Unit 6 microeconomics: 4 Market Failures
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
17 Terms
5 Characteristics of Free Market
little government involvement in the economy
Individuals own resources and determine what to produce, how to produce, and who buys it.
The opportunity to make profit gives people incentive to produce quality items efficiently.
wide variety of goods available to consumers
competition and self-interest work together to regulate the economy.
What is Market Failure?
situation in which the free-market system fails to satisfy society’s wants
private markets do not efficiently bring about allocation of resources.
The government must step into satisfy society’s wants
Markey Failure 1: Public Goods
It’s impractical for the free-market to provide the goods because there is little opportunity to earn profit.
Free Riders are individuals that benefit without paying
keeps firms form making profits
if left to free market, essential services would be underproduced
Definition of public goods
nonexclusive:
Everyone can use the good.
Cannot exclude people from enjoying the benefits
Shared Consumption:
one person’s consumption of a good does not reduce the usefulness to other people.
maximizing rule for Public goods
Marginal social benefits >/= marginal social costs
Market failure 2: externalities
external benefits/costs to someone other than the original decision maker.
with no gov involvement, there would be too much or too little of a good.
Negative externalities
spillover costs
overallocation of resource
negative effect to others, too much produced
Two supply curves: MSC and MPC
ex: cigarettes
solved by per unit taxes
positive externalities
spillover benefits
underallocation of resource
positive effect to others, too little produced
Two supply curves: MSB and MPB
ex: vaccines
solved by per unit subsidy
pollution in negative externalities
Cannot fully get rid of pollution because it is not possible
instead, government can sell the right to pollute and control amount
reduces pollution bc it costs $$
Market failure 3: monopolies
Monopolies destroy the key of a Free Market system - competition
Antitrust laws
Laws designed to prevent monopolies from forming and promoting competition
How to fix monopolies market failure?
government involvement in all 3 branches
legislative branch: passed laws designed to stop monopolies
executive branch: federal trade commission must approve all corporates merges
judicial branch: supreme court finds the firms guilty or not and assigns punishment
The Lorenz Curve
Lorenz curve shows the actual distribution of income
the wider it is the more unequal the income distribution is

Gini Coefficient
the area between the line pf equality and the lorenz curve
G coefficient of 0 =perfect income equality
G coefficient of 1 = perfect income inequality
Why does the government tax?
finance government operations such as public goods and fund gov programs
Influence economic behavior of firms and individuals such as excise taxes to discourage or subsidies to encourage
Types of Taxes
progressive taxes: takes larger % of income from high income
proportional taxes: taxes same % of income for everyone
regressive taxes: takes larger % from low income (sales tax)
designed to push rich people to spend more bc taxed less
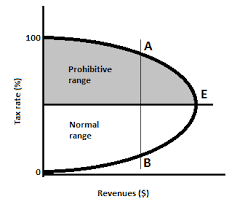
Laffer Curve
shows relationship between tax rate and tax revenue
if the government increases tax rate, tax revenue will increase
if tax rates become too high, tax revenue will fall since workers have no incentive to work harder