BMD310 - Exam 4
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/290
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:22 AM on 11/11/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
291 Terms
1
New cards
closed
arteries, veins, capillaries
arteries, veins, capillaries
The cardiovascular system consists of the heart and a ----- system of blood vessels called -----, -----, -----.
2
New cards
arteries
Transport blood away from the heart.
Most carry OXYGENATED blood, except for the pulmonary ones.
Most carry OXYGENATED blood, except for the pulmonary ones.
3
New cards
veins
Transport blood back to the heart
Most carry DEOXYGENATED blood, except for the pulmonary ones.
Most carry DEOXYGENATED blood, except for the pulmonary ones.
4
New cards
circulatory
The cardiovascular system containing arteries, veins, and capillaries is also called the ------ system.
5
New cards
mediastinum
left
left
The heart is located deep to the sternum in the ----- of the thoracic cavity.
- superior to the diaphragm
- 2/3 of the heart is ---- of the midline.
- superior to the diaphragm
- 2/3 of the heart is ---- of the midline.
6
New cards
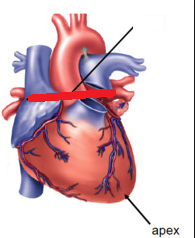
base of heart
superior border of the heart
- formed by the atria (primarily the left atrium), ascending aorta, and pulmonary trunk
- formed by the atria (primarily the left atrium), ascending aorta, and pulmonary trunk
7
New cards
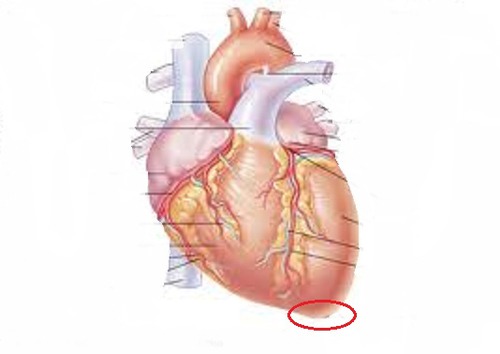
apex of the heart
inferior border of the heart
formed by the left ventricle
- PMI: point of maximal impulse
formed by the left ventricle
- PMI: point of maximal impulse
8
New cards
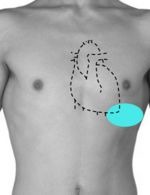
Point of maximal impulse (PMI)
the point where the apex of the heart touches the anterior chest wall and heart movements are most easily observed and palpated
- palpable left midclavicular line 5th intercostal space.
- palpable left midclavicular line 5th intercostal space.
9
New cards
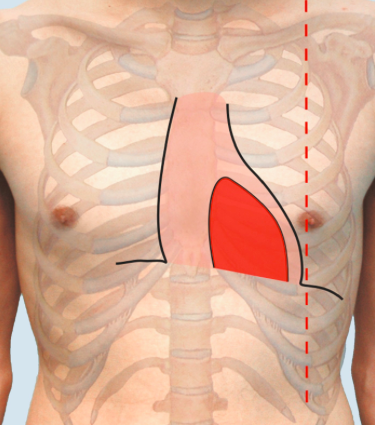
midclavicular line
imaginary vertical line bisecting the middle of the clavicle in each hemithorax
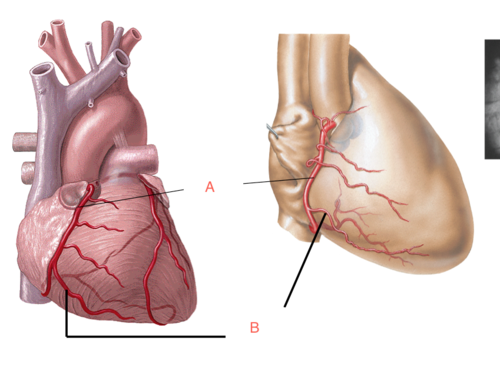
10
New cards
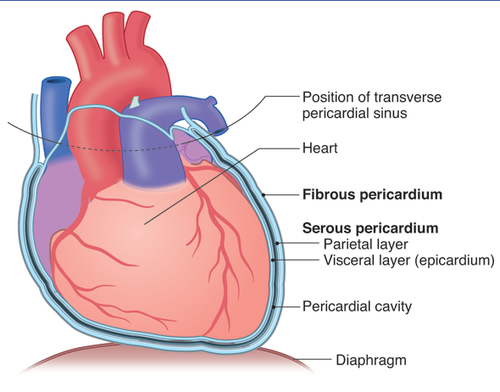
pericardium
restricts movement and stabilizes (gives support) the heart in the thoracic cavity from the surrounding organs
- the outer sac
- the outer sac
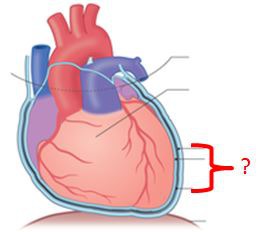
11
New cards
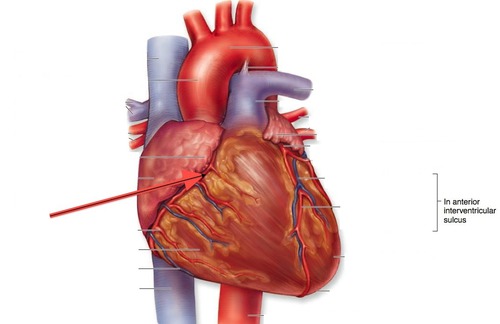
fibrous
serous
parietal
visceral
serous
parietal
visceral
In the pericardium, there is....
1. ----- pericardium: dense, inelastic irregular connective tissue (outer layer)
2. ----- pericardium: inner lining
a. ----- layer: fused to the fibrous pericardium
b. ----- layer: fused to the heart surface
1. ----- pericardium: dense, inelastic irregular connective tissue (outer layer)
2. ----- pericardium: inner lining
a. ----- layer: fused to the fibrous pericardium
b. ----- layer: fused to the heart surface
12
New cards
Epicardium
visceral layer of the serous pericardium
- contains blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves that supply the myocardium
- contains blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerves that supply the myocardium
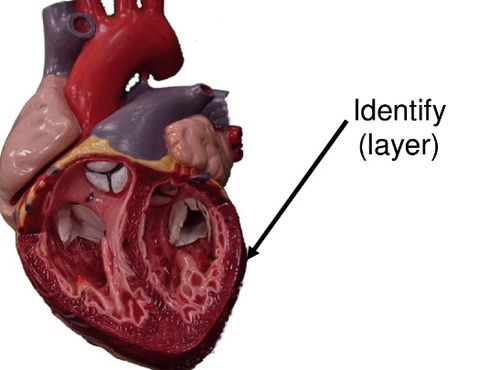
13
New cards
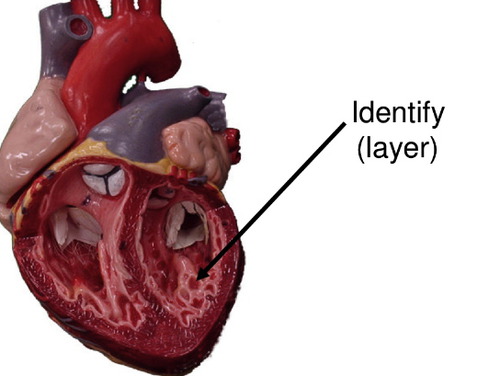
myocardium
composed of cardiac muscle tissue
- striated involuntary muscle
- contraction generates the force necessary to pump blood
- striated involuntary muscle
- contraction generates the force necessary to pump blood
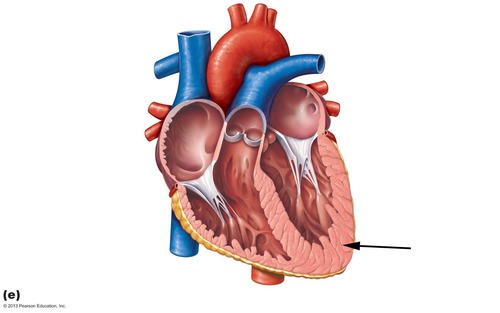
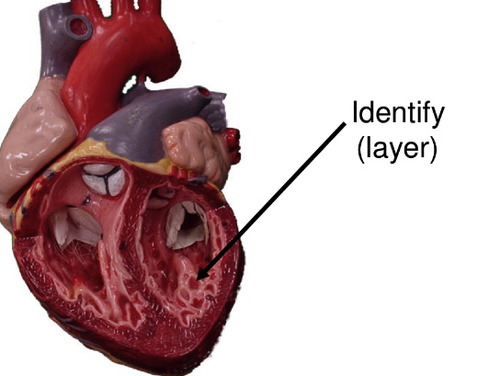
14
New cards
Endocardium
inner lining which makes the heart smooth
- composed of simple squamous epithelium cells and underlying layer of connective tissue
- lines the chambers of the heart and valves
- composed of simple squamous epithelium cells and underlying layer of connective tissue
- lines the chambers of the heart and valves
15
New cards
endothelium
In the endocardium, there is the ----- which continuous epithelium that lines the blood vessels.
16
New cards
epicardium, myocardium, endocardium
The heart wall structure is formed by the -----, ------, and -----.
17
New cards
fibrous pericardium
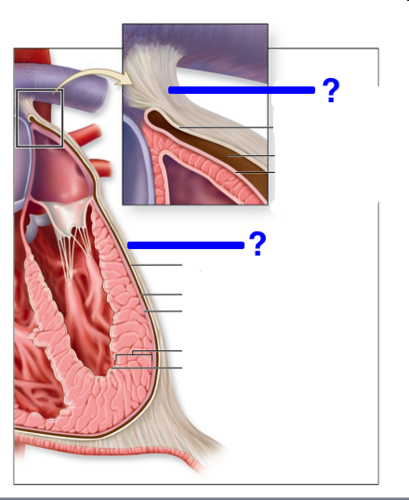
18
New cards
serous pericardium (parietal layer)
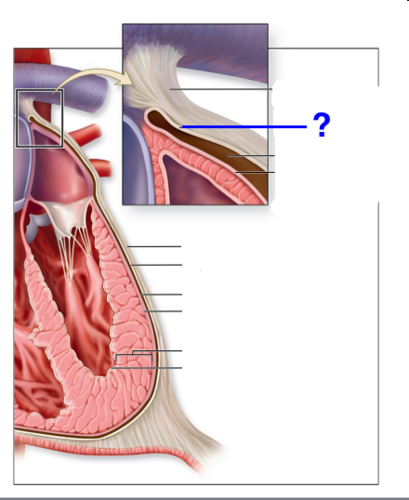
19
New cards
serous pericardium (visceral layer)
epicardium
20
New cards
myocardium
muscular, middle layer of the heart
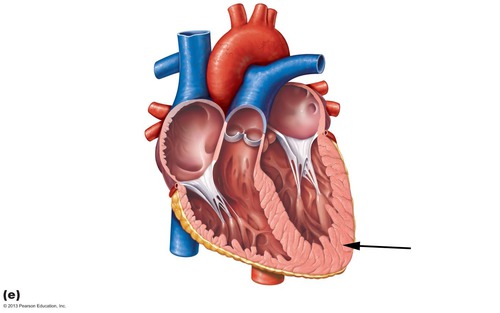
21
New cards
trabeculae of heart
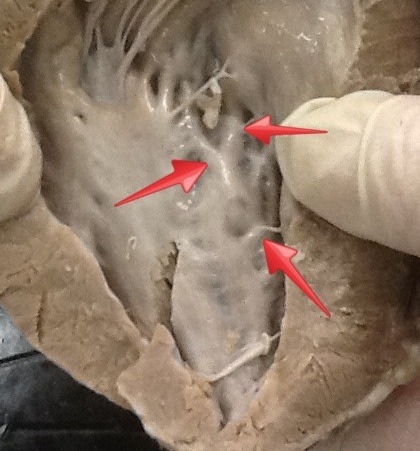
22
New cards
endocardium
inner endothelial lining covering trabeculae
23
New cards
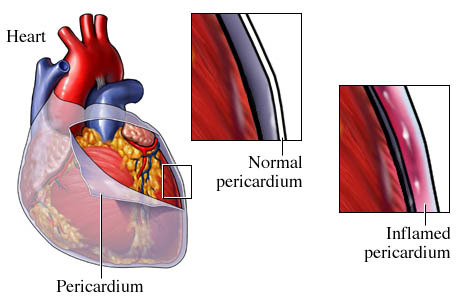
pericarditis
inflammation of the pericardium
- typically an infection of the heart
- layers can adhere to one another
- interferes with the heart contractions
- typically an infection of the heart
- layers can adhere to one another
- interferes with the heart contractions
24
New cards
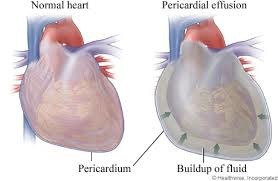
pericardial effusion
collection of fluid within the pericardial cavity
- common causes are pericarditis, trauma (bleeding into the space), heart failure
- can lead to tamponade
- common causes are pericarditis, trauma (bleeding into the space), heart failure
- can lead to tamponade
25
New cards
tamponade (cardiac)
compression of the heart by fluid that restricts heartbeat
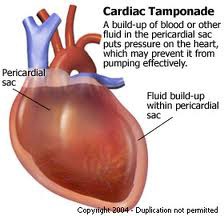
26
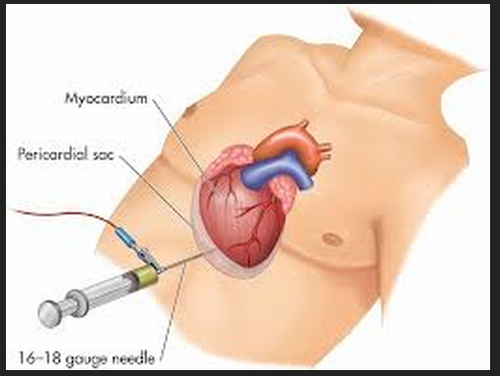
New cards
pericardiocentesis
drainage of fluid from the pericardial cavity; Is usually necessary to relieve cardiac tamponade
27
New cards
Atria
right
left
ventricles
right
left
right
left
ventricles
right
left
Four chambers of the heart:
1. ----- : blood coming into the heart
- thin walled chambers located superiorly
- receives blood from the veins
a. -----: receives deoxygenated blood
b. -----: receives oxygenated blood
2. ------: blood is leaving the heart
- thicker walled chambers located inferiorly
- pumps blood into the arteries
a. -----: pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs (through the pulmonary artery)
b. -----: pumps oxygenated blood to the body (through the aorta)
1. ----- : blood coming into the heart
- thin walled chambers located superiorly
- receives blood from the veins
a. -----: receives deoxygenated blood
b. -----: receives oxygenated blood
2. ------: blood is leaving the heart
- thicker walled chambers located inferiorly
- pumps blood into the arteries
a. -----: pumps deoxygenated blood to the lungs (through the pulmonary artery)
b. -----: pumps oxygenated blood to the body (through the aorta)
28
New cards
atria
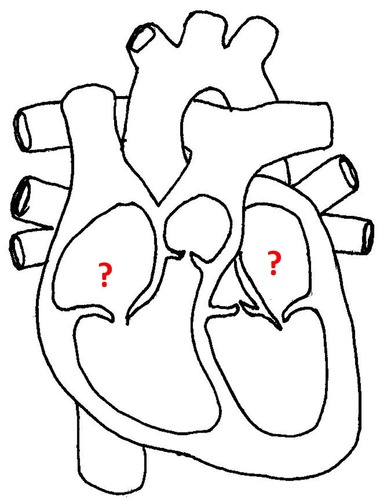
29
New cards
ventricles of heart
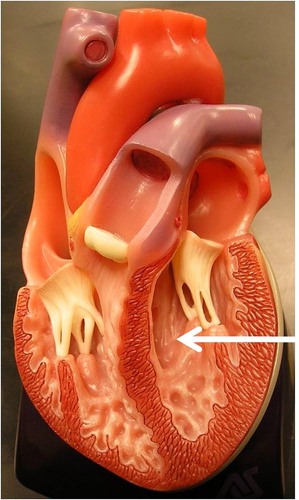
30
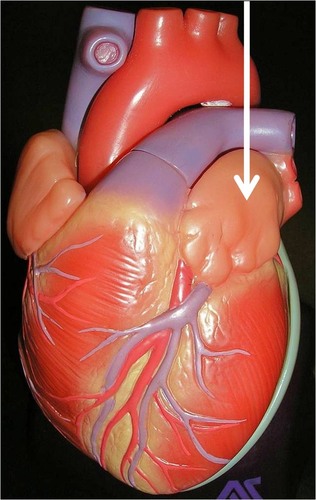
New cards
auricle
increases in volume when atria are filling with blood
31
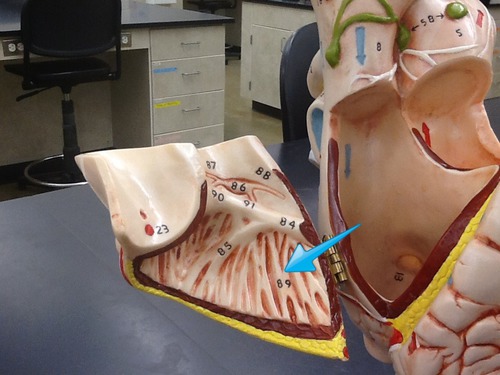
New cards
pectinate mm.
muscular ridges that line the auricle and anterior wall
32
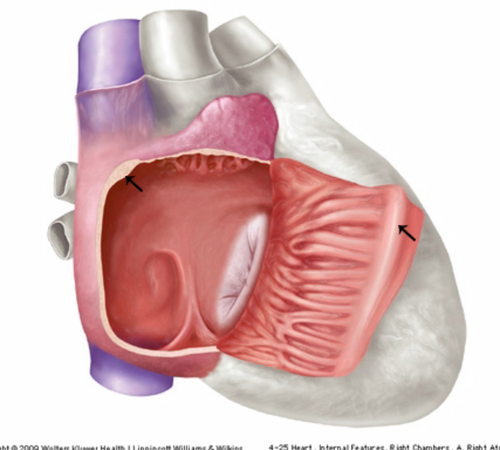
New cards
crista terminalis
smooth ridge of tissue that extends from the SVC to the IVC
33
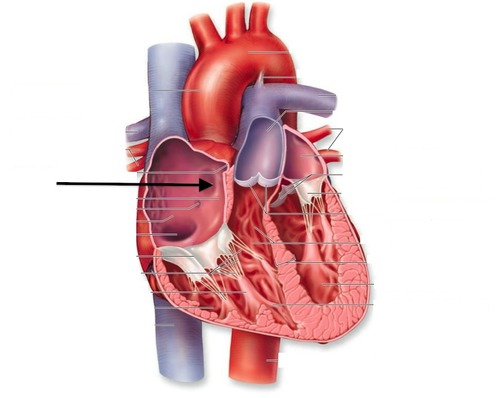
New cards
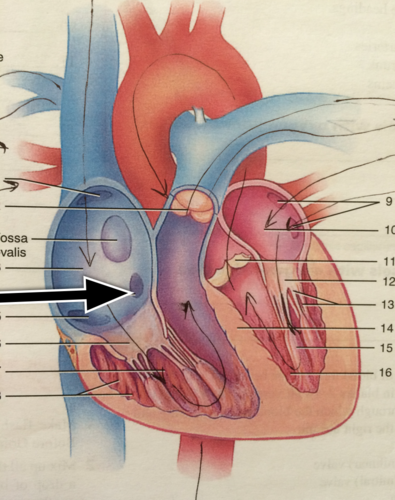
fossa ovalis
former location of the fetal foramen oval, which shunted blood from the right atrium to the left atrium during fetal development
34
New cards
Thebesian valve
valve of coronary sinus
35
New cards
Inferior Vena Cava (IVC)
returns blood from portions of the body below the heart
36
New cards
interarterial septum
separating wall or partition between the right and left atria
37
New cards
superior vena cava
A vein that is the second largest vein in the human body and returns blood to the right atrium of the heart from the upper half of the body.
38
New cards
moderator band
connects the base of the anterior papillary muscle to the inter ventricular septum
- septal marginal trabeculae
- septal marginal trabeculae
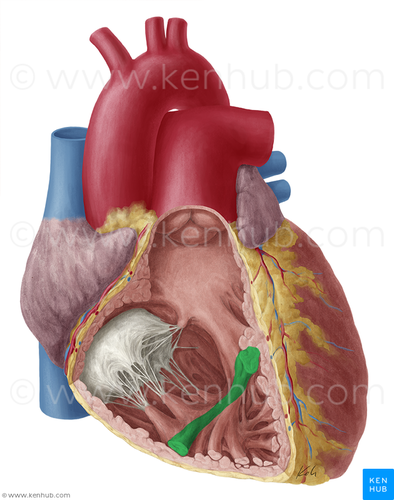
39
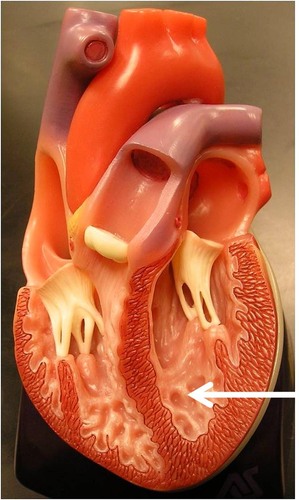
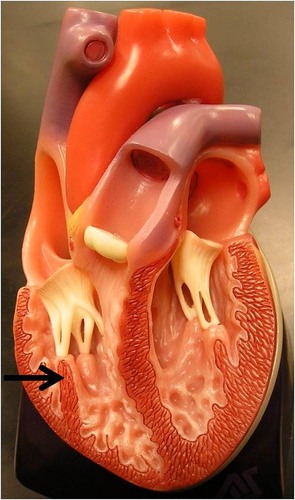
New cards
trabeculae carneae
large, smooth, irregular muscle ridges
40
New cards
chordae tendineae
prevent valve from everting and flapping into the atrium when the right ventricle is contracting
41
New cards
Papillary mm.
Stabilize the tricuspid valve to help prevent regurgitation of blood back into the right atrium during systole
- contract, pull on cords, and hold valve closed
- contract, pull on cords, and hold valve closed
42
New cards
tricuspid valve
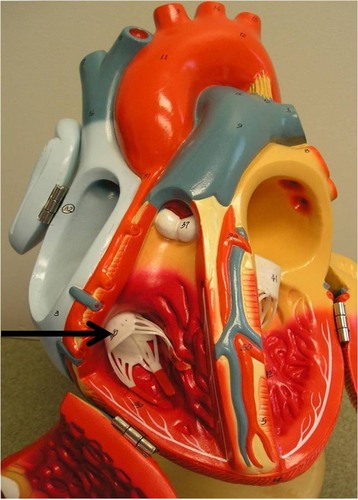
43
New cards
interventircular septum
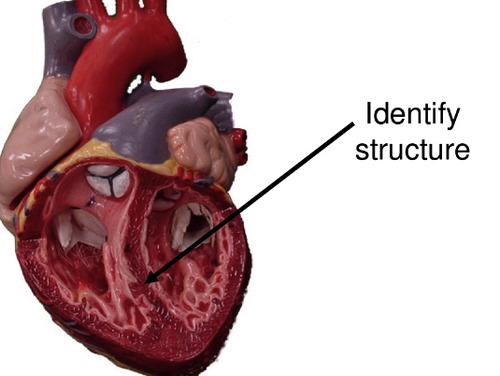
44
New cards
pulmonary semilunar valve
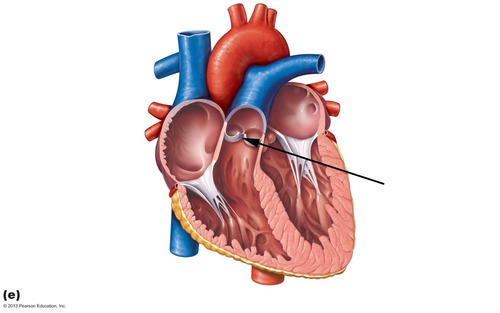
45
New cards
mitral valve
valve between the left atrium and the left ventricle; bicuspid valve
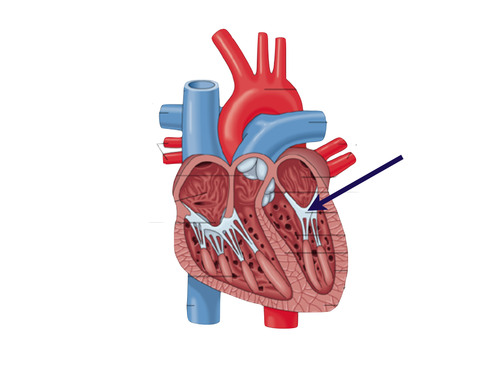
46
New cards
pulmonary arteries
carry deoxygenated blood out of the right ventricle and into the lungs
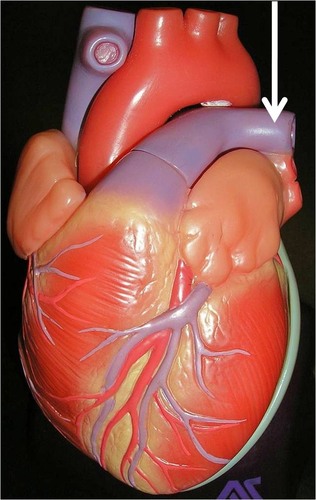
47
New cards
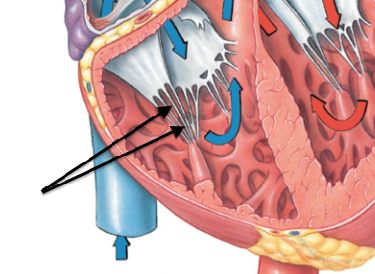
semilunar valves
passive valves- NO muscles to hold them closed
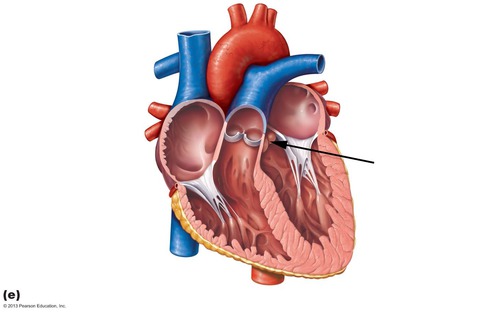
48
New cards
aortic semilunar valve
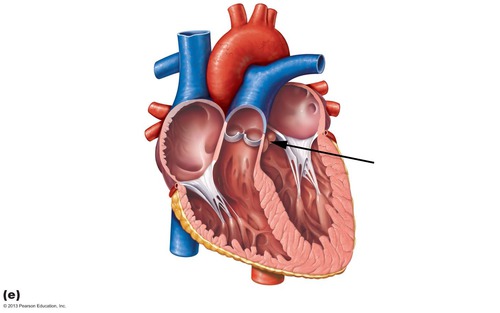
49
New cards
atrioventricular valves
active valves- papillary muscles contract to hold valves closed
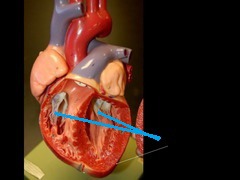
50
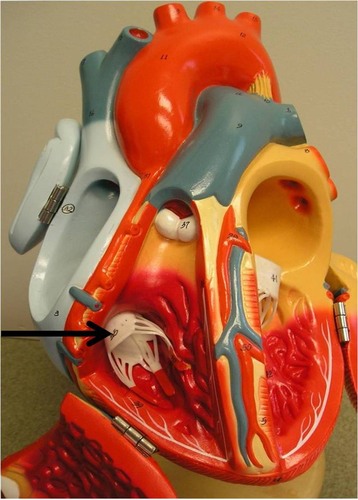
New cards
tricuspid valve
valve between the right atrium and the right ventricle
51
New cards
ventricular diastole
ventricles relax and fill with blood passing through the tricuspid and bicuspid valves
- the pulmonary and aortic valves are closed to prevent regurgitation of blood into the ventricles.
- the pulmonary and aortic valves are closed to prevent regurgitation of blood into the ventricles.
52
New cards
Ventricular Systole
ventricles contract and force blood past the pulmonary and aortic valves
- papillary muscles and tension of chordae tendineae keep the tricuspid and bicuspid valves
- papillary muscles and tension of chordae tendineae keep the tricuspid and bicuspid valves
53
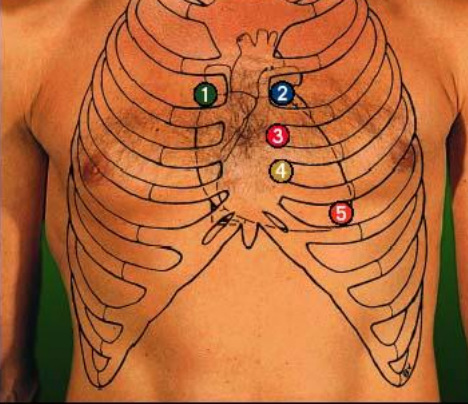
New cards
aortic
sternal margin of R 2nd intercostal
number 1
number 1
54
New cards
pulmonary
sternal margin of L 2nd intercostal
55
New cards
Right AV valve (tricuspid)
sternal margin of L 5th intercostal
56
New cards
Left AV Valve (bicuspid)
midclavicular line of L 5th intercostal
57
New cards
heart murmur
an abnormal sound produced by turbulent blood flow
- first indication of heart valve problems
- first indication of heart valve problems
58
New cards
valvular insufficiency
cardiac valve leakage because valve cusps do not close properly
- leads to regurgitation of blood back through the valve
- caused by inflammation or disease
- leads to regurgitation of blood back through the valve
- caused by inflammation or disease
59
New cards
valvular stenosis
incomplete opening of valves because of partial fusion of valve cusps
- leads to resistance of flow of blood - decreasing chamber output
- chamber undergoes hypertrophy and dilates - both conditions that may have dangerous consequences
- primary cause - Rheumatic heart disease; which typically follows a streptococcus infection of the throat
- leads to resistance of flow of blood - decreasing chamber output
- chamber undergoes hypertrophy and dilates - both conditions that may have dangerous consequences
- primary cause - Rheumatic heart disease; which typically follows a streptococcus infection of the throat
60
New cards
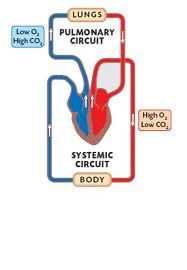
pulmonary circulation
transports deoxygenated blood form the right side of the heart to the lungs
61
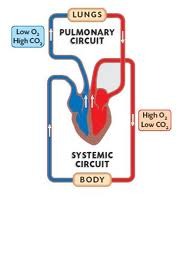
New cards
systemic circulation
transports oxygenated blood from the left side of the heart to the body
62
New cards
Right Atrium receives deoxygenated blood from the systemic circulation and the heart• Three major vessels: (1) superior and (2) inferior venae cavae, and (3) coronary sinus
Step 1 of blood circulation through the heart:
63
New cards
Deoxygenated blood is pumped through the Tricuspid Valve to get to the Right Ventricle
Step 2 of blood circulation through the heart:
64
New cards
Then, deoxygenated blood is pumped through the Pulmonary Semilunar Valve and the Pulmonary Arteries to get to the Lungs
Step 3 of blood circulation through the heart:
65
New cards
Left Atrium receives oxygenated blood from the lungs through the Pulmonary Veins
Step 4 of blood circulation through the heart:
66
New cards
Oxygenated blood is pumped through the Bicuspid Valve to get to the Left Ventricle
Step 5 of blood circulation through the heart:
67
New cards
Then, oxygenated blood is pumped through the Aortic Semilunar Valve and the Aorta to get to the Body
Step 6 of blood circulation through the heart:
68
New cards
right coronary artery
artery vascularizing the right side of the heart
69
New cards
right marginal artery
serves the myocardium of the lateral right side of the heart
70
New cards
left coronary artery
supplies blood to the left ventricle, left atrium, and interventricular septum
71
New cards
circumflex artery
supplies the left atrium and the posterior walls of the left ventricle
72
New cards
anterior interventricular artery
Also called the left anterior descending artery
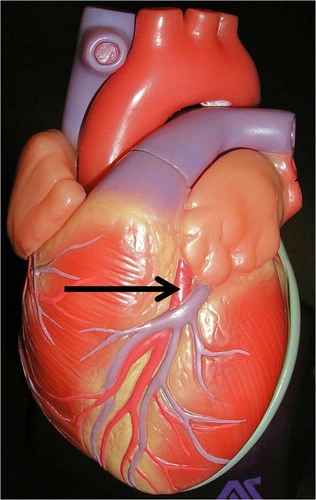
73
New cards
posterior interventricular artery
runs to the heart apex and supplies the posterior ventricular walls
74
New cards
sulcus
sulci
sulci
In the coronary arteries, the coronary ---- and interventricular ---- mark the boundaries of the four heart chambers.
75
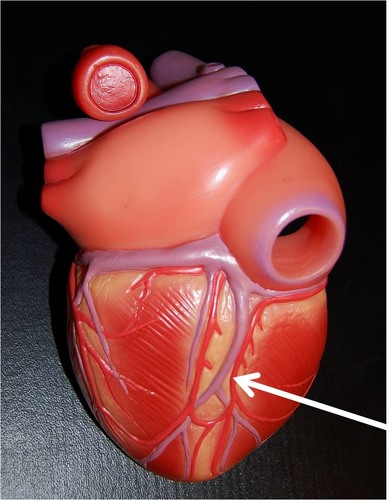
New cards
coronary sulcus
groove between the atria and ventricles that extends to the circumference of the heart
- left and right coronary arteries
- left circumflex artery
- left and right coronary arteries
- left circumflex artery
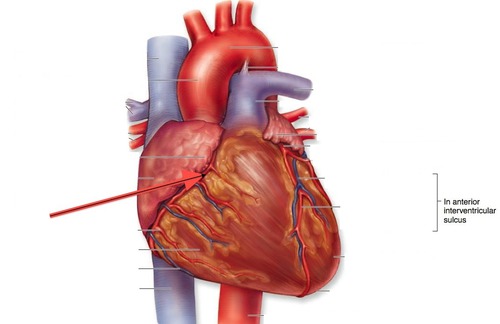
76
New cards
interventricular sulcus
groove between the ventricles that extends inferiorly from the coronary sulcus toward the apex
- anterior interventricular artery (LAD)
- posterior interventricular artery
- anterior interventricular artery (LAD)
- posterior interventricular artery
77
New cards
myocardial infarction
commonly referred to as a heart attack
- an area of myocardium that has undergone necrosis, due to the obstructed blood flow
- potentially lethal condition resulting from sudden and complete occlusion of a coronary artery
- an area of myocardium that has undergone necrosis, due to the obstructed blood flow
- potentially lethal condition resulting from sudden and complete occlusion of a coronary artery
78
New cards
ischemia
hypoxia
infarct
hypoxia
infarct
myocardial infarction:
1. -----: reduced blood flow
2. -----: reduced oxygen
3. -----: death of tissue due to lack of blood supply
1. -----: reduced blood flow
2. -----: reduced oxygen
3. -----: death of tissue due to lack of blood supply
79
New cards
1. The anterior IV (LAD) branch of the LCA (40-50%)
2. The RCA (30-40%)
3. The circumflex branch of the LCA (15-20%)
2. The RCA (30-40%)
3. The circumflex branch of the LCA (15-20%)
What are the 3 most common sites of coronary artery occlusion?
80
New cards
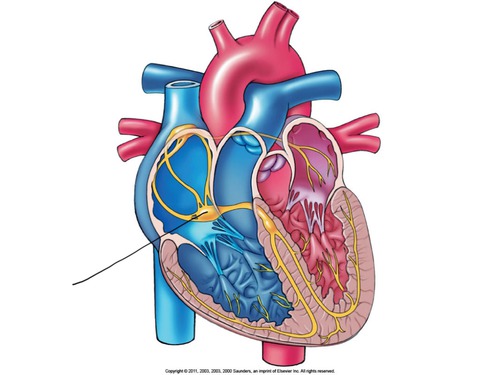
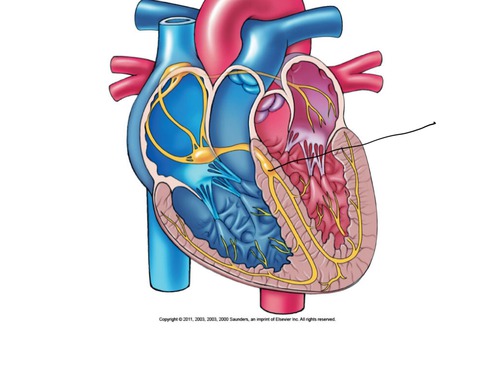
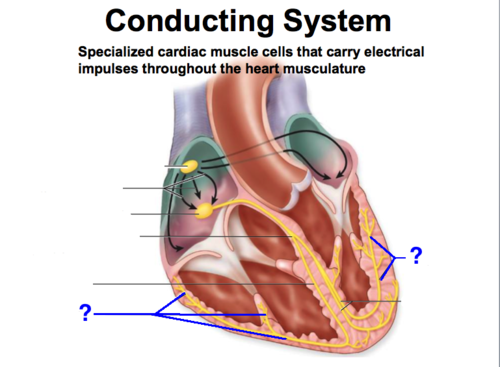
sinoatrial node (SA node)
pacemaker of the heart
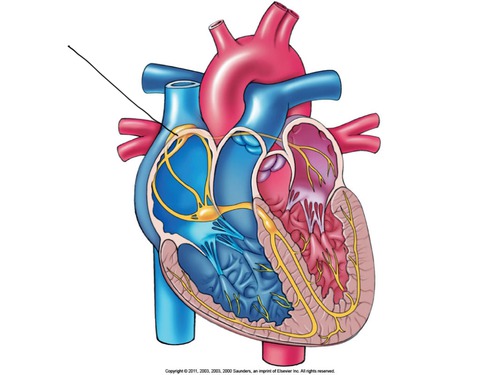
81
New cards
atrioventricular (AV) node
a node of specialized heart muscle located in the septal wall of the right atrium; receives impulses from the sinoatrial node and transmits them to the atrioventricular bundle
82
New cards
AV bundle (bundle of His)
fibers in the heart that relay a nerve impulse from the AV node to the ventricles
83
New cards
Purkinje fibers
fibers in the ventricles that transmit impulses to the right and left ventricles, causing them to contract
- in myocardium and under endocardium
- in myocardium and under endocardium
84
New cards
plasma (55%) and formed elements (45%)
A sample of whole blood is made up of ----- and -----.
85
New cards
plasma proteins and water
Plasma consists of ---- and -----.
86
New cards
platelets, white blood cells, and red blood cells (99.9%)
formed elements consists of -----, ------, and -----.
87
New cards
platelets
fragments of megakaryocytes critical for clotting
- not cells themselves
- not cells themselves
88
New cards
leukocytes
white blood cells; defense against infection
- neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, lymphocytes, monocytes
- neutrophils, eosinophils, basophils, lymphocytes, monocytes
89
New cards
erythrocytes
red blood cells
- deliver oxygen and remove carbon dioxide
- deliver oxygen and remove carbon dioxide
90
New cards
temperature
albumins
globulins
clotting factors
albumins
globulins
clotting factors
Plasma is the liquid fraction of the blood.
1. water: more than 90% of plasma by volume
- helps blood function as ----- buffer (absorbs heat)
2. plasma proteins:
-----: too large to leave the bloodstream; regulate osmolarity and function as carrier molecules
-----: also function as carrier proteins
-----: play an essential role in blood clotting
These are water soluble hormones
1. water: more than 90% of plasma by volume
- helps blood function as ----- buffer (absorbs heat)
2. plasma proteins:
-----: too large to leave the bloodstream; regulate osmolarity and function as carrier molecules
-----: also function as carrier proteins
-----: play an essential role in blood clotting
These are water soluble hormones
91
New cards
Buffy coat
erythrocytes
erythrocytes
formed elements include cells and their fragments
1. ----- -----: leukocytes and thrombocytes (white blood cells)
2. ------ : red blood cells
1. ----- -----: leukocytes and thrombocytes (white blood cells)
2. ------ : red blood cells
92
New cards
function
Erythrocyte structure complements -----.
93
New cards
biconcave
anucleate
anucleate
In erythrocytes:
------ shape allows red blood cells to bend, fold, and stack to prevent blockage in tiny blood vessels
- this also increases surface area for gas exchange
-------: non-mitotic, carry very little DNA, unable to synthesize proteins (lack a nucleus)
- prone to apoptosis
------ shape allows red blood cells to bend, fold, and stack to prevent blockage in tiny blood vessels
- this also increases surface area for gas exchange
-------: non-mitotic, carry very little DNA, unable to synthesize proteins (lack a nucleus)
- prone to apoptosis
94
New cards
erythropoiesis
----- is the process of red blood cell formation
95
New cards
adults
red bone marrow
reticulocyte
myeloid
4
spleen
red bone marrow
reticulocyte
myeloid
4
spleen
In erythropoiesis,
- you are not making many RBC's as ------
- The first step begins at ------ and the last step ends with the -----.
The ---- stem cell can become either a red or white blood cell.
RBC's last for about --- months and are then broken down by the -----
- you are not making many RBC's as ------
- The first step begins at ------ and the last step ends with the -----.
The ---- stem cell can become either a red or white blood cell.
RBC's last for about --- months and are then broken down by the -----
96
New cards
bone marrow transplant
- Treatment option for blood borne cancers (in combination with chemotherapy, immunosuppressive therapy)
- Bone marrow is obtained from an anesthetized donor through the iliac crest
- Donor is typically the individual themselves (autograft) or close relative (allograft)
- Replenishes blood cells to avoid permanent myoablation
- Bone marrow is obtained from an anesthetized donor through the iliac crest
- Donor is typically the individual themselves (autograft) or close relative (allograft)
- Replenishes blood cells to avoid permanent myoablation
97
New cards
EPO
The regulation of erythropoiesis is kept by the hormone ------, which signals the production of Red Blood Cells
98
New cards
maturation
blood doping
anemia
blood doping
anemia
In EPO,
- Hypoxia and testosterone both signal EPO release
• EPO drives erythrocyte -----
• "----- ------": artificially inducing polycythemia by taking testosterone, EPO or highly-packed RBC suspensions
• -------: blood disorders characterized by the body's failure to supply tissues with adequate O2
- Hypoxia and testosterone both signal EPO release
• EPO drives erythrocyte -----
• "----- ------": artificially inducing polycythemia by taking testosterone, EPO or highly-packed RBC suspensions
• -------: blood disorders characterized by the body's failure to supply tissues with adequate O2
99
New cards
Hemoglobin
----- reversibly binds to blood gases within erythrocytes.
100
New cards
oxyhemoglobin
deoxyhemoglobin
deoxyhemoglobin
In a hemoglobin molecule,
• Globular, tetrameric protein formed from 2 alpha and 2 beta chains (adult) or 2 alpha and 2 gamma chains (fetus)
• Each chain contains a heme group that binds oxygen using iron
• ------- = bound to O2
• ------- = no O2 bound
• Binding sites for O2 are cooperative
• Globular, tetrameric protein formed from 2 alpha and 2 beta chains (adult) or 2 alpha and 2 gamma chains (fetus)
• Each chain contains a heme group that binds oxygen using iron
• ------- = bound to O2
• ------- = no O2 bound
• Binding sites for O2 are cooperative