PSYCH 375: Cognition exam 1
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
mental modules (or organs)
-programmed by genes, shaped by evolution
-think in stages of info processing
-each module is independent of others
What are the questions we ask when deciding what to research
What is worth studying/ What’s important to explain
cognitive perspective
-Emphasizes info and how it is transformed
-Think in terms of stages in which info is transformed
-stages communicate w/ one another, but one stage doesn’t know what the other is doing
Heuristic
“rule of thumb” that will get you the correct answer most of the time
Bias
in context of reasoning and decision making, systematic errors that violate rules of rationality
Three Greek assumptions
the world is predictable
humans are part of the world-predictable
explanations should consist of physical events/ the rel world
Early Middle ages
focus became religion and religious community rather than secularism and the individual
Renaissance
Focus on observation
knowledge: nativists and empiricist
Perception and association in memory
Determinism vs nondeterminism
what does a nativist believe
ideas are innate (born with knowledge)
not really greek
What does an empiricist believe
knowledge comes from experience
greek
Perception
knowledge comes from our senses
Memory
rises from association between simple sensory info
Determinism
behavior is predicatble from known inputs
Nondeterminism
Not predictable- guiding force that passeth all understanding
Willhelm Wundt
father of introspectionism
Introspectionism
follow own thought process but trained
structuralist
Structralism
trying to understand structures that comprise thought
Functionalism
trying to understand the function of mental processes
John B Watson
published paper in 1913 saying introspection didn’t work
focused on oberservable behavior
led to behaviorism
Basic Unit of Behavior
reflex
Classical conditioning
associate an involuntary response and a stimulus
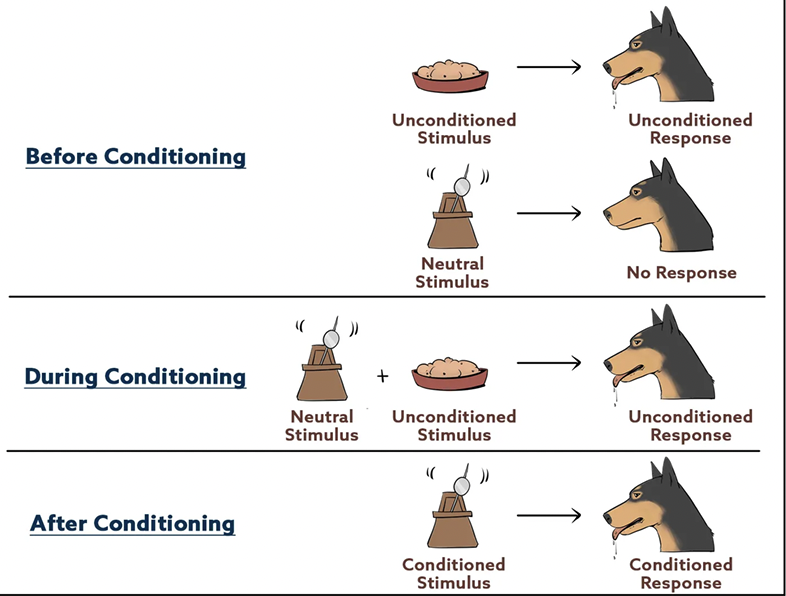
Pavlovs dogs
classical conditioning
Operant conditioning
associate a voluntary behavior and a consequence
two things behaviorism couldn’t explain
fixed action patterns (complex mating rituals)
critical periods (bonding with mother in birds)
what did Chomsky bring up that went against behaviorism
language is generative
What did HM (Henry Molasson)show about memory after bilateral medial temporal lobe region was removed
could’t make new memories so area is critical for encoding short-term memory into long-term memory
Three elements of the scientific method
Empiricism: knowledge comes from experience
develop hypotheses and then test them
public: results have to be open for examination and critique
nowadays more push for the raw data to be published as well
falsifiable: hypotheses have to be able to be proves wrong
Three Classes or research
Descriptive, correlational, experimental
Validity
how well results generalize
Reliability
how consistent the results
Descriptive research
self-reports, naturalistic, case studies
Phineas Gage
guy with beam through the eye had his personality change which tell us certain areas of the brain have differnt functions
What is a process according to the book
a series of steps that manipulates a representation
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
giant magnet aligns protons and then detected signal as they revert back to typical spin states (see where things are not function)
DTI (Diffusion Weighted Imaging)
measures directional water diffusions to infer connectivity (seeing where things are not function)
EEGs (Electroencephalography)
records neural activity from the surface of the skull
cheap,safe, repeatable, great temporal resoulution
poor spatial resolution,hard to analyze
PET (Positron Emission Tomography)
inject short half-life radioactive tracer into blood
can show cellular level changes with oxygen use, glucose metabolims.
fMRI (Functional MRI)
show oxygenated blood flow in the brain, safe, noninvasive, repeatable and high spatial resolution but slow and very expensive
What are PET scans most useful for
detecting tumors or diseases in body
MEG (magnetoencephalography)
measures magnetic signals produce by neurons themselves
subjects (kids)
schemas
memory representations of a type or category of event pre-programmed
Neuropsych
imagin helps observe abd track abstrat construct
ecological validity
how valid is the study in the real wold; how well does it apply to actual scenarios
internal validity
how confident someone is in their findings, based on good methodology and practices within the actual experiment (how well the experiment was carried out)
validity and reliability of controlled experiment
High internal validity and reliability, lower ecologial validiity
converging methods
multiple methods of study converging
thalamus
sensory information processing and rely within the brain
hypothalamus
hormonal regulation in the body
cerebellium
motor coordination and conditioning
Basal ganglia
motor coordination
Amygdala
emotional processing
Hippocampus
involved in learning and memory
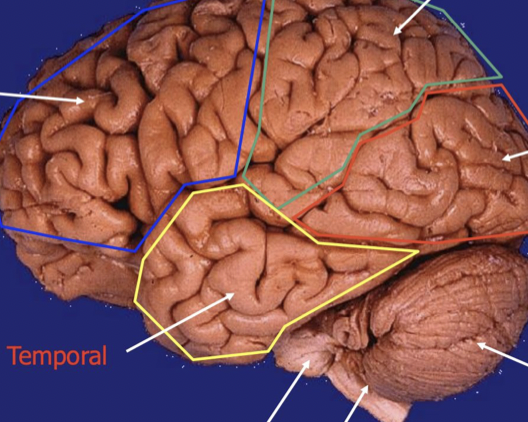
Top left
Frontal lobe
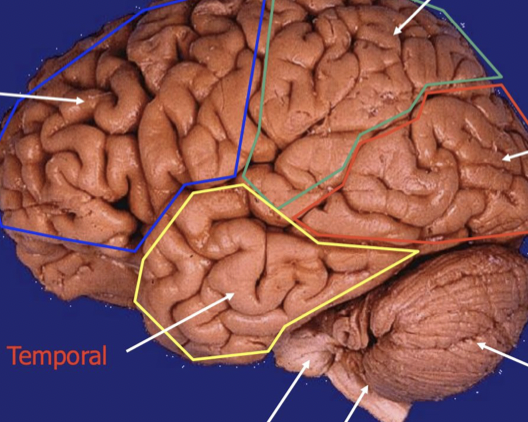
Top Middle
Parietal lobe
Visual ambiguity three ambuties
shape + orentation
Light + Reflectance + shadow
Size + distance
liklihood principle
-assume world is 3d
see corners as right angles
How to solve ambiguities
lilihood principle
depth cues
illusory conjuntion
The tendency to mistakenly perceive a correlation between two events or variables, even when there is no actual relationship.
Oculomotor Depth cue
Accommodation lens: when objects get closer to the eye the lens of the eye must change shape in order to focus an image
convergence lens: as an object gets closer your eye cross increasingly more to gaze at it
retinal image cues
stereopsis: we have two eyes that field of vision combines
Pictorial cues
familiar size
Pictorial cues
-movment cues
-relative height
-lineaar perspective
-texture gradiesnt
-atmospheric perspective
Bottom up processing
Bottom-up processing: Information processing that starts with the sensory input and moves towards higher-level cognitive processing.
Top-down processing
The use of prior knowledge and expectations to interpret sensory information and make sense of it. It starts with a general idea or concept and then fills in the details based on what is already known.
inferential approach
A method used to draw conclusions about a population based on a sample. It involves analyzing data and making inferences or predictions.
ecological approach
It considers how various factors, such as culture, social norms, and physical settings, influence human behavior and development.
facial processing
facila processing is different then other processing
two-stream hypothesis
Dorsal “where” Ventral “What”
Allocentric
object-centered
different oreintations-same relationship of parts
geons
Egocentric
Viwer-cnetered
parts relative to person
mental rotation-a cognitive process
attention is
limited and selective
What is cognitive psychology
understand the abstract, representations and processes (discrete stages)
conjuctive search
more than one feature differentiatiates the target from other distractors
Disjunctive
one feature differnctaialtes the target
Feature integration theory
attention binds together objects in space
endogenous attention
conscious, directed, controlled, focused on specific task
exogensus attention
are active in the background, checking for environmental cues that could eb important
automaticity
requires few attentional resources
it happens without attention
it happens when you don’t overfocus on doing the task
Multitasking
we aren’t really doing it just switching attention quickly
response selection
our brain can’t choose what to do for two different tasks at the same time
schemas
Mental frameworks that organize and interpret information based on our past experiences, beliefs, and knowledge. They help us make sense of new information by filling in gaps and making assumptions.
Neuropsych
imaging helps observe and track abstract constructs (HM)
Converging methods
multiple methods of study converging on one answer increases confidence; better to use a combination of methods for most strength
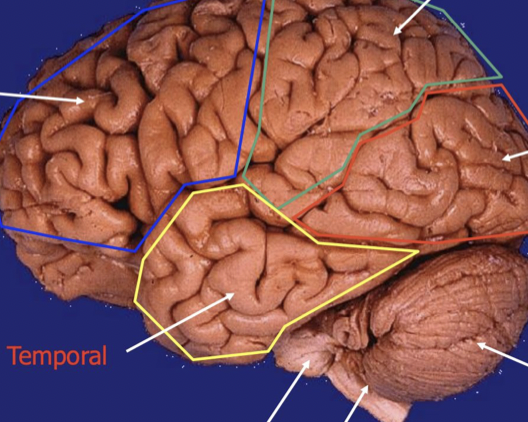
back of head
Occipital
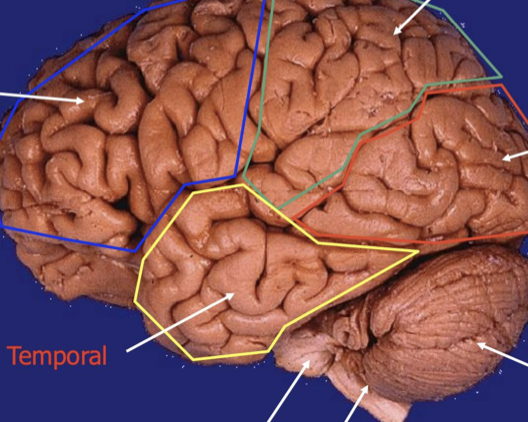
Bottom right
cerebellum
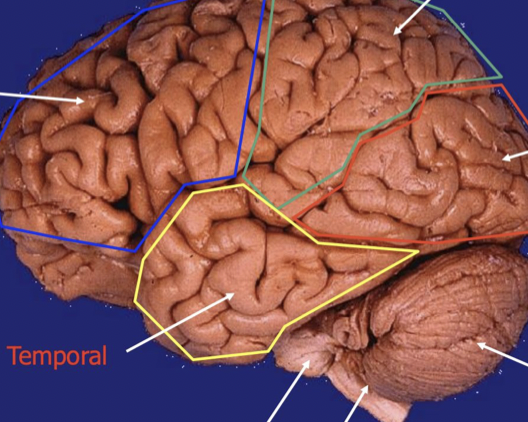
stick
Brainstem (Pones, medulla)
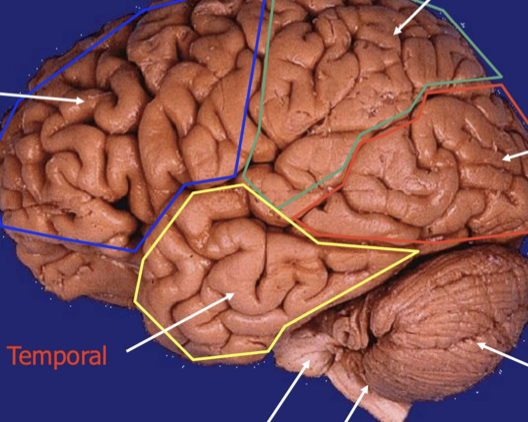
Bottom left
temporal lobe
Dorsal
top
Ventral
bottom
Anterior
front
posterior
back
medial
middle
sides
lateral
Consciousness
not the same as attention, we can be aware of stuff going on but not attend to them
Early filter theory
attends to physical characteristics like pitch and tone then filters
Late Filter theory
Attends to physical and semantic characteristics and filters out irrelevant stuff
cocktail party effect
Dichotic listening task
put in headphones and listen two different audios
Pictorial cue: relative height
objects lower on the picture plane are assumed to be closer to the viewer
linear perspective
parallel lines in 2d converge if you extend them enough in 3d
Texture gradient
more detail= closer
atmospheric perspective
objects in the distance have a blue haze