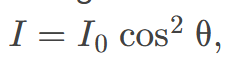Chapter 27: Wave Optics
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
axis of a polarizing filter
the direction along which the filter passes the electric field of an EM wave
birefringent
crystals that split an unpolarized beam of light into two beams
Brewster’s angle
𝜃b=tan−1(𝑛2𝑛1), where 𝑛2 is the index of refraction of the medium from which the light is reflected and 𝑛1 is the index of refraction of the medium in which the reflected light travels
Brewster’s law
tan𝜃b=𝑛2𝑛1, where 𝑛1 is the medium in which the incident and reflected light travel and 𝑛2 is the index of refraction of the medium that forms the interface that reflects the light
coherent
waves are in phase or have a definite phase relationship
confocal microscopes
microscopes that use the extended focal region to obtain three-dimensional images rather than two-dimensional images
constructive interference for a diffraction grating
occurs when the condition 𝑑sin𝜃=𝑚𝜆(for𝑚=0,1,–1,2,–2,…) is satisfied, where 𝑑 is the distance between slits in the grating, 𝜆 is the wavelength of light, and 𝑚 is the order of the maximum
constructive interference for a double slit
the path length difference must be an integral multiple of the wavelength
contrast
the difference in intensity between objects and the background on which they are observed
destructive interference for a double slit
the path length difference must be a half-integral multiple of the wavelength
destructive interference for a single slit
occurs when 𝐷sin𝜃=mλ,(for𝑚=1,–1,2,–2,3,…), where 𝐷 is the slit width, 𝜆 is the light’s wavelength, 𝜃 is the angle relative to the original direction of the light, and 𝑚 is the order of the minimum
diffraction
the bending of a wave around the edges of an opening or an obstacle
diffraction grating
a large number of evenly spaced parallel slits
direction of polarization
the direction parallel to the electric field for EM waves
horizontally polarized
the oscillations are in a horizontal plane
Huygens’s principle
every point on a wavefront is a source of wavelets that spread out in the forward direction at the same speed as the wave itself. The new wavefront is a line tangent to all of the wavelets
incoherent
waves have random phase relationships
interference microscopes
microscopes that enhance contrast between objects and background by superimposing a reference beam of light upon the light emerging from the sample
optically active
substances that rotate the plane of polarization of light passing through them
order
the integer 𝑚 used in the equations for constructive and destructive interference for a double slit
phase-contrast microscope
microscope utilizing wave interference and differences in phases to enhance contrast
polarization
the attribute that wave oscillations have a definite direction relative to the direction of propagation of the wave
polarization microscope
microscope that enhances contrast by utilizing a wave characteristic of light, useful for objects that are optically active
polarized
waves having the electric and magnetic field oscillations in a definite direction
Rayleigh criterion
two images are just resolvable when the center of the diffraction pattern of one is directly over the first minimum of the diffraction pattern of the other

reflected light that is completely polarized
light reflected at the angle of reflection 𝜃b, known as Brewster’s angle
thin film interference
interference between light reflected from different surfaces of a thin film
ultraviolet (UV) microscopes
microscopes constructed with special lenses that transmit UV rays and utilize photographic or electronic techniques to record images
unpolarized
waves that are randomly polarized
vertically polarized
the oscillations are in a vertical plane
wavelength in a medium
𝜆n=𝜆/𝑛, where 𝜆 is the wavelength in vacuum, and 𝑛 is the index of refraction of the medium
Like all EM waves, the following relationship is valid in vacuum:
𝑐=𝜈𝜆, where 𝑐 is the speed of light, 𝜈 is the frequency, and 𝜆 is the wavelength.
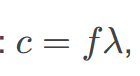
The wavelength 𝜆n of light in a medium with index of refraction
is given by the formula 𝜆n=𝜆/𝑛, indicating how the speed of light is altered in different media.
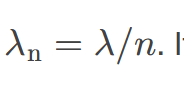
constructive interference (Young’s Double Slit Experiment)
occurs when waves combine in phase, resulting in increased amplitude and brightness at certain points.
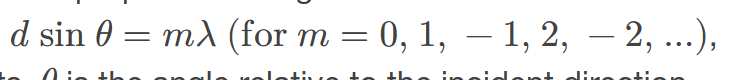
destructive interference (Young’s Double Slit Experiment)
occurs when waves combine out of phase, resulting in a lower intensity or cancellation of light at certain angles.
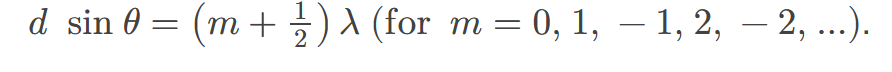
constructive interference for a diffraction grating
occurs when light waves from multiple slits align in phase, producing bright fringes and enhanced light intensity at specific angles.

destructive interference for a single slit
occurs when light waves from a single slit combine out of phase, leading to a reduction in intensity and dark regions in the diffraction pattern.

The intensity 𝐼 of polarized light after passing through a polarizing filter
is described by Malus's Law, which states that 𝐼 = 𝐼₀ cos²(θ), where 𝐼₀ is the initial intensity and θ is the angle between the light's polarization direction and the filter's axis.