ECE Statistics Vocabulary: Chapter 1 + 2
1/20
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
Statistics
A collection of
procedures and principles for
gathering data and analyzing
information in order to help
people make decisions when
faced with uncertainty.
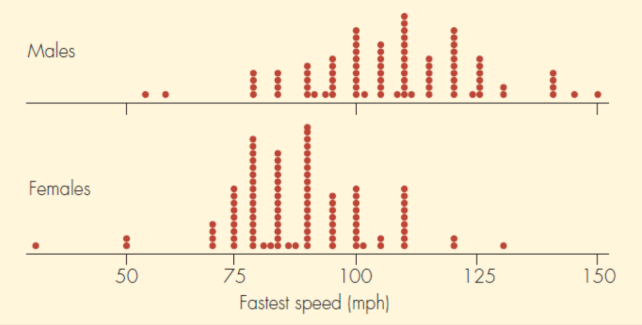
Dotplot
A graph that organizes data as plots individually.
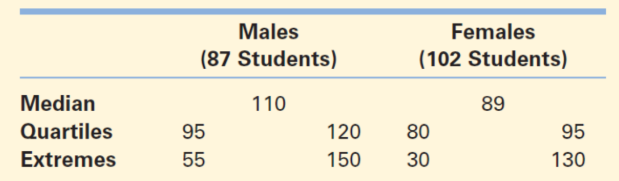
Five-number summary
the lowest value
the cut off points for ¼
½
¾ of the data
highest value
Rate
A measure of the frequency of an event in a specified time period, often expressed as a ratio or percentage.
Margin of error
The range of values within which the true population parameter is expected to lie, often associated with survey results or statistical estimates.
Nonparticipation
Nonresponse
Self-selected
All-volunteer
Biased
A tendency of a sample or survey to favor one outcome over another, leading to inaccurate or misleading results.
Observational study
A type of research method where the researcher observes and records behavior without manipulating any variables.
Confounding variables.
Variables that influence both the independent and dependent variables, making it difficult to determine causal relationships.
Randomized experiment
A study sample is divided into one group that will receive the intervention being studied (the treatment group) and another group that will not receive the intervention (the control group).
Randomization
The process of assigning subjects in an experiment to different groups (e.g., treatment or control) by chance to minimize bias and ensure groups are comparable in all other factors except the variable being tested.
False positive
Occurs when a test or experiment incorrectly indicates a positive result when the actual situation is negative or true.
Raw data
For numbers and category labels that have been collected but have not yet been processed in any way.
Observation
An individual entity in a study.
Variable
A characteristic that may differ among individuals.