Human Anatomy Torres Exam 1 Tissues
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
allowing the propagation of electrochemical signals in the form of nerve impulses that communicate between different regions of the body (also excitable)
function of the nervous tissue
Where is nervous tissue in our bodies ?
brain, spinal cord and nerves
"excitable"; responding to stimuli and contracting to provide movement
function of the muscle tissue
what are the 3 types of muscle tissue
skeletal, cardiac, smooth
covers exterior surfaces of the body, line internal cavities and passageways & form certain glands
epithelial tissue
binds the cells & organs of the body together & functions in the protection, support, & integration of all parts of the body
connective tissue
This tissue is :
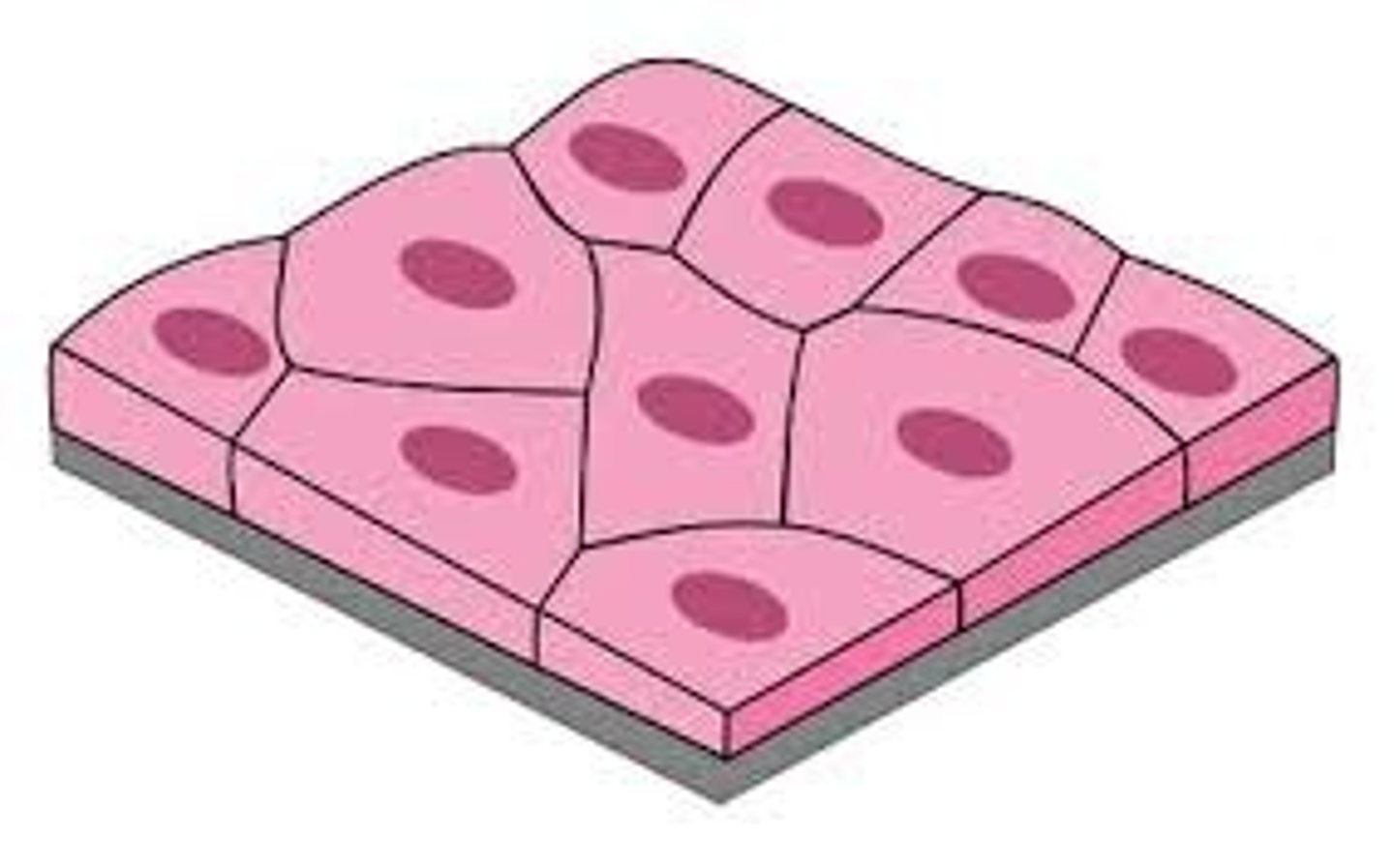
Located in air sacs of lungs and the lining of the heart, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels
Function: allows materials to pass through by diffusion and filtration, and secretes lubricating substance
Simple squamous epithelium
This tissue is :
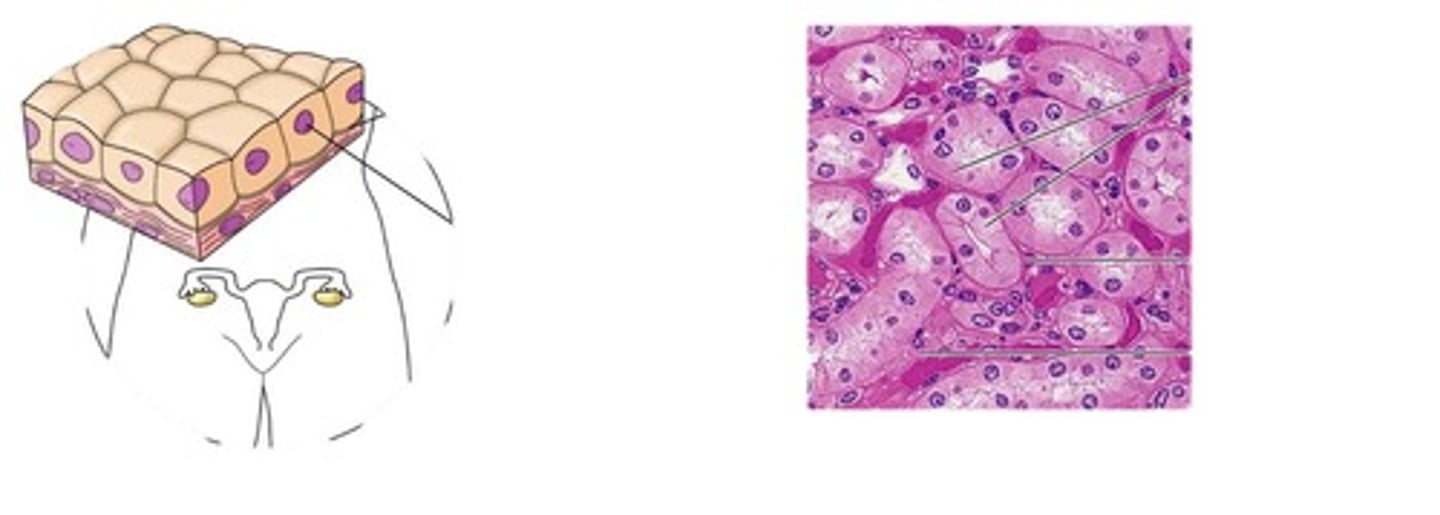
Located in ducts and secretory portions of small glands and in kidney tubules
Function: secretes and absorbs
Simple cuboidal epithelium
This tissue is:
Located in Ciliated tissues are in larger bronchioles, uterine tubes, and uterus; smooth (nonciliated tissues) are in the digestive tract, bladder
Function: Absorbs; it also secretes mucus and enzymes
Simple columnar epithelium
This tissue is:
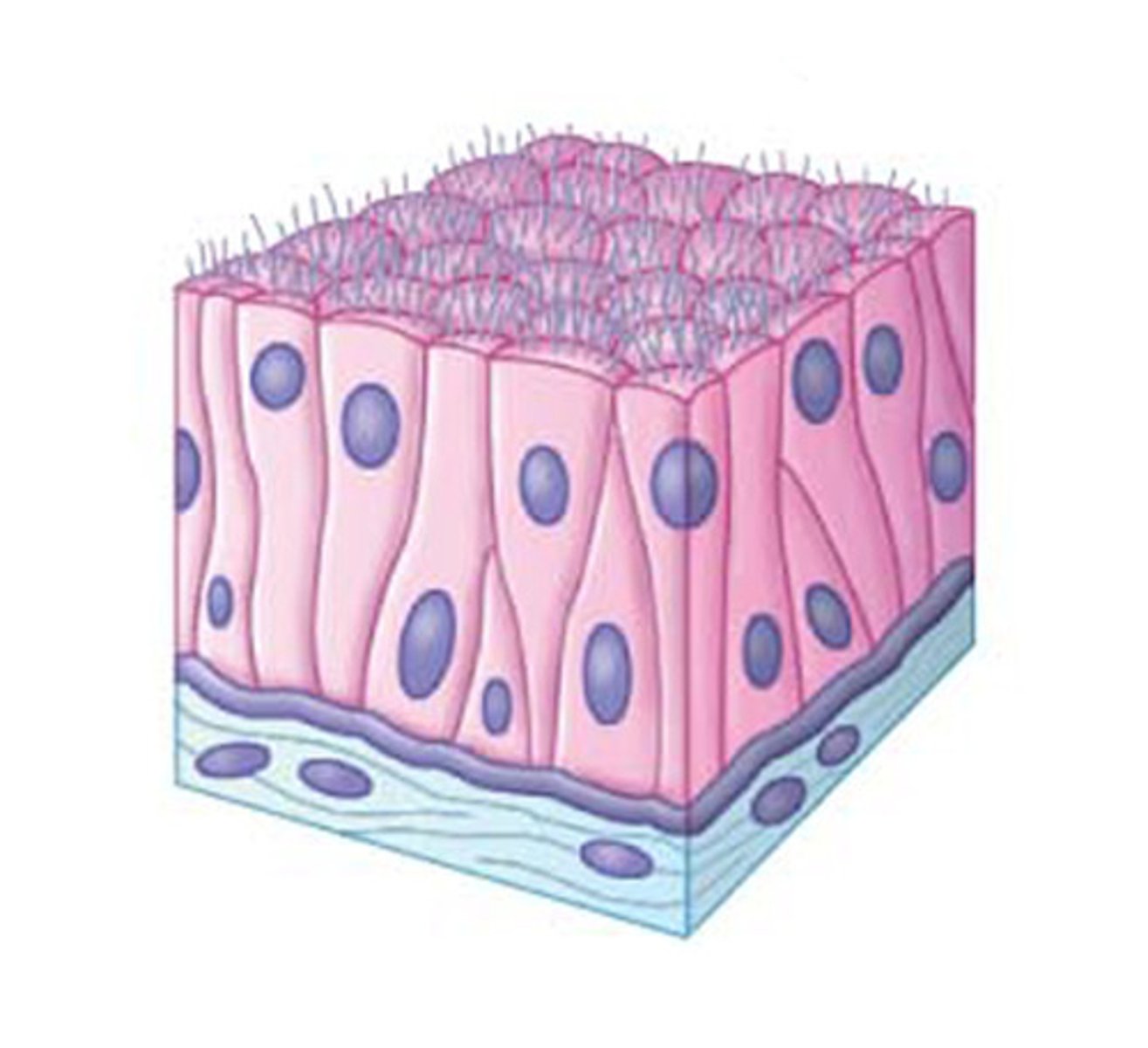
Ciliated tissue lines the bronchi, trachea, and much of the upper respiratory tract
Function: Secretes mucus; ciliated tissue moves mucus
Pseudostratified columnar epithelium
This tissue is:
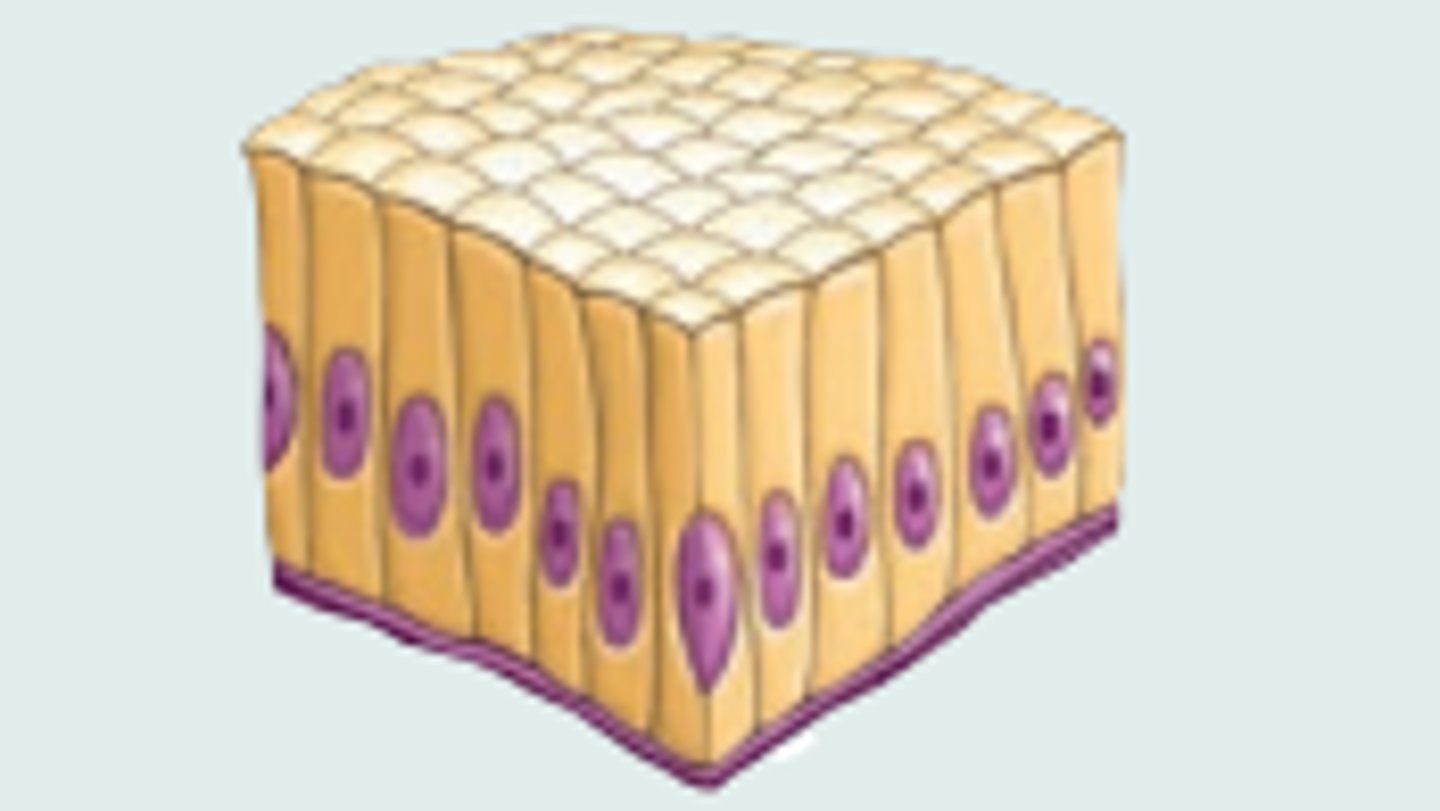
Lines the esophagus, mouth, and vagina
Function: Protects against abrasion
Stratified squamous epithelium
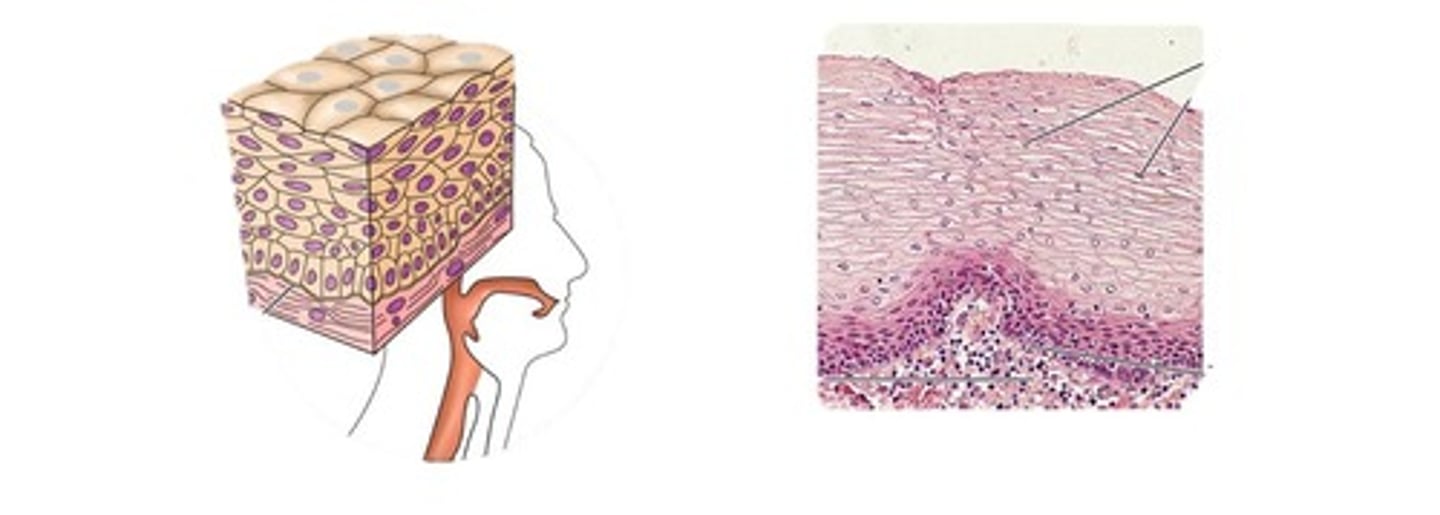
This tissue is:
IN Sweat glands, salivary glands, and the mammary glands
Function: Protective tissue
Stratified cuboidal epithelium
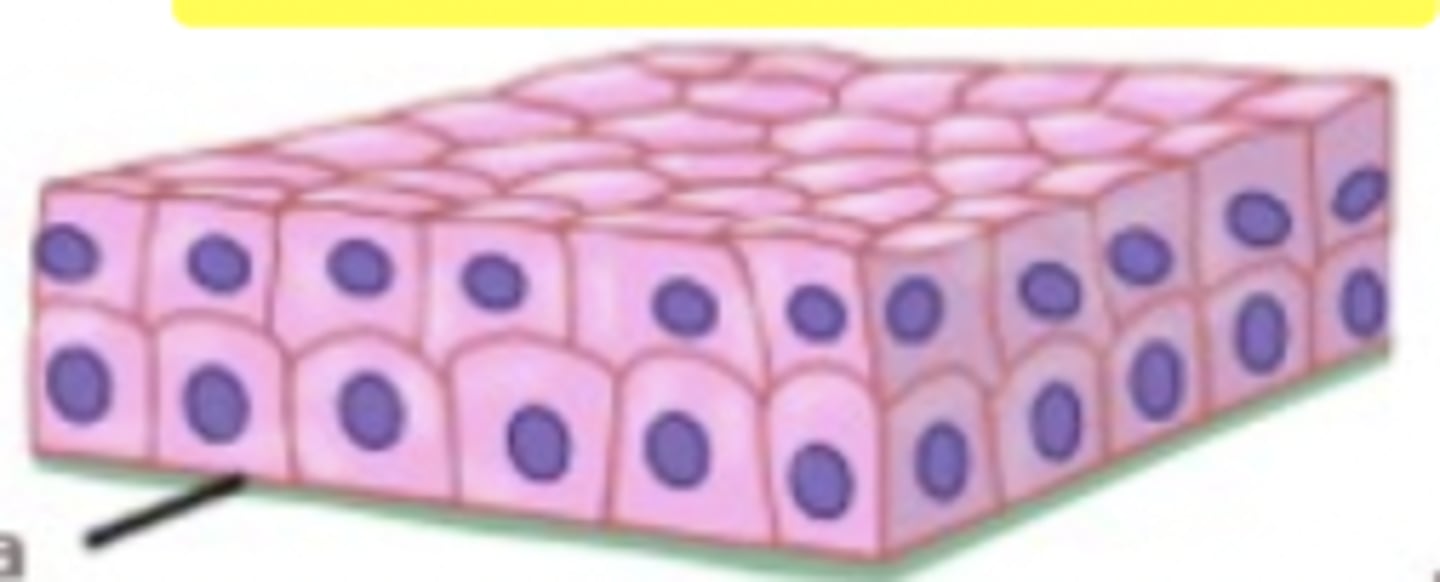
This tissue is :
The male and female urethrae and the ducts of some glands
Function: Secretes and protects
Stratified columnar epithelium
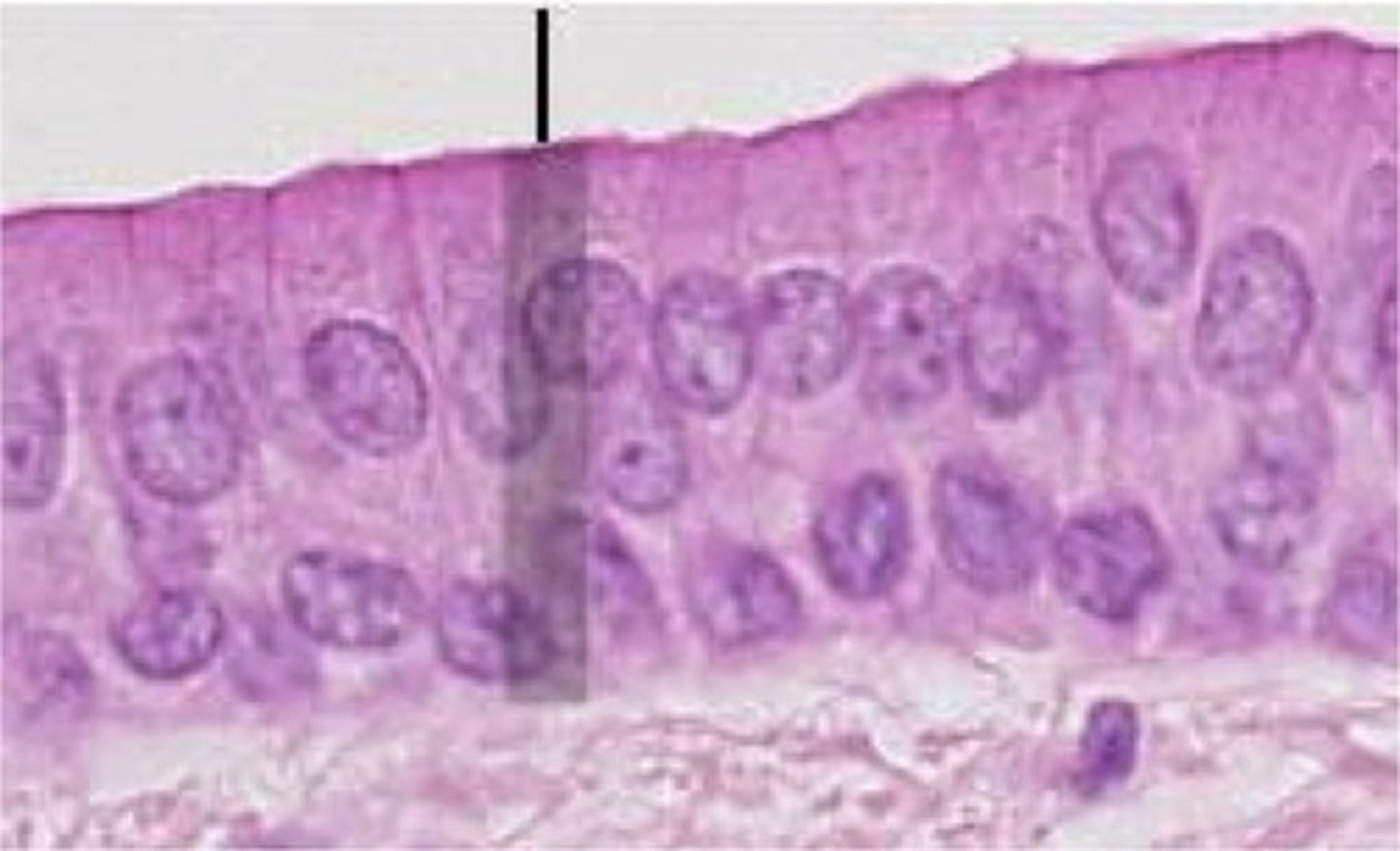
This tissue is:
Lines the bladder, urethra, and the ureters
Function Allows the urinary organs to expand and stretch
Transitional epithelium
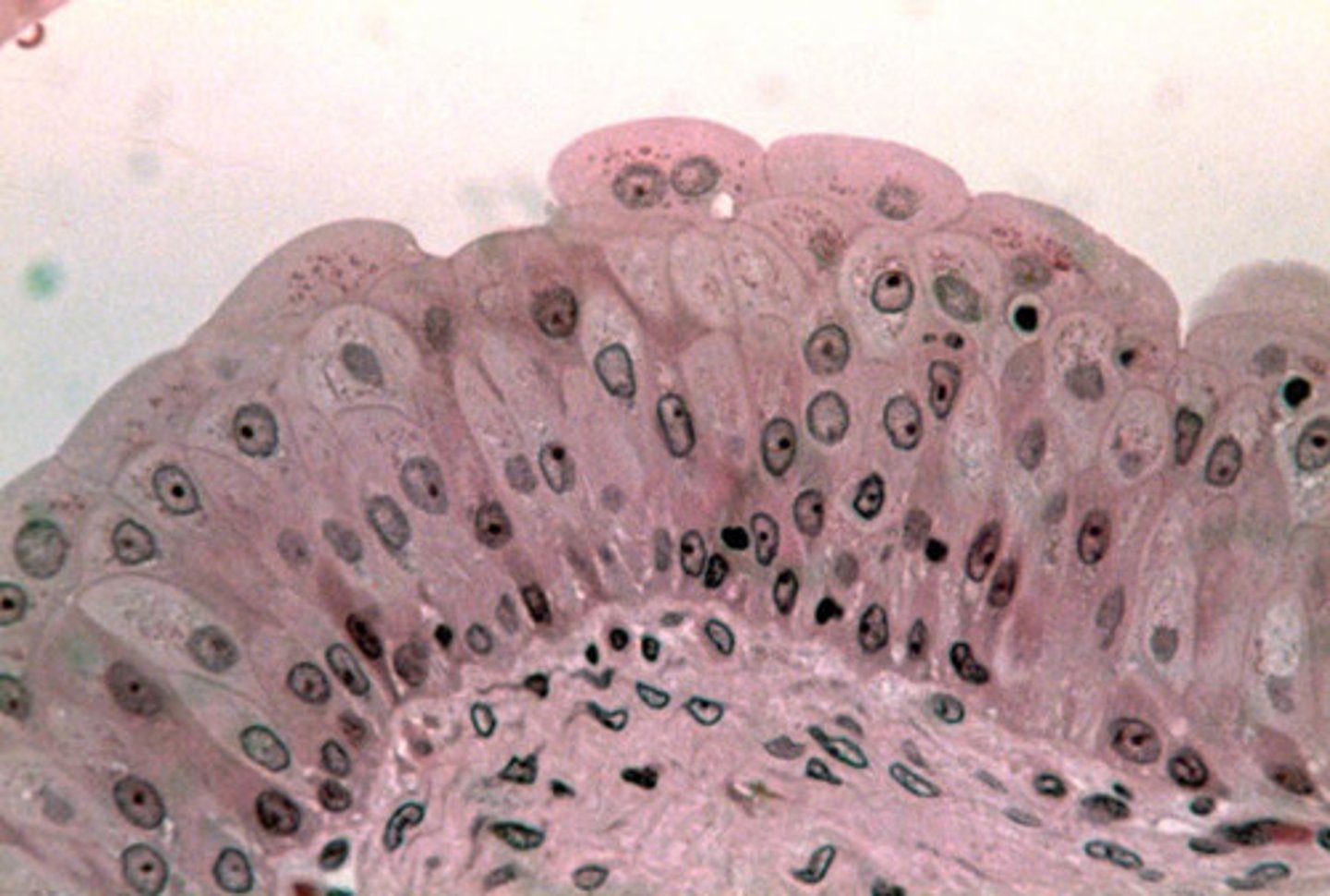
What are the two types of glands ? What do they do ?
endocrine secrets directly into surrounding tissues/fluids (no ducts) and exocrine secrets to the external environment via ducts (indirectly or directly)
Cell creates chemical, released through pores. What secretion is this ?
merocrine secretion
no pores, pieces of cell membrane break off, wrap around chemical & is released cell membrane "regenerates". What secretion is this ?
apocrine secretion
no pores, pieces of cell membrane break off, wrap around chemical & is released, cell does NOT regenerate it will eventually die. What secretion is this ?
holocrine secretion
What are the 3 general types of connective tissue ?
connective tissue proper, supportive connective tissue and fluid connective tissue
This tissue supports, attachment and protection of structures, & immune functions.
connective tissue
What are the common cells of connective tissue proper ?
fibroblasts, adipocytes and macrophages
fibroblasts function
most common, produce the matrix
adipocytes function
(fat cells) for energy storage
macrophages
immune cells, help destroy infectious agents
What are the two main subtypes of connective tissue proper ?
loose and dense connective tissue
it is common between organs, absorbs shock & binds and allows substances to pass through
loose connective tissue
higher abundance of collagen fibers in the matrix than loose, allow for greater resistance to stretching
dense connective tissue
What is supportive connective tissue ? What are the two types ?
maintains body posture/position, protects internal organs ; two types is cartilage and bone
Chondrocytes are
cartilage cells in lacunae
The cartilage matrix is
avascular- nutrients must diffuse through matrix to reach chondrocytes
What are the three types of cartilage ?
hyaline, elastic, fibrocartilage
Hyaline cartilage is
strong and flexible; most common
fibrocartilage is
the strongest
elastic cartilage is
most flexible
Osteocytes are
bone cells within lacunae
bone matrix is
vascular- blood carries nutrients to osteocytes- bone heals quickly
matrix contains
collagen fibers for flexibility
Within the matrix contains
hydroxyapatite for rigidity
what is fluid connective tissue ? And what do they carry?
carry materials throughout body ; blood and lymph
Erythrocytes are
red blood cells, carry oxygen and carbon dioxide
Leukocytes are
white blood cells, immune response
allows mobility of body parts. What tissue am I
muscle tissue
The excitation of ________ causes muscles to contract or relax
myocytes
The three types of muscle tissue is
skeletal, cardiac and smooth
skeletal muscle function
voluntary movement, most common
cardiac muscle function
forms the heart, involuntary
smooth muscle function
involuntary movements of internal organs
allows transmission and processing of information about the internal and external environments
nervous tissue function
nervous tissue cell types (2)
neurons and neuroglia
Neurons have 3 major components: what are they ?
cell body, dendrite and axon
cell body contains
most organelles
Dendrites do what?
receives signals from other cells
Axons function
sends signals to other cells
synapse function
junction between two neurons