🍔
Lower reaction's activation energy (amt of E needed to begin)
Substrates (reactants) bind to active sites
Affected by temperature, pH, regulatory molecules (activators/inhibitors), & enzyme/substrate concentrations
Reusable ♻️
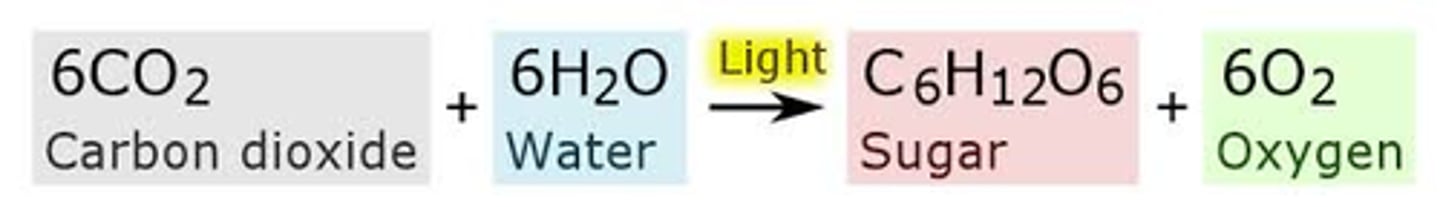
PHOTOSYNTHESIS🌿☀️🌧️
Glucose can be used to make ATP and provides carbon to be fixed (incorporated into organic molecules)
Includes light-dependent reactions and Calvin cycle
LIGHT-DEPENDENT REACTIONS💡
Use light energy to make ATP & NADPH (in thylakoid membrane of chloroplasts)
1. Light absorbed in Photosystem II --> boosts an e⁻ to a high energy level
2. e⁻ is passed to acceptor molecule & replaced with e⁻ from water (releases O2)
3. e⁻ releases energy --> creates H+ gradient
4. H+ flow down gradient through ATP synthase --> drives ATP production
5. In PSI, e⁻ boosted to high energy level
6. Passed to NADP+ --> NADPH
CALVIN CYCLE🩲
Light-independent, Carbon fixed into sugars, (in stroma)
1. Carbon fixation: CO2 combines with RuBP, (catalyzed by rubisco)
2. Reduction: ATP & NADPH used to reduce to G3P
3. Regeneration: Some G3P molecules go to make glucose
CELLULAR RESPIRATION🫁
1. Glycolysis: glucose converted into 2 pyruvate (ATP is made, NAD+ converted to NADH
2. Pyruvate oxidation: pyruvate enters mitochondrial matrix, converted to acetyl CoA (CO2 released, NADH generated)
3. Krebs Cycle: ATP, NADH, FADH2 produced
4. Oxidative phosphorylation: NADPH & FADH2 deposit electrons in ETC
Lactic Acid Fermentation
NADH transfers its electrons directly to pyruvate, generating lactate as a byproduct
Types of Signaling
Paracrine: nearby
Synaptic: neurotransmitters diffuse across synapse
Endocrine: hormones in body fluids
Autocrine: targets itself
Juxtacrine: touching
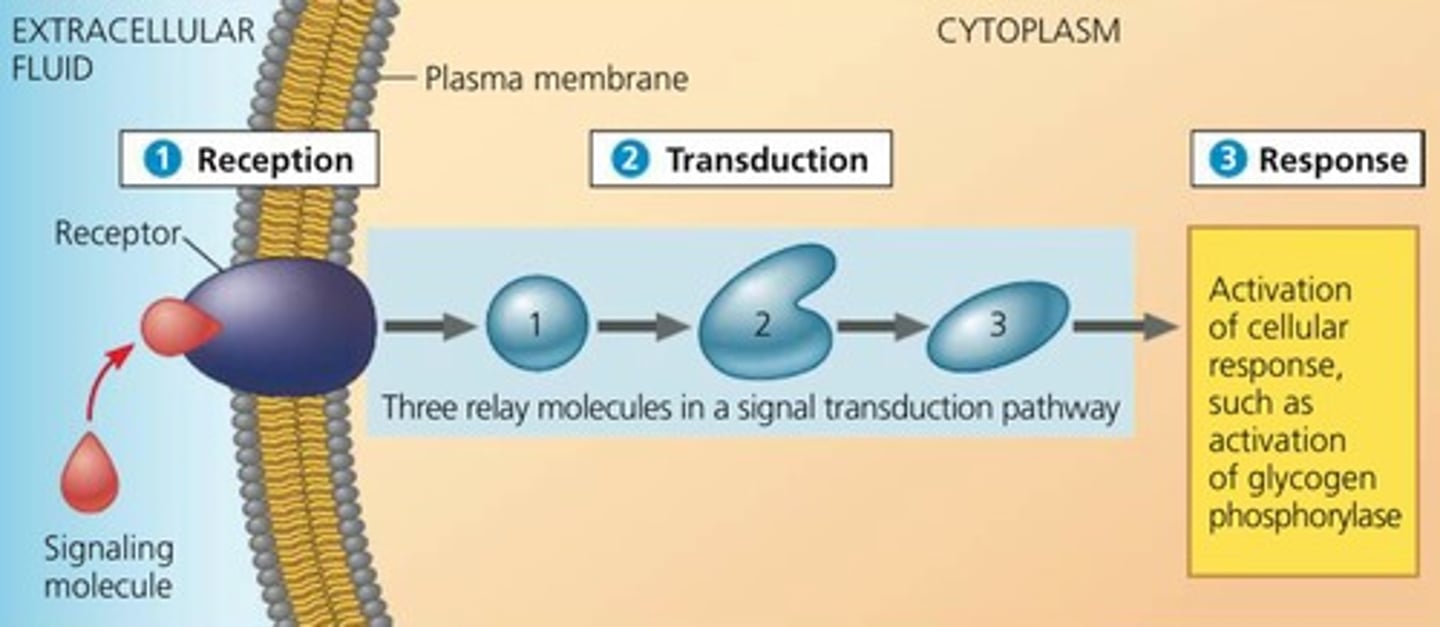
Stages of Cell Signaling
Signal Reception: ligand binds to receptor protein
Signal Transduction: converts signal to a form that can bring about a cellular response
-Pathway: activates proteins through protein kinase --> phosphorylation cascade, amplifies signals, easier regulation
Cellular Response
Endocrine Glands
Hypothalamus: regulates anterior pituitary, which releases hormones -- tropic hormones stimulate other glands
Pancreas: Insulin & Glucagon
Thyroid: metabolic processes
Adrenal glands: blood sugar, metabolism
Ovaries: estrogen
Testes: androgen
Innate Immunity
Barrier Defenses: mucous membranes, skin
Phagocytes (type of white blood cell, engulf): macrophages, neutrophils
Natural Killer cells (release cytotoxic molecules)
Dendritic cells capture/present antigens to T cells
Mast cells release histamine
Adaptive Immunity
B cells differentiate into plasma cells that produce antibodies, activated by helper T cells
Helper T cells release cytokins that signal other immune cells, activated by antigen-presenting cells
Cytotoxic T cells kill infected cells
Memory cells
Antibodies
Proteins produced by B cells that bind to specific antigens on pathogens, marking them for destruction
Major Histocompatibility Complex (MHC)
Molecules on cell surfaces that present antigens to T cells
Active vs Passive Immunity
Active: body produces its own antibodies against pathogens
Passive: receive antibodies from other source (i.e. breast milk)
Lymphatic System
Lymphatic vessles transport white blood cells & remove waste/pathogens from tissues
Lymph nodes trap pathogens to be destroyed by lymphocytes (WBCs)
Redox Process
photosynthesis is a redox process in which H2O is oxidized and CO2 is reduced
Laws of Thermodynamics
1: energy can't be created/destroyed
2: heat flows from hotter to colder regions, every energy transfer increases the entropy of the universe & reduces the amount of usable energy available
Hydrolysis of ATP
P_i is an inorganic phosphate group
Reversing this requires energy

Reaction coupling
an energetically favorable reaction is directly linked with an energetically unfavorable (endergonic) reaction, a product (shared intermediate) of one reaction is "picked up" and used as a reactant in the second reaction
Anabolic and catabolic pathways
Anabolic: build complex molecules from simpler ones and typically need an input of energy
Catabolic: breakdown of complex molecules into simpler ones and typically release energy
Leaf Structure
Stomata let CO2 in and O2 out of mesophyll
Mesophyll > chloroplasts > grana > thylakoids > chlorophylls
Stroma: space around grana
Pyrimidine vs Purine Nitrogenous bases
Pyrimidines: 1 ring (T, U, C)
Purine: 2 rings (A & G)
Connected by H bonds
DNA vs RNA
DNA has deoxyribose (missing hydroxyl group)
RNA has ribose, T replaced with U (binds w/ A)
DNA/RNA Directionality
DNA created in 5' to 3' direction
Antiparallel: coding strand runs opposite to template strand
Prokaryote DNA
Found in the nucleoid.
Single circular chromosome.
Plasmid: rings of non-essential DNA outside the chromosome, can be transferred to other prokaryotes in a population
DNA Replication
Semiconservative
Leading strand: made continuously
Lagging strand: made in Okazaki fragments
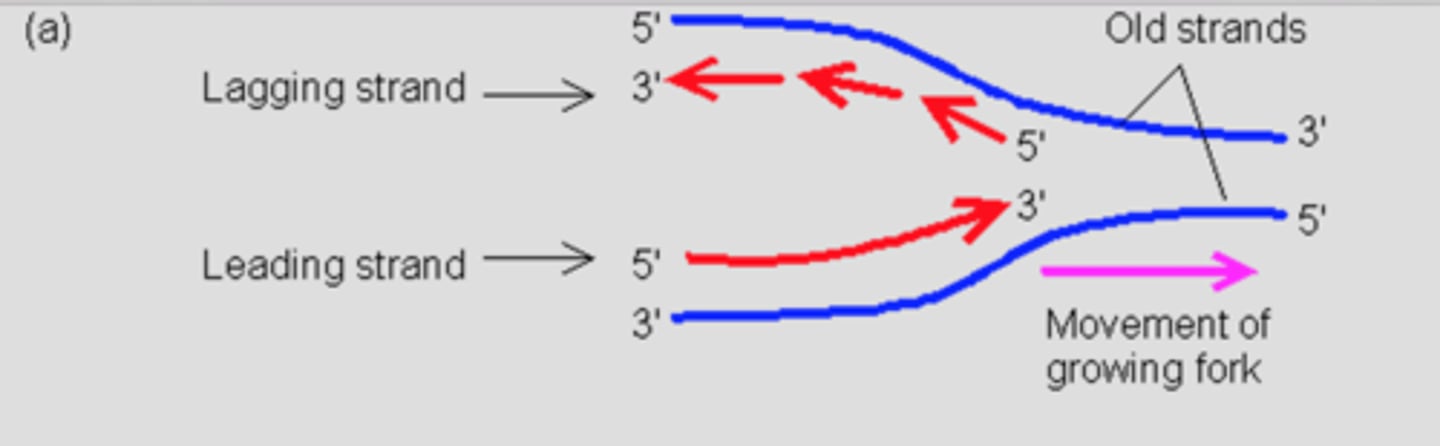
Enzymes involved in DNA Replication
Polymerase III: synthesizes and proofreads in 5' to 3' direction (of the strand being made), require a primer
Polymerase I: replaces primers w/ DNA
Primase: creates primers
Helicase: separates strands
Ligase: joins strands
Transcription
Initiation: RNA Polymerase II binds to promoter & seperates strands
Elongation: reads template strand from 3' to 5' & makes mRNA transcripts from 5' to 3'
Termination: terminator sequences cause RNA polymerase to release transcript
RNA Modifications
Protection: 5' cap & poly-A tail (3' end) --> pre-mRNA
Splicing: spliceosome removes introns --> primary mRNA
Alternative Splicing
pre-mRNA can be spliced in multiple ways depending on which exons are kept
Translation
Initiation: ribosome assembles around mRNA, tRNA carrying met attaches to AUG codon
Elongation: admino acids added
Termination: UAA/UAG/UGA --> release polypeptide chain
Eukaryotic vs Prokaryotic RNA Processing
Eukaryotes: transcription takes place in nucleus, mRNA goes through protection and splicing, protein synthesis takes place in cytosol
Prokaryotes: transcription and translation in cytosol (no nucleus)
Operon
Group of genes w/ on/off switch
-Promoter: where RNA polymerase attaches
-Operator: controls access of RNA polymerase
Inducible vs Repressible
Inducible: usually off, turned on by inducer (lac)
Repressible: usually on, turned off by corepressor (trp)
Transcription Factors
Proteins that help turn genes on/off by binding to DNA
Activators boost transcription.
Repressors decrease transcription.
Groups of transcription factor binding sites called enhancers and silencers can turn a gene on/off.
Chromosomal Rearrangements
Duplication: part is repeated
Deletion: part is removed
Inversion: region is flipped around
Translocation: a piece of one gets attached to another
Genetic variation in prokaryotes
Transformation: takes up DNA from environment
Transduction: virus moves DNA from one to another
Conjugation: DNA transferred through tube between cells
Transposable elements: chunks of DNA that jump from one place to another
Mutations
Point: any mutation involving a single base
Insertion/Deletion --> frameshift
Gel Electrophoresis
Small fragments move farther than large ones
Polymerase chain reaction
Laboratory technique to amplify specific DNA sequences, by making copies of a fragment
Genetic Drift
Allele frequencies change over generations due to chance.
Strongest effects in small pop. -- bottleneck effect or founder effect (split off)
--> loss or fixation (100% freq.) of alleles
Microevolution & Macroevolution
Micro: Change in allele frequencies
Macro: large-scale
Polygenic traits
traits determined by many genes, typically form a spectrum
Three types of selection
Stabilizing: intermediate more fit than extreme
Directional: one extreme more fit
Disruptive: two extremes more fit
Hardy-Weinberg assumptions
no mutation, random mating, no gene flow, infinite population size, and no selection.
Mechanisms of evolution correspond to violations of the assumptions
Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium
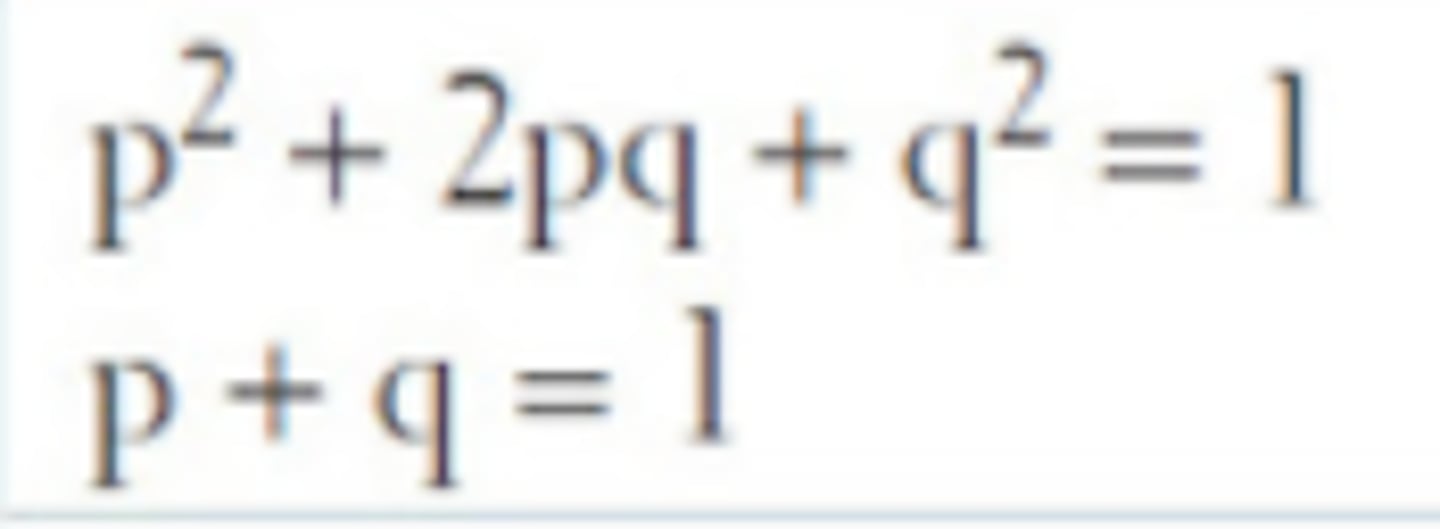
Homologous vs Analogous features
Homo: from a common ancestor --> vestigial structures
Ana: from convergent evolution
Homologous genes
"Same" inherited gene, use DNA differences to determine relation
Biological Species Concept
A group of organisms that can potentially mate to produce viable, fertile offspring.
Prezygotic barriers (reproductive isolation)
Habitat
Temporal (times of day/year)
Behavioral (courtship rituals)
Gametic (egg/sperm cells can't combine)
Mechanical (reproductive structures don't fit)
Postzygotic barriers
Often related to the hybrid embryo's mixed set of chromosomes, which may not match up correctly or carry a complete set of information.
Allopatric vs Sympatric Speciation
Allopatric: geographic separation
Sympatric: reamining in one location (common in plants through polyploidy --> diff #s of chromosomes)
Adaptive Radiation: a single species or small group of species rapidly diversifies into many new species
Hypotheses for the Origins of Life
Oparin-Haldane: arose from inorganic molecules forming “building blocks” like amino acids then complex polymers
Miller-Urey experiment: organic molecules could be formed from inorganic components
RNA World: first life was self-replicating RNA
Metabolism-first: first life was self-sustaining networks of metabolic reactions
Innate vs. Learned Behaviors
Innate: genetically hardwires, inherited
Learned: develop from experience
Partly both: genetically programmed to develop a behavior, but the form the behavior takes depends on the individual's experience
Reflex
involuntary and rapid response to a stimulus
Kinesis and taxis
Kinesis: changes movement in a non-directional way (ex: speed)
Taxis: movement towards/away from stimulus
Fixed action patterns
predictable series of actions triggered by a cue; automatic and involuntary
Types of learned behaviors
Habituation: stops responding to stimulus after repeated exposure
Imprinting
Conditioned
-Classical: neutral stimulus paired w/ a one w/ a natural response
-Operant: awards/punishment, doesn't rely on existing stimulus/response
Cognition: awareness, reasoining, recollection, judgement
Social Learning: observe others
Types of Signals in Animal Communication
Pheromones
Visual
Tactile
Auditory

Metabolism & metabolic rate
sum total of the biochemical reactions that take place in an organism's body
how quickly fuels (such as sugars) are broken down to keep the organism's cells running
Endotherms vs Ectotherms
Endotherms use metabolic heat to keep a stable body temperature (BMR), while ectotherms do not (SMR).
Torpor, hibernation, and estivation
Torpor: state of decreased activity to conserve energy
-Hibernation
-Estivation (hot/dry)
Autotrophs vs. Heterotrophs
Autotrophs: make own food
-Photoautotrophs
-Chemoautotophs
Heterotophs: eat organisms/byproducts
Density-(in)dependent limiting factors
Dependent: competition, predation, disease, parasites, waste accumulation
Independent: natural disaster, weather, pollution
interspecific interactions
Competition -/-
Predation +/-
Herbivory +/-
Mutualism +/+
Commensalism +/0
Parasitism +/-
competitive exclusion principle
two species can't coexist if they occupy exactly the same niche (competing for identical resources) --> resource partitioning
Species Richness & Diversity
Richess: # of species
DIversity: depends on # of species and relative abundances
Foundation and keystone species
Foundation: create & define community (kelp/coral)
Keystone: large effect on community relative to biomass/abundance