PSIO 201 Exam 3
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
118 Terms
What are the functions of the muscular system?
Locomotion
Posture and body position
Control of body openings/passages
Regulation of body temp
Metabolism and endocrine functions
Is skeletal muscle contraction voluntary or involuntary?
Voluntary; requires nervous system input
*Some skeletal muscles activate automatically (diaphragm)
How do muscles work with bones to move?
Muscles pull on bones
Define origin and insertion
Origin: place where muscle starts on a bone
Insertion: place where muscle ends on a bone
They must be connected across a joint
Define flexion and extension
Flexion: decreasing angle at a joint
Extension: increasing angle at a joint
Define abduction and adduction (and DO IT!)
Abduction: movement away from midline (you’re getting abducted by aliens!)
Adduction: movement toward the midline (…and you’re being returned :))
Define pronation and supination (DO IT TOO!)
Pronation: Palm facing down
Supination: palm facing up
What is the movement around an axis?
Rotation
What is an agonist?
(aka prime movers)
the principal muscle in movement
What is an antagonist?
Muscle that opposes the movement of the agonist; return to initial position
What is a synergist?
Muscles that assist the agonist; additional force, stability, and control
What is a fixator?
A specific type of synergist; Stabilizer muscle prevents any unwanted movement
Inability to fixate muscles → limits range of motion
What are the basic fxns of muscle?
Generate tension (via contraction)
What is reverse muscle action?
The ORIGIN moving toward the insertion (i.e. pull ups)
What is mechanical advantage? What is the tradeoff?
The most efficient a muscle can move based on the effort:load ratio
Greater distance between effort and fulcrum [than load and fulcrum]
Tradeoff: same force across a longer distance
What is the “fulcrum”, “load”, and “effort” in the body?
Fulcrum: joints
Effort: tension in muscle
Load: weight
What is the formula for a first class lever?
Give an example
e F l
Nodding yes
E: neck muscles pulling down
F: atlanto-occipital joint
L: mass of the head
*Seesaw
What is the formula for a second class lever?
Give an example
f L e
Standing on tip toes
F: ball of toes
L: weight of body on foot
E: body mass
*Wheelbarrow
What is the formula for a third class lever?
Give an example
f E l
Biceps curl
F: Elbow
E: Biceps pulling on radius
L: weight of hand
What is hyperplasia and hypertrophy?
Hyperplasia: increase in cell NUMBER
muscle dev. before birth
Hypertrophy: increase in cell SIZE
muscle dev. after birth
What do tendons do?
Attach muscle to bone
What is the C.T. surrounding muscles? What is inside the muscle?
Epimysium (collagen CT)
Fasicles
What are fascicles? What C.T. surrounds them?
Bundles of muscle fibers
Perimysium (collagen CT
What CT surrounds muscle fibers? What are membrane are muscle fibers covered in?
Endomysium
Sarcolemma
(Both collagen CT)
What are myocytes made of?
Myofibrils
Made up of primarily actin and myosin
What characteristics do perimysium, endomysium, and epimysium have that are important for the muscle?
Transmits generated force where the muscle attaches
Spring-like properties aiding in movement efficiency
What is the myotendinous junction?
(White part)
CT that pulls on the bone through which muscle generates force
repetitive movements = repetitive stressors on these junctions
What separates muscle compartments?
Fascia: a connective tissue border
What is the superficial fascia?
Network of CT all over the body
Collagen & elastin
“Liquid crystal”-like: can change between liquid and solid
Receptors (pain and mechano)
Pain: 5-10x more pain receptors in fascia than in muscle
Mechano: body’s location in 3D space
Provides stability in body movement
True or false: the contraction of skeletal muscle leads to release hormones into the blood stream
True
True or false: flexing the forearm via the biceps brachii is an example of a second class lever
False; that is a third class lever
What are the three units of subcellular organization?
Conduction of electrical signals
Via sarcolemma + T-tubules
Control
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Contraction
Myofibrils
Actin
Myosin
What is the function of the t-tubules?
Allows for the action potential to reach the interior of the muscle cell
What is the function of the sarcoplasmic reticulum?
Stores Ca+
What makes up the “triad”?
T-tubules
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
terminal cisterns
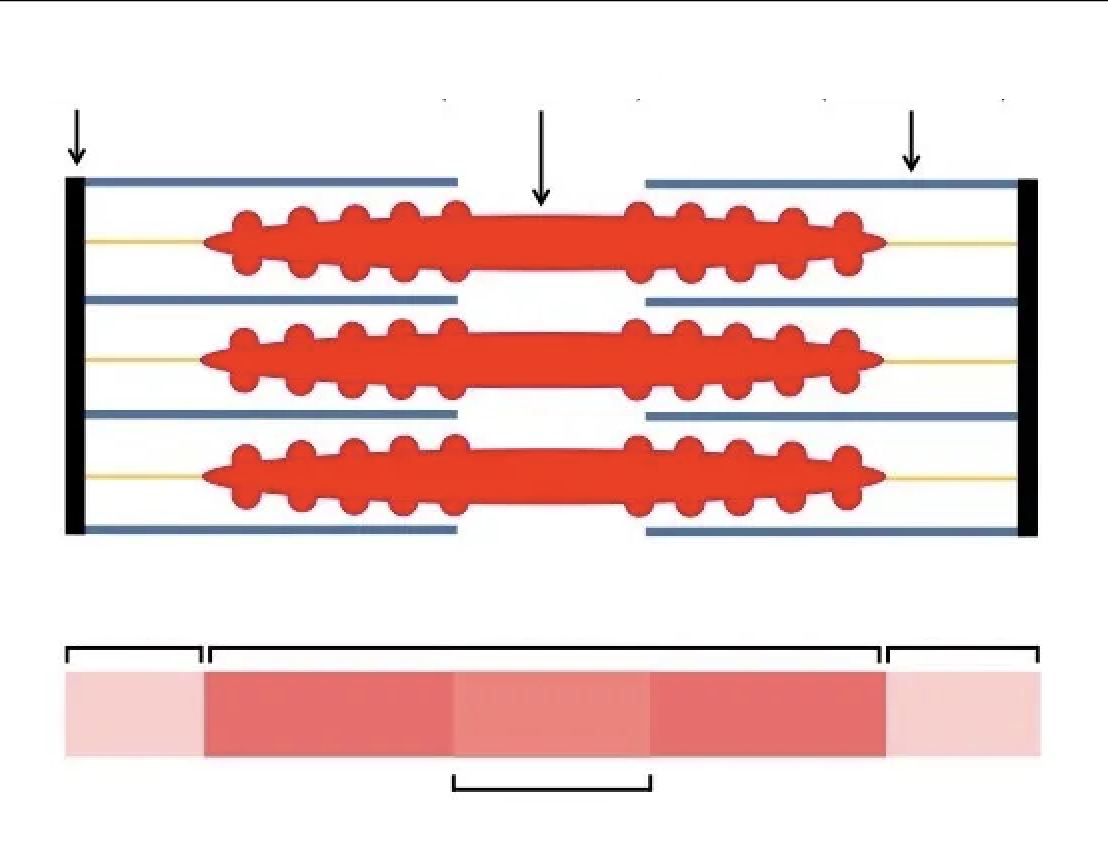
Label this diagram
*Missing M-line and Zone of Overlap
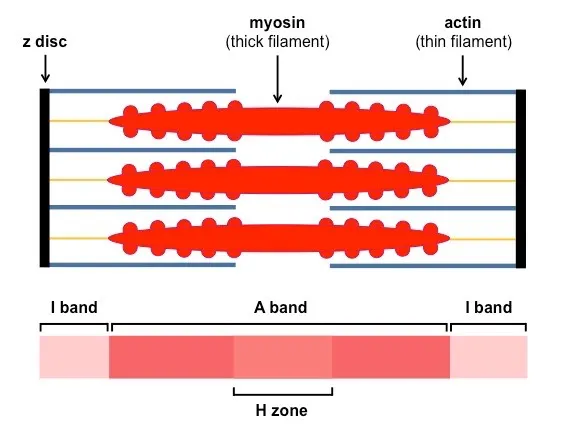
What effects does contraction have on the sarcomere?
Z-lines are brought closer together
H zone is gone
I band decreases
What part of the sarcomere does nebulin form?
Length of the thin filament
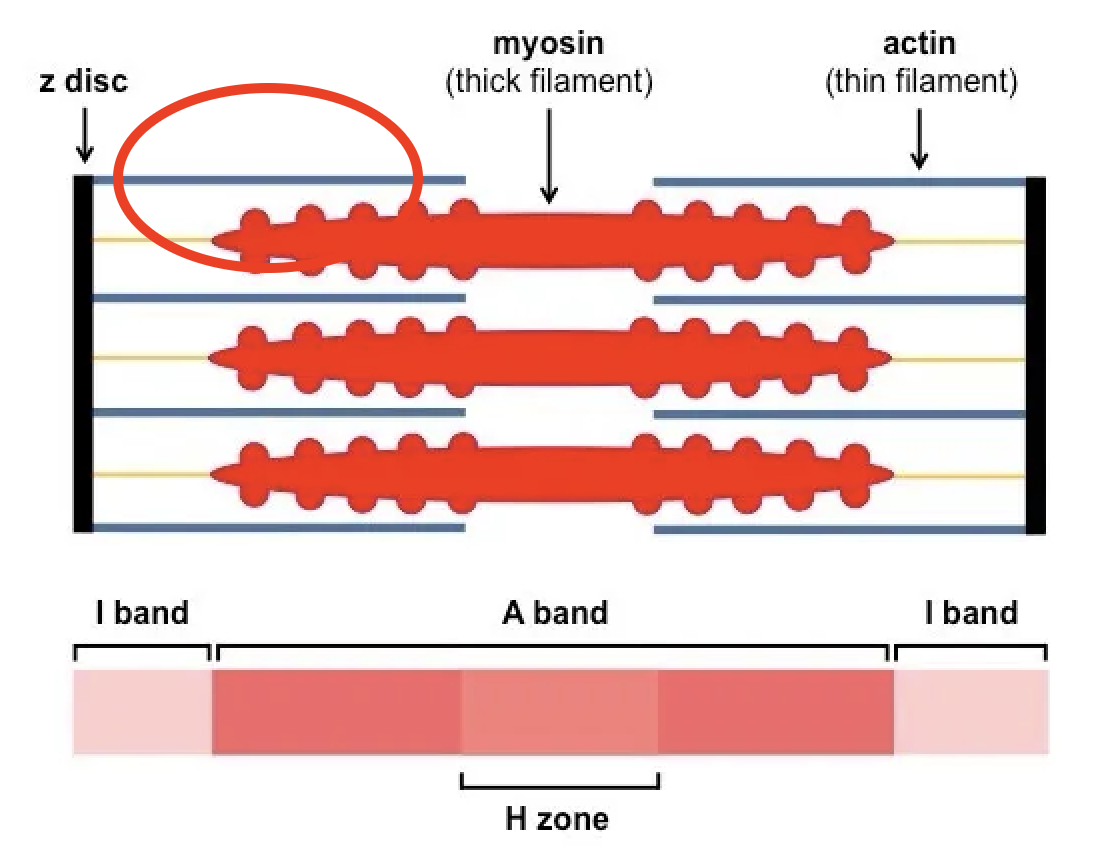
What part of the sarcomere does α-actinin form?
The Z-line; anchors thin filaments
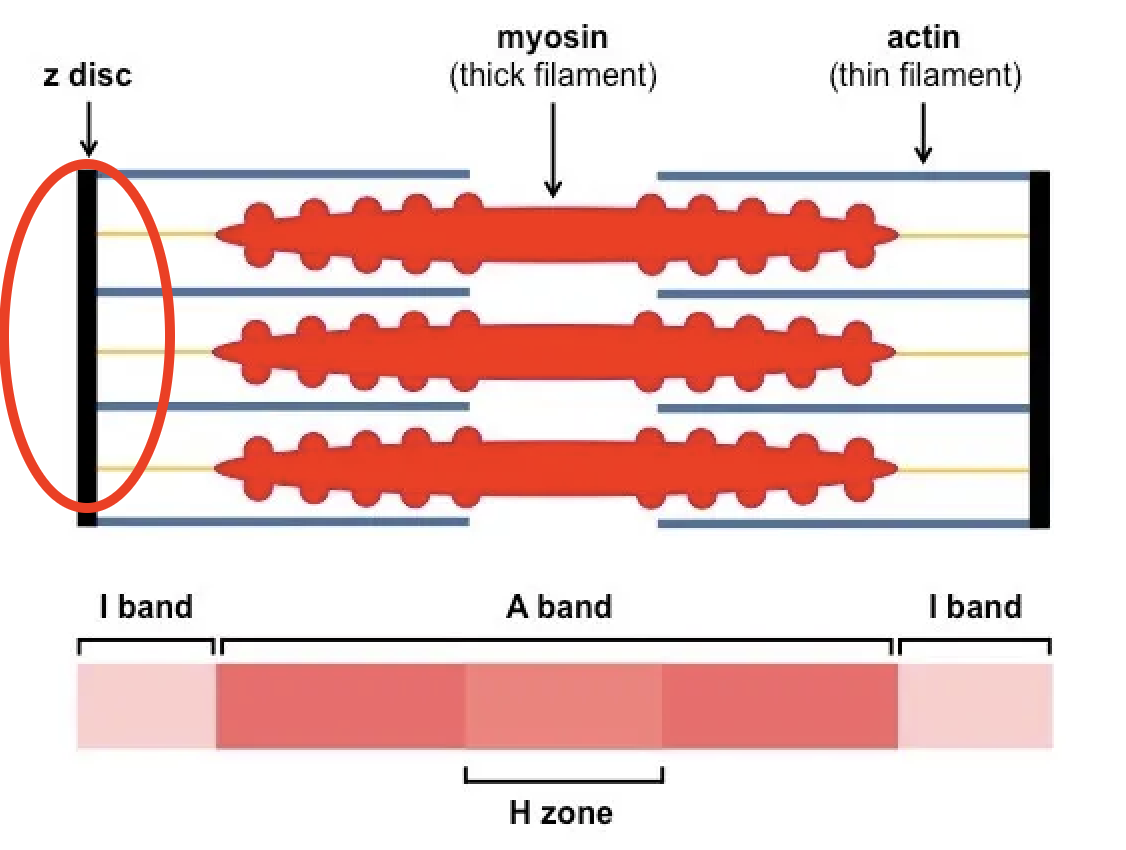
What part of the sarcomere does titin form?
Spring-like protein, connects z-discs to the M line
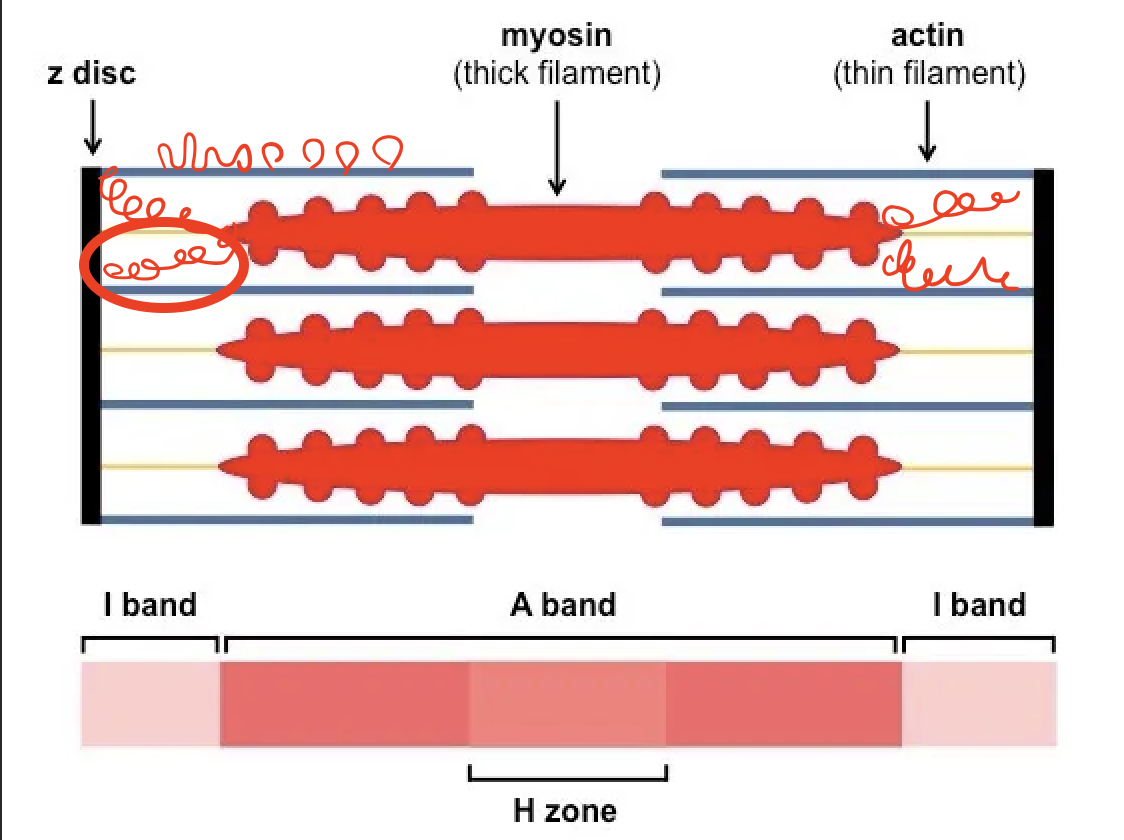
What part of the sarcomere does myomesin form?
A chain in the middle of the sarcomere; links adjacent thick filaments
What does dystrophin do for the sarcomere?
Connects it to the sarcolemma → CT → tendon → bone
How can myosin bind to actin?
Troponin binds to Ca+ which moves tropomyosin away from actin’s binding site. Myosin heads bind here.
What are the components of myosin?
Myosin heavy chain
Has a head and tail
Actin binding site
ATPase site
What is a crossbridge? Where does it form?
Forms in the Zone of Overlap; where actin and myosin bind
How do neurons and muscle cells generate electrical signals?
Controlling movement of ions across their membranes
What causes depolarization in the myocyte?
Influx of Na+ ions
What neurotransmitter is released inside the sarcolemma? And what enzyme get rids of it?
Acetylcholine (ACh)
acetylcholinesterase (AChE) to cease action potentials
What is the specialized region on the sarcolemma for the NMJ?
Motor end plate
What does deep fascia do?
Separates muscle compartments
What does superficial fascia do?
Anchors muscle to skin
What are the steps of crossbridging?
Readying of the Myosin Head
ATP hydrolysis separates
Leads to cocking of the head
Binding myosin and actin
If calcium is present
“Power stroke” - myosin pulls actin
Phosphate pops off the myosin head
Detachment - requires ATP (binds to rigor complex)
What causes rigor mortis?
Without ATP generation, you cannot detach myosin and actin
What makes up the neuromuscular junction?
Axon terminal
Synaptic cleft
Motor end plate
Sarcolemma
When the action potential reaches the axon terminal, what triggers an influx of calcium?
Calcium voltage gate
What does an influx of calcium do?
Encourages the synaptic vessels to fuse with the axon terminal / release ACh into the synaptic cleft
What does ACh bind to on the motor end plate?
Nicotinic ACh receptors
When the nicotinic ACh receptors bind with ACh, what happens?
Influx of Na+ into the muscle cell
What does an influx of Na trigger?
It triggers the voltage-sensitive protein on the t-tubules
What does the voltage sensitive protein do?
Opens the Ryanodine receptor (cap) of the sarcoplasmic reticulum
When the Ryanodine receptor is ‘opened’, what happens?
The intracellular concentration of Ca+ increases
^[Ca]i
What happens when the intracellular concentration of Ca+ increases?
Calcium binds to troponin… moving tropomyosin… myosin binds to actin
What makes up a motor unit?
Motor neuron + muscle fibers it innervates
What is the difference between a large v.s. small motor unit?
The # of fibers a neuron innervates (controls)
What does the calcium pump (on the SR) do?
Cleans up calcium, pumps it back into the sarcoplasmic reticulum
What is the function of the small motor units?
aka slow twitch fibers, fine motor control
What is the function of the intermediate motor units?
fast twitch fibers; moderate force and endurance activities
What is the function of the large motor units?
Fast twitch fibers, contract powerfully and fatigue quickly
What characteristics of muscle contraction do motor units determine?
Size & force
Speed is determined by ___
muscle fiber types
What is temporal summation?
Increasing the frequency of nerve impulses to a muscle; T = time
What is spatial summation?
Allows for more muscle fibers to contract; S = surface area
What is isometric contraction?
Muscle generates tension w/o changing the length
What is isotonic contraction?
Muscle changes size while contraction?
What are the two different types of isotonic contraction?
Eccentric: lengthens under contraction (lowering a dumbbell under control)
Concentric: shortens under contraction (lifting a dumbbell)
What begins the process of relaxation?
ACh esterase breaks down ACh
Ca ATPase cleans up all of the Ca
Allow titin to return to the original length
What does the liver do for muscle energetics?
Chains together glucose to make glycogen: for energy storage
Gets first dibs on substances
What are the two types of metabolism?
Aerobic metabolism
Anaerobic metabolism
Describe aerobic metabolism
Glucose breaks down into two 3-carbon molecules (pyruvate)
One pyruvate heads to the mitochondria to generate lots of ATP
Oxygen is needed in the mitochondria
Describe anaerobic metabolism
Glucose breaks down into two 3-carbon molecules (pyruvate)
The other pyruvate forms lactate → leaves cell, goes into blood
What is the phosphagen system?
Quickest way to make ATP; only lasts 15 seconds
Creatine phosphate: stores energy within the bonds
Hydrolysis of ATP
What is the timeline for ATP usage in high intensity activity?
ATP-Creatine phosphate (15 seconds)
Glycolysis (1-2 min)
Anaerobic metabolism (prolonged, lower intensity activity ~40 min)
What are the systems involved in fatigue?
Psychological, nervous system, muscular system
What are some of the possible causes of fatigue?
Depletion of ATP & CP
Glycogen depletion
Metabolic acid production
H+ from hydrolysis
Phosphate levels
Ion imbalances
What happens when you load your blood with glucose?
The pancreas releases insulin
Binds to receptors of the skeletal muscle
Increases glucose transporters to the sarcoplasm
*Exercise also does this!
What does creatine kinase do?
Takes the phosphate from creatine phosphate and attaches it to ADP → ATP
Pyruvate + ___ = latate
H+ ion from hydrolyzed ATP
What process occurs as a product of oxygen debt?
The Cori Cycle
Briefly describe the Cori Cycle
Glucose undergoes glycolysis in the muscles, resulting in the production of lactate
The liver then takes lactate and forms glucose through gluconeogenesis
What is the purpose of the Cori Cycle?
Restore glucose/glycogen
Resynthesize creatine phosphate
Replace oxygen removed from myoglobin
What is VO2 max?
Max oxygen consumption during exercise; associated with longevity
What are the three types of muscle contraction?
Eccentric: muscle lengthening during contraction (more damage)
Concentric: muscle shortening during contraction
Isometric: No shortening/lengthening
What are the three types of motor units?
Slow oxidative fibers (type I)
Fast oxidative glycolytic (type IIa)
Fast glycolytic fibers (type IIx)
What are the characteristics of slow oxidative fibers?
Slow speed
Small amount of force
High resistance to fatigue
Posture, marathon, etc.
High in mitochondria
What are the characteristics of fast oxidative glycolytic fibers?
Fast speed
Medium amount of force
Medium resistance to fatigue
Walk, high rep strength
What are the characteristics of fast glycolytic fibers?
Fast speed
High force
Low resistance to fatigue
Sprinting, power lifting
Low in mitochondria
Temporal Summation
Increase frequency of electrical stimuli
Spatial summation
Recruiting more motor units → more tension
Briefly describe the length-tension relationship
Bigger zone of overlap = more tension
BUT too much overlap = bad
What is power?
Speed * Force
(that a muscle generates)