Chromosome Structure and DNA Packaging in Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
What is the primary structure of DNA?
The nucleotide sequence.
What is the secondary structure of DNA?
The double helical structure.
What is the tertiary structure of DNA?
The folding of the double helix to fit into the cell.
What type of chromosome structure do prokaryotes have?
One circular chromosome, which is a single DNA molecule.
How is prokaryotic DNA structured within the cell?
It is looped and probably anchored by proteins, clumping in one place called the nucleoid.
What is the difference in chromosome structure between prokaryotes and eukaryotes?
Eukaryotes have linear chromosomes, while prokaryotes have circular chromosomes.
What is chromatin?
A mixture of DNA and protein.
What are the two types of chromatin?
Euchromatin and heterochromatin.
What is the function of histone proteins?
They compact DNA and may play a role in activating or silencing regions of DNA.
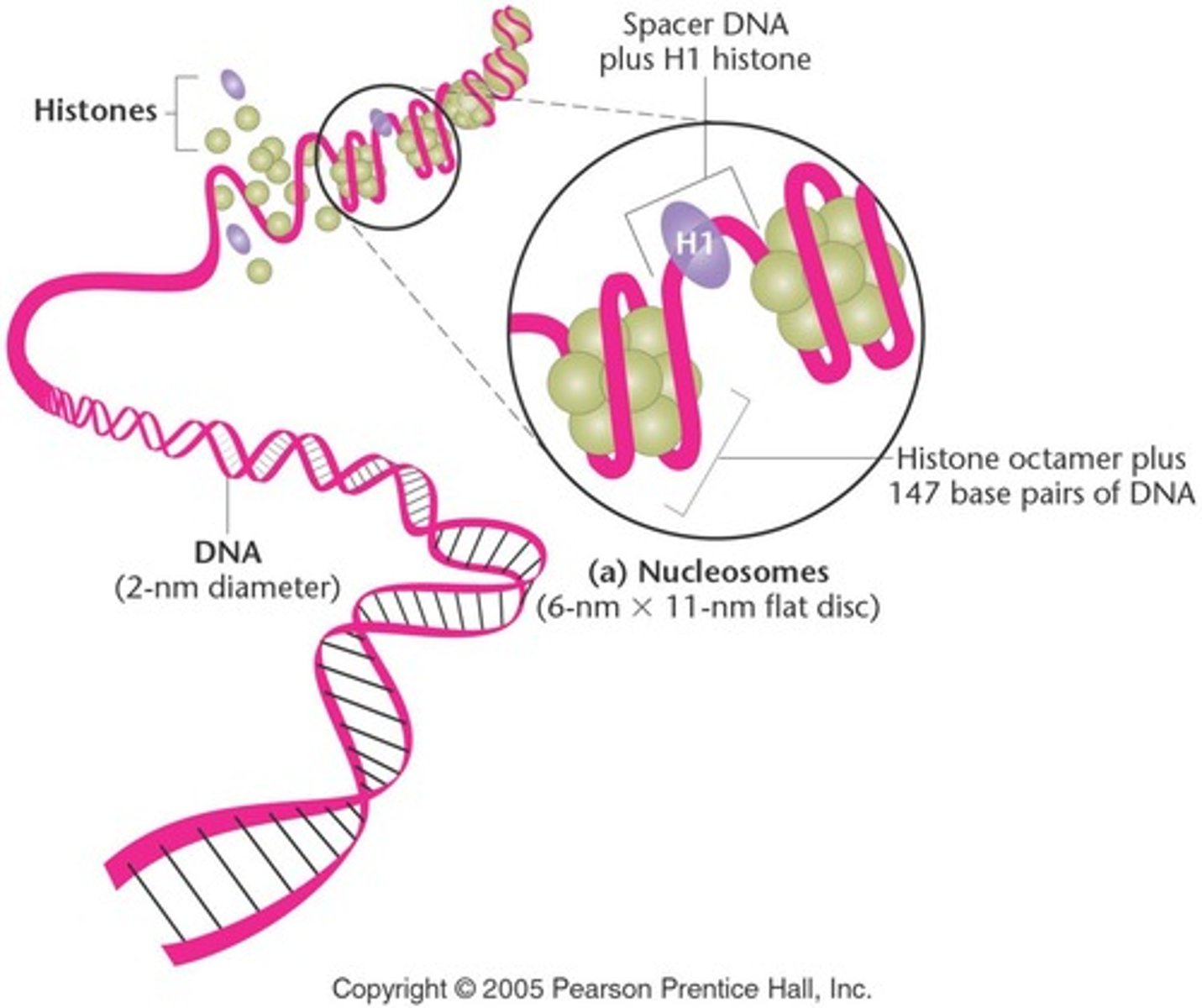
What is the structure of a nucleosome?
145-147 nucleotide pairs of DNA wrapped around a histone octamer.

What is the role of the centromere?
It is the binding site for the kinetochore complex and is essential for proper chromosome segregation during mitosis.

What is unique about the telomere?
It protects the ends of the DNA molecule from unraveling or degrading.
What is the vertebrate telomere repeat sequence?
5'-TTAGGG-3'.
What happens to nucleosomes during DNA replication?
Nucleosomes replicate semi-conservatively.
What is the structure of the telomere?
It consists of repeated sequences, specifically 5'-T1-4A0-1G1-8-3', repeated many times.
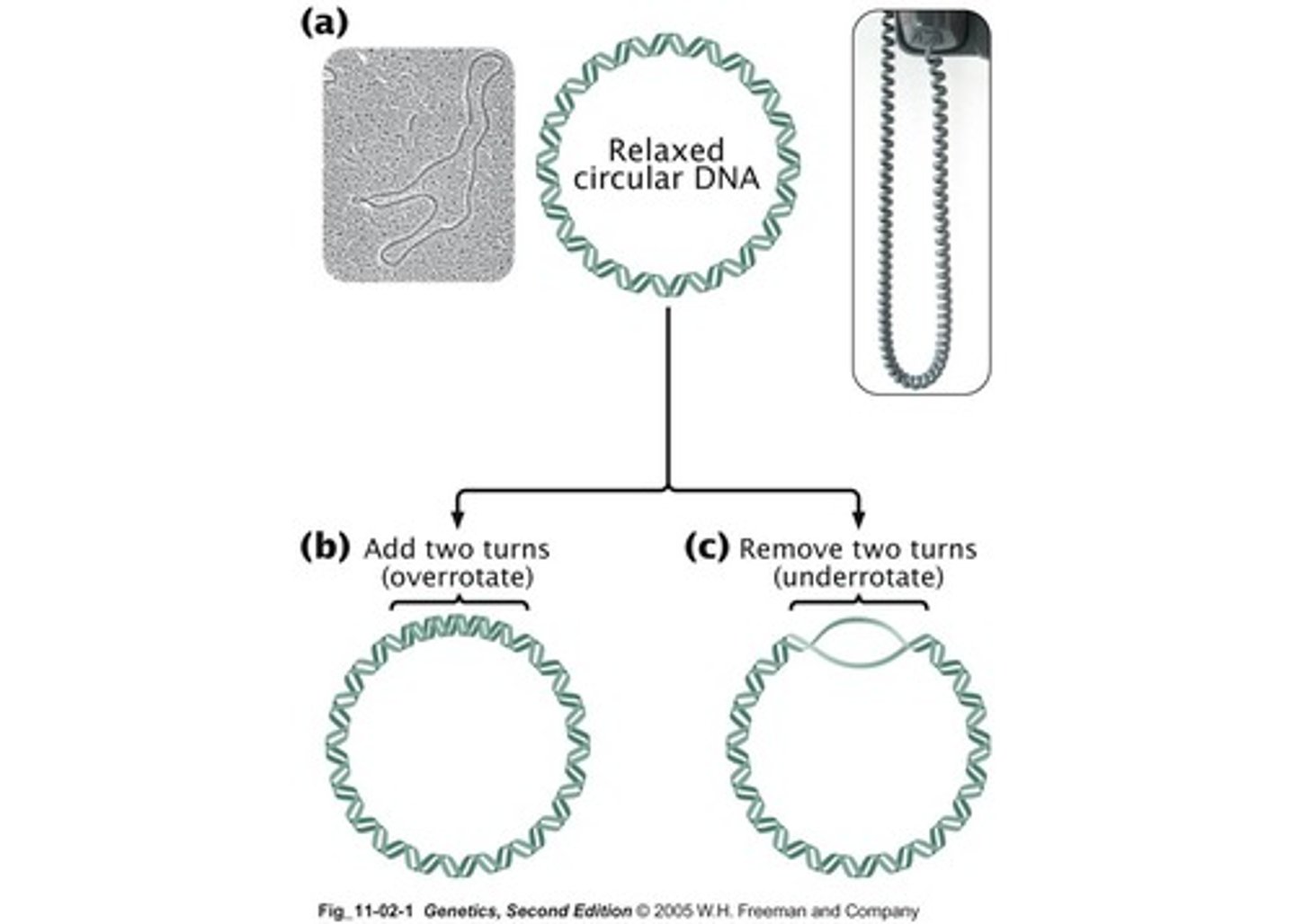
What is supercoiling in circular DNA?
It is when DNA twists up on itself due to the absence of free ends.
What is the significance of the nucleosome plus linker?
It represents approximately 200 base pairs of DNA.
What is the role of non-histone proteins in chromatin?
They help in the structural organization and function of chromatin.
What is the function of scaffold proteins in chromosome structure?
They anchor DNA loops and help in the organization of chromatin fibers.
What is the consequence of chromosomes lacking centromeres?
They are lost during mitosis.
What is the significance of the G-rich single-stranded run at the end of telomeres?
It folds back and bonds with itself to create a protective cap.
What is the typical length of the bacterial chromosome?
Approximately 1200 micrometers, equivalent to 4.6 million base pairs.
What are the four levels of DNA compaction in eukaryotes?
1. DNA wound on nucleosomes, 2. Nucleosomes supercoiled into solenoids, 3. Solenoids form loops on a scaffold, 4. Loops condensed into chromatin fibers.
