DNA Structure and Replication
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
DNA Replication
The process of making identical copies of DNA before cell division; occurs during the S phase of interphase.
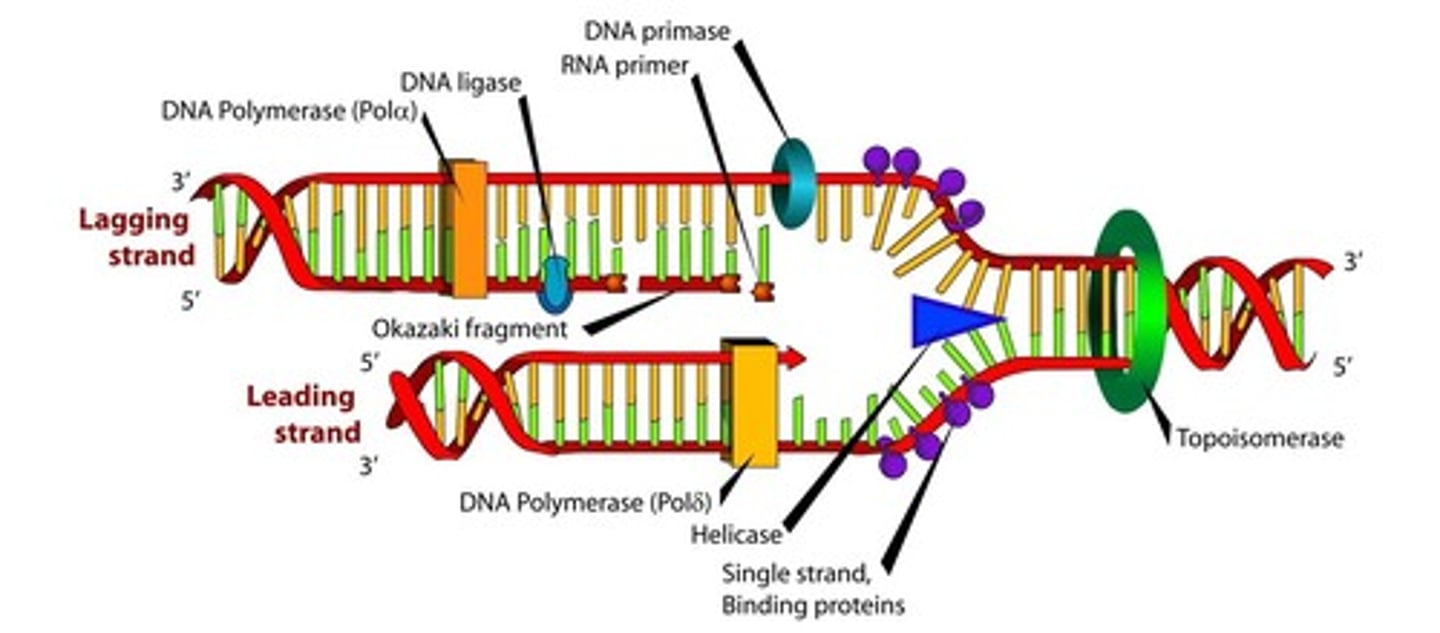
Replication Fork
The Y-shaped region that results when the two strands separate.
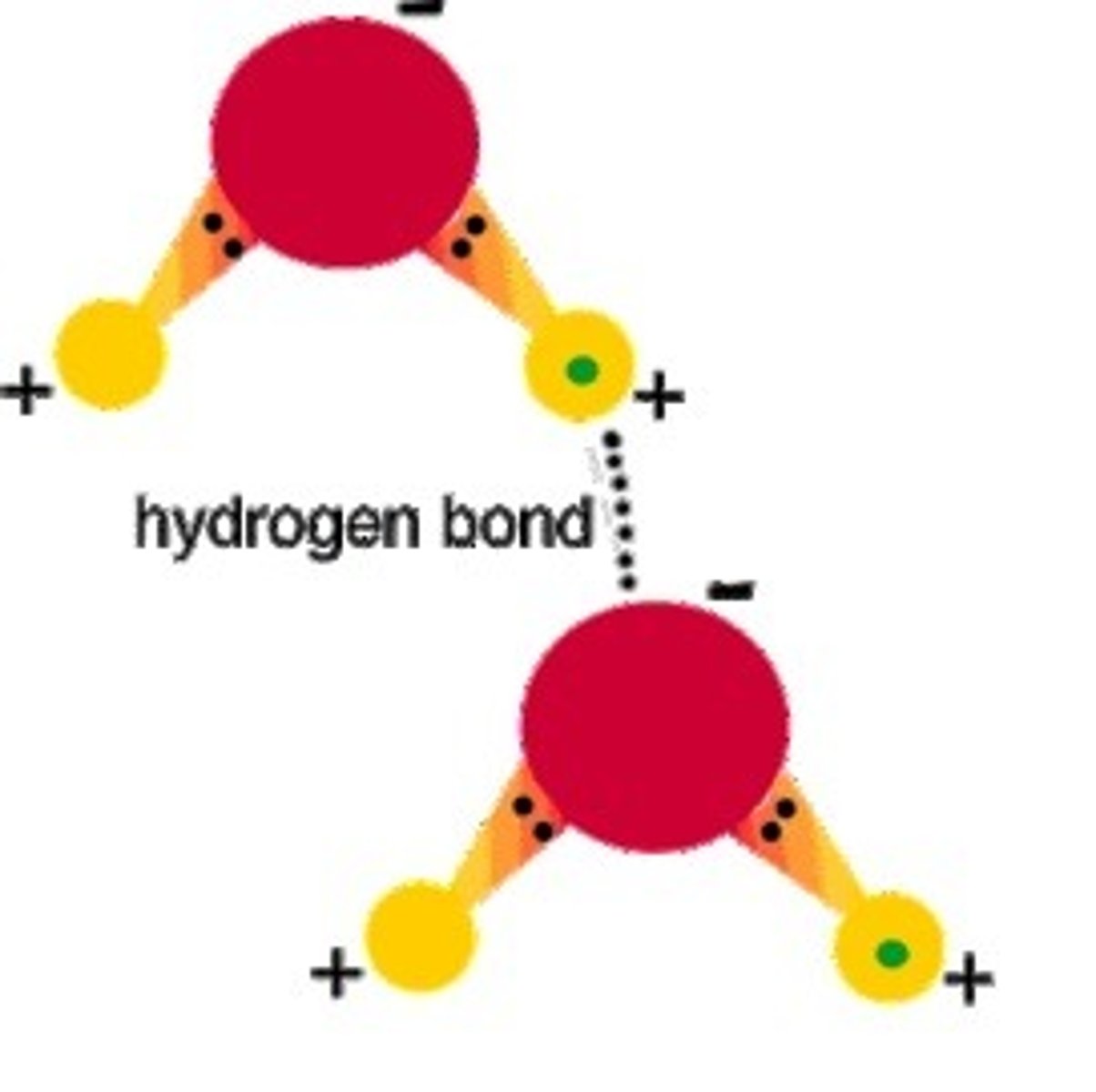
Hydrogen bond
type of bond that holds DNA bases together; weak
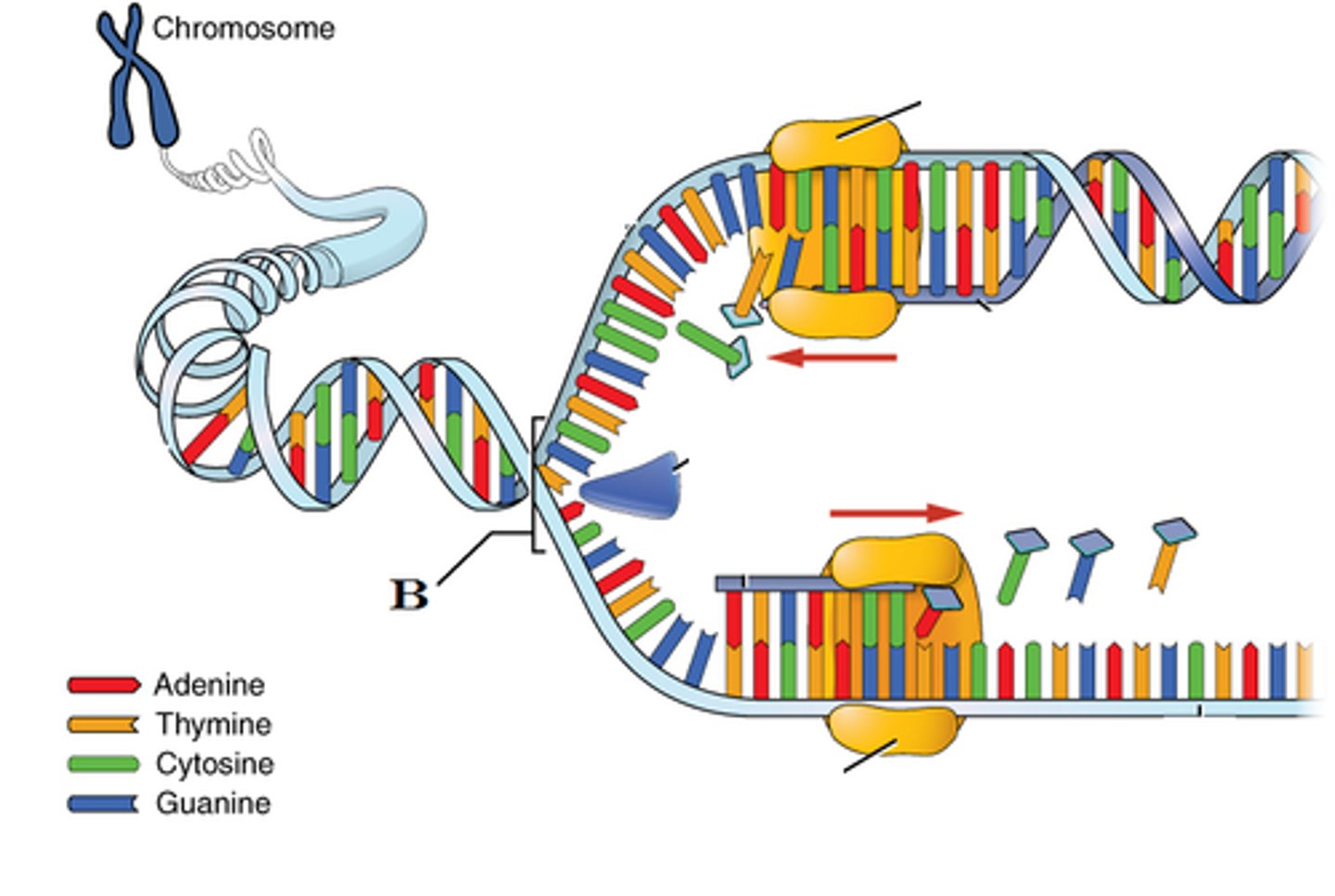
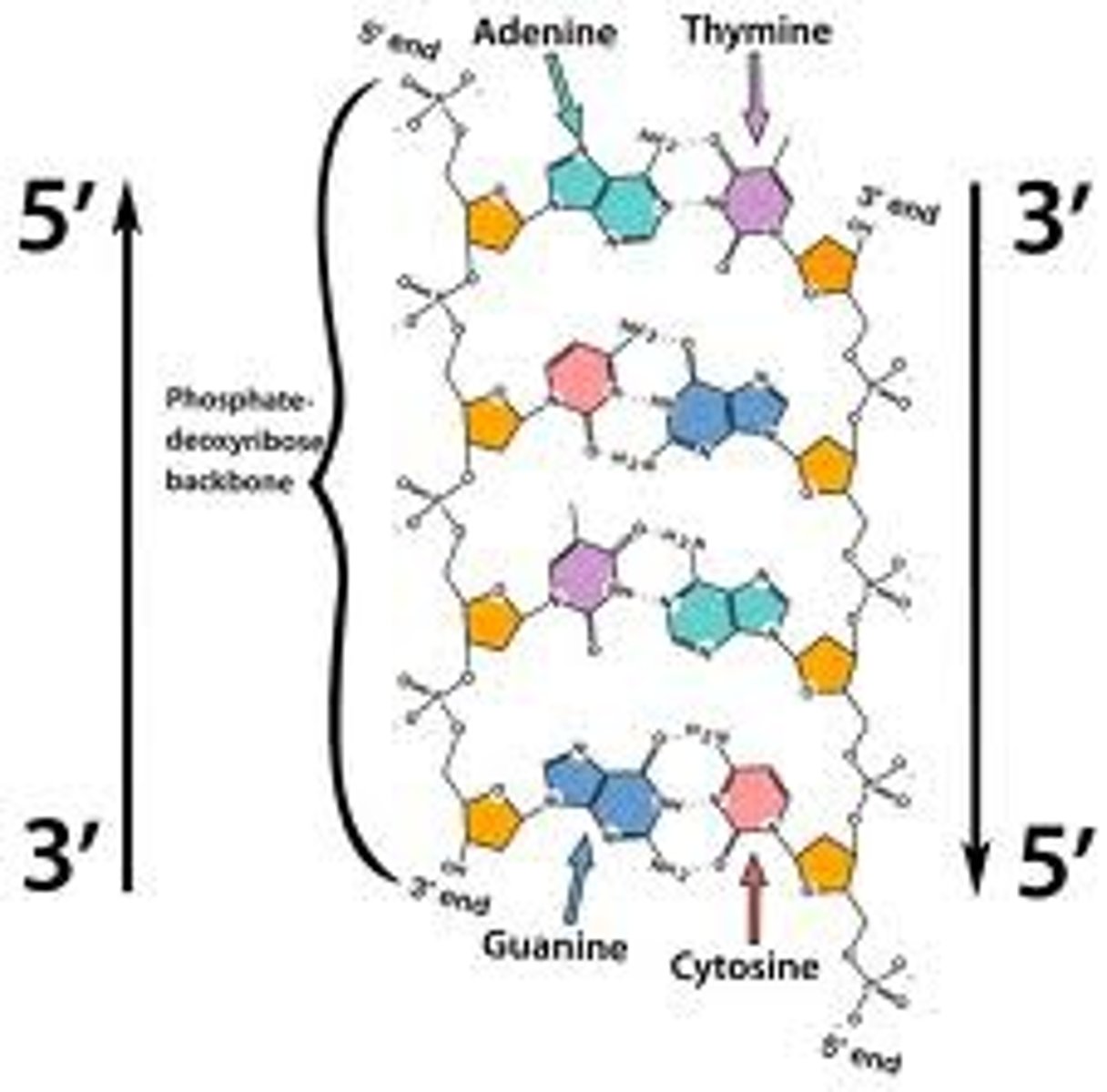
Double Helix
DNA's structure; twisted ladder.
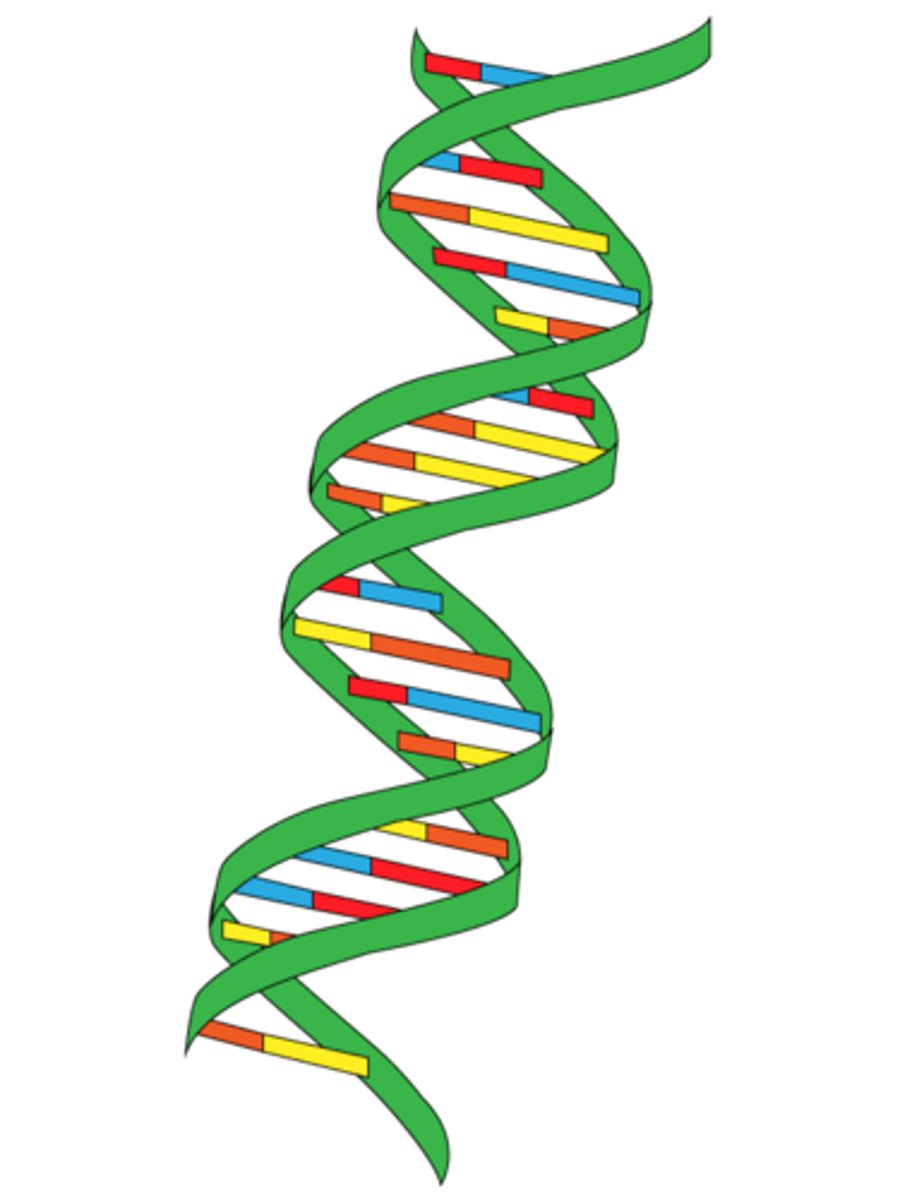
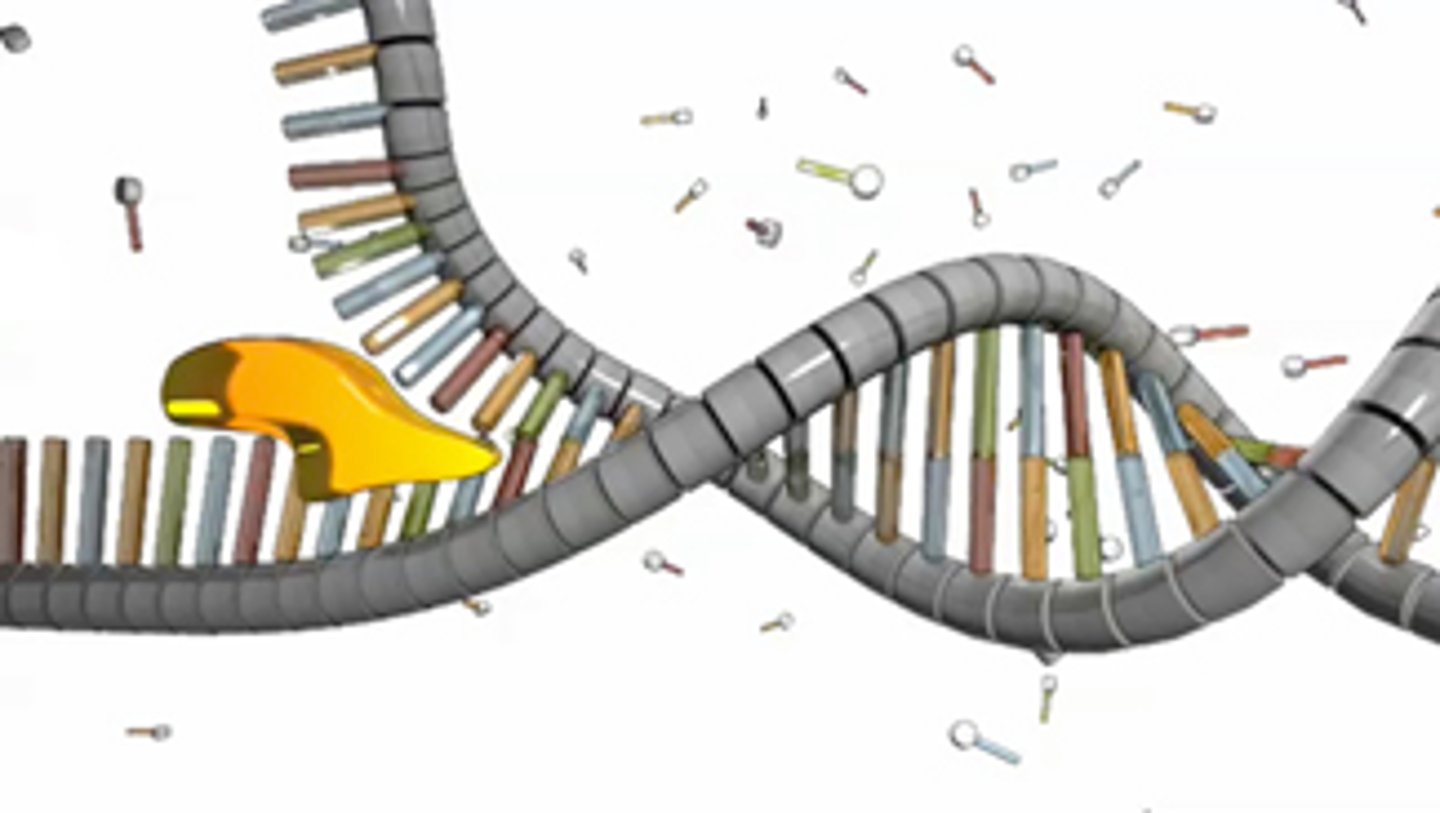
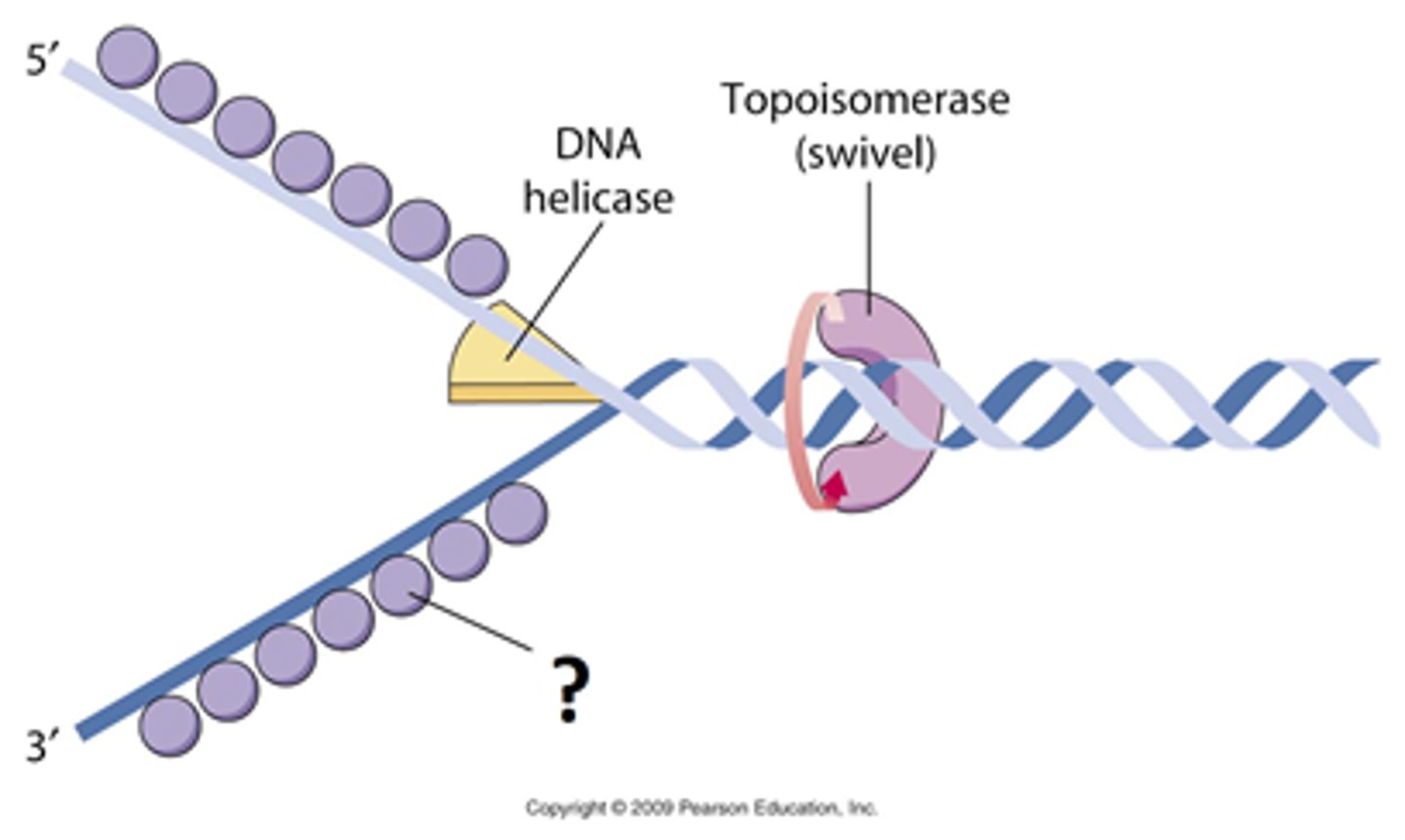
DNA Helicase
An enzyme that unwinds the double helix of DNA and separates the DNA strands in preparation for DNA replication.
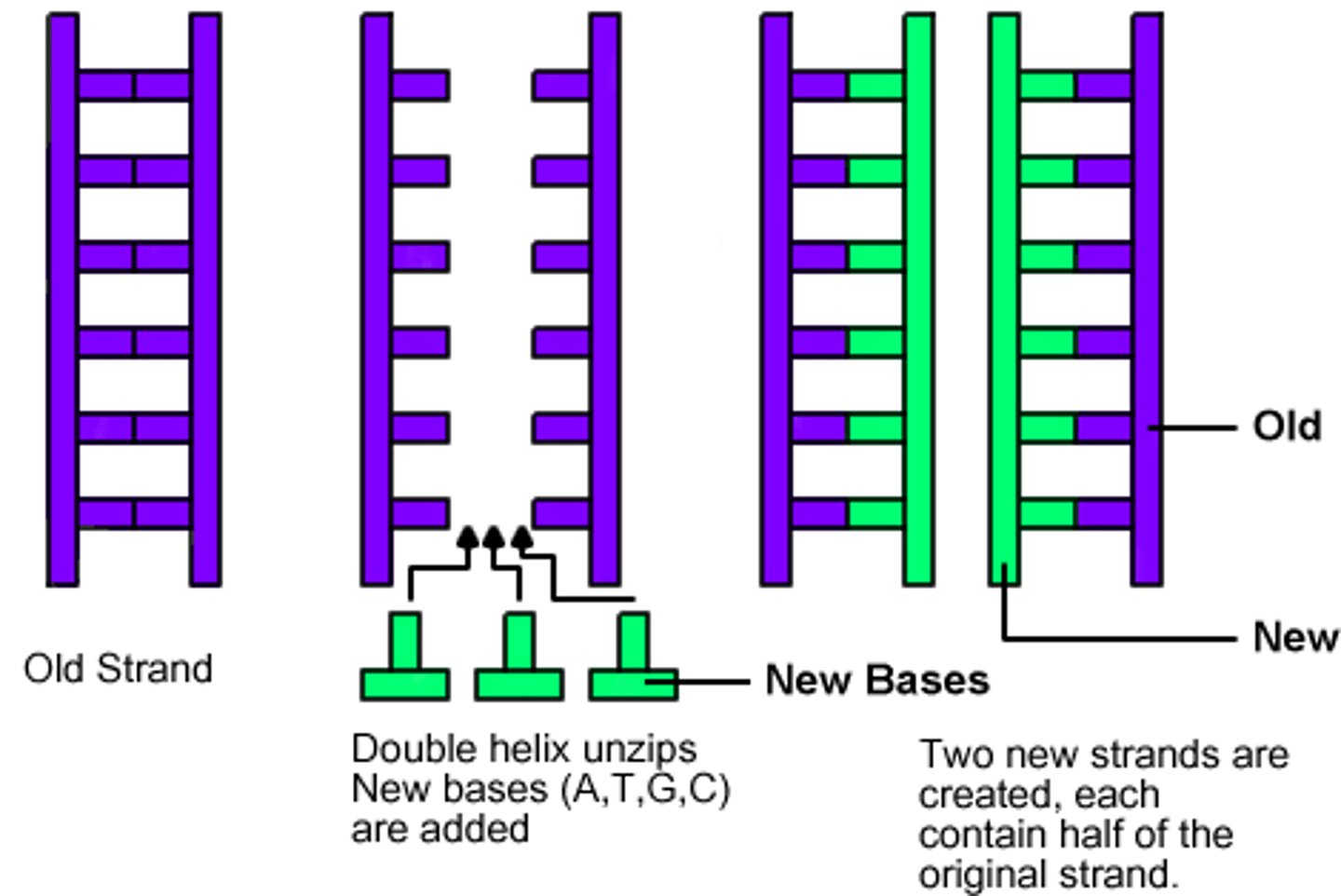
Semiconservative Replication
The two new DNA molecules each have one old and one new strand.
5' to 3'
the direction in which DNA is synthesized and read
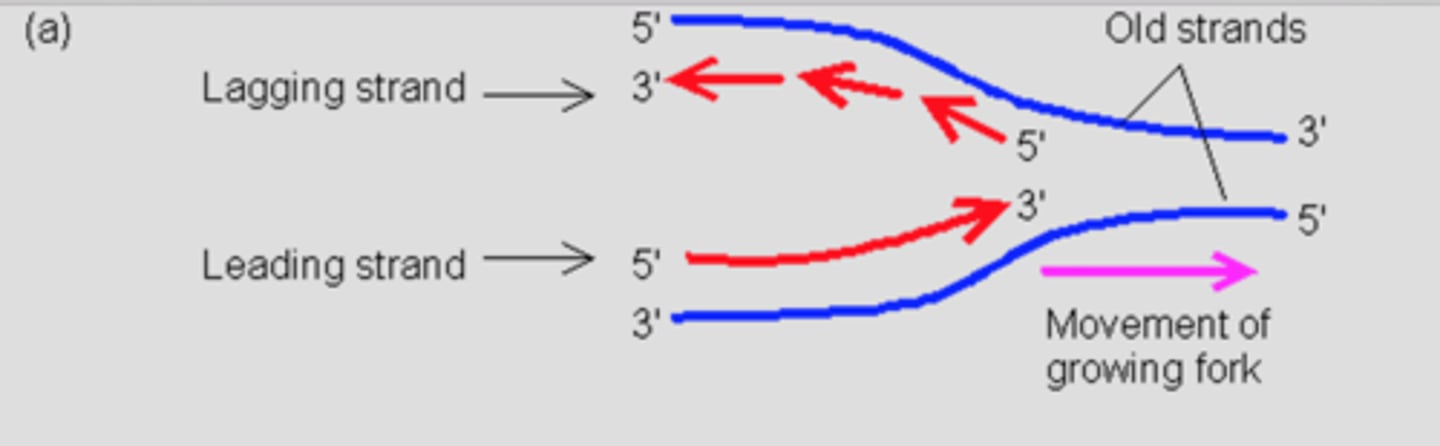
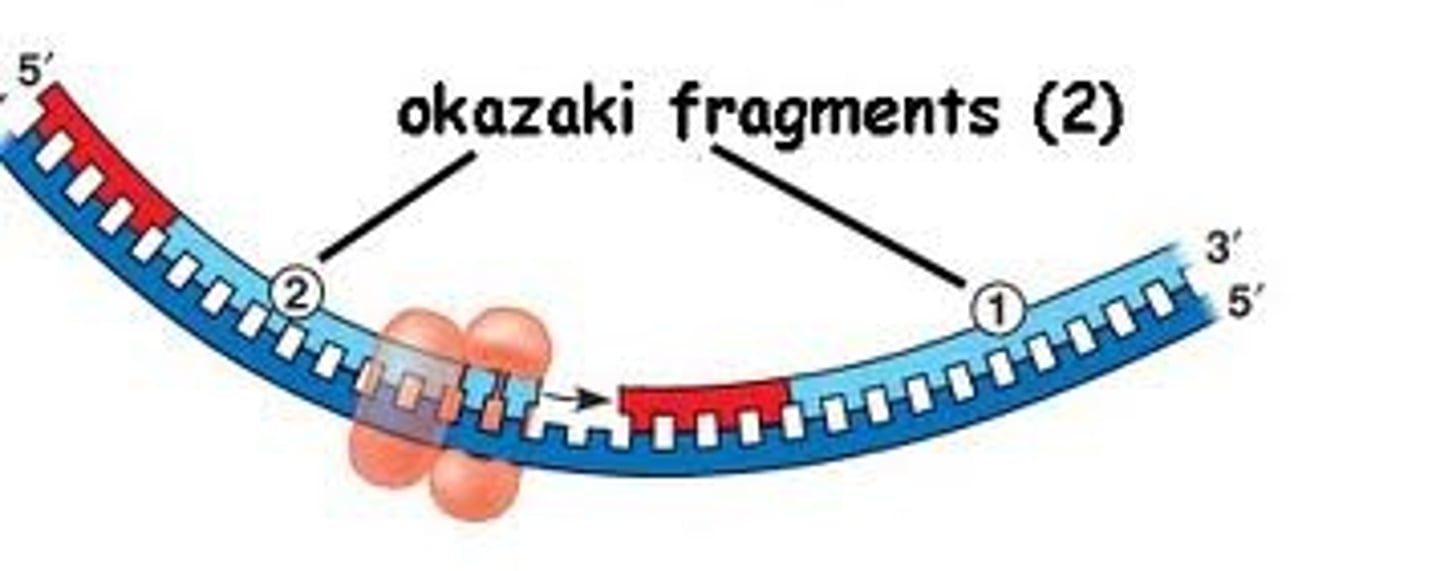
Okazaki fragments
short segments of DNA that are synthesized in short choppy fragments on the lagging strand
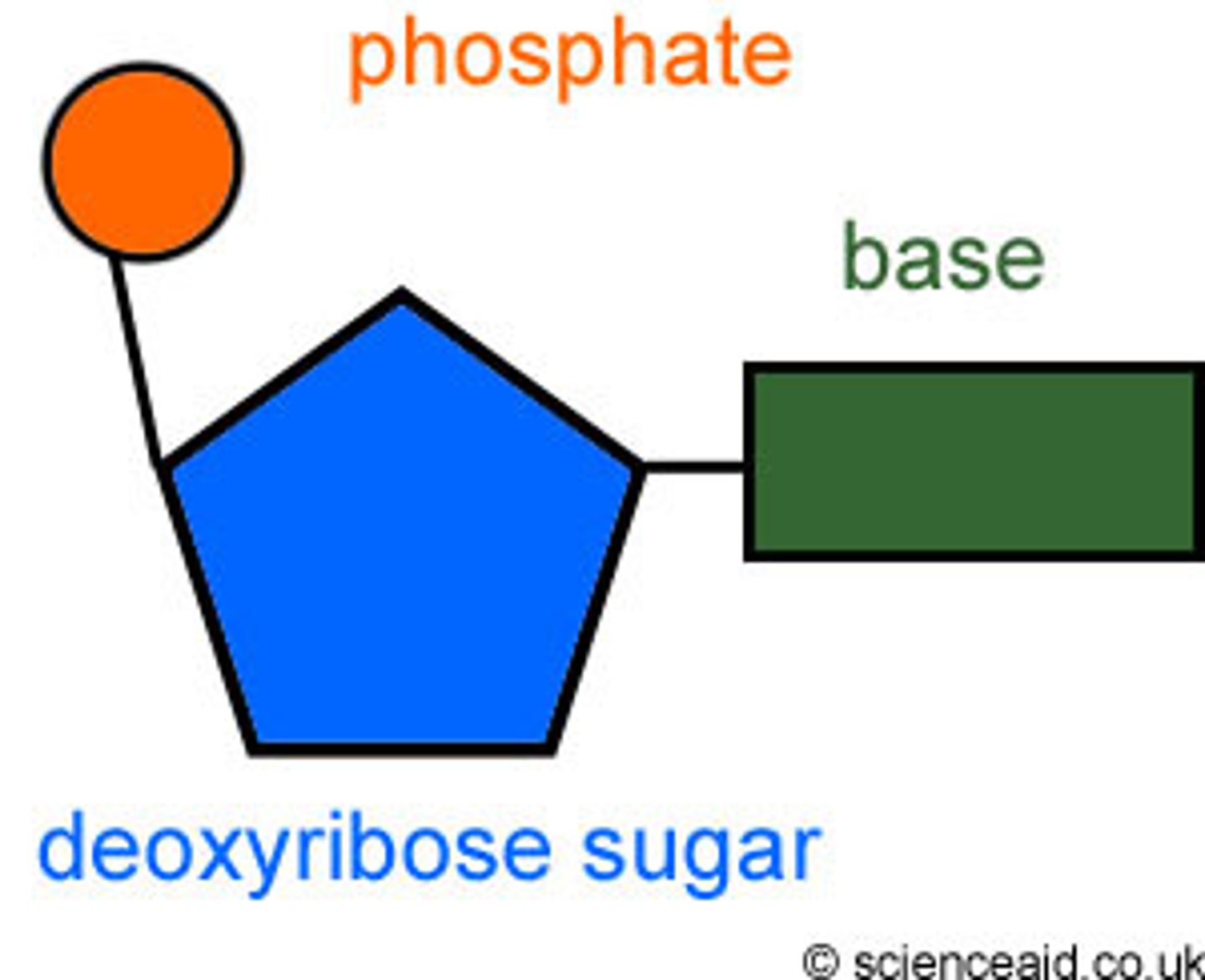
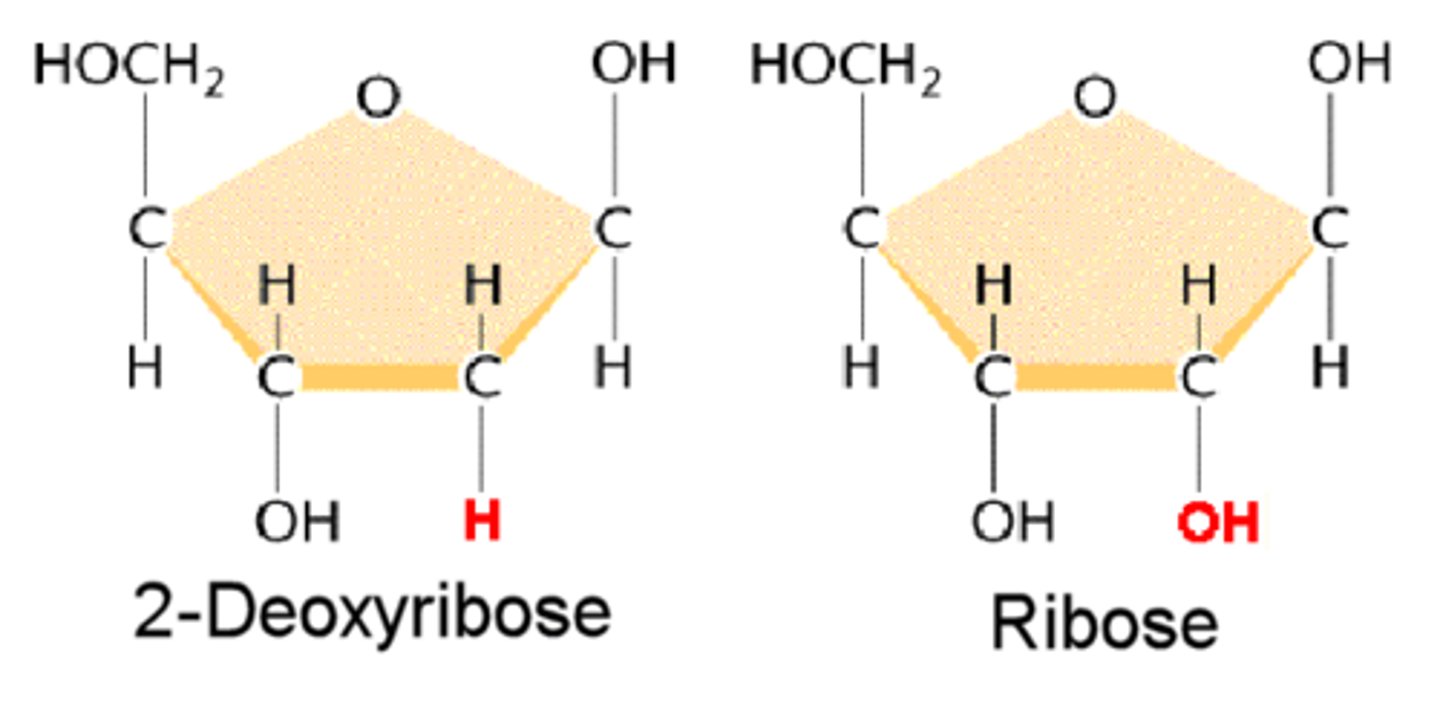
Deoxyribose
5-carbon sugar DNA is named for
SSBP (Single Stranded Binding Proteins)
proteins that keep DNA unwound during replication
Leading Strand
the strand of DNA that is replicated continously toward the replication fork
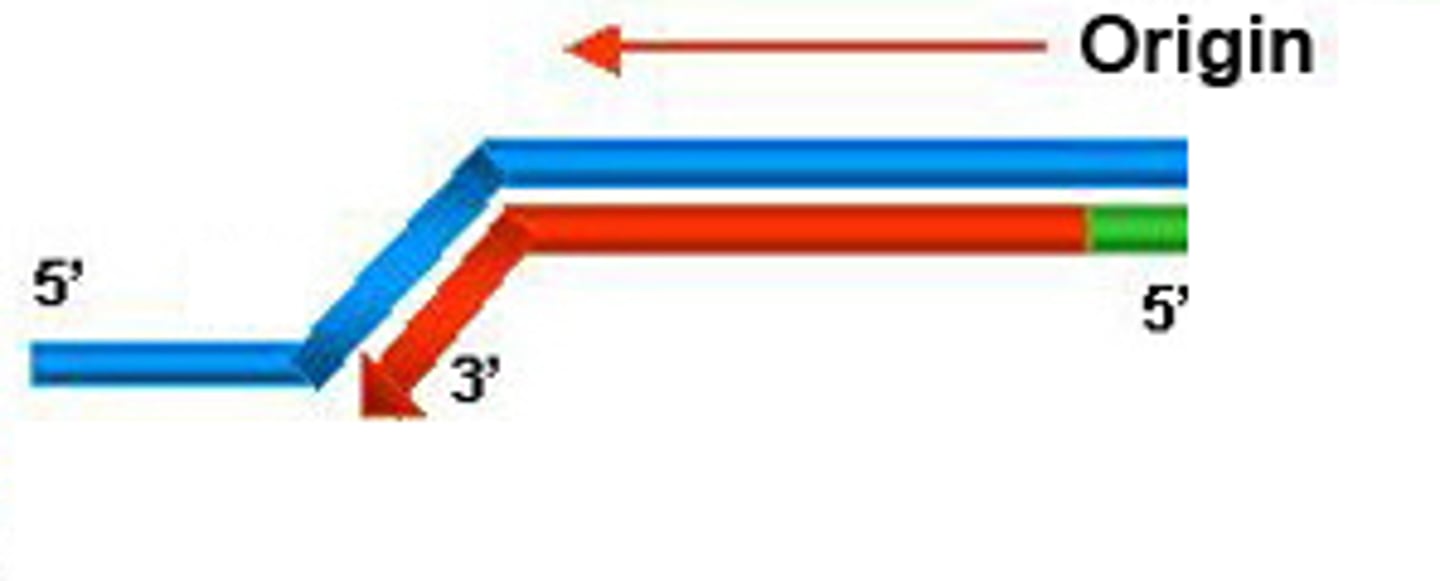
Lagging Strand
strand of DNA that is replicated discontinously away from the fork; made up of Okazaki Fragments
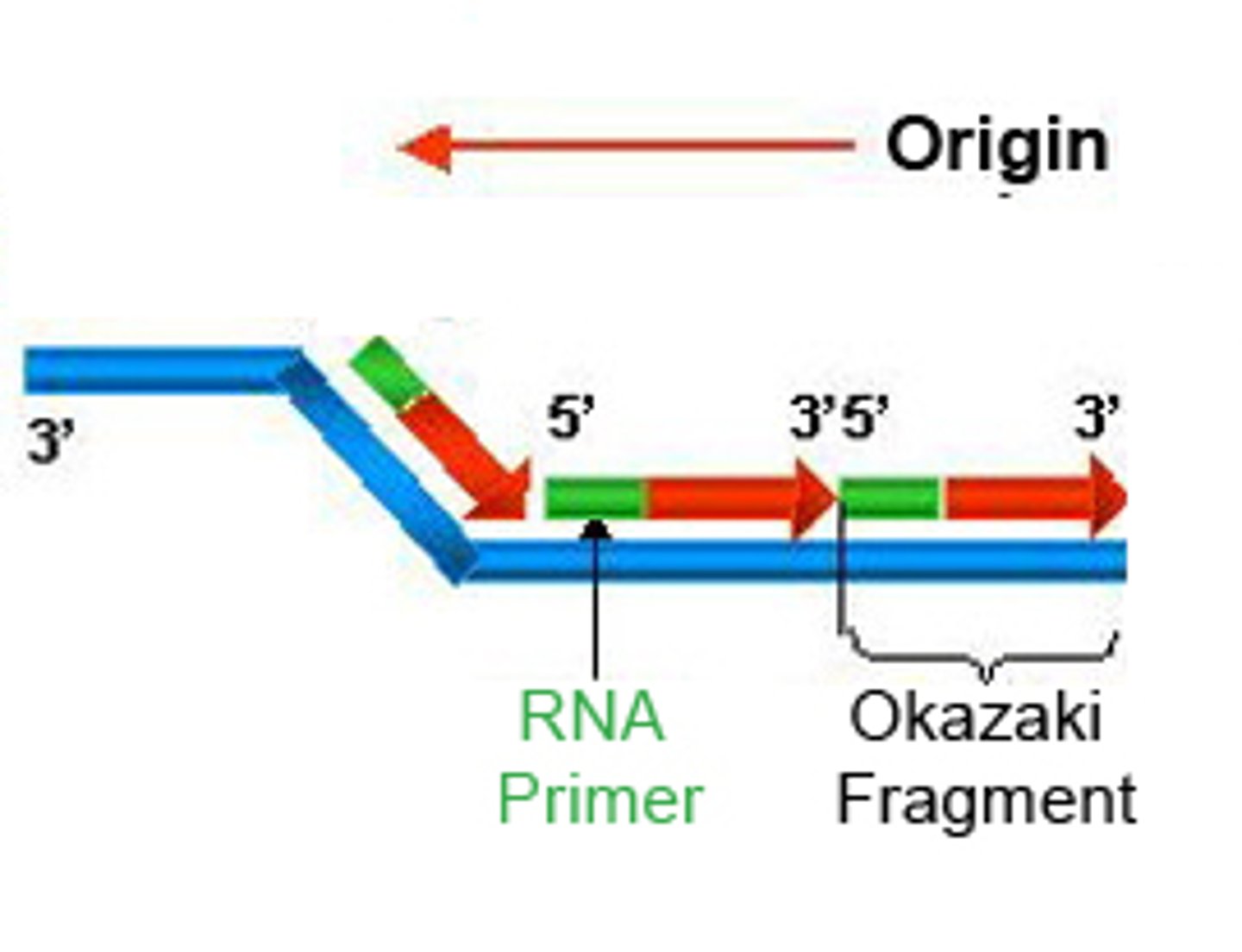
(DNA) Ligase
enzyme that "stitches" the Okazaki Fragments together

DNA polymerase
adds DNA nucleotides to the DNA templates/parent strands; proofreads the chain for mistakes
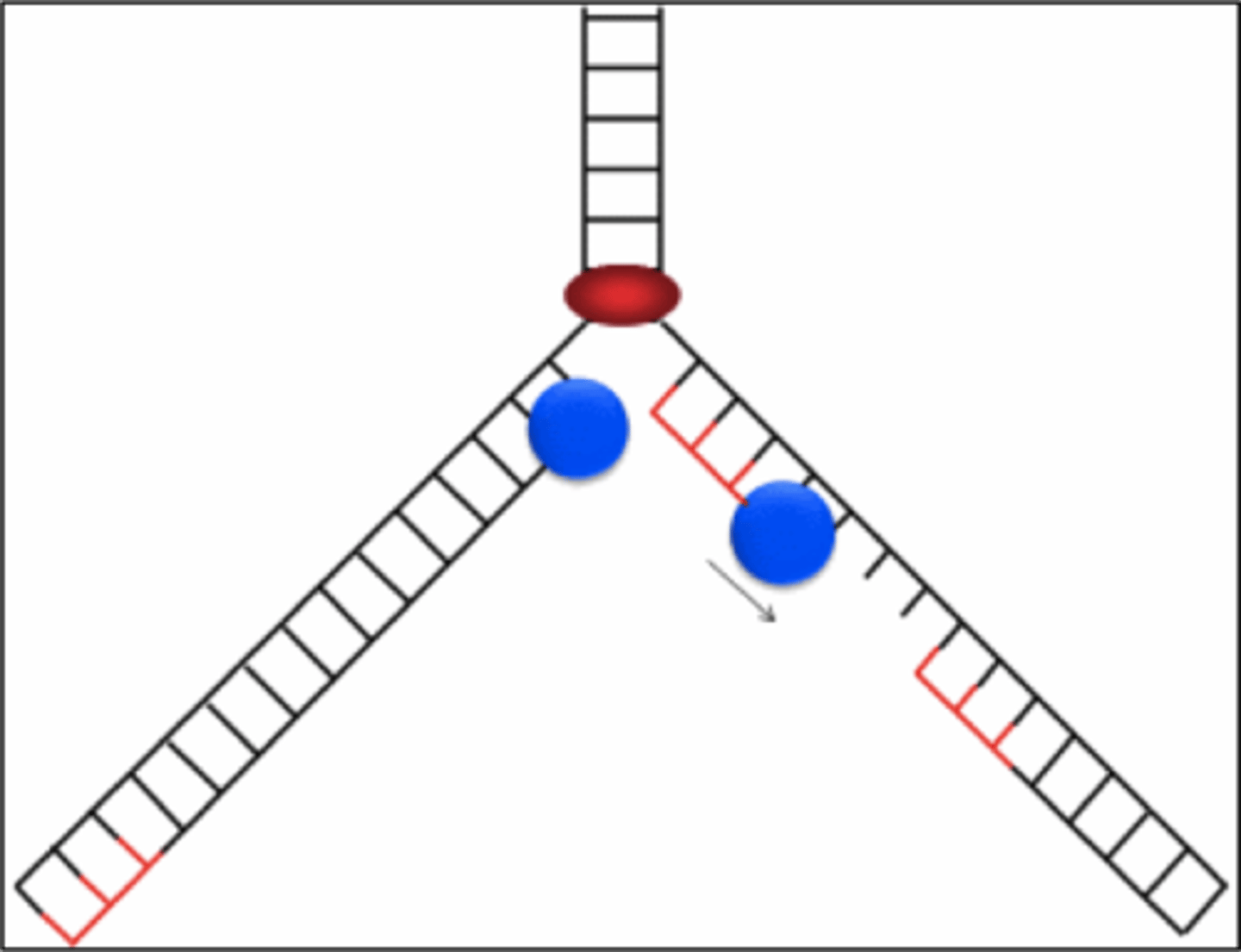
antiparallel
The opposite arrangement of the sugar-phosphate backbones in a DNA double helix.
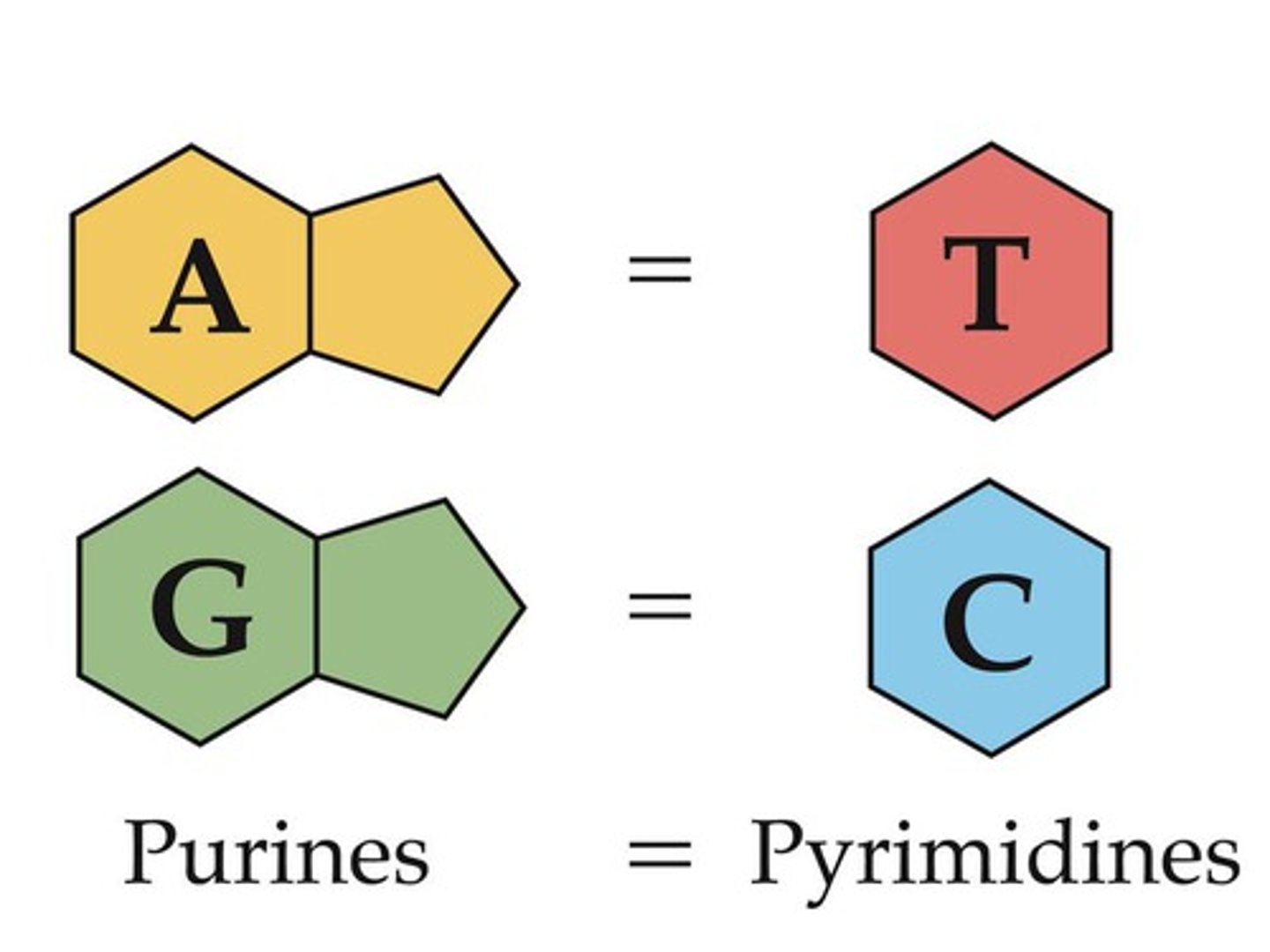
Chargaff Rule
The amount of Adenine will equal the amount of Thymine and the amount of Guanine will equal the amount of cytosine
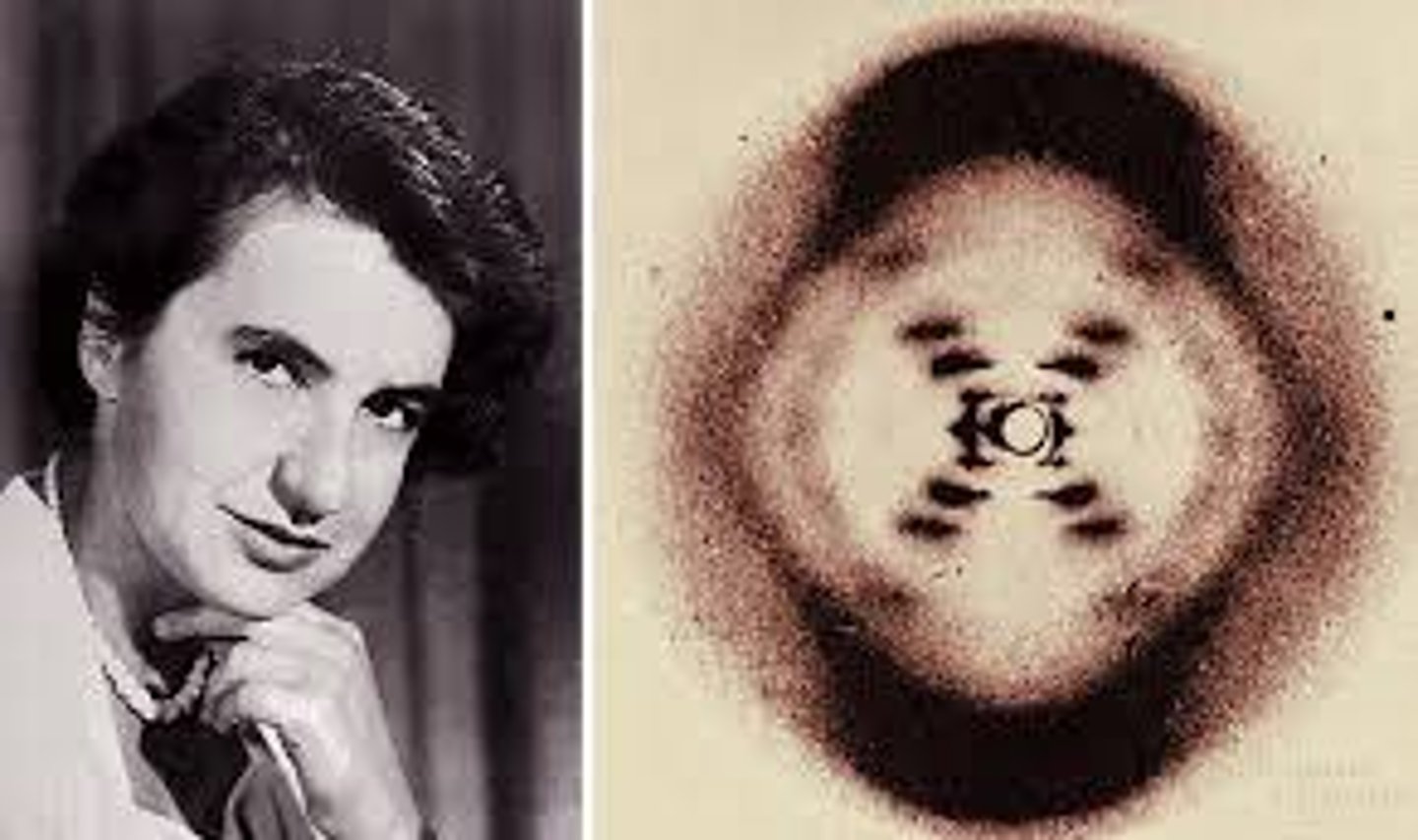
Rosalind Franklin
Woman who generated x-ray images of DNA, she provided Watson and Crick with key data about DNA

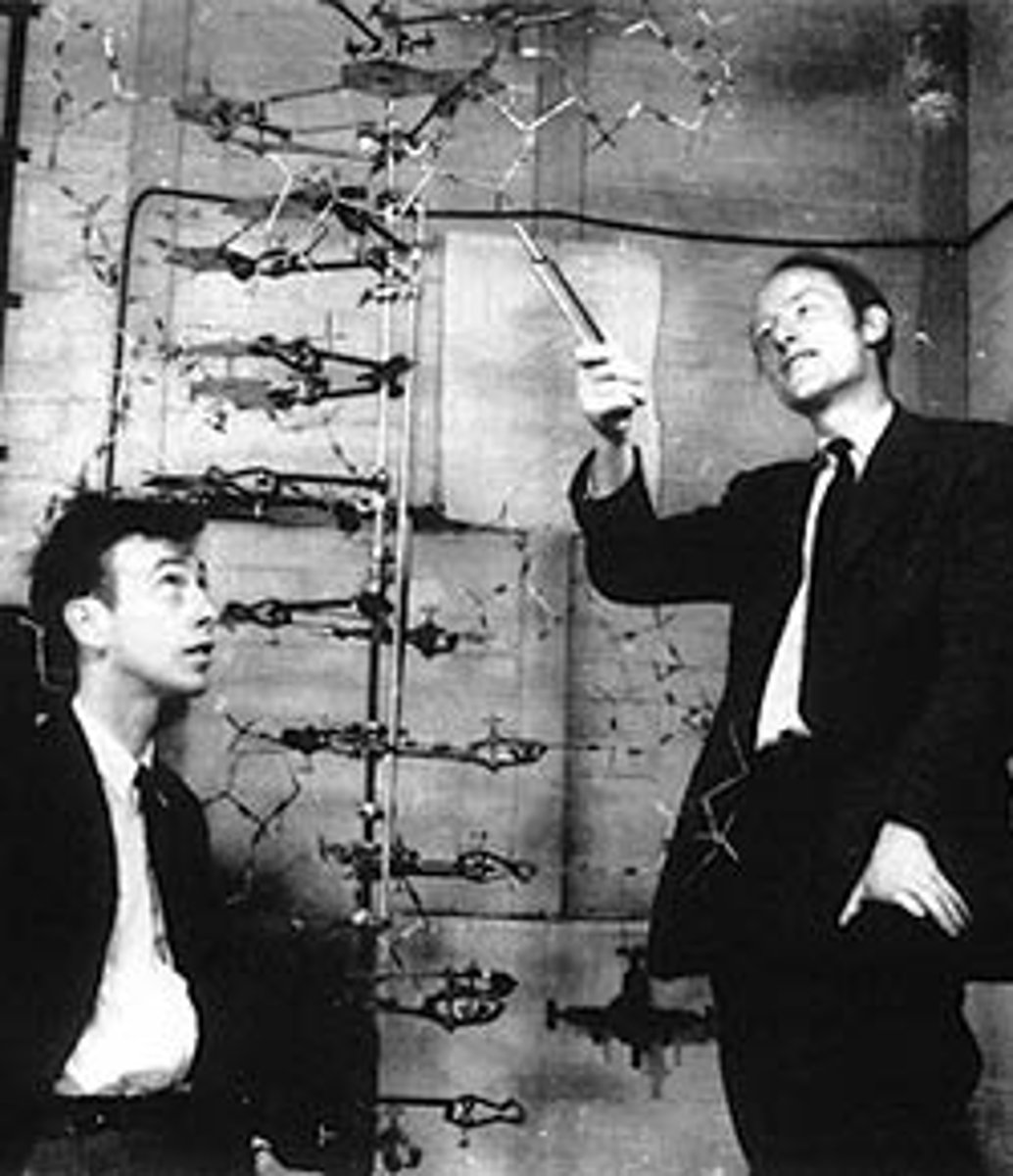
James Watson and Francis Crick
The scientists credited with building the first correct model of the structure of DNA

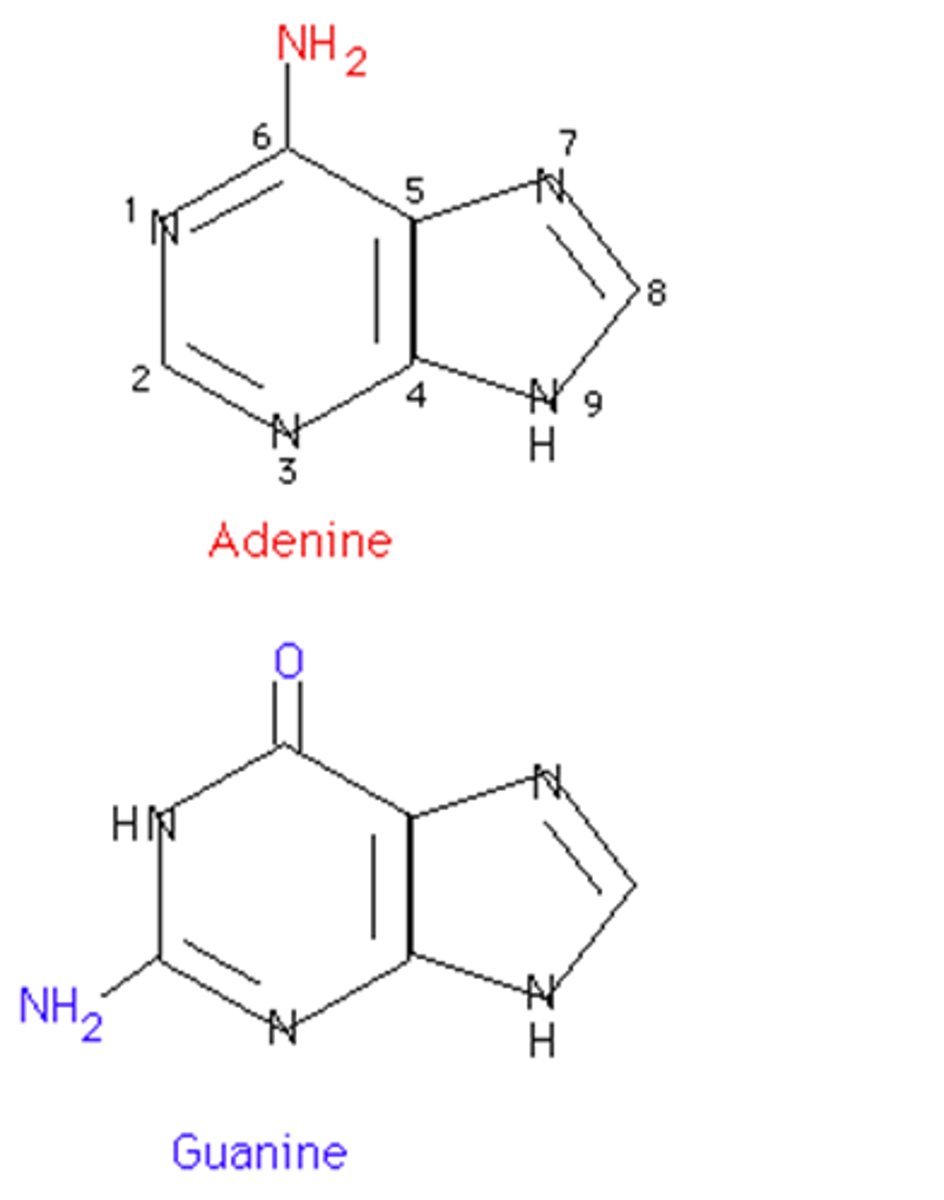
Purines
Bases with a double-ring structure.
Adenine and Guanine
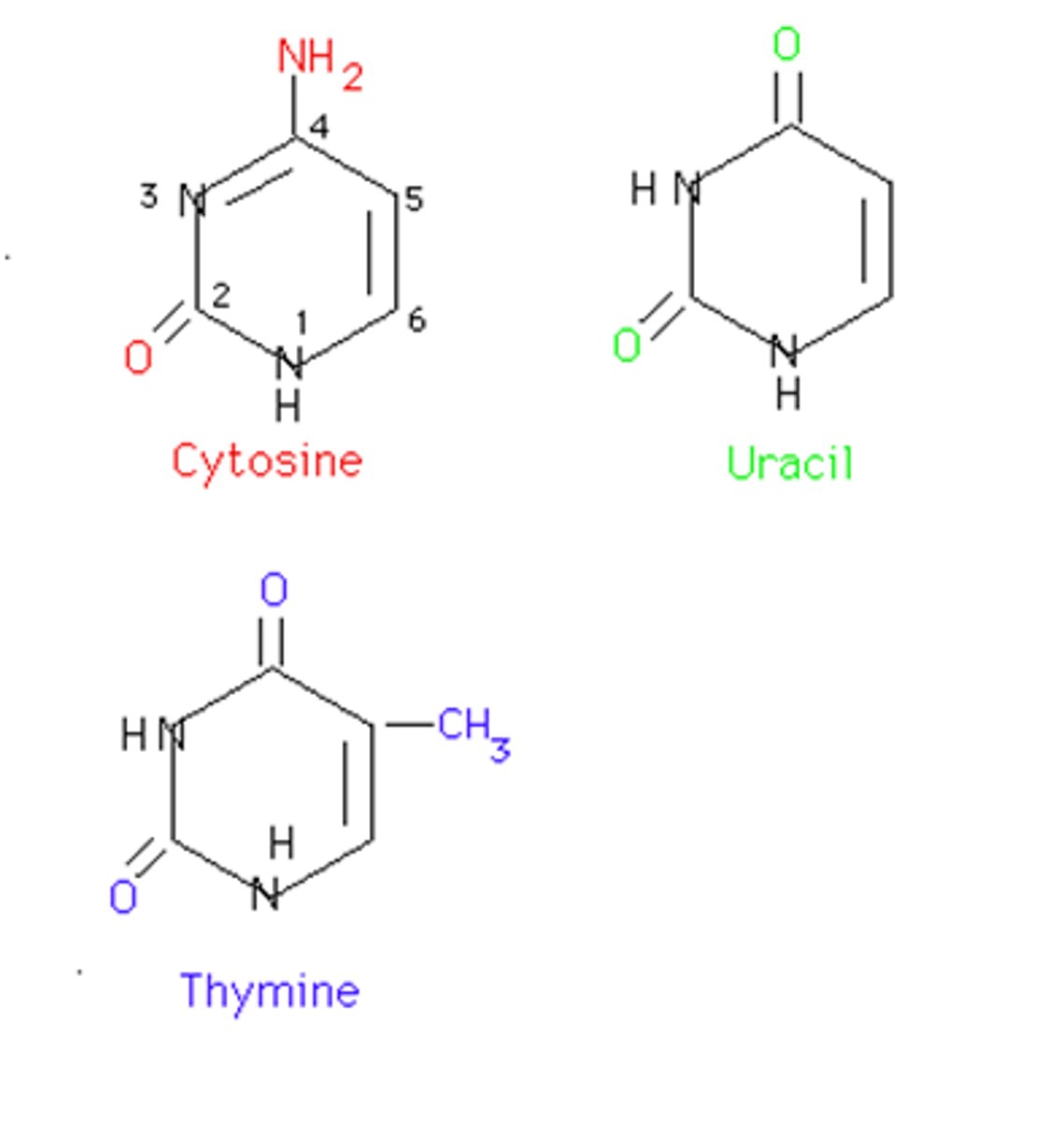
Pyrimidines
Bases with a single-ring structure.
Thymine and Cytosine
Nucleotide
monomer of nucleic acids made up of a 5-carbon sugar, a phosphate group, and a nitrogenous base