AP BIO UNIT 1.3
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
43 Terms
What are reactants?
molecules on the left side of the arrow which substances present at the start of the reaction.
What are products
molecules on the right side of Arrow which the new substances forms from the reaction.
what is activation energy?
Activation energy is the minimum amount of energy required to start a chemical reaction.
for activation energy what is typically the form of the activation energy in?
the form of heat.
the reactions that have high activation Energies __.
occur slowly.
the reactions that have small activation Energies__
occur quickly.
enzymes are __that act as _ in cells and organism
Proteins and catalysts.
enzymes _metabolic reactions by _the activation energy
speed up & lowering
why is the shape of an enzyme important?
it allows it to bind to the reactants needed for chemical reaction and insist in the breaking and forming of new bonds.
the region on the enzyme were substance bind to is called the_?
active site.
The Binding of a substrate to the active cite creates an induced fit what does this mean?
The enzyme changes shape to embrace the substrates to ensure it does not detach until the reaction is complete.
can enzymes be used again in a chemical reaction?
yes.
What is a catalyst?
do they go away? do they change shape?
a chemical that speeds up a reaction without being consumed by the reaction meaning these never go away and never change shape.
Why do enzymes have a specific shape and active site.
they only bind to a specific substrate this means that the enzymes control very specific reactions.
What type of substrates binds to the active site on enzymes+EX?
weak interactions. ionic bonds hydrogen bonding and polar / no polar interactions.
why don't substrates bind to active sites of covalent bonds?
they are too strong.
do substrates actually touch the active site?
no they kind of levitate above them it's like a magnet.
the name of the enzymes always ends with what?
-ase
how can the rate of enzyme activity be sped up?
by increasing the subject concentration in a solution.
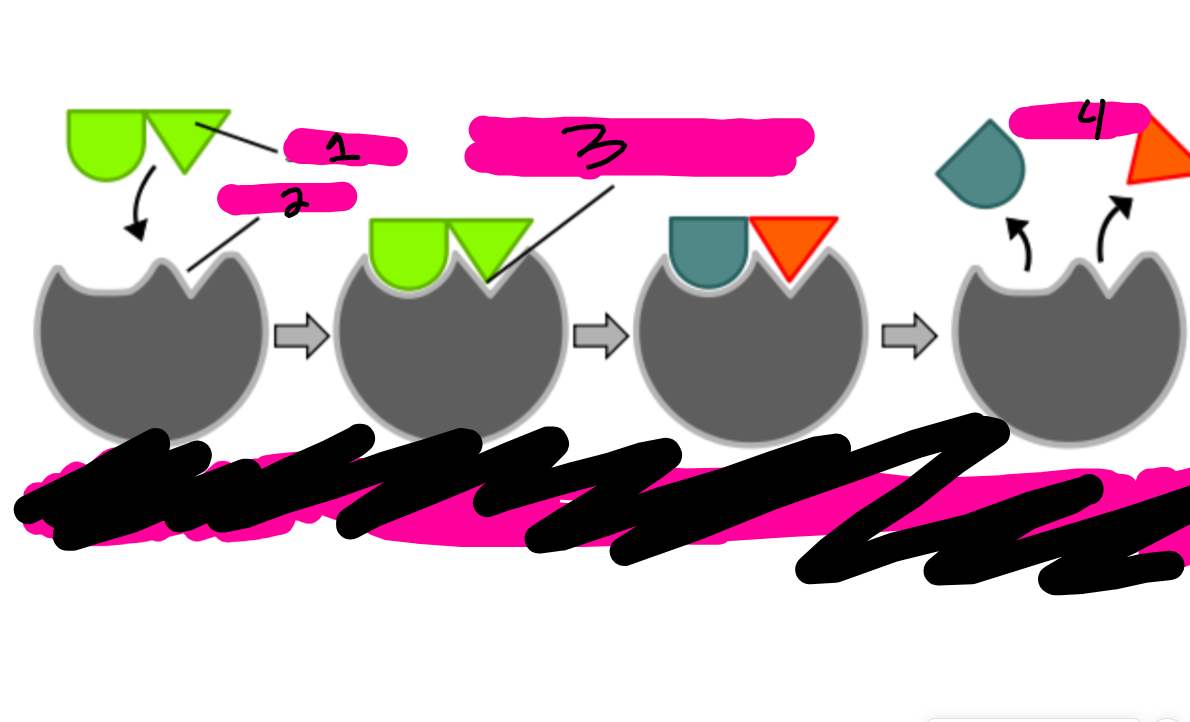
label the image.
1:subrate. 2:active site. 3:complex. 4:products
Whenever all of the enzyme molecules in a solution are being bonded with a substrate what are the enzymes?
they are saturated.
at enzymes saturation, the enzymes are all working at Max Speed and rate of the reaction. how can these factors be increased?
by adding more enzymes. each enzyme can only work with each substrate.
what are the three factors that cause enzymes to denature?
salinity. temperature. Ph.
how does salinity affect our enzymes?
it's a temporary change
how does temperature change our enzymes
if the temperature is hot it is permanently damaged the enzyme. if it's cold it's just a temporary.
What are the optimal pH values for enzymes+effects? what are the exceptions?
6 to 8.These changes are temporary. some exceptions like pepsin a digestive enzymes that's in the stomach works best of a pH of 2.trypsin a digestive enzyme in the intestine works best at a pH of 8.
How do the mutations of the amino acid sequence of a protein affect our enzyme?
if an amino acid is found in the active site of an enzyme and it is changed it can lead to an enzyme no longer being able to bind to the substrate if it's outside of the active site it can also affect the folding of the enzyme in the shape of its active site.
many enzymes require non-protein helpers called __to help them catalyze reactions?
COFACTORS
what is an inorganic and organic cofactor?
inorganic cofactors include things such as metal ions.
organic cofactors are coenzymes include things such as vitamins organic molecules with carbon.
How to Inhibitors affect our enzymes?
they selectively attached to an enzyme and stop it from binding to its subject causing a reduction in its reaction rate.
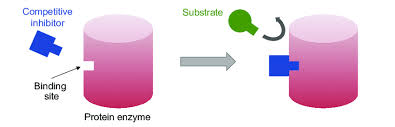
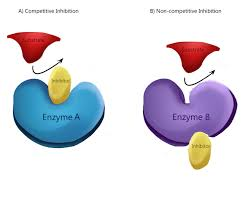
what is it a competitive inhibitor?
reduce the productivity of an enzyme by attaching to the enzymes active site and blocking substrates from attaching.temporary.
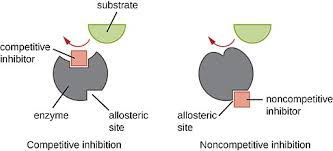
what is a non-competitive inhibitor?
bind to the enzyme at location that is not the active site causing the enzyme and its active site to change shape and preventing the enzymes active site from attaching to the substrate.
Bind to an allosteric (other) site,
changing protein shape
what is a reversible inhibitor?
they temporary associate with the binding site of the enzyme without forming any permanent bonds eventually they fell off.
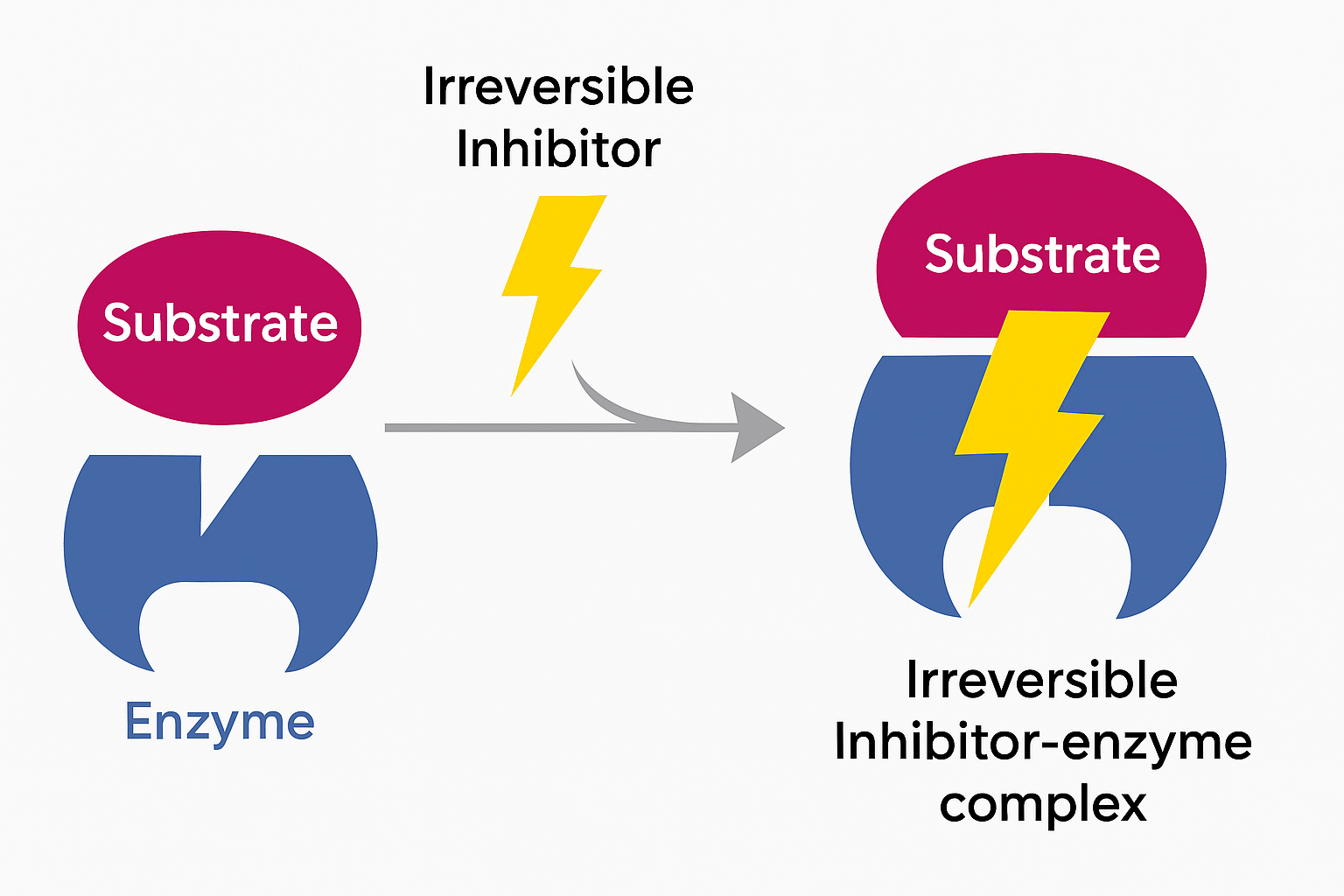
what is an irreversible inhibitor?
when an inhibitor binds to an enzyme in such a way that the enzyme's activity is permanently disrupted. This type of inhibition typically involves the formation of a covalent bond between the inhibitor and the enzyme, leading to a long-lasting effect on the enzyme's function.
how can the reversible competitive Inhibitors overcome?
they increase the concentration of substrate
By adding enough substrate, you can outcompete the inhibitor, forcing the enzyme to bind to the substrate and form product
how can non-competitive Inhibitors overcome?
they can't. they cannot become overcome by increasing the substrate concentration because it's a permanent solution .
Why do enzymes have allosteric regulation?
this means that they can be turned on and off.
what is an allosteric activation?
stimulates an increase of enzyme activity. occurs when The Binding of a regulatory molecule called an activator stabilizes with the accurate conformation of the enzyme. It's like there's this switch that can push the enzyme into overdrive—zooming super fast .
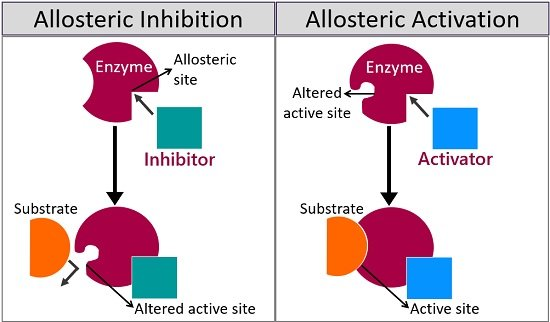
What is an allosteric inhibition?
decreases enzyme activity. Allosteric inhibition occurs when a molecule binds to an enzyme at a site other than the active site, causing a shape change that reduces its activity. This regulatory mechanism helps control metabolic pathways. It’s often used in feedback inhibition, where the end product of a pathway slows its own production.
What is a metabolic pathway?
a series of chemical reactions that are needed to take a certain substrate and turn it into a desired final product.
what is feedback inhibition?
when the final product of a metabolic pathway stops an enzyme earlier in the same pathway from working, which prevents the overproduction of that product. Think of it like a thermostat: when the room reaches the desired temperature (the end product), it signals the heater (the enzyme) to shut off, and the heating process (metabolic pathway) stops.
what does feedback inhibition prevent?
prevents a cell from forming synthesizing more product that is needed in wasting chemical resources.
Why is it okay for cells to complementalize where reactions take place within the cell?
this increases the efficiency of the cell because it prevents conflicting types of reactions from competing with one another. cells accomplish this by making sure that certain enzymes are located to many certain areas within the cell. Example: the enzyme ATP synthesizes is embedded in the inner membrane of the mitochondria organelle where ATP synthesis occurs.